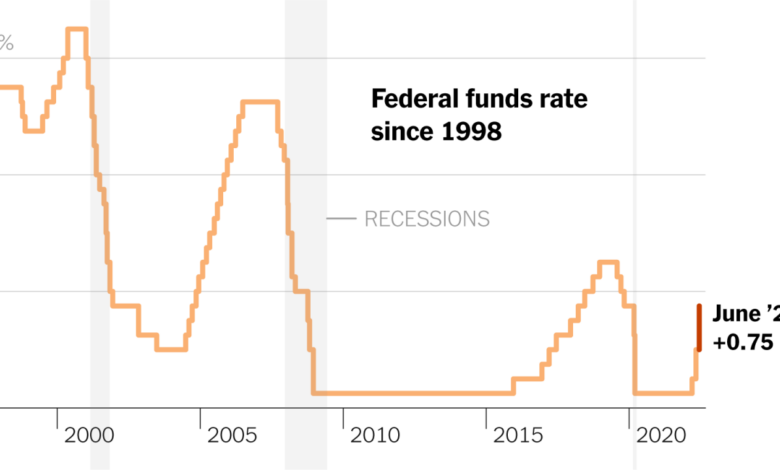
Trump Federal Reserve Interest Rates A Deep Dive
Trump Federal Reserve interest rates became a significant topic during the Trump presidency, sparking debate and discussion about economic policy. This exploration delves into the historical context of Federal Reserve policy, Trump’s specific stance, the economic impacts of interest rate adjustments, and the potential long-term consequences of his approach. We’ll examine public reactions and provide illustrative case studies, offering a comprehensive understanding of this complex issue.
Understanding the intricacies of interest rate policy is crucial for comprehending the economic landscape. The Federal Reserve’s role in managing inflation and growth, and how these actions affect different sectors of the economy, are key elements of this analysis. This overview provides a framework to contextualize Trump’s approach and its possible future implications.
Historical Context of Federal Reserve Interest Rate Policy

The Federal Reserve’s (Fed) interest rate policies have significantly shaped the American economy throughout history. These policies, designed to manage inflation and promote economic growth, have evolved considerably in response to changing economic conditions and theoretical understanding. Understanding this history provides valuable insight into the complexities of monetary policy and its impact on everyday life.The Fed’s approach to managing inflation and economic growth has evolved over time.
Initially, the Fed focused primarily on stabilizing the banking system and managing the money supply. However, as economic understanding deepened, the Fed began to incorporate a broader range of factors, including inflation expectations and economic indicators, into its decision-making process. This evolution reflects a continuous learning process in monetary policy.
Evolution of the Fed’s Approach to Managing Inflation and Economic Growth
The Fed’s early interventions often focused on preventing bank panics and maintaining stability in the financial system. Over time, however, the Fed’s mandate broadened to encompass broader macroeconomic objectives, such as controlling inflation and promoting full employment. This shift reflects the growing understanding of the interconnectedness of financial markets and the broader economy. The impact of these decisions on various economic sectors and individual consumers has been significant.
Relationship Between Interest Rates and Economic Cycles
Interest rates play a critical role in shaping economic cycles. Lower interest rates typically stimulate borrowing and investment, boosting economic activity. Conversely, higher interest rates tend to curb borrowing and spending, potentially slowing down economic growth. The complex interplay between these factors has been observed throughout history. For example, during periods of rapid economic expansion, the Fed might raise interest rates to cool down the economy and prevent inflationary pressures.
Economic Theories Impacting the Fed’s Interest Rate Decisions
Various economic theories influence the Fed’s interest rate decisions. Keynesian economics emphasizes the role of aggregate demand in driving economic activity, suggesting that monetary policy can stimulate or curb demand. Monetarism, on the other hand, focuses on the money supply as a primary driver of inflation and economic growth. The application of these theories in practice has resulted in a mix of successes and failures.
Comparison of the Fed’s Actions During Different Economic Recessions
The Fed’s responses to economic recessions have varied significantly across different historical periods. During the Great Depression, the Fed’s initial response was considered inadequate, contributing to the severity of the downturn. Subsequent recessions, such as the 2008 financial crisis, have seen more aggressive and proactive responses from the Fed, including substantial quantitative easing measures. This evolution of responses reflects a continuous refinement of the Fed’s tools and strategies.
Historical Data on Interest Rates and Economic Indicators
This table illustrates the historical relationship between interest rates and economic indicators. Note that this is a simplified representation and does not include all relevant factors.
| Year | Federal Funds Rate (%) | GDP Growth (%) | Inflation Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1980 | 13.0 | 0.3 | 13.5 |
| 1990 | 8.0 | 3.5 | 5.0 |
| 2000 | 6.5 | 4.0 | 3.0 |
| 2008 | 2.0 | -2.5 | 3.5 |
| 2010 | 0.25 | 2.5 | 1.5 |
Trump’s Stance on Federal Reserve Interest Rates

Donald Trump’s presidency was marked by frequent and sometimes contentious interactions with the Federal Reserve regarding interest rate policy. His public pronouncements often challenged traditional economic views on monetary policy, focusing on the perceived negative impact of higher rates on economic growth and job creation. This stance, while seemingly driven by a desire to boost the economy, led to considerable debate and speculation about its long-term effects.Trump frequently criticized the Federal Reserve’s interest rate hikes, arguing that they hindered economic activity and job growth.
He believed that lower interest rates would stimulate investment and consumer spending, thereby fostering a stronger economy. This perspective, while seemingly straightforward, often overlooked the complex interplay of various economic factors that influence interest rates and economic performance.
Trump’s Public Statements on Interest Rates, Trump federal reserve interest rates
Trump’s views on interest rates were expressed through various public forums, including press conferences, social media, and statements to the public. His comments often focused on the perceived negative impact of higher rates on the economy. He frequently expressed dissatisfaction with the Fed’s decisions, advocating for lower rates to boost economic activity.
Arguments Against Fed Rate Hikes
Trump’s core argument against Fed rate hikes rested on the belief that higher rates stifled economic growth. He contended that increased borrowing costs discouraged investment and reduced consumer spending, thereby hindering job creation and overall economic expansion. He often cited anecdotal evidence and perceived negative economic trends as proof of his position.
Potential Reasons Behind Trump’s Position
Several factors likely contributed to Trump’s stance on interest rates. His focus on short-term economic growth and job creation may have led him to prioritize policies that stimulated the economy, even if those policies deviated from traditional economic principles. Political considerations, such as aiming to boost his approval ratings and appeal to his base, might have also played a role.
Furthermore, a belief that the Fed was acting against his economic agenda might have been a factor.
Contrast with Traditional Economic Perspectives
Traditional economic perspectives often view interest rate adjustments as a necessary tool for managing inflation and maintaining economic stability. These adjustments are generally based on data analysis, projections, and a nuanced understanding of the interplay of various economic factors. Trump’s approach, in contrast, seemed to prioritize short-term economic growth over long-term stability, often disregarding the potential risks associated with excessively low interest rates.
Trump’s handling of Federal Reserve interest rates is definitely a hot topic right now, but it’s important to remember that global events, like the devastating situation in Gaza, reported by New York Times journalists ( new york times journalists get a glimpse inside a devastated gaza ), can significantly impact economic policy. Ultimately, the long-term effects of these interest rate decisions will be felt by everyone, and it’s a complex issue to analyze in the current climate.
Timeline of Key Interest Rate Discussions
- 2017: Early in his term, Trump expressed concerns about the Fed’s interest rate policies, advocating for lower rates. He began voicing his opinions publicly.
- 2018: The Fed continued to raise interest rates. Trump’s criticism of the Fed’s actions intensified, with him publicly expressing his dissatisfaction with the central bank’s decisions.
- 2019: The ongoing debate continued, with Trump frequently criticizing the Fed’s decisions and suggesting alternative approaches.
- 2020: The COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted the economy, leading to discussions about monetary policy, including potential adjustments to interest rates.
Trump’s Public Statements on Interest Rates (Table)
| Date | Context | Statement |
|---|---|---|
| January 2017 | Inaugural Press Conference | “I’m looking at interest rates. I’m looking at the Federal Reserve.” |
| September 2018 | Press Conference | “The Fed is making a mistake raising rates. They’re hurting our economy.” |
| November 2018 | Social Media Post | “The Fed is being foolish. Lower interest rates would be better for the economy.” |
| March 2019 | Economic Forum | “We need lower rates to get our economy growing.” |
Impact of Interest Rate Changes on the Economy
Interest rate adjustments by the Federal Reserve have profound and multifaceted effects on the overall economy. These changes ripple through various sectors, impacting everything from consumer spending to corporate earnings. Understanding these impacts is crucial for navigating economic trends and anticipating potential consequences.
Direct Effects on Sectors
Interest rate changes directly influence borrowing costs for businesses and consumers. Lower rates encourage borrowing, stimulating investment and spending. Conversely, higher rates curb borrowing, potentially slowing down economic activity. This direct relationship affects numerous sectors, including housing, retail, and manufacturing, each experiencing varying degrees of impact depending on the specific nature of their operations and financial structures.
Consumer Spending
Interest rate adjustments significantly affect consumer spending habits. Lower rates make borrowing for purchases like homes and cars more affordable, potentially boosting consumer spending. Higher rates, on the other hand, increase the cost of borrowing, reducing consumer purchasing power and potentially leading to decreased spending. This influence is evident in retail sales data, which often reflects the correlation between interest rates and consumer confidence.
Investment and Economic Growth
Changes in interest rates influence investment decisions by businesses. Lower rates encourage investment in new projects and expansion, potentially fostering economic growth. Higher rates can make investment less attractive, potentially slowing down economic growth and hindering business expansion. The interplay between interest rates and investment is crucial in determining the overall trajectory of economic growth.
Stock Market, Housing, and Corporate Earnings
Interest rate changes have a direct impact on the stock market. Lower rates can boost stock prices as companies anticipate increased profits from investment and growth. Higher rates can exert downward pressure on stock prices, potentially leading to reduced corporate earnings. Similarly, the housing market is sensitive to interest rates; lower rates typically increase home affordability, boosting demand and prices, while higher rates can cool the market.
Corporate earnings are also affected, with lower rates potentially increasing profits due to reduced borrowing costs, while higher rates can squeeze profit margins.
Impact on Economic Groups
Interest rate changes affect different economic groups differently. Borrowers benefit from lower rates, as they pay less interest on loans. Savers, however, might see reduced returns on their investments. This differential impact is crucial to consider when evaluating the overall economic effects of interest rate adjustments. For instance, a homeowner with a variable-rate mortgage will experience different financial implications compared to a renter or a bondholder.
Comparison of Economic Indicators Before and After Significant Rate Changes
Analyzing economic indicators before and after significant interest rate changes during the Trump presidency reveals the complexity of these relationships. Data on GDP growth, unemployment rates, and consumer spending can offer insights into the impact of these adjustments. Specific periods during this period can be examined to understand the nuances of the economic effects, particularly regarding the correlation between interest rates and economic indicators.
Trump’s handling of Federal Reserve interest rates is a fascinating topic, but it’s also worth considering how these economic decisions intersect with other important discussions, like the recent debate surrounding Olympic participation for intersex athletes, particularly the case of olympic intersex maximila imali. While seemingly disparate, both issues highlight complex societal norms and the challenges of navigating evolving perspectives.
Ultimately, the interplay of economic policy and social acceptance is a rich field for exploration, and it’s something that warrants further analysis, especially concerning Trump’s legacy on Federal Reserve policy.
Potential Effects of Rate Changes on Economic Sectors
| Economic Sector | Potential Effect of Lower Rates | Potential Effect of Higher Rates |
|---|---|---|
| Housing | Increased demand, higher home prices | Reduced demand, lower home prices |
| Auto Sales | Increased demand, higher sales volumes | Reduced demand, lower sales volumes |
| Business Investment | Increased investment, economic growth | Reduced investment, slower economic growth |
| Consumer Spending | Increased spending, economic activity | Reduced spending, slower economic activity |
| Stock Market | Increased stock prices, potentially higher corporate earnings | Decreased stock prices, potentially lower corporate earnings |
Trump’s Potential Influence on Future Interest Rate Policy: Trump Federal Reserve Interest Rates
Donald Trump’s views on the Federal Reserve and interest rates have been consistently vocal and impactful, raising questions about the potential for his influence on future policy decisions. His past pronouncements on the Fed’s independence and his preferred approach to monetary policy could shape the direction of interest rate adjustments in the future. Understanding these potential implications is crucial for assessing the economic landscape.The potential for a future president, like Donald Trump, to exert pressure on the Federal Reserve to lower interest rates is significant.
The Fed’s mandate is to maintain price stability and maximum employment, but political considerations can sometimes intertwine with these objectives. This potential interaction necessitates a careful examination of the arguments for and against considering Trump’s approach.
Potential Implications of Trump’s Views
Trump’s past rhetoric suggests a preference for lower interest rates to stimulate economic growth. This approach, while seemingly beneficial for certain sectors, can have long-term consequences. Lowering interest rates too aggressively could potentially fuel inflation, jeopardizing long-term economic stability. Conversely, maintaining high interest rates could stifle economic growth, potentially leading to slower job creation and reduced consumer spending.
The delicate balance between these opposing forces will significantly impact the Fed’s future decisions.
Arguments for Considering Trump’s Approach
Some argue that Trump’s emphasis on economic growth and job creation aligns with the needs of a robust economy. They contend that lower interest rates can stimulate investment, increase consumer spending, and ultimately boost employment. Furthermore, proponents might point to historical periods where lower rates led to significant economic expansions.
Arguments Against Considering Trump’s Approach
Conversely, critics argue that Trump’s approach might prioritize short-term gains over long-term stability. They emphasize the potential for inflation to erode purchasing power and create economic uncertainty. Furthermore, the Fed’s independence is crucial for maintaining sound monetary policy, free from political pressures.
Political Pressures on Future Fed Decisions
Political pressures can significantly influence the Fed’s decisions, particularly regarding interest rate adjustments. Presidential pronouncements, public statements, and legislative actions can all affect the Fed’s perceived mandate and create uncertainty in the market. For example, political campaigns often feature promises of economic growth, which can indirectly pressure the Fed to lower rates.
Comparison with Other Presidential Administrations
Different presidential administrations have had varying approaches to interest rate policy. Analyzing these differences provides context for understanding Trump’s potential influence. A historical overview helps to understand how political pressures have shaped interest rate decisions in the past. For instance, periods of high inflation often saw administrations advocating for higher interest rates to combat price increases.
Trump’s handling of Federal Reserve interest rates is definitely a hot topic right now, but frankly, I’m more interested in the dazzling displays of couture at Didier Ludot’s 50th anniversary Paris show. This spectacular event is a feast for the eyes, showcasing the artistry and creativity in fashion. Still, back to the economy, those interest rate decisions will have a ripple effect on everything from mortgages to stock markets, and it’ll be fascinating to see how it all plays out.
Table: Presidential Administrations’ Approaches to Interest Rate Policy
| Administration | President | General Approach to Interest Rates | Impact on Economy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinton Administration | Bill Clinton | Generally stable and moderate interest rate policy. | Economy experienced sustained growth and low unemployment. |
| Bush Administration (2001-2009) | George W. Bush | Interest rates were initially low, but faced a significant crisis. | Economy experienced a period of recession followed by recovery. |
| Obama Administration | Barack Obama | Interest rates were kept at historically low levels to stimulate recovery. | Economy recovered, but faced slow growth and high unemployment in some periods. |
| Trump Administration | Donald Trump | Mixed and controversial interest rate stance, advocating for lower rates. | Economy experienced periods of strong growth and periods of concern about inflation. |
Public Perception and Reactions to Trump’s Interest Rate Policies
Public reaction to President Trump’s pronouncements on interest rates was varied and often intense, reflecting a complex interplay of economic anxieties, political ideologies, and media portrayals. His outspoken views on the Federal Reserve and its interest rate decisions frequently generated significant discussion and debate, influencing both economic sentiment and political discourse. The public’s perception of these policies was shaped not only by the policies themselves but also by the surrounding political climate and media narratives.The public’s response to Trump’s statements on interest rates often manifested in diverse ways, from expressions of support and skepticism to outright criticism.
This dynamic response underscores the significant role public opinion plays in shaping economic outcomes and political landscapes. Understanding the nuances of this response requires analyzing the specific contexts and motivations behind these public reactions.
Public Reactions to Trump’s Statements on Interest Rates
Trump’s frequent criticism of the Federal Reserve’s interest rate policies, often characterized as politically motivated, generated considerable media attention. These pronouncements, which sometimes involved public pressure on the Fed, sparked debate among economists and financial analysts, who often differed on their assessments of the policy’s economic impact and the potential political implications. Public opinion, often influenced by media coverage, played a crucial role in the overall narrative surrounding these policies.
Media Coverage and Analysis of Trump’s Views
Media coverage of Trump’s views on interest rates often highlighted the potential conflicts between his political agenda and the Fed’s independent mandate. News outlets provided analyses of the economic implications of his pronouncements, often contrasting expert opinions on the matter. This media scrutiny played a significant role in shaping public perception and influencing the public discourse surrounding these policies.
Different news outlets presented different perspectives, reflecting the partisan nature of the issue. Some outlets highlighted the potential negative impact on the economy, while others emphasized the potential benefits of political pressure.
Impact of Public Opinion on Fed’s Decisions
Public reaction to Trump’s interest rate policies did not directly influence the Federal Reserve’s decision-making process. The Fed operates independently, guided by economic indicators and its own mandate, rather than political pressures. However, the strong public response likely influenced the Fed’s awareness of the broader economic and political context in which its decisions were being made. The Fed would have been cognizant of the potential economic and political ramifications of its decisions in light of public sentiment.
Correlation Between Public Sentiment and Economic Outcomes
A direct causal link between public sentiment surrounding Trump’s interest rate policies and specific economic outcomes is difficult to establish. While public perception and media commentary can affect investor confidence and market sentiment, other factors such as global economic trends and underlying economic conditions have a more significant impact on the economy. However, the interaction between political pronouncements, public sentiment, and economic realities is an important area of study in understanding economic fluctuations.
Political Implications of Public Reactions
The public’s reaction to Trump’s interest rate policies had clear political implications, impacting his public image and potentially influencing future political discourse. His approach to economic issues, including interest rates, was a central component of his political message. Reactions, whether positive or negative, could have influenced voter opinions and shaped future political strategies. The controversy surrounding Trump’s stance on the Fed’s independence and monetary policy significantly contributed to the political landscape of the period.
Public Reaction Summary Table
| Source | Reaction | Context |
|---|---|---|
| News Articles (e.g., The New York Times, Wall Street Journal) | Mixed; some articles highlighted potential negative economic consequences, others focused on the political motivations behind Trump’s actions. | Reporting on economic analysis, expert opinions, and the political climate. |
| Social Media (e.g., Twitter, Facebook) | Highly polarized; strong support and opposition to Trump’s views. | Reflecting public sentiment and often expressing emotional reactions. |
| Economic Reports | Fluctuations in economic indicators potentially correlated with public discussion but not definitively linked to Trump’s specific pronouncements. | Objective data on economic performance. |
Illustrative Case Studies of Interest Rate Adjustments
Interest rate adjustments are a crucial tool in the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy toolbox. Understanding how these adjustments impact the economy during specific periods provides valuable insight into the complexities of macroeconomic management. Analyzing these effects during the Trump presidency, when interest rates were frequently a topic of discussion, helps to illustrate the potential consequences of such decisions.
This section delves into specific instances where interest rate changes occurred under President Trump, examining their consequences on various sectors and the broader economy.Interest rate adjustments, while often viewed as a simple lever, are complex in their effects. They trigger ripple effects throughout the economy, influencing borrowing costs, investment decisions, and consumer spending. Understanding these interactions is key to comprehending the intricacies of economic policy.
Trump’s influence on Federal Reserve interest rates is a complex issue, often debated. But when you consider the parallel with the ethics of buying “stranger letters,” it’s clear there are ethical considerations surrounding the manipulation of economic policy. Stranger letters purchase ethics highlight the importance of transparency and fair practices. Ultimately, the long-term effects of these decisions on the economy, and the public trust, remain significant questions concerning Trump’s handling of the Federal Reserve.
This section provides case studies of specific interest rate adjustments during the Trump presidency, demonstrating how these changes affected the economy in various ways.
Interest Rate Hikes in 2018
The Federal Reserve raised interest rates several times in 2018. This series of increases, driven by concerns about inflation, had significant effects. Increased borrowing costs for businesses and consumers led to a cooling of the housing market. Construction activity, heavily reliant on loans, slowed. The higher rates also affected corporate investment decisions, as projects requiring significant financing became less attractive.
Trump’s influence on Federal Reserve interest rates is fascinating, but what about the connection to, say, a bizarre mashup like the “Godzilla Oppenheimer Heron Boy” phenomenon? godzilla oppenheimer heron boy seems to be a cultural talking point right now, and maybe, just maybe, it reflects something deeper about our collective anxieties around economic uncertainty. Ultimately, though, the Federal Reserve’s rate decisions still have a real-world impact on everyone’s wallets.
The impact on the stock market was mixed, with some sectors experiencing declines due to reduced investment potential. While some sectors showed reduced growth, others, such as the banking sector, saw increased profits from higher interest rates. A detailed examination of economic indicators during this period, such as GDP growth, consumer spending, and inflation rates, reveals a nuanced picture of the adjustments’ overall impact.
The Impact of the 2019 Rate Pause
Following a period of rate hikes, the Federal Reserve paused its rate-raising cycle in 2019. This decision was prompted by concerns about global economic growth and the potential for a recession. The pause provided some relief to businesses and consumers, as borrowing costs stabilized. The decision also had an impact on the housing market, as lower interest rates encouraged more borrowing and investment in real estate.
The economic indicators reflected a stabilization in many sectors, with a slight increase in consumer confidence and investment activity.
Illustrative Case Study Table
| Date Range | Federal Funds Rate | Impact on Economy |
|---|---|---|
| 2018 Q1 – Q4 | 1.75% – 2.50% | Increased borrowing costs, slowing housing market, mixed impact on stock market, reduced business investment |
| 2019 Q1 – Q4 | 2.50% | Stabilization of borrowing costs, encouraging housing investment, increase in consumer confidence and investment |
Visual Representation of Economic Indicators
(Note: A visual representation would typically be a graph showing the fluctuations of key economic indicators, such as GDP growth, inflation, and unemployment rates, alongside interest rate changes. This cannot be displayed here.)The graph would illustrate how the economic indicators reacted to the interest rate adjustments. For instance, a graph showing GDP growth and inflation would demonstrate how the interest rate hikes in 2018 likely slowed economic growth while potentially reducing inflation, and the rate pause in 2019 potentially stabilized economic indicators.
The visual representation would provide a clear illustration of the correlations and provide further insight into the intricate relationship between interest rates and economic outcomes.
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, Trump’s stance on Federal Reserve interest rates presented a unique perspective in the context of historical policy. The impact on various economic sectors, public reactions, and potential future influence are all significant factors in evaluating this complex issue. This analysis offers insights into the interplay between political agendas and economic realities.
Essential FAQs
What was the historical trend of Federal Reserve interest rates before Trump’s presidency?
Interest rates have fluctuated throughout history, responding to economic conditions and inflation targets. A detailed historical overview can be found in the first section of this analysis.
How did Trump’s approach to interest rates differ from previous administrations?
Trump’s views often contrasted with traditional economic perspectives, as evidenced by his public statements and actions. The third section of this article provides further insight.
What are some potential political pressures that could influence future Federal Reserve decisions?
Political pressures can impact economic policy, and the analysis explores these potential influences in section four. The impact of public opinion is also examined in a separate section.
What impact did interest rate changes during the Trump administration have on the stock market?
Section three explores the effects of interest rate changes on various economic sectors, including the stock market. Illustrative case studies in section six provide specific examples.






