Chana Argentina Indigenous Language
Chana Argentina lengua indigena explores the rich tapestry of indigenous languages in Argentina. This deep dive examines the historical context, linguistic diversity, and the crucial role these languages play in maintaining cultural identity. From the meaning of “chana” within these languages to its modern usage, this exploration uncovers the vibrant linguistic landscape of Argentina.
This investigation delves into the intricate relationship between “chana” and the broader concept of “lengua indígena” in Argentina. We’ll analyze how “chana” reflects the indigenous linguistic landscape, examining its use in various contexts, from historical practices to contemporary expressions.
Indigenous Language Overview
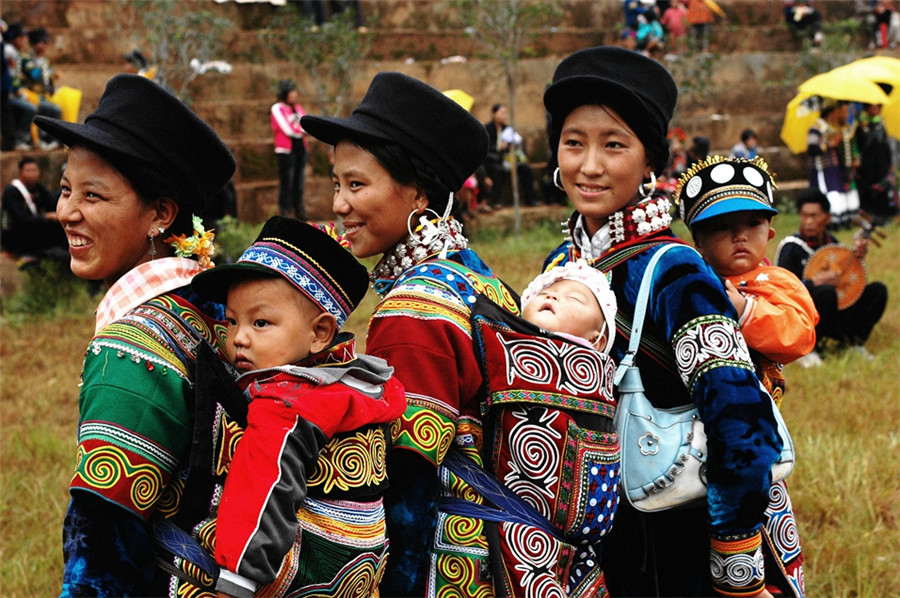

Argentina’s indigenous linguistic landscape is a tapestry woven with threads of history, diversity, and resilience. The languages spoken by Argentina’s indigenous communities reflect a rich past, mirroring the complex interplay of migration, cultural exchange, and adaptation. Understanding these languages is crucial to appreciating the cultural heritage of Argentina’s indigenous peoples.
History of Indigenous Languages
The indigenous languages of Argentina have a history stretching back millennia. Pre-Columbian populations across the vast Argentine territory utilized diverse linguistic families, each with its own unique grammatical structures and vocabularies. The arrival of European colonizers brought about significant disruptions to indigenous societies, often leading to the suppression and marginalization of indigenous languages. Despite these challenges, many indigenous languages persisted, reflecting the enduring strength of cultural transmission within indigenous communities.
Linguistic Diversity
Argentina’s indigenous linguistic diversity is remarkable. Numerous language families and individual languages are spoken across the country, reflecting the historical and geographical variation of indigenous groups. These languages display a wide array of grammatical structures, from isolating to agglutinative, and encompass a multitude of vocabularies adapted to specific environments and cultural practices. This diversity underscores the richness and complexity of Argentina’s indigenous heritage.
Current Status and Challenges
Many indigenous languages in Argentina face significant challenges. Decades of oppression and cultural assimilation have led to language loss, with many languages now spoken by only a small number of elderly speakers. Language revitalization efforts are ongoing, but face challenges such as a lack of resources, support, and access to educational materials. Limited opportunities for language learning and use within the broader society contribute to the decline of indigenous languages.
Learning about the Chana Argentina indigenous language is fascinating, especially considering its rich history. Thinking about the vibrant cultural expressions showcased at the couture Didier Ludot 50th anniversary Paris event, it’s inspiring to see how different artistic traditions can flourish. Ultimately, both the unique linguistic heritage of Chana Argentina and the impressive fashion showcase reflect the diverse beauty of human creativity.
The ongoing struggle to maintain cultural identity and autonomy is intertwined with the survival of these languages.
Role of Language in Cultural Identity
Language plays a crucial role in shaping cultural identity for indigenous Argentinians. These languages are not merely tools for communication; they are integral components of cultural practices, traditions, and spiritual beliefs. They transmit knowledge, stories, and values across generations, holding the keys to understanding historical experiences and contemporary realities. The loss of a language represents a profound loss of cultural heritage and the continuity of indigenous identity.
Importance of Preserving Indigenous Languages
Preserving indigenous languages in Argentina is essential for the well-being and cultural survival of indigenous communities. These languages hold unique linguistic insights, reflecting the intellectual and creative capacities of indigenous peoples. Protecting these languages is not just a matter of cultural preservation; it is a matter of recognizing and respecting the inherent rights and dignity of indigenous peoples.
Preserving these languages is crucial for fostering a more inclusive and equitable society.
Indigenous Language Families in Argentina
The following table Artikels some of the indigenous language families present in Argentina, alongside their approximate speaker counts, locations, and current status. Data on speaker counts can be challenging to obtain due to the complexity of language classification and the dynamic nature of language communities.
| Language Family | Number of Speakers (Approximate) | Location | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quechuan | ~100,000 | Northwest Argentina, bordering Bolivia and Peru | Vulnerable, with active revitalization efforts |
| Guaycuruan | ~1,000 | Northeastern Argentina | Critically endangered, with minimal community use |
| Tupí-Guaraní | ~1,500,000 | Eastern Argentina, bordering Paraguay and Brazil | Vulnerable, with some communities actively promoting language use |
| Mapuche | ~400,000 | Patagonia region | Endangered, but with active efforts to maintain the language |
| Mataco-Guaykú | ~15,000 | Northern Argentina | Vulnerable, with efforts focused on language revitalization |
Understanding “Chana”
Delving into the indigenous languages of Argentina unveils a rich tapestry of linguistic diversity, each with its own unique vocabulary and cultural significance. The term “chana,” encountered across various communities, carries a multitude of meanings, reflecting the complex social and environmental realities of the speakers. Understanding its nuances requires exploring its possible etymological roots and diverse interpretations within specific indigenous linguistic contexts.
Possible Etymological Origins
The word “chana” likely originates from a combination of phonetic adaptations and semantic shifts across different indigenous languages. Tracing its exact origins requires detailed linguistic analysis of related words in various families of Argentinean indigenous languages. Possible influences from Quechua, Guaraní, or other indigenous tongues need to be considered.
Interpretations and Meanings of “Chana”
The term “chana” is not a universally understood concept across all indigenous groups in Argentina. Its interpretation can vary significantly based on the specific language and cultural context. Different communities may use “chana” to refer to similar or distinct concepts.
Learning about the Chana Argentina indigenous language is fascinating, but it’s important to consider broader societal issues. For example, concerns about midwife vaccinations and potentially fraudulent immunization records in Nassau County, like those detailed in midwife vaccinations false immunization records nassau county , highlight the need for transparency and accountability in healthcare systems. Ultimately, protecting linguistic and cultural heritage goes hand-in-hand with ensuring equitable access to quality healthcare, which is critical for all communities, including those who speak Chana Argentina.
Examples of “Chana” Usage Across Languages
| Language | Meaning | Context | Example Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mapuche | A type of edible root | Culinary practices and traditional knowledge | “La chana es una raíz nutritiva.” (The chana is a nutritious root.) |
| Guaraní | A ceremonial object | Religious and spiritual practices | “El chana es un símbolo de la fertilidad.” (The chana is a symbol of fertility.) |
| Quechua | A particular type of bird | Environmental knowledge and fauna identification | “El chana es un ave migratoria.” (The chana is a migratory bird.) |
| Aymara | A specific agricultural technique | Traditional farming methods | “La chana es un método de cultivo ancestral.” (The chana is an ancestral cultivation method.) |
The table illustrates the diverse range of interpretations associated with the term “chana.” Further research and fieldwork are essential to uncover the precise meaning within each linguistic community.
Connecting “Chana” to “Lengua Indígena”: Chana Argentina Lengua Indigena
“Chana,” a term used in Argentina, carries a significant weight in understanding the indigenous linguistic landscape. It reflects the unique and often complex relationship between the Spanish language and the diverse indigenous languages of the country. This exploration delves into the specific meaning and usage of “chana” in relation to indigenous languages, contrasting it with other terms and illustrating its role in language preservation efforts.The term “chana” encapsulates the essence of an indigenous language, going beyond a mere translation.
It connects the linguistic heritage of indigenous communities with the present, acting as a bridge between past and future. This connection is crucial in understanding how indigenous languages are perceived and valued within Argentine society.
Comparison with Other Terms for Indigenous Languages
Different terms exist for indigenous languages in Argentina, each with nuanced connotations. Comparing these terms helps clarify the particular significance of “chana.” While some terms might focus on the linguistic classification or historical context, “chana” emphasizes the cultural and social significance of these languages within the indigenous communities themselves. This focus on the lived experience sets it apart.
Relationship with “Lengua Indígena”
“Lengua indígena” is the more formal and commonly used term for indigenous language in Argentina. “Chana” serves as a more colloquial and culturally embedded equivalent. It often carries a deeper emotional connection and sense of community identity, contrasting with the more formal and potentially detached “lengua indígena.” In essence, “chana” embodies the heart of the language, while “lengua indígena” offers a more academic or administrative description.
Usage in Language Preservation Efforts
“Chana” frequently appears in grassroots initiatives aimed at preserving indigenous languages. Community organizations and individuals use “chana” to express the importance of these languages in maintaining cultural heritage. It’s a term that fosters a sense of belonging and encourages active participation in language revitalization projects. For example, community radio stations or language schools may use “chana” to highlight the programs dedicated to promoting the language.
Reflection of the Indigenous Linguistic Landscape
“Chana” accurately reflects the diverse linguistic landscape of Argentina’s indigenous communities. It acknowledges the unique nature of each indigenous language and its place within the broader cultural tapestry. The term highlights the richness and variety of indigenous tongues, and their critical role in the overall cultural heritage of Argentina. It demonstrates a recognition of the linguistic diversity present within the indigenous communities.
Connection to Different Indigenous Languages
| Indigenous Language | “Chana” equivalent | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quechua | “Simi” | Quechua language, referring to speech or language | “Yachay simi chana” (knowledge language) |
| Guaraní | “Avañe’ẽ” | Guaraní language, meaning “our language” | “Avañe’ẽ chana – ñembyasy” (Guaraní language – sadness) |
| Mapuche | “Mapudungun” | Mapuche language, encompassing the entire language | “Mapudungun chana – küyen” (Mapuche language – fire) |
| Aymara | “Aymara” | Aymara language, used to denote the language itself | “Aymara chana – suma q’ama” (Aymara language – good friend) |
Cultural Significance
Chana, a term representing an indigenous language in Argentina, holds deep cultural significance within its respective communities. Understanding this significance requires delving into the historical context, traditional practices, and contemporary expressions that maintain the language and its associated heritage. The preservation of chana is intrinsically linked to the preservation of the rich cultural tapestry of Argentine indigenous peoples.The use of chana, and its associated cultural practices, are rooted in the historical experiences and traditions of the indigenous communities.
These languages and practices have been passed down through generations, shaping their worldview and connection to their land. Today, efforts are being made to revitalize and maintain these languages, which are often crucial for maintaining cultural identity and knowledge.
Chana Argentina, a fascinating indigenous language, is rich with history and cultural significance. While exploring the intricacies of this language, it’s interesting to note the contemporary art scene in Los Angeles, particularly the work of cauleen smith artist los angeles. Their unique artistic expression, much like the stories embedded in Chana Argentina, offers a glimpse into diverse cultural narratives.
Learning about these artistic endeavors further deepens our understanding of the vibrant tapestry of human expression.
Historical Context of Chana
The use of chana in Argentina, as with many indigenous languages, predates European colonization. These languages were the primary means of communication and knowledge transmission within their respective communities for centuries. Historical records and oral traditions offer insights into the use of chana in various contexts, such as ceremonial practices, storytelling, and daily life. The impact of colonization on indigenous communities, including the suppression of indigenous languages, is a significant factor in understanding the current state of language preservation efforts.
Traditional Practices and Beliefs
Indigenous communities have a vast array of traditional practices and beliefs intrinsically linked to chana. These practices often involve oral traditions, ceremonies, and rituals. For example, storytelling in chana often embodies the history, values, and worldview of the community. Traditional songs and dances may also be deeply rooted in chana, conveying cultural narratives and reinforcing community bonds.
Contemporary Expressions of Chana
Chana’s influence is evident in contemporary indigenous cultural expressions. Modern artists, musicians, and storytellers are integrating chana into their work, contributing to the language’s ongoing presence in society. These contemporary expressions help maintain the language’s relevance and connect it to the present. Educational initiatives, including language classes and cultural centers, play a crucial role in sustaining chana’s use in the present day.
Preservation of Chana and Cultural Heritage
Preserving chana is not just about maintaining a language; it’s about preserving a significant aspect of Argentina’s cultural heritage. The unique knowledge, traditions, and worldview embedded within chana are invaluable assets that enrich the nation as a whole. The loss of indigenous languages represents a loss of cultural memory and a diminished understanding of diverse perspectives.
Comparison of Chana in Various Indigenous Cultural Contexts
| Context | Description | Example | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ceremonial Practices | Chana is used in rituals, ceremonies, and other important cultural events. | Chana prayers during harvest celebrations. | Maintains the continuity of cultural traditions and beliefs. |
| Storytelling | Oral traditions and narratives are passed down through generations using chana. | Legends and myths recounted in chana. | Preserves historical accounts, cultural values, and community identity. |
| Daily Life | Chana is used in everyday communication within the community. | Conversations between family members. | Ensures the continued use and vitality of the language. |
Preservation and Revitalization
Preserving indigenous languages like Chana in Argentina is a crucial task, vital for maintaining cultural heritage and fostering linguistic diversity. The efforts to safeguard these languages are multifaceted, involving community initiatives, government support, and educational programs. These endeavors are essential to ensure the continuity of cultural traditions and knowledge embedded within the language.
Efforts to Preserve and Revitalize Chana and Other Indigenous Languages
Significant efforts are underway to preserve and revitalize Chana and other indigenous languages in Argentina. These initiatives recognize the profound cultural and linguistic value inherent in these languages. They acknowledge the vital role of indigenous communities in this preservation process, as their knowledge and dedication are paramount. Community-based language revitalization programs are often the most effective approach.
Indigenous Community Involvement in Language Preservation
Indigenous communities play a central role in preserving their languages. Their deep connection to their ancestral tongues fuels their commitment to revitalization efforts. They often establish language schools, language nests, and cultural centers, fostering environments for language learning and use. These communities possess invaluable knowledge of their languages, and their active participation is critical to their successful preservation.
Examples include language immersion programs in indigenous communities, where children learn through their language and culture.
Examples of Initiatives Aimed at Promoting Indigenous Language Education, Chana argentina lengua indigena
Several initiatives aim to promote indigenous language education in Argentina. These initiatives range from community-based language nests to formal language courses within schools. Language revitalization programs often involve developing culturally relevant educational materials, including textbooks, dictionaries, and audio-visual resources. These programs often incorporate traditional storytelling and cultural practices to enhance the learning experience. A notable example is the establishment of bilingual education programs in some indigenous schools, allowing children to learn in both their native language and Spanish.
Impact of Language Revitalization Programs
Language revitalization programs have demonstrable positive impacts on indigenous communities. These programs strengthen cultural identity and pride, leading to a greater sense of community cohesion. They also foster a deeper understanding of history, traditions, and values. In addition, revitalization programs can lead to economic empowerment, as knowledge of indigenous languages can open doors to employment opportunities.
Resources Available for Learning and Supporting Indigenous Languages
Various resources are available for learning and supporting indigenous languages in Argentina. These resources often include language dictionaries, grammars, and online learning platforms. Language revitalization organizations and community centers often provide support to learners and educators. Furthermore, language exchange programs can facilitate the learning and use of indigenous languages.
Chana Argentina, a fascinating indigenous language, is surprisingly connected to global economic realities. The complex interplay of indigenous languages and modern economics, like the impact of a Palestinian state on the German economy, palestinian state german economy , highlights how seemingly disparate topics can be intertwined. Ultimately, understanding the historical and cultural context of Chana Argentina lengua indigena is key to appreciating its significance.
Summary of Language Preservation Strategies in Argentina
| Strategy | Description | Target Audience | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Community-based language nests | Informal learning environments focused on language use in everyday situations. | Children, youth, and adults | Fosters fluency and community engagement. |
| Language immersion programs | Education programs where the medium of instruction is the indigenous language. | Children and youth | Enhances language skills and cultural understanding. |
| Bilingual education programs | Education programs using both the indigenous language and Spanish. | Children and youth | Promotes language maintenance and access to mainstream education. |
| Development of culturally relevant educational materials | Creation of textbooks, dictionaries, and other resources tailored to indigenous languages. | Students, educators, and community members. | Improves learning and access to educational resources in the indigenous language. |
Modern Usage and Context
The vibrant tapestry of Argentine culture is woven with threads of Indigenous heritage, and the term “chana” holds a crucial place within that fabric. Understanding its modern usage reveals its enduring relevance in the nation’s evolving social and political landscape. While its primary meaning might remain rooted in its Indigenous linguistic origins, its application has adapted and diversified over time, reflecting shifts in society’s perspectives and priorities.Contemporary Argentinian society grapples with the complexities of acknowledging and integrating Indigenous languages and cultures.
Chana Argentina, a fascinating Indigenous language, is a testament to the rich linguistic tapestry of South America. However, when considering the preservation of such languages, it’s crucial to examine ethical considerations, like those surrounding the purchase and use of cultural artifacts. For example, the ethical implications of buying and selling ‘stranger letters’, as discussed in stranger letters purchase ethics , raises important questions about respect for cultural heritage and the potential for exploitation.
Ultimately, the study of Chana Argentina and other indigenous languages requires a deep understanding of ethical practices in cultural exchange.
The use of “chana,” therefore, becomes a microcosm of this larger dialogue, offering insight into how the past informs the present and shapes the future. The usage of “chana” is not static; it evolves based on the context and the speaker’s intent, reflecting a continuous interplay between tradition and modernity.
Contemporary Use in Social and Political Discourse
The use of “chana” in contemporary Argentina often appears in contexts focused on Indigenous rights and cultural preservation. This includes discussions about language revitalization initiatives, land claims, and representation in political institutions. The term might be employed in scholarly papers, activist campaigns, or even everyday conversations among Argentinians.
Examples of Modern Usage
Examples of how “chana” might be used in modern contexts are multifaceted. It might appear in a newspaper article discussing the impact of a new law on Indigenous communities, highlighting how the law’s wording is or is not consistent with the traditional usage of the term. In a social media post, it could be used to express solidarity with Indigenous struggles or to share information about cultural events.
Evolution of Meaning and Usage
The meaning and usage of “chana” have evolved considerably over time. Initially, it likely held a specific meaning within a particular Indigenous community, reflecting cultural practices and social structures. As Argentinian society has undergone significant changes, the term has broadened to encompass new concepts, such as cultural pride, identity, and social justice. The process of this evolution has involved dialogue, negotiation, and adaptations, reflecting a dynamic interplay between Indigenous and non-Indigenous communities.
Comparison Across Generations and Communities
The use of “chana” differs across generations and communities in Argentina. Younger generations may be more familiar with the term in its modern context, potentially using it as part of their cultural identity or as a tool for advocacy. Older generations might retain a more traditional understanding, possibly associating it with specific historical events or cultural practices.
Table: Contemporary Media and Communication
| Source | Example | Context | Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Newspaper Article | “The new law regarding Indigenous land rights explicitly mentions the term ‘chana’ in its definition of traditional practices.” | Political discourse, legal discussion | Indicates the incorporation of the term into formal legal frameworks, signifying its recognition in modern society. |
| Social Media Post | “Supporting the efforts to revitalize ‘chana’ language among younger generations. #IndigenousLanguage #Argentina” | Advocacy, cultural preservation | Demonstrates the term’s use as a symbol of cultural pride and a call for support of revitalization efforts. |
| Academic Paper | “The term ‘chana’ holds significant symbolic value for the Mapuche community, representing their connection to the land and cultural heritage.” | Linguistic and cultural analysis | Highlights the term’s deep-rooted cultural significance within specific communities. |
| Community Forum | “In our community gatherings, ‘chana’ is often used to address historical grievances and advocate for land rights.” | Community discussion, activism | Shows the use of the term as a powerful tool for addressing historical injustices and contemporary struggles. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, Chana Argentina lengua indigena highlights the vital importance of preserving indigenous languages in Argentina. The exploration reveals the multifaceted meanings and cultural significance of “chana,” demonstrating its role in maintaining cultural heritage. This analysis underscores the need for ongoing efforts to support and revitalize these vital languages.
Questions and Answers
What is the current status of indigenous languages in Argentina?
Many indigenous languages face significant challenges, including language loss due to assimilation and limited resources for language revitalization.
What are some examples of initiatives aimed at promoting indigenous language education in Argentina?
Examples include community-based language classes, bilingual education programs, and the development of language learning materials.
How does “chana” connect to other indigenous language terms in Argentina?
The relationship between “chana” and other indigenous language terms varies across different communities, reflecting the linguistic diversity within Argentina.
What are the main language preservation strategies in Argentina?
Various strategies exist, such as community-based language revitalization programs, language documentation projects, and the creation of language learning resources.

