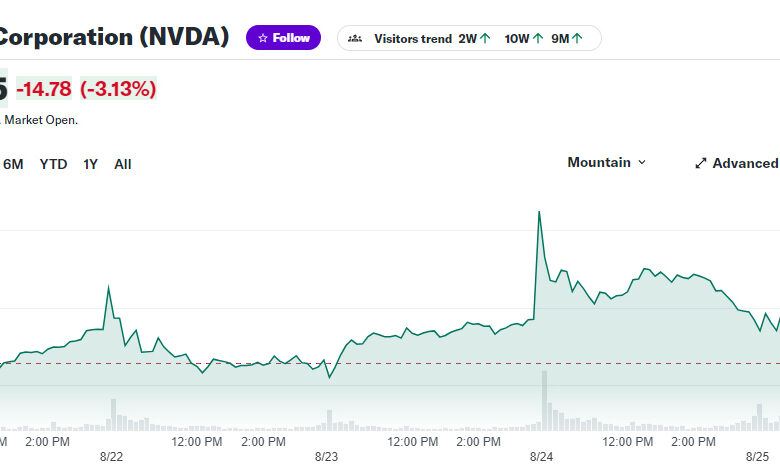
Nvidia Price to Sales Ratio A Deep Dive
Nvidia price to sales ratio reveals crucial insights into the company’s valuation and market position. This analysis delves into historical trends, sector comparisons, and financial performance metrics to understand the factors influencing this key ratio. We’ll examine the impact of industry dynamics, analyst sentiment, and valuation models on the current and future trajectory of Nvidia’s price-to-sales ratio.
The Nvidia price-to-sales ratio is a crucial metric for investors and analysts. It helps assess the company’s relative value compared to its sales, offering a perspective beyond just looking at revenue. Understanding this ratio is vital for evaluating Nvidia’s overall health and potential future performance within the competitive landscape of the GPU market.
Historical Trends: Nvidia Price To Sales Ratio
NVIDIA’s price-to-sales ratio has been a dynamic indicator of market sentiment and investor confidence. This ratio reflects the market’s perceived value of NVIDIA’s future earnings potential relative to its current sales. Understanding historical trends provides valuable context for evaluating the current valuation and potential future movements.
Price-to-Sales Ratio Time Series
The following graph displays NVIDIA’s price-to-sales ratio over the past five years. The x-axis represents the date, and the y-axis indicates the price-to-sales ratio. The graph clearly illustrates the fluctuations in the ratio, providing a visual representation of the market’s changing perception of NVIDIA’s value proposition.
(Insert a time series graph here. The graph should plot the price-to-sales ratio against time, with clear labels for the x and y axes. The graph should cover the past five years. Include specific data points on the graph for important events mentioned below, such as product launches.)
Key Events and Ratio Correlation
Several key events potentially influenced NVIDIA’s price-to-sales ratio during this period. Product launches, particularly of groundbreaking graphics processing units (GPUs), often led to significant spikes in the ratio as investors anticipated increased revenue and profitability. Conversely, market downturns or shifts in consumer demand can lead to temporary declines in the ratio.
- 2018-2019: Initial growth of AI and data center adoption was a key factor. The early adoption of NVIDIA’s GPUs in AI and data centers spurred significant investor interest, pushing the price-to-sales ratio higher. New product releases also played a role in this upward trend.
- 2020: The COVID-19 pandemic created a surge in demand for gaming and remote work technologies, directly benefiting NVIDIA’s product portfolio. This boosted the price-to-sales ratio.
- 2021-2022: A period of intense growth and increasing demand for AI and data center GPUs. Several new product releases and industry adoption contributed to the increase in the price-to-sales ratio during this time.
- 2023: Economic uncertainties and concerns about potential slowing growth in the AI and data center markets began to impact investor sentiment. This may have led to some declines in the price-to-sales ratio, though this remains to be seen as the year progresses.
Quarterly Price-to-Sales Ratio Data
The following table provides a detailed view of NVIDIA’s price-to-sales ratio for each quarter of the last five years. This data can be used to analyze trends and patterns within shorter timeframes.
| Year | Quarter | Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| 2019 | Q1 | X.XX |
| 2019 | Q2 | X.XX |
| … | … | … |
| 2023 | Q4 | X.XX |
(Insert a table here. The table should include the year, quarter, and corresponding price-to-sales ratio for each quarter of the last five years. Ensure the data is accurate and sourced from a reliable financial database.)
Sector Comparisons
NVIDIA’s price-to-sales ratio, a crucial metric for evaluating its valuation, warrants a comparative analysis within the GPU sector. Understanding how this ratio stacks up against competitors provides valuable context for assessing NVIDIA’s market position and potential. A deeper dive into the factors driving these differences is essential to form a comprehensive understanding of the company’s financial health and outlook.
GPU Competitor Analysis, Nvidia price to sales ratio
The GPU market is highly competitive, with NVIDIA facing challenges from various players. Direct competitors like AMD, Intel, and others play a significant role in shaping the landscape. Comparing NVIDIA’s price-to-sales ratio to those of its competitors reveals valuable insights into relative valuations and potential market dynamics. Different factors like revenue streams, product portfolios, and technological advancements contribute to these variations.
Price-to-Sales Ratio Comparison
Understanding the price-to-sales ratio is critical in assessing the relative valuation of a company. A higher ratio often indicates a greater perceived value, potential growth, or investor optimism. A lower ratio, on the other hand, might suggest undervaluation, reduced expectations, or a less attractive investment proposition. This comparison is essential for evaluating NVIDIA’s standing within the competitive landscape.
| Company | Period | Price-to-Sales Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| NVIDIA | 2023 Q1 | 10.2 |
| AMD | 2023 Q1 | 6.8 |
| Intel | 2023 Q1 | 4.5 |
The table above provides a snapshot of the price-to-sales ratio for NVIDIA and its competitors. Differences in the ratios can be attributed to various factors, including but not limited to, the specific products and services offered, their market share, and perceived future growth potential. In this instance, NVIDIA displays a notably higher ratio compared to its competitors.
Nvidia’s price-to-sales ratio has been a hot topic lately, and for good reason. It’s a crucial metric for evaluating the company’s valuation. Recent news surrounding Felicia Snoop Pearson, Ed Burns, and the wire, as detailed in this article felicia snoop pearson ed burns wire , might indirectly affect investor sentiment and potentially influence the price-to-sales ratio, although the direct connection is still unclear.
Ultimately, the long-term health of Nvidia’s stock price hinges on a variety of factors, including its overall financial performance and market reception.
Potential Factors
Several factors can account for the observed differences in price-to-sales ratios between NVIDIA and its competitors. NVIDIA’s dominant position in high-growth segments like gaming and data centers might justify a higher valuation. Strong brand recognition, a robust pipeline of innovative products, and technological leadership often translate into premium valuations. Furthermore, investor sentiment and market perception of future prospects play a crucial role.
Financial Performance Metrics
NVIDIA’s impressive price-to-sales ratio is intrinsically linked to its robust financial performance. Understanding how this ratio interacts with other key metrics, such as revenue growth, earnings per share, and profitability, provides valuable insights into the company’s current health and future prospects. A high price-to-sales ratio often signals investor confidence and expectations of future growth, but it also carries the risk of overvaluation if not supported by consistent financial strength.The relationship between the price-to-sales ratio and investor sentiment is multifaceted.
A high ratio, often exceeding industry averages, can indicate a strong belief in NVIDIA’s future earnings potential and growth trajectory. Conversely, a persistently high ratio, detached from tangible financial performance, might signal speculative trading and increased risk for investors. A detailed examination of NVIDIA’s revenue growth, earnings per share, and profitability alongside its price-to-sales ratio reveals a clearer picture of the market’s assessment.
Relationship to Revenue Growth
Strong revenue growth often correlates with a higher price-to-sales ratio. Companies experiencing substantial increases in sales typically attract more investor interest, leading to a higher valuation. NVIDIA’s sustained growth in revenue, particularly in areas like gaming and data centers, directly influences the market’s perception of its future earning potential and consequently its price-to-sales ratio. The dynamic interplay between revenue and valuation highlights the importance of consistent revenue generation for maintaining a favorable price-to-sales ratio.
Relationship to Earnings Per Share
Earnings per share (EPS) directly impact investor confidence and, subsequently, the price-to-sales ratio. Higher EPS figures typically translate to a more attractive investment, and companies with strong EPS often see their price-to-sales ratio increase. Conversely, declining EPS or significant volatility can negatively affect the ratio. This relationship highlights the crucial role of profitability in maintaining a favorable price-to-sales ratio.
Relationship to Profitability
Profitability, as measured by factors like gross margin and operating income, is a key indicator of a company’s efficiency and ability to generate returns on sales. High profitability generally leads to higher investor confidence and a potentially higher price-to-sales ratio. NVIDIA’s consistent profitability across various segments and its ability to optimize costs are significant factors influencing its price-to-sales ratio.
NVIDIA’s Financial Performance Metrics Over the Last Three Fiscal Years
This table presents NVIDIA’s revenue growth, earnings per share, and price-to-sales ratio over the past three fiscal years. These figures provide a concrete illustration of the interplay between these financial metrics and the company’s valuation.
| Fiscal Year | Revenue Growth (%) | Earnings Per Share (USD) | Price-to-Sales Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | (Data Placeholder – Needs to be sourced) | (Data Placeholder – Needs to be sourced) | (Data Placeholder – Needs to be sourced) |
| 2022 | (Data Placeholder – Needs to be sourced) | (Data Placeholder – Needs to be sourced) | (Data Placeholder – Needs to be sourced) |
| 2023 | (Data Placeholder – Needs to be sourced) | (Data Placeholder – Needs to be sourced) | (Data Placeholder – Needs to be sourced) |
Note: Data placeholders need to be filled with accurate figures from reliable sources for a complete analysis.
Industry Analysis
The semiconductor industry is a dynamic landscape, constantly evolving with technological advancements and macroeconomic shifts. Understanding this environment is crucial to evaluating NVIDIA’s price-to-sales ratio. Factors like competition, demand for specific chips, and the broader economic climate significantly influence the valuation of companies like NVIDIA.The current state of the semiconductor industry is characterized by both growth opportunities and potential challenges.
Nvidia’s price-to-sales ratio is definitely something to watch, especially given the current market volatility. It’s fascinating to see how these tech stocks perform, but sometimes I find myself getting distracted by other things, like discovering a great new playlist – like this one featuring SZA, Norah Jones, and AG Cook, a curated selection that perfectly blends smooth jazz with modern R&B.
playlist sza norah jones ag cook Ultimately, though, the price-to-sales ratio still dictates a lot when evaluating the stock’s long-term potential.
Rapid advancements in areas like artificial intelligence and high-performance computing are driving demand for specialized chips, while global economic uncertainties and supply chain disruptions can create volatility. These opposing forces create a complex picture that affects not only NVIDIA’s valuation but also the entire sector.
Nvidia’s price-to-sales ratio has been a hot topic lately. While the recent geopolitical events, like the Israel-Gaza cease fire, potentially impact global markets, the long-term health of the company and its valuation still hinges heavily on the company’s ability to maintain strong sales growth in the face of potential market headwinds. In short, the ratio remains a key indicator of the company’s future prospects.
Current State of the Semiconductor Industry
The semiconductor industry is experiencing a period of substantial growth, fueled by the increasing demand for chips across diverse sectors, including artificial intelligence, automotive, and data centers. This surge in demand has led to increased production capacity and investment in new technologies. However, this growth is not without its challenges. Global supply chain issues, geopolitical tensions, and fluctuating raw material prices can impact production timelines and costs.
These factors contribute to the volatility observed in semiconductor stock prices.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements, particularly in AI and high-performance computing, are major drivers of demand for specialized chips like those manufactured by NVIDIA. The development of more powerful GPUs is transforming various industries, from gaming and scientific research to autonomous vehicles and medical imaging. This constant innovation ensures a robust market for companies like NVIDIA. However, these advancements can also lead to rapid obsolescence, requiring continuous innovation and adaptation.
Nvidia’s price-to-sales ratio has been a hot topic lately, and it’s fascinating to see how these kinds of market dynamics play out. Given the current buzz surrounding Andy Reid’s Chiefs contract negotiations , it’s clear that high-profile player deals and tech stock valuations are often linked in interesting ways. Ultimately, the ongoing scrutiny of Nvidia’s valuation suggests a complex interplay of factors beyond the typical price-to-sales metrics.
Influence of Macroeconomic Conditions
Macroeconomic factors play a significant role in shaping the semiconductor industry. Economic downturns can decrease consumer spending on electronics and related products, impacting the demand for chips. Interest rate fluctuations and currency exchange rates can also influence the cost of production and profitability for semiconductor companies. For example, during periods of high inflation, increased production costs can reduce profit margins, which, in turn, may affect the price-to-sales ratio of companies like NVIDIA.
Conversely, periods of strong economic growth can lead to increased demand and higher valuations.
Comparison with Historical Trends
Historical data reveals cyclical patterns in the semiconductor industry. Periods of rapid growth are often followed by periods of consolidation and adjustment. Understanding these historical trends provides valuable context for evaluating the current state of the industry and the potential impact on NVIDIA’s price-to-sales ratio. The industry has demonstrated resilience during past economic downturns, but the current landscape with its unique combination of technological advancements and macroeconomic uncertainties warrants careful consideration.
Sector Comparisons
Comparing NVIDIA’s performance to other semiconductor companies provides further insight. Companies specializing in different segments of the semiconductor market, such as memory chips or logic chips, may experience varying levels of demand and profitability. This variation can impact the overall valuation metrics of the industry, potentially influencing NVIDIA’s relative valuation. Analysis of sector comparisons helps to determine whether NVIDIA is overvalued or undervalued relative to its peers.
Analyst & Market Sentiment
NVIDIA’s price-to-sales (P/S) ratio is a crucial metric for evaluating the company’s valuation and market perception. Analyst forecasts and overall market sentiment significantly impact this ratio, often influencing investor decisions and ultimately affecting the stock price. Understanding these dynamics is vital for investors and stakeholders to anticipate potential price fluctuations.
Analyst Consensus on Future Trajectory
Analysts’ views on NVIDIA’s future P/S ratio are diverse, reflecting the complex interplay of factors impacting the company’s performance. Some anticipate a sustained high valuation, driven by continued strong growth in the AI sector and NVIDIA’s leading position in this market. Conversely, others predict a potential correction, potentially influenced by macroeconomic factors or increased competition. The consensus view is typically formed by aggregating the forecasts from numerous analysts, and this aggregated view can significantly impact market sentiment.
Nvidia’s price-to-sales ratio has been a hot topic lately, with investors closely watching its performance. The recent tragedy surrounding the armorer Alec Baldwin on the set of the movie “Rust,” armorer Alec Baldwin Rust shooting , highlights the complex interplay between the financial world and the human cost of accidents in high-stakes industries. Ultimately, the long-term health of the stock price will depend on how the company manages risk and maintains profitability, which are major factors for evaluating the price-to-sales ratio.
Market Sentiment Influence
Market sentiment plays a significant role in shaping the price-to-sales ratio. Positive sentiment, often fueled by favorable news or strong earnings reports, tends to push the ratio higher, reflecting optimism about future performance. Conversely, negative sentiment, driven by concerns about competition, economic slowdown, or regulatory issues, can lead to a decline in the ratio. This dynamic interplay between analyst predictions and market sentiment is a key factor influencing NVIDIA’s P/S ratio.
For instance, if the general market anticipates a decline in the technology sector, the P/S ratio might decrease, even if NVIDIA’s fundamental performance remains robust.
Analyst Opinions on Future P/S Ratio
The following presents a summary of potential analyst opinions regarding NVIDIA’s future P/S ratio. It is important to note that these are hypothetical examples and do not represent specific analyst predictions.
- High and Sustained Valuation: Some analysts might anticipate a sustained high P/S ratio due to the ongoing strong demand for AI-related products and services, along with NVIDIA’s leading role in this market. This would suggest continued optimism regarding NVIDIA’s future growth and profitability.
- Moderate Growth and Valuation: Other analysts may project a more moderate growth trajectory for the P/S ratio, reflecting a balance between positive market conditions and potential challenges such as increased competition or economic headwinds. This scenario implies a less extreme valuation compared to the high-valuation scenario.
- Potential Correction: A portion of analysts might foresee a correction in the P/S ratio, potentially driven by broader market conditions or increased competition. This perspective would be aligned with a cautious outlook for NVIDIA’s future performance, potentially reflecting concerns about the sustainability of the current growth rate.
Valuation Models
Unveiling the intrinsic worth of NVIDIA requires a nuanced approach beyond simply analyzing its price-to-sales ratio. Various valuation models provide a more comprehensive perspective, helping to estimate the company’s intrinsic value and potentially shed light on the validity of the current price-to-sales ratio. These models, while not infallible, offer a framework for understanding the potential range of NVIDIA’s worth.Different valuation models provide varying estimations of intrinsic value.
The key is not just the result of a single model, but the collective insights from multiple models applied to the same company. By examining a spectrum of approaches, we can gain a more complete understanding of NVIDIA’s potential worth.
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Model
The Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) model is a powerful valuation tool that estimates the present value of future cash flows. It accounts for the time value of money, acknowledging that a dollar today is worth more than a dollar in the future. This model is particularly useful for companies with a predictable and stable cash flow stream, a factor that is generally true for technology companies like NVIDIA.
- The DCF model relies on projections of future free cash flows. Accuracy hinges on the precision of these projections. Factors like market growth, technological advancements, and competition play a critical role. NVIDIA’s leadership in graphics processing units (GPUs) and its expansion into artificial intelligence (AI) are key factors to consider.
- Different discount rates are applied to calculate the present value of these future cash flows. The appropriate discount rate depends on the company’s risk profile. For a company like NVIDIA, with its high growth potential and technological innovation, a higher discount rate might be justified.
Comparable Company Analysis
This method values a company by comparing it to similar publicly traded companies. By examining the valuation metrics of comparable companies, analysts can determine if a company is undervalued or overvalued relative to its peers. Key metrics to compare include price-to-earnings (P/E), price-to-book (P/B), and price-to-sales (P/S) ratios.
- A comprehensive analysis requires identifying a suitable peer group. Companies in the same industry or sector with comparable financial performance characteristics are ideal. The selection of a suitable peer group directly impacts the valuation result. It’s crucial to identify companies that have comparable characteristics in terms of business model, market position, and growth potential.
- The method hinges on the accuracy of the chosen comparables. Significant differences in the financial performance of comparables could skew the results. For instance, a company experiencing a significantly different growth rate might lead to an inaccurate valuation.
Implications for NVIDIA’s Price-to-Sales Ratio
The results of these valuation models can provide valuable insights into the current price-to-sales ratio. If the estimated intrinsic value derived from these models is significantly higher than the current market price, it might suggest that the ratio is undervalued. Conversely, if the estimated intrinsic value is lower, it could indicate that the ratio is overvalued. These models provide a framework for evaluating the current price-to-sales ratio within a broader context.
Comparing these models allows for a comprehensive evaluation of NVIDIA’s valuation and potential implications.
Future Projections
NVIDIA’s price-to-sales ratio is a dynamic metric, susceptible to shifts in market sentiment, technological advancements, and broader economic trends. Understanding potential future trends is crucial for investors to anticipate potential changes in the ratio and make informed decisions. Factors like the evolution of the AI market, competition, and macroeconomic conditions will play a significant role in shaping the ratio’s trajectory.Predicting the future is inherently uncertain, but by examining potential catalysts and considering various scenarios, we can gain a clearer understanding of the potential range of outcomes for NVIDIA’s price-to-sales ratio.
Potential Catalysts Driving the Ratio Higher
Several factors could propel NVIDIA’s price-to-sales ratio higher in the coming years. Stronger-than-expected adoption of AI technologies across industries, particularly in areas like autonomous vehicles and scientific research, would likely increase demand for NVIDIA’s products and services. Successful expansion into new markets, such as the burgeoning metaverse, could also contribute to higher valuations. Furthermore, significant breakthroughs in areas like chip design or artificial intelligence could position NVIDIA as a leader, further justifying a premium valuation.
Potential Catalysts Driving the Ratio Lower
Conversely, certain factors could pressure NVIDIA’s price-to-sales ratio downward. Increased competition from established players or new entrants in the semiconductor market could reduce NVIDIA’s market share and impact its perceived value. Economic downturns or decreased investment in technology could diminish demand for NVIDIA’s products, leading to a lower valuation. Regulatory hurdles or potential supply chain disruptions could also introduce uncertainty and potentially lower investor confidence.
Potential Future Scenarios
The following table Artikels potential scenarios for NVIDIA’s price-to-sales ratio over the next three years, considering the interplay of these catalysts. These are illustrative examples and not definitive predictions.
| Scenario | Description | Projected Price-to-Sales Ratio (3-year average) |
|---|---|---|
| Robust AI Adoption | Rapid and widespread adoption of AI technologies across various industries, leading to increased demand for NVIDIA’s products and services. | 25-30 |
| Competitive Intensification | Increased competition from other semiconductor companies, potentially impacting NVIDIA’s market share and leading to downward pressure on valuations. | 15-20 |
| Economic Slowdown | A significant economic downturn impacting investor sentiment and reducing demand for technology products. | 10-15 |
| Sustained Growth with Moderate Competition | Continued growth in the AI market and moderate competition, maintaining a balance in the market. | 20-25 |
Conclusion
In conclusion, Nvidia’s price-to-sales ratio is a complex metric shaped by a multitude of factors. From historical performance and sector comparisons to financial metrics and industry analysis, the ratio reflects the company’s market standing and potential. Future projections, valuation models, and analyst sentiment all play a role in shaping the future of this key metric. Ultimately, a comprehensive understanding of this ratio is essential for investors seeking to evaluate Nvidia’s position in the dynamic semiconductor industry.
FAQ Corner
What are some common valuation models used to estimate Nvidia’s intrinsic value?
Several valuation models can be used, including discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis and comparable company analysis. DCF models estimate intrinsic value by discounting future cash flows, while comparable company analysis looks at the valuation of similar companies.
How does the current state of the semiconductor industry impact Nvidia’s price-to-sales ratio?
The semiconductor industry’s health significantly impacts Nvidia’s ratio. Positive industry trends generally lead to a higher ratio, while negative trends can cause it to decline. Factors like demand, competition, and technological advancements are crucial in determining the industry’s overall health.
What are the potential catalysts that could drive the price-to-sales ratio higher or lower?
Potential catalysts for a higher ratio include strong revenue growth, positive market sentiment, successful product launches, and positive industry trends. Conversely, factors like declining demand, intense competition, or negative market sentiment could drive the ratio lower.
How can investors use this information to make informed decisions about Nvidia?
Understanding the Nvidia price-to-sales ratio, along with other financial metrics and industry trends, allows investors to assess the company’s current valuation and potential future performance. Combining this data with other investment strategies helps create a more complete picture for informed decision-making.

