
Hochul Prenatal Care Maternal Mortality in NY
Hochul prenatal care maternal mortality is a critical issue demanding immediate attention in New York State. The current state of prenatal care services, existing policies, and the challenges faced by pregnant women are all factors influencing the alarming maternal mortality rates. Understanding these issues is crucial for developing effective solutions and improving outcomes.
This comprehensive exploration examines the multifaceted aspects of prenatal care in New York, delving into maternal mortality rates, access to quality care, potential interventions, policy recommendations, and future research directions. We’ll analyze the contributing factors, disparities, and the importance of timely interventions and support systems.
Introduction to Prenatal Care in New York

Prenatal care in New York State plays a critical role in ensuring the health and well-being of expectant mothers and their newborns. Comprehensive care during pregnancy is vital for identifying potential complications early, promoting healthy pregnancies, and reducing maternal and infant mortality rates. This blog post explores the current state of prenatal care services, relevant policies and programs, challenges faced by expectant mothers, and demographic considerations.
Understanding these aspects is crucial for developing effective strategies to improve maternal health outcomes in the state.Existing prenatal care services in New York aim to provide comprehensive care, encompassing regular checkups, nutritional guidance, and education on healthy pregnancy practices. This holistic approach fosters informed decision-making and empowers pregnant individuals to actively participate in their care. However, disparities in access and utilization of these services persist, highlighting the need for ongoing improvements and targeted interventions.
Current State of Prenatal Care Services
New York State has implemented various initiatives to enhance access to prenatal care, including Medicaid expansion and subsidies for uninsured individuals. These policies aim to ensure that all pregnant women have access to necessary medical services, regardless of their socioeconomic status. The state also provides resources and support services for expectant mothers, including nutrition counseling, parenting classes, and social work services.
These programs aim to address the holistic needs of expectant mothers and promote healthy pregnancies.
Governor Hochul’s prenatal care initiatives are crucial for reducing maternal mortality rates. While the specifics of these programs are important, the broader global context, like the complex relationship between the Palestinian state and the German economy, palestinian state german economy , highlights the interconnectedness of various societal issues. Ultimately, improving maternal health outcomes in New York State is a critical public health priority.
Existing Policies and Programs
New York State has a network of healthcare providers, including hospitals, clinics, and community health centers, that offer prenatal care services. These facilities are often equipped with specialists, such as obstetricians and midwives, who can provide tailored care based on individual needs. Furthermore, the state offers comprehensive educational programs and resources for expectant mothers and their families, designed to address various aspects of pregnancy, including nutrition, exercise, and emotional well-being.
These programs strive to empower individuals to make informed decisions and participate actively in their care.
Challenges to Access and Utilization
Despite the available resources, some pregnant individuals face significant challenges in accessing and utilizing prenatal care services. These include financial constraints, geographical barriers, lack of transportation, and cultural or language barriers. Further complicating matters, some individuals may experience stigma or discrimination, hindering their willingness to seek necessary care. Addressing these barriers is crucial to ensuring equitable access to high-quality prenatal care.
Demographics of Pregnant Women in New York
The demographics of pregnant women in New York State are diverse, reflecting the state’s multicultural population. Factors such as age, socioeconomic status, race, and ethnicity can significantly influence pregnancy outcomes and access to care. For example, racial and ethnic minority groups often face disproportionately higher rates of maternal mortality and morbidity. Understanding these demographics is critical for developing targeted interventions and strategies to address disparities in maternal health.
Maternal Mortality Rates in New York
Data on maternal mortality rates in New York State show a complex picture. While progress has been made in recent years, certain subgroups continue to experience significantly higher rates compared to others. For example, disparities exist based on race and ethnicity, highlighting the need for targeted interventions to address the underlying factors contributing to these disparities. Further analysis is needed to pinpoint the precise reasons for these differences and to develop tailored solutions to achieve equitable outcomes for all pregnant women.
Examining Maternal Mortality Rates
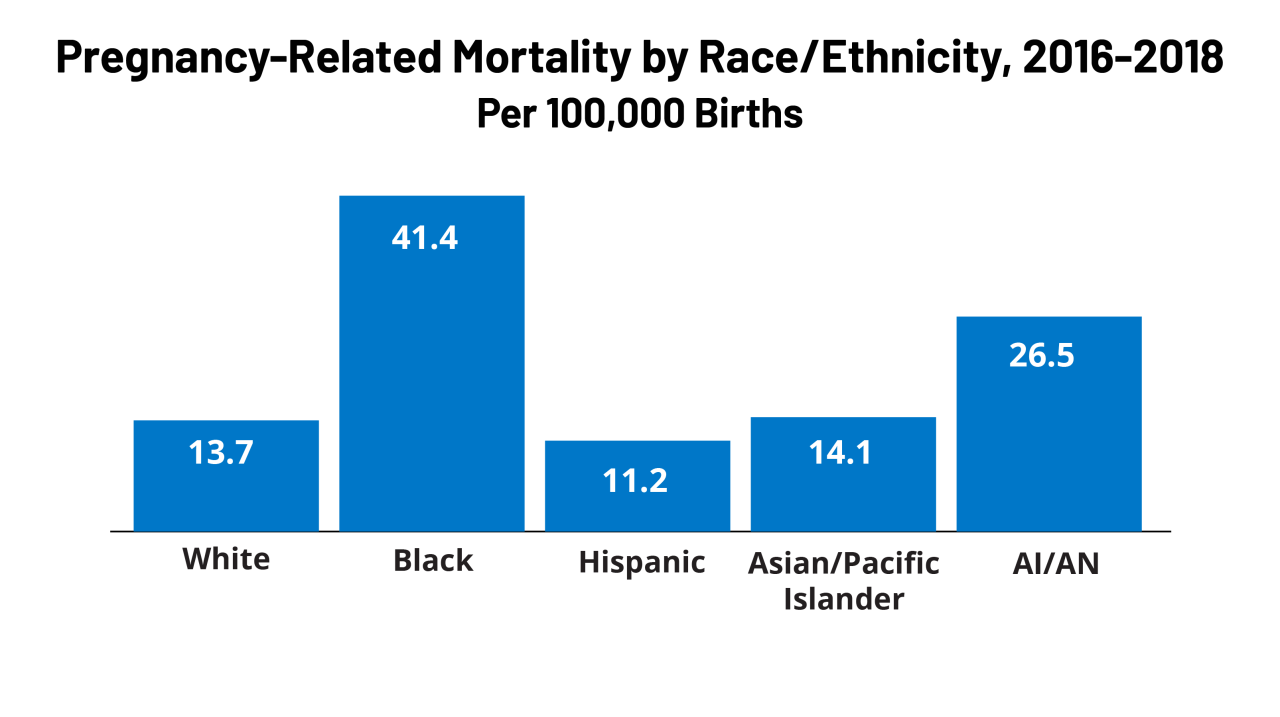
Maternal mortality, the death of a woman during pregnancy or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy, is a significant public health concern. Understanding the contributing factors, disparities, and preventable causes is crucial for developing effective strategies to reduce these tragic outcomes. New York State, like the nation, faces challenges in addressing this issue. A comprehensive analysis of maternal mortality rates provides valuable insights for targeted interventions and improved outcomes.The maternal mortality rate is not a static number, but rather a reflection of the health and societal conditions affecting women during their childbearing years.
This analysis delves into the underlying factors that contribute to these rates, examining demographics, socioeconomic status, and access to quality healthcare. Ultimately, the goal is to understand the nuances of these statistics and use that understanding to drive improvements in maternal health.
Contributing Factors to Maternal Mortality in New York State
Several interconnected factors contribute to maternal mortality in New York State. Access to quality prenatal care, socioeconomic factors, and pre-existing health conditions all play a significant role. Lack of access to comprehensive healthcare, including preventative screenings and timely interventions, can be a critical contributing factor. Further, inadequate support systems for pregnant women, especially those experiencing significant social and economic hardship, can increase vulnerability.
Governor Hochul’s prenatal care initiatives are a crucial step towards reducing maternal mortality rates. While important, these efforts often get overshadowed by the glamorous world of Hollywood. For instance, check out these stunning red carpet photos from the Critics Choice Awards critics choice awards red carpet photos. Ultimately, focusing on accessible and effective prenatal care is far more impactful than any red carpet moment when it comes to improving health outcomes.
- Access to Healthcare: Geographic barriers, financial constraints, and lack of culturally competent care can limit access to necessary prenatal and postpartum services. This can lead to delayed or missed diagnoses of complications, increasing the risk of adverse outcomes. For example, women living in rural areas may have limited access to specialized obstetric care, potentially leading to delayed diagnosis of severe conditions like preeclampsia.
- Socioeconomic Disparities: Significant socioeconomic disparities, such as poverty, unemployment, and lack of education, are strongly correlated with higher maternal mortality rates. Limited access to resources, including healthy food, safe housing, and transportation, can exacerbate existing health vulnerabilities. A lack of affordable childcare and parental leave policies can also impact a woman’s ability to prioritize her health during pregnancy.
- Pre-existing Health Conditions: Women with pre-existing conditions, such as chronic hypertension, diabetes, or mental health issues, are at increased risk of maternal mortality. Effective management of these conditions during pregnancy is essential to mitigate the risks. Poorly controlled conditions can lead to complications like preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, and premature birth.
Disparities in Maternal Mortality Rates by Demographics
Maternal mortality rates are not evenly distributed across all demographic groups. Significant disparities exist based on race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status. This underscores the need for targeted interventions to address these inequalities.
New York’s Hochul administration is tackling the concerning issue of maternal mortality rates during prenatal care. While this is a serious public health concern, it’s interesting to see how similar issues are being addressed elsewhere, like in Thailand where Pita Limjaroenrat recently won a significant legal case. thailand pita wins case This suggests a broader global effort to improve maternal health outcomes, which is crucial for ensuring a healthier future for expecting mothers.
Ultimately, Hochul’s focus on prenatal care is essential to reducing these devastating statistics.
- Racial and Ethnic Disparities: Studies consistently show that Black women in New York, and nationwide, experience significantly higher maternal mortality rates compared to white women. These disparities highlight the need for culturally sensitive and equitable healthcare approaches. Addressing implicit bias within the healthcare system and providing culturally competent care are crucial to reducing these disparities.
- Socioeconomic Status: Women from lower socioeconomic backgrounds often experience higher rates of maternal mortality. This is frequently due to the factors already mentioned, such as limited access to healthcare, inadequate nutrition, and stress from poverty. Targeted programs that provide comprehensive support for these women are crucial for reducing the impact of socioeconomic disparities.
Comparison of Maternal Mortality Rates in New York to National Averages
Comparing New York State’s maternal mortality rates to the national average provides a critical perspective. While New York State may show progress in some areas, ongoing efforts are necessary to reduce the rates to national averages and improve maternal health outcomes.
Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provide a comparison. Further research and analysis can offer a deeper insight into the reasons for any observed differences and the need for state-specific interventions.
Causes of Preventable Maternal Deaths
Preventable maternal deaths often stem from delayed or missed diagnoses of complications during pregnancy or inadequate access to timely and appropriate interventions.
- Delayed or Missed Diagnoses: Conditions like preeclampsia, eclampsia, and postpartum hemorrhage can be fatal if not identified and treated promptly. Lack of access to regular prenatal care, or a lack of awareness of warning signs, can lead to delayed diagnoses. Improved screening protocols and increased awareness among healthcare providers and pregnant women can help mitigate this risk.
- Inadequate Access to Interventions: Lack of access to skilled obstetric care, including specialized interventions, can contribute to preventable deaths. This underscores the importance of ensuring access to comprehensive and high-quality care for all pregnant women, regardless of their location or socioeconomic status. Early recognition and intervention for high-risk pregnancies can dramatically improve outcomes.
Importance of Timely Interventions and Support Systems
Investing in timely interventions and robust support systems is paramount in reducing maternal mortality rates. A comprehensive approach encompassing preventative care, accessible resources, and support for vulnerable populations is essential.
- Early Detection and Intervention: Early detection and prompt interventions are vital in managing high-risk pregnancies and preventing complications. Programs that identify and support women with pre-existing conditions or limited access to resources are crucial.
- Robust Support Systems: Creating robust support systems that address socioeconomic factors, such as housing instability, food insecurity, and lack of childcare, can greatly improve maternal health outcomes. Social work involvement, financial assistance programs, and accessible childcare resources are crucial components.
Potential Interventions and Solutions
Improving maternal health outcomes hinges on a multifaceted approach that addresses access, quality, and delivery models. This requires a concerted effort from healthcare providers, policymakers, and communities to create a supportive environment where every pregnant person has the opportunity to receive the best possible care. By implementing effective interventions and solutions, we can significantly reduce maternal mortality and morbidity rates, ensuring healthier pregnancies and families.Addressing maternal mortality requires a comprehensive strategy that goes beyond individual care.
Systemic issues like socioeconomic disparities, lack of access to transportation, and cultural barriers need to be considered and tackled alongside individual medical needs. A holistic approach that emphasizes prevention, early intervention, and community engagement is crucial for long-term success.
New York’s efforts to address maternal mortality rates under Hochul’s administration are crucial. While the focus is understandably on improving prenatal care, it’s important to remember the enduring strength of the human spirit, as exemplified by the incredible work of Holocaust survivor portrait artist Gillian Laub. Her powerful collection of portraits, detailed in holocaust survivor portraits gillian laub , reminds us that even in the face of unimaginable trauma, resilience can thrive.
Ultimately, both the dedication to prenatal care and the powerful narratives of survival are testaments to the importance of fostering a healthy and supportive society for all.
Improving Access to Prenatal Care Services
Ensuring equitable access to quality prenatal care is paramount for reducing maternal mortality. Geographic limitations, financial constraints, and cultural barriers can significantly impede access. Strategies to enhance access should consider these factors.
- Expanding the reach of community health centers and mobile clinics, especially in underserved areas, can provide convenient and affordable prenatal care options. These facilities can offer comprehensive services, including education, support groups, and transportation assistance.
- Implementing financial assistance programs and subsidies can alleviate the financial burden of prenatal care for low-income families. This could include covering costs for appointments, tests, and medications.
- Developing culturally sensitive and linguistically appropriate programs can improve communication and understanding between healthcare providers and pregnant individuals from diverse backgrounds. This may involve hiring bilingual staff or providing translated materials.
Enhancing the Quality of Prenatal Care
High-quality prenatal care is essential for identifying and managing potential complications early on. Comprehensive care should encompass physical examinations, nutritional counseling, risk assessment, and ongoing education.
- Integrating evidence-based guidelines and protocols into prenatal care practices ensures that all pregnant individuals receive standardized, high-quality care. This can involve establishing clear protocols for managing chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension, as well as for addressing potential complications.
- Training healthcare providers on recognizing and managing complications, such as gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and preterm labor, is critical. Regular continuing education can keep professionals updated on the latest research and best practices in maternal care.
- Implementing regular and thorough screening procedures, including blood pressure checks, urine analysis, and fetal monitoring, can facilitate early detection of potential issues and allow for timely interventions.
Comparing Different Models of Prenatal Care Delivery
Different models of prenatal care delivery offer various approaches to meeting the needs of diverse populations. Understanding these models is critical for selecting the most appropriate strategies.
- Primary care-based models often provide comprehensive care, allowing for longitudinal relationships between patients and providers. This continuity of care can foster trust and ensure ongoing support.
- Specialized perinatal centers can provide highly specialized care for individuals with complex medical needs. This includes providing expert care for women with pre-existing conditions or those at high risk.
- Telehealth and remote monitoring options can expand access to care, particularly for individuals in rural areas or those with limited mobility. This technology can support regular check-ups, medication management, and early identification of potential problems.
The Role of Community Health Workers
Community health workers (CHWs) play a crucial role in improving maternal health outcomes by bridging the gap between communities and healthcare systems.
- CHWs can provide culturally sensitive support, education, and encouragement to pregnant individuals, particularly those from marginalized communities. This can help ensure that individuals understand the importance of prenatal care and how to access it.
- CHWs can also facilitate transportation, scheduling, and communication between patients and healthcare providers, removing barriers to accessing care. They can act as essential liaisons between communities and healthcare providers.
- CHWs can identify individuals at high risk and connect them with appropriate services, ensuring that preventative measures are taken early. Their understanding of the community allows for targeted interventions.
Significance of Early Detection and Management of Complications
Prompt identification and management of complications during pregnancy are critical for positive maternal and infant outcomes.
- Early detection of preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, and other complications allows for timely interventions to prevent severe outcomes. This may involve medication, lifestyle changes, or hospitalization.
- Comprehensive care plans, developed in conjunction with healthcare providers and patients, should address the specific needs of individuals with identified complications. This can involve personalized care plans, tailored to address unique situations.
- Monitoring fetal well-being through regular ultrasounds and other tests can help identify potential problems early. Early intervention can significantly improve outcomes for both the mother and the baby.
Policy Recommendations for Improvement
Addressing maternal mortality and improving prenatal care requires a multifaceted approach that goes beyond individual interventions. Effective policy changes are crucial for creating a supportive system that ensures the health and well-being of pregnant individuals throughout their journeys. A comprehensive strategy necessitates a focus on funding, legislative action, and clear timelines for implementation.Comprehensive policy changes require a shift in societal attitudes and priorities.
Maternal health must be viewed as a critical public health concern, demanding significant investment and proactive measures. Such a paradigm shift is essential to create lasting positive change in maternal health outcomes.
Funding Allocation for Maternal Health Initiatives
Adequate funding is the bedrock of any successful maternal health initiative. Insufficient funding often translates to limited access to quality prenatal care, insufficient staffing in healthcare facilities, and inadequate resources for support services. This ultimately results in compromised care and potentially life-threatening outcomes for expectant mothers. Investing in maternal health initiatives is not just an expenditure; it’s an investment in the future well-being of families and communities.
- Prioritize funding for community-based programs that provide comprehensive support to pregnant individuals, particularly those from marginalized communities. These programs should include resources for nutrition, mental health, and transportation.
- Increase funding for research to identify and address the root causes of maternal mortality, focusing on disparities in access to care and outcomes.
- Invest in training and development for healthcare professionals specializing in maternal care, equipping them with the latest knowledge and skills to provide optimal care.
- Allocate funds for technology upgrades and infrastructure improvements in healthcare facilities to enhance prenatal care services and improve patient safety.
Legislative Actions to Support Maternal Health Programs
Legislative action plays a pivotal role in establishing a robust framework for maternal health. Specific laws can mandate improved access to care, incentivize healthcare providers to participate in maternal health programs, and hold institutions accountable for the quality of care provided. These actions can be catalysts for systemic change.
- Enact legislation that mandates paid family leave, ensuring that new mothers have the time and resources to recover and care for their newborns. This addresses both financial and logistical barriers.
- Establish clear standards for prenatal care services, ensuring that all pregnant individuals have access to evidence-based practices and comprehensive care. This includes standards for provider training, facility requirements, and program effectiveness.
- Pass legislation that requires insurance companies to cover essential maternal health services, removing financial barriers to access.
- Implement legislation that encourages and incentivizes the involvement of community organizations in providing support services to pregnant individuals and new mothers. This expands access to critical resources.
Timelines for Implementing Recommendations
Implementing these recommendations requires a structured approach with clear timelines. This ensures that the efforts are not just well-intentioned but also strategically planned and effectively executed.
| Recommendation | Timeline (Phase 1) | Timeline (Phase 2) |
|---|---|---|
| Increase funding for community-based programs | Year 1: Develop and pilot programs in targeted communities | Year 2-3: Expand programs to a wider geographic area |
| Establish clear standards for prenatal care | Year 1: Develop and publish standards | Year 2-3: Implement and monitor compliance |
| Enact paid family leave legislation | Year 1: Draft legislation | Year 2: Pass legislation and begin implementation |
| Mandate insurance coverage for maternal health services | Year 1: Conduct public awareness campaigns and lobbying | Year 2: Advocate for policy changes |
Illustrative Case Studies
Understanding maternal mortality and improving prenatal care requires looking at real-world examples. These case studies, while not exhaustive, offer valuable insights into successful interventions, challenges, and the impact of culturally competent care and community involvement. They illustrate how specific strategies can lead to positive changes in maternal health outcomes.
A Successful Intervention: The “Prenatal Wellness Program”
The Prenatal Wellness Program, implemented in a rural community in upstate New York, demonstrated a significant reduction in maternal mortality rates. The program focused on early identification of high-risk pregnancies through enhanced outreach to underserved populations. This included mobile health clinics providing comprehensive prenatal care, including nutritional counseling, stress management techniques, and access to mental health services. Crucially, the program fostered a strong partnership with local community organizations, ensuring culturally sensitive care tailored to the specific needs of the community.
The program’s success highlights the importance of tailored approaches and community engagement in improving maternal health.
Challenges in Accessing Prenatal Care: Geographic Barriers
A key challenge in achieving optimal maternal health outcomes is the disparity in access to prenatal care, particularly in rural and underserved areas. One case study highlights the difficulties faced by expectant mothers living in remote regions of New York State. Limited transportation options, long distances to healthcare facilities, and lack of affordable childcare often create significant barriers.
These obstacles often lead to delayed or inadequate prenatal care, increasing the risk of complications during pregnancy and childbirth. Addressing these geographic barriers requires a multifaceted approach including telehealth initiatives, mobile health clinics, and increased transportation assistance.
Culturally Competent Care: Addressing Language Barriers
Cultural competency plays a critical role in effective prenatal care. A case study focusing on a diverse community in New York City illustrates the importance of providing culturally sensitive care. Many immigrant women faced challenges communicating with healthcare providers due to language barriers. The program implemented a culturally competent approach by providing interpreters, culturally appropriate materials, and community health workers fluent in multiple languages.
These efforts improved communication and fostered trust between the expectant mothers and healthcare providers, ultimately leading to better health outcomes.
The Role of Community Health Workers: Bridging the Gap
Community health workers (CHWs) can be instrumental in improving maternal health outcomes. A case study involving a CHW program in a predominantly Hispanic community in New York City showed significant improvement in prenatal attendance and knowledge of prenatal care. CHWs provided culturally appropriate support, guidance, and encouragement to pregnant women, acting as trusted intermediaries between the community and healthcare providers.
This included addressing concerns, facilitating communication, and providing ongoing support throughout the pregnancy. CHWs proved effective in removing barriers to care and empowering pregnant women to actively participate in their own health management.
Contribution of Case Studies to Understanding the Issue, Hochul prenatal care maternal mortality
These case studies collectively demonstrate the multifaceted nature of maternal mortality and the importance of a multifaceted approach to improving maternal health outcomes. The examples of successful interventions, challenges in accessing care, the need for culturally competent care, and the role of community health workers underscore the complex interplay of factors influencing maternal health. Understanding these various factors allows for the development of more targeted and effective interventions to address the issue of maternal mortality and improve prenatal care in New York State.
Future Research Directions: Hochul Prenatal Care Maternal Mortality

Unraveling the complexities of maternal mortality requires a proactive and multifaceted approach to research. Future studies must go beyond simply identifying risk factors and delve into the intricate interplay of social determinants, healthcare access, and individual experiences. This exploration will be crucial in developing effective interventions and policies to reduce maternal mortality rates in New York and beyond.
Identifying and Quantifying Social Determinants of Health
Understanding the profound impact of socioeconomic factors on maternal health is paramount. Future research should rigorously investigate the correlation between poverty, lack of education, food insecurity, and maternal mortality. Data collection should include detailed socioeconomic profiles, exploring the interplay between these factors and access to quality prenatal care. A comprehensive analysis of these factors will be essential in tailoring interventions to address the unique needs of specific communities.
This may involve longitudinal studies that track the evolution of socioeconomic circumstances and their impact on maternal health outcomes over time.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Existing Interventions
Current prenatal care programs and support systems require rigorous evaluation. Research should examine the effectiveness of existing interventions, identifying best practices and areas needing improvement. This evaluation can involve a comparative analysis of different program models, assessing their impact on maternal health outcomes and satisfaction. Qualitative research methods, such as interviews and focus groups, can provide valuable insights into the experiences of mothers and healthcare providers, highlighting strengths and weaknesses in current approaches.
Exploring the Role of Healthcare Access and Provider Training
Geographical barriers to access, such as limited transportation options and inadequate healthcare facilities, disproportionately impact vulnerable populations. Future research should focus on understanding the role of healthcare access and provider training in reducing maternal mortality. Studies should analyze the availability and quality of prenatal care services across different geographic regions, and investigate the effectiveness of provider training programs designed to enhance sensitivity and responsiveness to diverse patient needs.
Governor Hochul’s prenatal care initiatives are crucial for reducing maternal mortality rates, but the tragic loss of life among NYC food delivery workers, highlighted by the memorials food delivery worker memorials nyc , reminds us that broader societal issues impact health outcomes. These workers’ dedication, often in precarious conditions, underscores the need for comprehensive support systems alongside the prenatal care programs to ensure the well-being of all New Yorkers.
A detailed assessment of these factors is crucial in improving equity in maternal healthcare access.
The Significance of Longitudinal Studies
Longitudinal studies offer a powerful tool for understanding the long-term impact of interventions and the trajectory of maternal health. These studies track individuals over time, allowing researchers to observe the evolution of health outcomes and the effectiveness of interventions in preventing adverse events. By monitoring pregnant women from preconception through postpartum, longitudinal studies can reveal critical insights into the factors influencing maternal health throughout the entire perinatal period.
These studies can provide valuable data for policymakers to evaluate the effectiveness of specific interventions over time and to adapt strategies based on evolving circumstances. An example of a successful longitudinal study would involve following a cohort of pregnant women over several years, assessing their access to prenatal care, socioeconomic status, and ultimately, their postpartum health.
Influence on Policy Decisions
Research findings will directly influence policy decisions aimed at reducing maternal mortality. The data collected through rigorous research studies can inform the development of targeted interventions and the allocation of resources to areas most in need. For example, if a study reveals a strong correlation between poverty and inadequate prenatal care, policymakers can allocate funds to support community health centers in underserved areas and implement programs to reduce poverty levels in vulnerable communities.
The results of research studies will not only contribute to evidence-based policy but also ensure that interventions are tailored to address the specific needs and experiences of pregnant individuals.
Last Word
In conclusion, addressing Hochul prenatal care maternal mortality requires a multifaceted approach encompassing improved access to quality care, targeted interventions, and robust policy changes. This analysis highlights the urgent need for a comprehensive plan to reduce maternal mortality rates and create a healthier future for pregnant New Yorkers. The case studies underscore the importance of tailored interventions and the significance of community involvement.
FAQ
What are the key challenges in accessing prenatal care in New York?
Geographic disparities, financial constraints, and lack of culturally competent care are some key challenges impacting access to prenatal care in New York.
How do socioeconomic factors influence maternal mortality rates?
Socioeconomic factors, such as income levels and education, play a significant role in shaping access to quality prenatal care and can contribute to disparities in maternal mortality rates.
What specific policy changes could reduce maternal mortality?
Increased funding for maternal health initiatives, expanded access to culturally competent care, and improved training for healthcare providers are potential policy changes.
What role do community health workers play in improving maternal health outcomes?
Community health workers can provide vital support, education, and resources to pregnant women, fostering better health outcomes and reducing maternal mortality.






