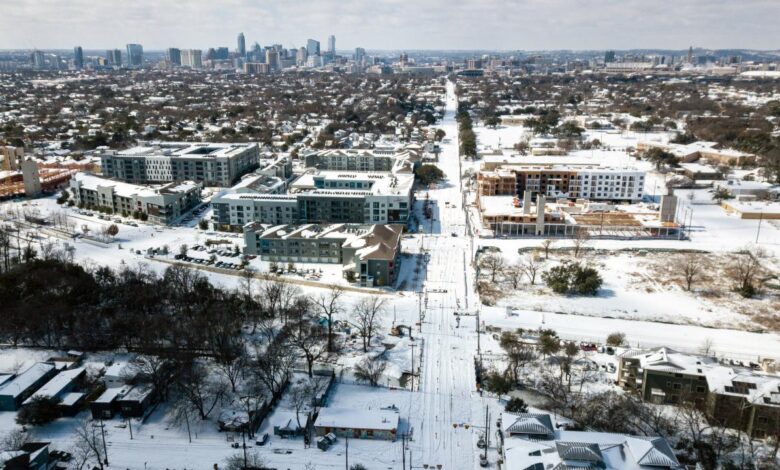
Texas Weather, Cold Power, Schools
Texas weather cold power schools faced unprecedented challenges during recent extreme cold events. These storms wreaked havoc on the power grid, impacting schools’ ability to operate and causing significant disruptions to learning. This exploration delves into the historical context of these events, examining the vulnerabilities of the Texas power grid, the responses of the educational system, and community preparedness strategies.
We also look at potential future mitigation strategies.
The severe winter storms exposed critical weaknesses in the state’s infrastructure, prompting discussions about long-term resilience. From power outages to school closures, the impact extended across various sectors, highlighting the interconnectedness of these systems and the need for comprehensive preparedness.
Texas Winter Weather Impacts
Texas, despite its reputation for warm weather, is vulnerable to severe winter storms. These storms, often accompanied by extreme cold, can disrupt daily life, strain infrastructure, and inflict economic hardship. Understanding the historical patterns, vulnerabilities, and consequences of these events is crucial for preparedness and mitigation strategies.
Historical Overview of Severe Cold Weather Events
Texas has a history of experiencing severe cold weather events. These events, characterized by prolonged periods of freezing temperatures, have significantly impacted daily life in the state. Notable examples include the deep freeze of 2021, which caused widespread power outages, and the milder but still impactful cold snap of 2011. These events highlight the unpredictable nature of winter weather in Texas and the need for robust preparedness strategies.
Historical records show that such events, while varying in intensity and duration, have recurring themes of significant disruption and stress on the state’s infrastructure.
Vulnerabilities of Texas Infrastructure to Cold Weather
Texas’s infrastructure, particularly its power generation and distribution systems, is vulnerable to extreme cold. The reliance on natural gas-powered plants makes these systems susceptible to freezing temperatures that can disrupt operations and lead to widespread outages. Furthermore, the distribution network, often built for warmer climates, is less equipped to handle the extreme conditions that can cause pipes to burst, further impacting services.
The interconnectedness of the systems exacerbates the impact of a single failure point. This interconnectedness, while beneficial in normal conditions, becomes a critical vulnerability when faced with widespread failures.
Long-Term Consequences on the Texas Economy
Severe cold weather events in Texas have significant long-term consequences for the state’s economy. Business disruptions, ranging from temporary closures to permanent damage, can result in lost revenue and reduced productivity. Agricultural losses, particularly in areas dependent on outdoor growing, are also substantial, affecting the supply chain and market prices. The impact extends beyond immediate losses to long-term economic stability.
Impact on Vulnerable Populations
Extreme cold can have a disproportionate impact on vulnerable populations, including the elderly and low-income families. These groups often lack access to adequate heating, making them more susceptible to health problems and even death during extended periods of extreme cold. The limited access to emergency resources can exacerbate the hardship, highlighting the importance of social safety nets during such events.
The vulnerability of these groups necessitates proactive measures to ensure their well-being during extreme weather events.
Comparison of Past Cold Snaps
| Cold Snap | Temperature Drop (Degrees Fahrenheit) | Duration (Days) | Power Outages (Estimated Number) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | >20 degrees | 5 | >4 Million |
| 2011 | 10-20 degrees | 3 | >100,000 |
| 2018 | 5-15 degrees | 2 | >50,000 |
This table provides a comparative overview of past cold snaps in Texas, highlighting the varying severity in terms of temperature drops, duration, and the scale of power outages. These data points underscore the potential for significant disruption and the need for proactive measures to mitigate future impacts.
Texas’s recent frigid weather has put a strain on power grids and school systems. Understanding the complexities of such situations requires looking at the bigger picture, like the upcoming Nevada caucus primary. For a deeper dive into the intricacies of the Nevada caucus primary, check out this explainer: nevada caucus primary explainer. Ultimately, though, the challenges of maintaining power and education in Texas during extreme weather events still need attention.
Power Grid Resilience: Texas Weather Cold Power Schools
The recent extreme cold weather event in Texas highlighted critical vulnerabilities in the state’s power grid. Understanding these weaknesses and the strategies for improvement is essential for ensuring future resilience. The widespread outages underscore the need for a robust and adaptable power infrastructure capable of withstanding extreme weather conditions.The Texas power grid, while generally reliable, demonstrated significant limitations in its capacity to handle the unprecedented cold temperatures.
Factors like the high concentration of natural gas-fired power plants, which are vulnerable to freezing temperatures, played a significant role in the widespread outages. This incident served as a stark reminder of the need for diversification in power generation sources and enhanced grid resilience measures.
Capacity and Resilience of the Texas Power Grid
The Texas power grid’s capacity and resilience were tested to their limits during the extreme cold weather event. Several factors contributed to the widespread outages, including the vulnerability of natural gas-fired power plants to freezing temperatures. The grid’s reliance on a single fuel source, natural gas, exposed it to significant risks during extreme weather events.
Texas weather can be brutally cold, impacting power grids and, consequently, schools. The extreme cold recently highlighted the vulnerability of the power systems, leading to school closures. It’s a sobering reminder of the fragility of our infrastructure, a stark contrast to the tragic history of love and loss, like that of Keren Blankfeld and József Debreczeni, whose story, tragically intertwined with the horrors of Auschwitz’s cold crematorium, is chillingly explored in this piece lovers in auschwitz keren blankfeld cold crematorium jozsef debreczeni.
These seemingly disparate events, nonetheless, force us to confront the human cost of extreme weather and the resilience of the human spirit, and ultimately highlight the need for stronger power grids in Texas.
Weaknesses in the Grid’s Design and Infrastructure
The Texas power grid’s design exhibited weaknesses that exacerbated the impact of the cold snap. A critical vulnerability was the high concentration of natural gas-fired power plants, which were significantly affected by the freezing temperatures. This reliance on a single fuel source left the grid vulnerable to supply chain disruptions and operational failures. Furthermore, insufficient transmission lines and backup generation capacity exacerbated the issue.
The grid’s ability to respond to widespread outages was also limited.
Role of Weather Forecasting and Early Warning Systems
Accurate weather forecasting and effective early warning systems are crucial in mitigating the impact of extreme cold on the power grid. Advanced weather models and real-time monitoring systems could provide valuable insights into potential disruptions. Early warnings would allow grid operators to take preventative measures, such as scheduling maintenance or activating backup generation sources. Improved communication systems between grid operators and power plant personnel are also necessary to ensure efficient responses.
Strategies to Enhance Power Grid Resilience
Several strategies are being implemented to enhance the power grid’s resilience to future cold snaps. Diversifying power generation sources is a crucial step. This includes investing in renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, to reduce reliance on natural gas. Strengthening transmission lines and increasing backup generation capacity will improve the grid’s ability to withstand outages.
Developing and implementing comprehensive emergency response plans is also critical to ensure a swift and effective recovery during extreme weather events.
Texas’s recent cold snap really hammered the power grid, impacting schools and everything else. Thinking about the ethical implications of buying and selling items like stranger letters, it makes you wonder about the ethics of some power company dealings during a crisis, like how are they allocating resources? Stranger letters purchase ethics raise similar questions about transparency and fair play, which, in turn, highlights the importance of proper resource management during severe weather events for schools and the wider community.
It all just underscores how interconnected everything is.
Table of Power Generation Types and Susceptibility to Cold Weather
| Power Generation Type | Susceptibility to Cold Weather | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Gas | High susceptibility to freezing temperatures, impacting plant operation. | Diversification of fuel sources, backup systems, and improved insulation. |
| Coal | Moderately susceptible to freezing temperatures, but typically with less impact compared to natural gas. | Improved insulation, preventative maintenance, and backup systems. |
| Nuclear | Low susceptibility to cold weather. However, freezing temperatures can impact auxiliary systems. | Robust auxiliary system design and maintenance. |
| Wind | Low susceptibility, but operational performance can be affected by high winds. | Improved grid integration and maintenance of wind turbine infrastructure. |
| Solar | Low susceptibility. Performance can be impacted by low sunlight hours. | Improved grid integration and storage solutions for intermittent power. |
Educational System Responses
The devastating impact of the 2021 Texas winter storm highlighted critical vulnerabilities in the state’s infrastructure, including the educational system. Schools across the state faced significant challenges in maintaining operations and ensuring student safety and learning continuity during the power outages and extreme cold. This section examines how Texas schools responded to these events, analyzes the effectiveness of different district responses, and explores innovative solutions implemented to overcome the crisis.
School Closures and Alternative Learning Methods
The widespread power outages and freezing temperatures forced numerous school closures across Texas. Many districts implemented immediate closures, prioritizing student and staff safety. Alternative learning methods, such as online learning platforms and remote instruction, became crucial in maintaining educational continuity. The extent and effectiveness of these responses varied significantly among school districts, depending on their pre-existing technological infrastructure and teacher training.
Effectiveness of Different District Responses
Some school districts demonstrated strong preparedness and swift responses to the crisis, effectively utilizing existing remote learning platforms and providing clear communication channels to parents. Conversely, districts with limited technological resources or insufficient teacher training faced greater challenges in transitioning to alternative learning models. This disparity in preparedness and execution underscored the need for statewide initiatives to support the educational infrastructure of Texas schools.
Texas weather’s been brutal lately, with the cold snap impacting power schools significantly. While everyone’s focused on keeping warm and the lights on, it’s fascinating to see the global fashion scene celebrating milestones like the Couture Didier Ludot 50th Anniversary Paris celebration. Hopefully, the power will be back on soon, and we can all get back to our regularly scheduled lives, minus the shivering.
Innovative Solutions for Student Safety and Learning Continuity
Several innovative solutions were implemented to ensure student safety and maintain learning continuity during power outages. Some districts leveraged community resources, such as partnering with local businesses or shelters to provide safe havens and warmth for students and staff. Others utilized existing school facilities equipped with generators to create temporary learning spaces during the outage. These examples demonstrate the importance of proactive planning and community partnerships during severe weather emergencies.
Challenges Faced by Schools
Schools encountered several challenges in maintaining operations during the extreme cold weather. Limited access to power and heat, coupled with the need for maintaining safety, often resulted in delayed or canceled classes. Inadequate internet connectivity, particularly in rural areas, presented further challenges to implementing remote learning effectively. Moreover, the logistical challenges of providing meals and childcare to students during closures impacted overall operational efficiency.
Mitigation Measures Taken by School Districts
| School District | Mitigation Measures |
|---|---|
| District A | Implemented emergency school closures; leveraged existing online learning platforms; communicated closures via multiple channels; established emergency warming centers at local facilities. |
| District B | Provided bus transportation to warming centers; activated backup generators at select schools; developed emergency communication protocols for parents and staff. |
| District C | Established partnerships with community organizations for student care and meals; deployed mobile hotspots to underserved areas; provided training to teachers on remote learning platforms. |
| District D | Provided early release days for students to avoid potential hazards; utilized school libraries and cafeterias for warming spaces; implemented a staggered reopening schedule to ensure building safety. |
This table highlights the varied strategies implemented by different Texas school districts to address the impact of the winter storm. Each approach reflected the unique characteristics and resources of the respective district, emphasizing the need for personalized strategies tailored to specific community needs.
Community Preparedness
Texas communities, recognizing the vulnerability to extreme cold weather, have proactively developed strategies for preparation and response. These efforts encompass a wide range of initiatives aimed at safeguarding residents, particularly those in vulnerable populations. From grassroots community organizations to local government agencies, the collective response demonstrates a commitment to resilience during winter storms.Community-based organizations and initiatives play a crucial role in bolstering preparedness and response capabilities.
These efforts often target vulnerable populations, ensuring equitable access to resources and support during cold snaps. The effectiveness of these initiatives varies based on factors such as community demographics, resources available, and the level of coordination with local government.
Texas weather’s been brutal lately, impacting power supplies and putting a strain on schools. Meanwhile, news out of Eugene about the Eugene Weekly’s embezzlement printing scandal eugene weekly embezzlement printing is raising eyebrows. Hopefully, these issues won’t significantly disrupt the educational experience for students in Texas.
Community-Based Initiatives for Vulnerable Populations
Various community groups and organizations implement programs and initiatives to assist vulnerable populations during severe cold weather. These include senior centers, churches, and local charities. These groups often provide warm spaces, emergency food supplies, and transportation assistance. This proactive approach proves vital in preventing health complications and ensuring access to essential services.
Successful Community-Led Efforts
Examples of successful community-led efforts include establishing “warm centers” in community centers and churches. These spaces offer safe havens with heating and essential resources for those without access to adequate shelter. Neighborhood watch programs also play a role by checking on vulnerable neighbors and reporting any urgent needs.
Role of Local Government Agencies
Local government agencies, including emergency management teams, play a critical role in supporting community preparedness efforts. These agencies often coordinate with community organizations to ensure a comprehensive response. Their involvement includes distributing information, providing resources, and facilitating communication channels between organizations and residents.
Resources and Support Systems
| Resource Category | Description | Availability |
|---|---|---|
| Emergency Shelters | Designated locations offering temporary shelter, heating, and basic necessities. | Often located at community centers, churches, and schools. |
| Food and Water Distribution | Provision of essential supplies, particularly to vulnerable populations. | Managed by local government agencies and community organizations. |
| Transportation Assistance | Transportation to and from shelters or essential services. | Available through community organizations or volunteer networks. |
| Health Services | Access to medical care, particularly for those experiencing cold-related illnesses. | Through local hospitals, clinics, and mobile health units. |
| Information and Communication | Dissemination of crucial information about weather alerts, safety guidelines, and available resources. | Delivered through local news outlets, community websites, and social media. |
“Community preparedness is crucial during severe cold weather events, especially for vulnerable populations.”
Future Mitigation Strategies
The devastating impact of the recent Texas winter storm highlights the critical need for long-term strategies to enhance the state’s resilience to extreme weather events. This necessitates a multi-faceted approach encompassing improvements to the power grid, educational systems, community preparedness, and policy changes. Addressing these vulnerabilities will not only protect Texans from future cold snaps but also demonstrate a proactive commitment to the well-being of the entire population.Investing in proactive measures to bolster infrastructure and technological advancements is essential for ensuring a more robust and resilient future.
This proactive stance is crucial for the continued safety and well-being of Texans in the face of future extreme weather events.
Power Grid Resilience Enhancements
Texas’ power grid experienced significant strain during the winter storm, highlighting critical vulnerabilities. To enhance resilience, investments in diversified energy sources, grid modernization, and improved transmission lines are crucial. Implementing smart grid technologies, such as advanced sensors and automated controls, can help anticipate and mitigate potential outages. Further, strengthening grid infrastructure by improving redundancy and geographical distribution of power sources can enhance the grid’s overall reliability.
Educational System Preparedness
The disruption to educational services during the storm underscores the need for robust plans to ensure continuity of learning. This requires developing and implementing clear protocols for remote learning, emergency communication systems, and secure backup power solutions for schools. The creation of robust contingency plans for different types of weather emergencies is crucial to minimize disruption and ensure the educational system can continue to operate during future severe weather events.
Community Preparedness and Support Systems
Effective community preparedness is essential for minimizing the impact of future extreme weather events. This involves developing and implementing community-based support systems, including public awareness campaigns on emergency preparedness, accessible resources, and communication strategies. Establishing community shelters with backup power, coordinating with local emergency services, and ensuring equitable access to essential resources for all communities are paramount.
Policy Changes and Regulatory Reforms
Regulatory reforms play a crucial role in enhancing the resilience of the power grid and other critical infrastructure. This may include stricter standards for energy infrastructure resilience to extreme weather, mandatory grid modernization, and establishing clear protocols for emergency response. These reforms must also account for the needs of vulnerable populations, ensuring that their access to essential services is prioritized.
Infrastructure Investments and Technological Advancements
Investing in infrastructure and technological advancements is critical to improving overall resilience to extreme weather. This includes investments in renewable energy sources, energy storage solutions, and advanced weather forecasting and early warning systems. Such investments will ensure the state can better withstand and recover from future extreme weather events. Technological advancements, such as real-time grid monitoring and predictive maintenance tools, can provide the data and insights necessary to enhance grid reliability and resilience.
Comparative Analysis of Mitigation Strategies, Texas weather cold power schools
| Mitigation Strategy | Cost-Effectiveness | Feasibility | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diversifying energy sources (e.g., solar, wind) | Moderate cost, high long-term savings | High, with supportive policies | Reduced reliance on fossil fuels, lower emissions |
| Grid modernization (smart grids, advanced sensors) | High initial cost, moderate long-term savings | Moderate, with phased implementation | Improved grid reliability, reduced outages |
| Community preparedness programs | Low to moderate cost | High, with community engagement | Enhanced public safety, reduced vulnerability |
| Regulatory reforms (stricter standards) | Low initial cost, high long-term savings | Moderate, requiring stakeholder collaboration | Increased grid resilience, improved safety standards |
| Investing in weather forecasting & early warning systems | Moderate cost | High, with ongoing research and development | Improved public awareness, faster response times |
Investing in these strategies will not only improve Texas’ resilience to extreme weather but also position the state as a leader in climate adaptation and sustainable development.
Epilogue
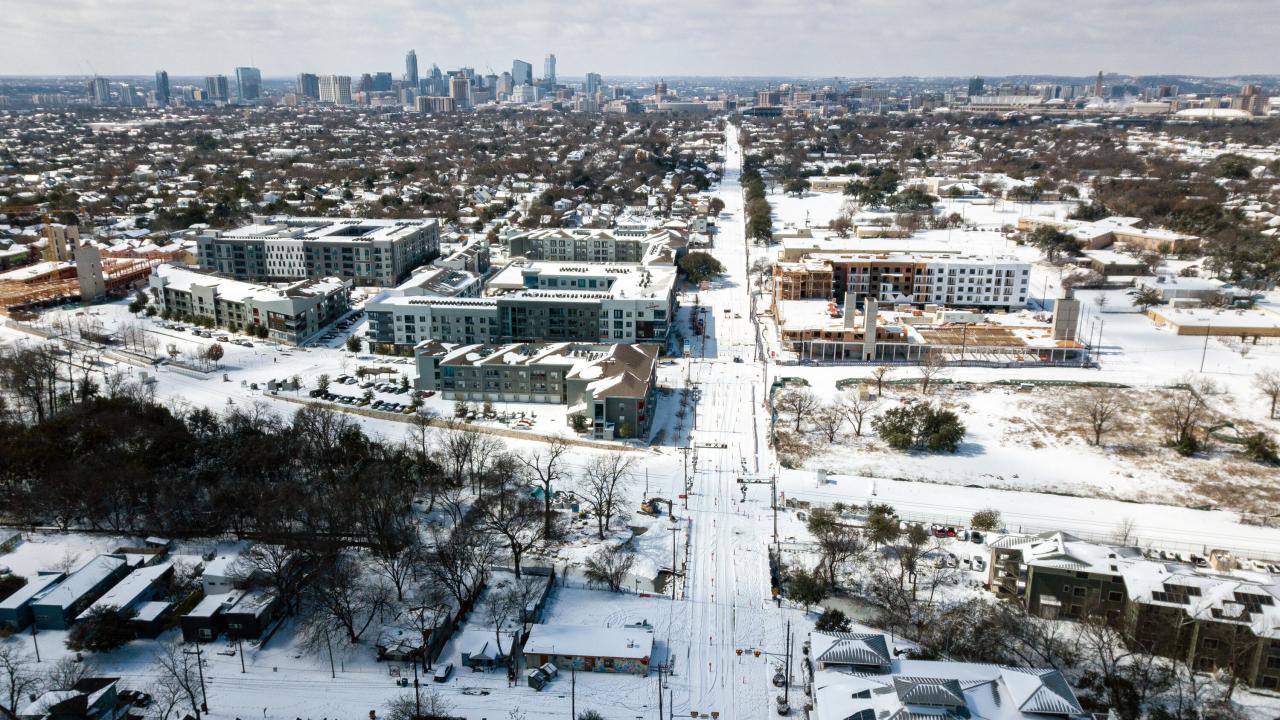

In conclusion, the Texas weather cold power schools crisis underscored the importance of comprehensive preparedness strategies. Strengthening the power grid, enhancing school responses, and bolstering community support systems are crucial for mitigating future impacts. The lessons learned from these events can inform policy changes and investments in infrastructure to build a more resilient future for Texas.
Commonly Asked Questions
What were the most significant power outages in Texas due to cold weather?
The 2021 winter storm was particularly devastating, causing widespread and prolonged power outages across the state. Subsequent analyses identified vulnerabilities in the state’s power grid’s design and infrastructure. Previous cold snaps, though less severe, also highlighted the need for improvements.
How did different school districts respond to the cold weather emergencies?
Responses varied greatly, with some districts implementing innovative solutions to ensure student safety and maintain continuity of learning during outages. Factors like available resources, communication strategies, and community support played a significant role in their effectiveness.
What are some potential policy changes to improve Texas’s resilience to future cold snaps?
Possible policy changes include stricter regulations on power grid infrastructure, increased investment in grid modernization, and enhanced communication protocols between utilities and local communities.
What role did local governments play in supporting community preparedness?
Local governments played a crucial role in coordinating resources, providing support to vulnerable populations, and implementing emergency response plans. Their efforts often involved partnerships with community organizations and agencies.