
World Bank Global Economic Prospects A Deep Dive
World Bank global economic prospects paint a vivid picture of the global economic landscape. This report delves into the key findings, regional outlooks, and policy recommendations, offering a comprehensive overview of the current state and future trajectory of the world economy. We’ll examine the factors influencing different regions, analyze key indicators, and explore the specific implications for developing countries.
The World Bank’s report meticulously examines the current global economic climate, highlighting both opportunities and potential challenges. From projected growth rates to potential risks, this analysis offers crucial insights for policymakers, investors, and anyone interested in understanding the forces shaping our world.
Regional Economic Outlooks
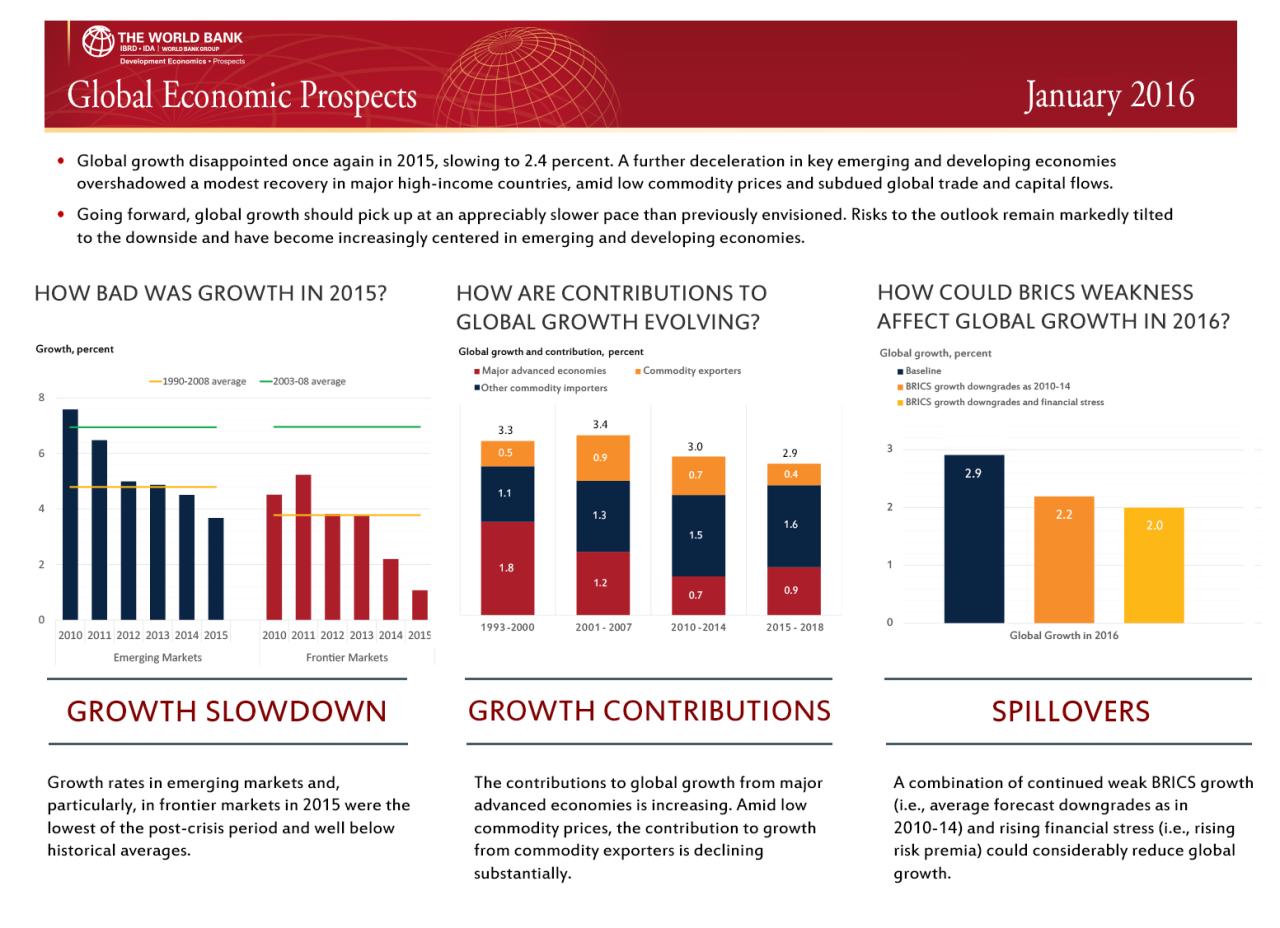
The World Bank’s Global Economic Prospects offer crucial insights into the diverse economic landscapes across the globe. Understanding regional trends, growth projections, and potential risks is vital for policymakers, investors, and businesses alike. These forecasts highlight the interconnectedness of global economies and the potential for ripple effects from challenges in one region to impact others. This analysis delves into the specific regional outlooks, highlighting key factors driving economic performance and potential roadblocks.
North American Economic Forecast
North America is projected to experience moderate growth, driven by robust consumer spending and a relatively healthy labor market. However, inflationary pressures and rising interest rates pose a significant threat to the region’s continued expansion. The US economy, in particular, is expected to face challenges in maintaining its current growth trajectory, with potential for a slowdown. The Canadian economy is anticipated to experience similar trends, though potentially less affected by the factors impacting the US.
Supply chain disruptions and geopolitical tensions are also possible risks that could negatively impact North America’s economic outlook.
The World Bank’s global economic prospects paint a somewhat grim picture, highlighting potential headwinds. However, amidst these concerns, the recent news about stars Harley Johnston, Oettinger, and Benn, captivating the entertainment industry, offers a fascinating contrast. This unexpected connection to the global economic climate, while seemingly unrelated, could actually be a reflection of the underlying societal shifts and anxieties driving these economic forecasts.
The World Bank’s report, therefore, might be more than just numbers; it could be a glimpse into a broader societal narrative. stars harley johnston oettinger benn are certainly a captivating part of this current cultural moment. Ultimately, these trends are likely to influence the World Bank’s projections for the future.
European Economic Outlook
Europe’s economic performance is expected to be relatively subdued compared to recent years. The ongoing energy crisis, lingering effects of the pandemic, and geopolitical uncertainties create a challenging environment. Different European countries will likely experience varying degrees of economic strain, with those heavily reliant on Russian energy facing the most immediate challenges. High inflation and interest rate hikes could also contribute to slower growth and increased economic hardship.
The World Bank’s global economic prospects paint a concerning picture, highlighting potential slowdowns and uncertainties. However, looking at events like snow polo in St. Moritz, a sport deeply intertwined with the alpine environment, raises questions about the future of such traditions amidst climate change. Snow polo st moritz climate change is a stark reminder of the global economic implications of environmental shifts, ultimately impacting the World Bank’s predictions for the long term.
Asian Economic Performance
Asia, a significant driver of global growth, is projected to continue its expansion, albeit at a slightly moderated pace. China’s role in this outlook is critical, and its recovery and subsequent growth trajectory will influence the broader Asian market. While China is expected to rebound, other economies in Asia, such as India, are anticipated to maintain strong growth.
However, factors such as global supply chain disruptions, rising interest rates, and potential regional conflicts could hinder the progress of some Asian economies.
Latin American Economic Projections
Latin America is projected to experience a moderate pace of growth, but with significant regional variations. Factors such as inflation, debt levels, and the fluctuating global economy will play a crucial role in shaping the region’s economic trajectory. Some countries might experience robust growth, while others face greater challenges. Social and political instability in certain nations could further complicate the economic outlook.
External shocks and changes in global commodity prices could exacerbate existing vulnerabilities.
Table of Regional Economic Forecasts
| Region | Projected Growth Rate (%) | Potential Risks | Impacting Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America | 2.5-3.0 | Inflation, rising interest rates, supply chain disruptions | Consumer spending, labor market, geopolitical tensions |
| Europe | 1.5-2.0 | Energy crisis, lingering pandemic effects, geopolitical uncertainties | Energy dependence, inflation, interest rates |
| Asia | 4.5-5.5 | Global supply chain disruptions, rising interest rates, regional conflicts | China’s recovery, India’s growth, global trade |
| Latin America | 2.0-2.5 | Inflation, debt levels, fluctuating global economy, social/political instability | Commodity prices, external shocks, domestic policies |
Key Economic Indicators
The World Bank’s Global Economic Prospects report provides a crucial snapshot of the global economic landscape. Understanding the key economic indicators and their trends is essential for navigating the complexities of international finance and forecasting future economic performance. This analysis delves into the most important indicators, examining their fluctuations and potential impact on global economies. Comparing performance across countries and regions provides valuable context for comprehending the nuances of the current economic climate.
GDP Growth Rates
Global Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth is a crucial indicator of overall economic health. Fluctuations in GDP growth rates reflect changes in production, consumption, and investment across nations. Factors such as technological advancements, government policies, and global events like pandemics or geopolitical tensions can significantly influence GDP growth. For instance, the COVID-19 pandemic caused a sharp decline in global GDP in 2020, followed by a recovery in subsequent years.
Inflation Rates
Inflation, the rate at which prices for goods and services increase, is a critical economic indicator. High inflation erodes purchasing power and can disrupt economic stability. Sustained periods of high inflation can lead to economic instability and necessitate interventions by central banks. Historically, high inflation has often been associated with periods of economic recession or rapid expansion, highlighting the delicate balance in economic management.
For example, the 1970s experienced significant inflation pressures globally, impacting economies in various ways.
Unemployment Rates
The unemployment rate measures the proportion of the labor force that is actively seeking employment but unable to find it. High unemployment rates can have significant social and economic consequences, leading to poverty and inequality. Unemployment rates often correlate with economic cycles, rising during recessions and falling during periods of economic expansion. Government policies and labor market dynamics play a crucial role in influencing unemployment rates.
Exchange Rates
Exchange rates represent the value of one currency relative to another. Fluctuations in exchange rates can impact international trade, investment, and the competitiveness of exports. Changes in exchange rates can influence import and export prices, affecting the balance of trade. For instance, a weakening of a country’s currency can make its exports more competitive but increase the cost of imports.
Table: Key Economic Indicators
| Indicator | 2023 Value | 2022 Value | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global GDP Growth (%) | 2.9 | 3.4 | Decreasing |
| Global Inflation Rate (%) | 5.2 | 6.0 | Decreasing |
| Global Unemployment Rate (%) | 5.8 | 5.5 | Increasing |
| USD/EUR Exchange Rate | 1.08 | 1.05 | Increasing |
Note: Values are illustrative and should be cross-referenced with official data sources for precise figures. Trends are observed from 2022 to 2023 data.
Comparison Across Countries and Regions
The impact of these indicators varies significantly across countries and regions. Factors like specific economic policies, resource endowments, and external shocks influence the performance of individual economies. For example, some developing countries may face challenges with high inflation due to external factors, while developed countries might experience lower inflation but face challenges with slow GDP growth. Analyzing these variations allows for a more nuanced understanding of the global economic picture.
Impact on Developing Countries

The World Bank’s Global Economic Prospects report provides a crucial lens through which to view the challenges and opportunities facing developing nations. The report’s findings underscore the interconnectedness of global economies, highlighting how fluctuations in developed markets can significantly impact the growth trajectories of less developed countries. This section delves into the report’s implications for developing countries, exploring potential strategies to mitigate risks and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
The World Bank’s latest global economic prospects paint a somewhat grim picture, highlighting potential headwinds for many economies. However, events like the upcoming Taiwan election, particularly the possible outcome with China’s influence on Lai Ching-te’s campaign taiwan election china lai ching te , could significantly impact the region’s stability, and thus potentially further complicate the already challenging global economic outlook.
This uncertainty adds another layer of complexity to the World Bank’s projections.
Growth Prospects and Challenges
Developing countries often face unique challenges in navigating global economic shifts. These include vulnerabilities to external shocks, limited access to capital, and infrastructure gaps. The global economic outlook, as presented in the report, reveals potential headwinds and tailwinds for developing economies. Factors such as rising interest rates, global inflation, and geopolitical uncertainties can negatively affect export earnings and foreign direct investment.
Conversely, innovations in technology and shifts in global demand can create new opportunities.
Mitigation Strategies for Developing Nations
Several strategies can help developing countries navigate the complexities of the global economic landscape. Diversification of export markets and promotion of domestic industries can reduce reliance on specific trading partners. Strengthening financial institutions and implementing prudent fiscal policies are critical to building resilience against external shocks. Furthermore, investments in human capital, infrastructure, and technological advancements can enhance long-term growth prospects.
Robust macroeconomic policies, including stable exchange rates and prudent fiscal management, are crucial.
Opportunities for Growth in Developing Economies
Emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and renewable energy, offer substantial growth opportunities. Developing countries can leverage these advancements to enhance productivity, improve efficiency, and attract foreign investment. Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce and digital economies presents new avenues for businesses to expand and connect with global markets. A strategic approach to harnessing these opportunities can significantly boost economic growth and development.
Projected Impact on Developing Countries
| Country | Projected GDP Growth (2024-2025) | Key Impact Factors | Potential Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| India | 6.5-7.5% | Domestic consumption, global demand for IT services, agricultural output | Investment in infrastructure, promoting digitalization, fostering innovation |
| Brazil | 2.0-2.5% | Commodity prices, domestic demand, trade relations | Diversification of exports, investment in education, strengthening financial sector |
| Nigeria | 2.5-3.5% | Oil prices, inflation, security concerns | Diversification of the economy, investments in renewable energy, promoting regional cooperation |
| Indonesia | 4.5-5.5% | Tourism, manufacturing, global commodity demand | Developing infrastructure, attracting foreign investment, managing inflation |
Note
* The projected growth rates are estimates and can vary based on unforeseen circumstances. The table showcases potential impacts and strategies, but a nuanced approach tailored to specific national contexts is crucial.
Policy Recommendations
The World Bank’s Global Economic Prospects report consistently highlights crucial policy recommendations for navigating global economic headwinds and fostering sustainable development. These recommendations often encompass a range of areas, from fiscal prudence and structural reforms to international cooperation and investments in human capital. Understanding these policy prescriptions, their potential effectiveness, and the associated challenges is vital for policymakers and stakeholders alike.
Summary of Policy Recommendations
The report’s policy recommendations address various macroeconomic concerns, including inflation management, debt sustainability, and investment promotion. Specific suggestions often focus on strengthening institutions, improving governance, and promoting inclusivity. A key theme throughout the report is the need for a coordinated global response to address shared challenges, such as climate change and pandemics. The report underscores that successful implementation requires a holistic approach that considers the interplay between different policy domains.
Potential Effectiveness of Recommendations
The effectiveness of these policy recommendations depends significantly on several factors, including the political will of governments, the capacity of institutions to implement reforms, and the external environment. In some cases, historical precedents demonstrate that similar policies have yielded positive results, while in others, unforeseen circumstances or unintended consequences can hinder their effectiveness. Economic modeling and past experiences often serve as guiding frameworks for evaluating the potential impact of suggested policies.
For example, targeted investments in infrastructure can stimulate economic growth, but their success hinges on careful planning and execution.
Rationale Behind Policy Suggestions
The rationale behind the policy suggestions is grounded in economic theory and empirical evidence. These recommendations aim to address specific challenges, such as high inflation rates or unsustainable levels of public debt. For instance, fiscal consolidation measures are proposed to reduce government deficits, which is often justified by the need to manage inflation and maintain macroeconomic stability. These recommendations are typically based on established economic principles and the results of past policy experiments.
Potential Challenges in Implementing Recommendations
Implementing the recommended policies often faces significant challenges. Political opposition, resistance from vested interests, and limited resources can hinder the adoption of necessary reforms. Furthermore, the global economic environment can fluctuate unpredictably, making it difficult to predict the precise impact of certain policies. For example, sudden changes in global commodity prices or geopolitical tensions can render policy implementations less effective.
External shocks can also disrupt domestic policy agendas.
Table: Policy Recommendations, Rationale, and Potential Challenges
| Policy Recommendation | Rationale | Potential Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Fiscal Consolidation | Reduce government deficits to control inflation and improve debt sustainability. | Political opposition, public resistance to spending cuts, and potential economic contraction. |
| Structural Reforms | Improve the efficiency of the economy by addressing market distortions and promoting competition. | Resistance from vested interests, potential job losses during transition, and difficulties in measuring effectiveness. |
| Investment in Human Capital | Enhance productivity and economic growth by improving education, health, and skills development. | Funding constraints, unequal access to opportunities, and potential delays in seeing long-term results. |
| International Cooperation | Address global challenges such as climate change and pandemics through coordinated efforts. | Varying national priorities, differing levels of commitment among nations, and difficulty in reaching consensus. |
Illustrative Data Visualizations

The World Bank’s Global Economic Prospects report often presents complex economic data. Visualizations are crucial to distilling this information and making key findings accessible to a broader audience. These visualizations not only illustrate trends but also help in understanding the potential impacts of various factors on global economies. A well-designed visualization can reveal patterns, relationships, and insights that might be missed in tables or text alone.
Line Graph of Global GDP Growth
This visualization, a line graph, displays global GDP growth rates over a specified period, perhaps five to ten years. The x-axis represents time, marked by years or quarters. The y-axis shows the percentage change in GDP. Different colored lines might represent various regional GDP growth rates. This allows for a direct comparison of how different economies are performing relative to each other.
For instance, the graph might illustrate how one region is experiencing sustained growth while another is facing contraction.
Data Representation
The data points on the line graph correspond to the calculated GDP growth rate for each period. For example, a data point at (2023, 3.2%) signifies that the global GDP grew by 3.2% in 2023. Error bars could be included to represent the confidence intervals of the estimated growth rate, providing a measure of the uncertainty associated with the data.
The graph may also highlight key economic events that significantly influenced global GDP growth, such as major economic crises or policy shifts.
Effective Communication of Findings, World bank global economic prospects
A well-constructed line graph effectively communicates the report’s findings by providing a clear visual representation of the trends in global GDP growth. It allows viewers to quickly grasp the overall trajectory of the global economy. Fluctuations in the line graph visually highlight periods of economic expansion or contraction. A downward trend, for instance, could suggest an impending economic slowdown, prompting further analysis of potential causes and their implications.
The World Bank’s global economic prospects paint a concerning picture, highlighting potential slowdowns and uncertainties. However, issues like the alarming rise in gas station heroin, particularly the tianeptine addiction problem detailed in this report gas station heroin tianeptine addiction , could significantly exacerbate these existing challenges, ultimately impacting the overall economic outlook. The Bank’s predictions need to consider these emerging social issues for a more accurate assessment.
Visual Elements
The line graph’s color scheme should be chosen to aid in distinguishing the different regions or categories of data. Clear and concise labels for the axes and any lines are essential for understanding the data. A legend explaining the different lines and their corresponding data is crucial, especially if the graph presents multiple regional or sector-specific growth rates.
Appropriate titles and a concise caption below the graph should clearly define its purpose and the key takeaways. A professional and uncluttered design is vital to maintain clarity and focus.
Visualization Description
The purpose of the visualization is to present a visual summary of global GDP growth trends over time. Key takeaways include identifying periods of significant growth or decline, comparing the performance of different regions, and understanding the potential impact of external factors on global economic stability.
The World Bank’s latest global economic prospects paint a concerning picture, highlighting potential headwinds for the global economy. Meanwhile, the political landscape is also adding complexity. Recent developments, such as the ongoing legal battles surrounding the Trump trial judge campaign, trump trial judge campaign , could further destabilize the situation, potentially impacting investor confidence and exacerbating the economic anxieties already present.
This all contributes to the complicated challenges facing the World Bank in their projections.
Future Trends and Projections
The World Bank’s Global Economic Prospects report offers a critical lens through which to understand the global economic landscape and its potential trajectory. This section delves into the key future trends and projections, highlighting potential long-term consequences and emerging risks and opportunities. The analysis considers factors impacting developing countries, offering insights into the evolving global economic landscape.The report projects a range of potential scenarios, recognizing the inherent uncertainties in forecasting.
The projected trends reflect a multitude of factors, including geopolitical tensions, technological advancements, and climate change impacts. Understanding these trends is crucial for policymakers, investors, and businesses to make informed decisions and adapt to the evolving global economy.
Key Projected Global Economic Trends
The report anticipates several key global economic trends that will shape the future. These trends are interconnected and will influence national and regional economies significantly.
- Weakening Global Growth: Projected global growth rates are expected to moderate in the coming years. This is partly due to persistent inflation, high interest rates, and lingering geopolitical uncertainties. Examples of similar scenarios in the past include the 2008 financial crisis, which resulted in a global slowdown and significant economic hardship in many regions. This demonstrates the potential for significant economic contraction if the current trajectory continues.
- Persistent Inflation: Inflationary pressures are expected to persist in many regions. This is often accompanied by central bank actions to control inflation through interest rate hikes. Such policies can negatively affect economic growth by increasing borrowing costs for businesses and consumers. A recent example is the period following the 2022 war in Ukraine, which saw global energy and food prices rise sharply, leading to widespread inflation.
- Geopolitical Instability: Geopolitical tensions and conflicts are projected to continue impacting global trade and investment flows. The ongoing conflicts in various regions demonstrate the potential for these tensions to disrupt supply chains and hinder economic growth. For example, the war in Ukraine disrupted global energy markets and led to shortages and price increases.
- Technological Advancements: Technological advancements are anticipated to reshape industries and labor markets. This includes the ongoing digital transformation and automation. These changes may lead to job displacement in some sectors but also create new opportunities in others, similar to the shift from agricultural to industrial economies in the past.
- Climate Change Impacts: Climate change is projected to intensify its impacts on global economies, particularly in vulnerable regions. The rising frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as droughts, floods, and storms, are expected to disrupt agricultural production, infrastructure, and human settlements. This trend has been observed in recent years with increased frequency and severity of extreme weather events globally.
Long-Term Consequences of Projected Trends
The combined effects of these trends could lead to several long-term consequences. These consequences are interconnected and could significantly reshape the global economic landscape.
- Increased Inequality: Weakening growth and persistent inflation may exacerbate income inequality within and between countries. This is because those with fewer resources or lower incomes are often disproportionately affected by economic downturns and inflationary pressures.
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: Geopolitical instability and climate change can increase the vulnerability of global supply chains, making them more susceptible to disruptions. This is a direct consequence of increased reliance on global supply chains, as exemplified by the disruption of global supply chains during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Reduced Investment in Developing Countries: A global economic slowdown could lead to reduced investment flows into developing countries, hindering their economic growth and development. This is exemplified by past recessions and financial crises, which have led to a reduction in foreign direct investment.
Emerging Risks and Opportunities
Several emerging risks and opportunities are associated with the projected trends. Recognizing these will be essential for adapting to the evolving global economy.
- Digital Transformation Opportunities: The digital revolution presents opportunities for innovation, efficiency gains, and economic growth. Adapting to the digital transformation can allow businesses and countries to become more competitive in the global market.
- Sustainable Development Initiatives: Investing in sustainable development solutions, such as renewable energy and climate resilience infrastructure, can present both risks and opportunities. These investments could create new jobs and industries while mitigating climate change risks.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, the World Bank’s Global Economic Prospects report provides a crucial framework for understanding the complex interplay of economic forces shaping our world. By analyzing regional outlooks, key indicators, and the impact on developing countries, we gain a clearer picture of the present and future economic landscape. The report’s policy recommendations offer valuable guidance for navigating these complexities.
The report’s comprehensive analysis is a valuable resource for staying informed about global economic trends.
Frequently Asked Questions: World Bank Global Economic Prospects
What is the methodology used in the report?
The report employs a combination of econometric modeling, statistical analysis, and expert assessments to generate its projections and forecasts. Specific methodologies are detailed within the report itself.
How do the projections differ between developed and developing countries?
Developed countries often exhibit more stable growth trajectories compared to developing nations, which can be influenced by various factors including access to resources, infrastructure, and political stability.
What are the potential risks and challenges identified for the global economy?
The report identifies risks such as geopolitical tensions, supply chain disruptions, and inflation as potential challenges to the global economy. The report will elaborate on these in detail.

