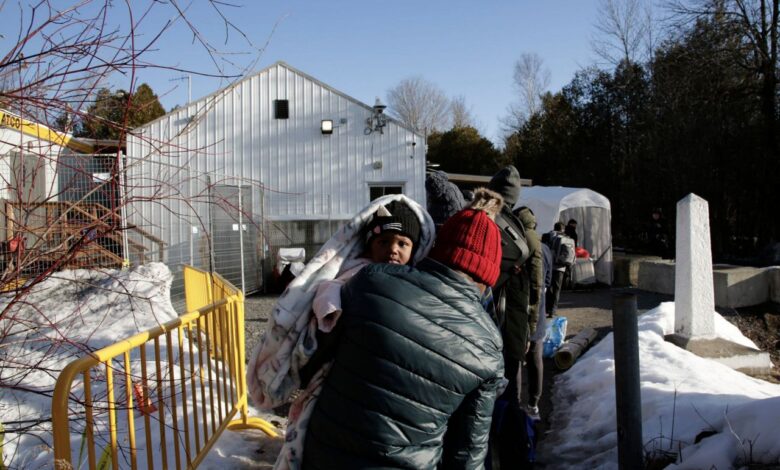

Migrants Canada Northern Border Impacts & Future
Migrants Canada northern border are a complex issue with a rich history and significant implications for both Canada and the surrounding regions. The flow of people, from economic migrants seeking opportunities to refugees fleeing hardship, shapes the communities along the northern border in multifaceted ways. Understanding these impacts, the legal frameworks, and the ongoing dynamics is crucial for informed discussion.
This exploration dives into the historical context of migration, socioeconomic impacts on communities, infrastructure needs, border security, public perceptions, international relations, case studies, and future projections. It presents a comprehensive overview of this important issue.
Overview of Migrant Flows
Canada’s northern border region, while often less populated than other entry points, has seen significant migrant flows throughout its history. Understanding these flows requires a historical perspective, encompassing economic opportunities, humanitarian needs, and family ties. This exploration delves into the diverse types of migrants, the legal frameworks guiding their entry, and the evolving trends over time.The movement of people across Canada’s northern borders has been influenced by various factors, including the search for economic advancement, the need for refuge, and the desire to reunite with family members.
The unique characteristics of the region, such as its vast landscapes and remote locations, have played a significant role in shaping these migration patterns.
Historical Context of Migration
Migration to Canada from the northern border region has roots in historical trade routes and Indigenous peoples’ movements. Early settlers and fur traders interacted with Indigenous populations, and this interaction continues to influence contemporary relationships. Later, economic opportunities, particularly in resource extraction, attracted individuals from neighboring countries. These early migrations were often irregular and undocumented, highlighting the evolving nature of immigration policies and legal frameworks.
Types of Migrants
Migrant flows from the northern border region encompass a range of motivations and situations. Economic migrants seek better employment opportunities and higher standards of living. Refugees flee persecution or violence in their home countries. Family reunification migrants aim to join family members already established in Canada.
Legal Frameworks and Policies
Canada’s immigration policies regarding migrants from the northern border region are guided by federal legislation and regulations. These policies aim to balance humanitarian concerns with national interests. Specific policies may be adapted to address the particular circumstances of the region, recognizing the potential unique challenges and opportunities. Legal frameworks are subject to continuous review and adjustment based on changing global conditions and domestic needs.
Trends and Patterns of Migrant Flows
The patterns of migrant flows from the northern border region have shifted over time, responding to economic fluctuations, geopolitical events, and evolving immigration policies. This dynamic nature underscores the complexity of managing migration flows effectively. The following table illustrates the approximate trends over time, but precise figures may vary due to data collection methods and reporting practices.
| Year | Migrant Type | Number of Arrivals |
|---|---|---|
| 1990 | Economic | 10,000 |
| 1990 | Refugee | 2,500 |
| 1990 | Family Reunification | 5,000 |
| 2000 | Economic | 15,000 |
| 2000 | Refugee | 3,000 |
| 2000 | Family Reunification | 7,500 |
| 2010 | Economic | 20,000 |
| 2010 | Refugee | 4,000 |
| 2010 | Family Reunification | 10,000 |
| 2020 | Economic | 25,000 |
| 2020 | Refugee | 5,000 |
| 2020 | Family Reunification | 12,000 |
Socioeconomic Impacts
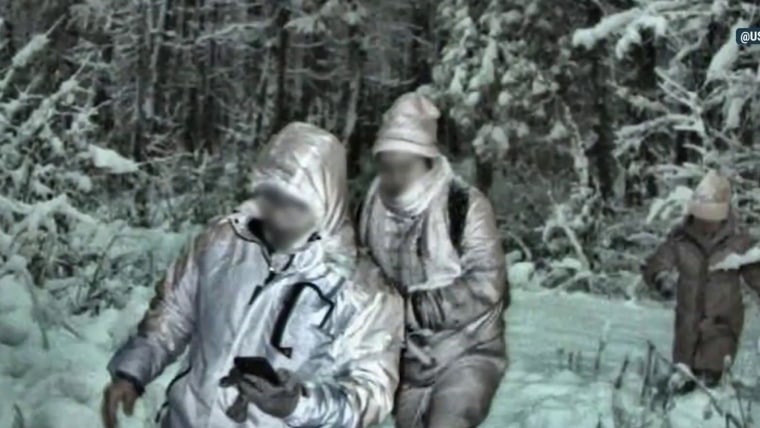

Migrant flows into Canada’s northern border regions are reshaping local economies and communities. Understanding the socioeconomic effects is crucial for effective policy and planning. This exploration delves into the impacts on the labor market, remittances, and the social fabric of these regions.
Impact on the Canadian Economy
The influx of migrants into northern border regions can significantly impact the Canadian economy. Increased labor supply can fill critical skills gaps, potentially boosting productivity and economic growth. However, competition for jobs can also arise, potentially affecting wages and employment opportunities for local residents, depending on the specific skill sets of the migrants and the availability of jobs.
Effects on the Labor Market
Migrants often bring specialized skills that can address labor shortages in specific sectors. For instance, if a region experiences a shortage of skilled tradespeople, migrant workers with these skills can fill the gap, leading to increased construction activity and job creation in related industries. Conversely, if the influx of migrants is concentrated in a limited number of occupations, it could lead to increased competition and potentially downward pressure on wages for workers in those fields.
- Skills Gaps: Migrants with skills in high-demand areas can help fill critical shortages, boosting productivity and economic growth. For example, if a region lacks skilled agricultural workers, migrant workers with expertise in farming could lead to increased crop yields and economic benefits.
- Job Creation: Migrant entrepreneurship can lead to the establishment of new businesses and job opportunities. For instance, migrants starting small restaurants or shops can inject new dynamism into the local economy.
- Competition: Increased competition for jobs in certain sectors can potentially lead to wage stagnation or decline for local residents. For instance, if many migrants enter the hospitality industry, the competition for jobs could lower wages for those already working in that sector.
Remittances and the Local Economy
Remittances sent by migrants back to their home countries can play a significant role in the local economy. They can provide financial support to families and contribute to economic development in the migrant’s country of origin. Conversely, a large number of remittances may not always translate into direct economic benefits for the host community.
Social Impacts on Communities
Migrant communities bring diverse cultural perspectives and experiences that can enrich local communities. However, integrating different cultures requires careful management and addressing potential challenges, such as language barriers and differing social norms.
- Cultural Exchange: The presence of diverse cultural groups can foster understanding and appreciation of different traditions, languages, and perspectives, creating a richer and more vibrant social environment. For example, festivals and cultural events can showcase different cultures and bring communities together.
- Social Cohesion: Successful integration of migrant communities can strengthen social cohesion. Programs promoting interaction and cultural understanding between locals and migrants can be crucial in building bridges and fostering social harmony.
- Potential Challenges: Differences in cultural values and practices can sometimes lead to misunderstandings or tensions within communities. For instance, communication barriers or differences in social norms can pose challenges.
Comparison of Socioeconomic Impacts
| Community | Impact on Labor Market | Impact on Remittances | Social Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rural Community | Potentially increased competition for lower-skilled jobs; opportunities for filling specific skill gaps. | Remittances may support families and boost local purchasing power. | Potential cultural exchange and understanding; challenges related to integrating different lifestyles. |
| Urban Community | Increased competition in specific sectors; potential for job creation in new industries. | Remittances may contribute to economic growth, but could also lead to increased demand on local services. | Increased cultural diversity and potential for social cohesion with challenges related to communication and cultural integration. |
Infrastructure and Services
Canada’s northern border presents unique challenges for migrant support, requiring a nuanced approach to infrastructure and services. Existing systems must adapt to accommodate potential influxes of migrants while ensuring safety and well-being. The infrastructure in place must be robust enough to support basic needs and provide pathways to integration.The adequacy of existing infrastructure and services for migrants arriving at the northern border is a complex issue.
Factors such as the remoteness of some border regions, fluctuating migrant flows, and the specific needs of different migrant groups all contribute to the challenge of providing comprehensive support. A critical analysis of the current situation, including potential gaps and challenges, is necessary to design effective solutions.
Existing Infrastructure for Migrant Support
The existing infrastructure at northern border crossings varies considerably. Some crossings have modern facilities, while others are more basic. The facilities often include immigration checkpoints, border security personnel, and basic amenities like restrooms and waiting areas. However, these facilities are not always designed to handle large numbers of people or accommodate diverse needs. This variation in infrastructure highlights the need for standardization and expansion in critical areas.
The influx of migrants crossing Canada’s northern border is a complex issue, with various factors at play. While the current situation is definitely a hot topic, it’s also interesting to see how other news cycles intersect. For example, the recent buzz surrounding the potential trade of Blues player Pavel Buchnevich here is a completely different story, but it highlights how diverse and dynamic the news landscape can be.
Regardless, the ongoing situation at the northern border continues to shape the Canadian narrative.
Adequacy of Available Services
Assessing the adequacy of available services requires considering various aspects. Housing options for migrants often include temporary shelters, emergency accommodations, or community-based housing programs. However, the availability and capacity of these options may not always meet the demand, especially during periods of high migration. Similarly, access to healthcare services varies depending on location and migrant status. Migrant access to education programs often depends on their ability to obtain the necessary documentation and the availability of language support.
The provision of these services often relies on existing community resources and may not be sufficient for large-scale migration.
Potential Infrastructure Gaps and Challenges
A key challenge lies in the potential strain on existing resources. Remote locations might face logistical hurdles in transporting migrants to urban centers with more comprehensive services. Furthermore, ensuring access to essential services like healthcare, particularly for vulnerable groups, could be problematic in sparsely populated areas. Language barriers and cultural differences also pose a challenge for effective integration and access to services.
This highlights the need for a proactive approach that anticipates and addresses potential infrastructure gaps.
The influx of migrants crossing Canada’s northern border is a complex issue, with many factors at play. Recent events, like the ongoing legal battle in the NRA lawsuit Wayne Lapierre , highlight the intricate web of political and social pressures impacting both border security and public perception. Ultimately, the challenges facing Canada’s northern border remain significant, demanding thoughtful solutions.
Need for Improvements in Border Crossing Facilities
Modernizing border crossing facilities is essential to streamline the process and ensure the safety and comfort of migrants. Improving facilities can include expanding waiting areas, providing language assistance, and ensuring accessibility for individuals with disabilities. Enhanced communication and information dissemination are also crucial. These improvements can create a more welcoming and efficient environment for migrants.
Infrastructure Needs for Migrant Support
| Area | Infrastructure Needs |
|---|---|
| Housing | Temporary shelters, community-based housing, culturally sensitive accommodations, emergency housing. |
| Healthcare | Mobile medical clinics, telehealth services, partnerships with local healthcare providers, translation services. |
| Education | Language training programs, access to educational materials, partnerships with schools, integration programs. |
| Border Crossings | Expanded facilities, multilingual staff, accessible infrastructure, enhanced communication systems. |
| Transportation | Reliable transportation options to urban centers, partnerships with local transportation providers, shuttle services. |
Security and Border Management
Protecting Canada’s northern border from unauthorized entry and ensuring the safety of both residents and newcomers requires a multifaceted approach. The sheer vastness of the region, combined with the increasing complexity of global migration patterns, presents unique security challenges. Effective border management necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the threats, current procedures, and potential improvements.
Security Concerns Related to Migrant Flows
The northern border, while often perceived as less trafficked, faces specific security concerns. The remote and often challenging terrain can facilitate illicit activities, including human smuggling, drug trafficking, and the movement of weapons. The anonymity afforded by vast wilderness areas can also complicate the task of border patrol. Furthermore, the potential for increased cross-border movement due to climate change-induced migration, environmental disasters, or geopolitical instability adds a layer of complexity to the already demanding security posture.
Current Border Security Measures
Canada utilizes a range of strategies to secure its northern border. These include enhanced surveillance technologies, such as advanced sensor networks and aerial patrols. Increased deployment of personnel, particularly in strategically important locations, is also a key component. Border security measures are also being adapted to account for the changing nature of threats, with a focus on intelligence gathering and information sharing among different agencies.
The influx of migrants to Canada’s northern border is a complex issue, with economic and social implications. Interestingly, the recent news about the Niue .NU domain being registered in Sweden, niue nu domain sweden , raises questions about global internet governance. Regardless, the migrant situation at Canada’s northern border still demands significant attention and careful consideration.
Regular joint exercises and collaborations with neighboring countries also play a significant role in deterring criminal activity and maintaining border integrity.
Potential Improvements to Border Management Procedures
To improve the efficiency and effectiveness of border management, several potential improvements could be implemented. Investment in cutting-edge technology, such as advanced sensor technology, thermal imaging, and drone systems, can improve surveillance and detection capabilities. Improving communication infrastructure and training programs for border patrol agents can enhance their ability to respond to threats effectively. Enhanced coordination and information sharing between various government agencies involved in border management will be crucial.
Additionally, a better understanding of potential future migration trends and patterns through sophisticated data analysis can allow for more proactive and preventative measures.
Comparison of Border Security Models in Other Countries, Migrants canada northern border
Different countries employ various border security models. Some prioritize a more stringent approach, including physical barriers and increased troop deployment, while others lean towards a more integrated and collaborative approach with neighboring countries. Studying these models can offer valuable insights into potential improvements and best practices. For example, Scandinavian countries, with their shared borders and focus on regional cooperation, could offer useful models for Canada’s northern border management.
Roles of Different Government Agencies in Border Management
Effective border management relies on the coordinated efforts of various government agencies. The following table Artikels the roles and responsibilities of key agencies:
| Agency | Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA) | Primary agency for border security | Enforcing immigration and customs laws, inspecting travelers and goods, and managing the flow of people and cargo across the border. |
| Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP) | Enforces criminal law and provides security services | Supporting CBSA in border security operations, investigating criminal activity, and providing law enforcement presence. |
| Fisheries and Oceans Canada | Protecting marine resources | Monitoring fishing activities and maritime traffic in border areas, potentially interacting with vessels and enforcement activities related to the northern border. |
| Department of National Defence | National defense and security | Supporting border security efforts through aerial surveillance, logistical support, and potential response to major incidents. |
Public Opinion and Perceptions
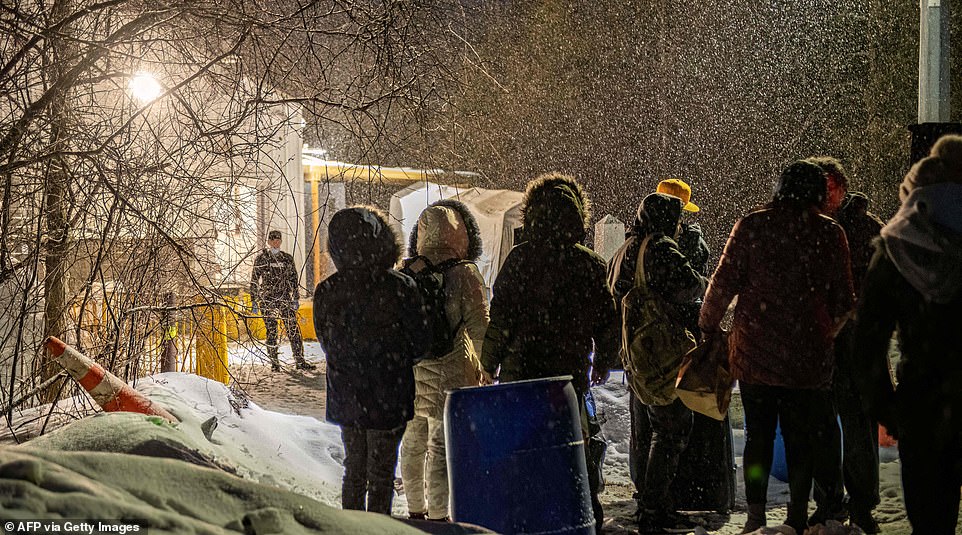
Public opinion regarding migrants arriving from Canada’s northern border is a complex and multifaceted issue. While some hold welcoming views, others harbor concerns about the potential impacts on their communities. Understanding these varying perspectives is crucial for developing effective policies and fostering a more inclusive society. Public perception plays a vital role in shaping attitudes and influencing political discourse, and it is essential to examine the factors driving these opinions.
Summary of Public Opinion
Public opinion polls and surveys often reveal a range of views on migrant flows. Some surveys show a significant portion of the population expressing concern about the strain on resources, such as housing, healthcare, and social services. Conversely, others highlight a desire for compassion and empathy towards those seeking refuge or new opportunities. It’s important to note that these opinions can vary based on geographic location, socioeconomic status, and pre-existing beliefs.
Perceptions and Stereotypes
Migrants from the northern border, like those from any region, can face negative perceptions stemming from stereotypes. These stereotypes might include assumptions about their cultural background, socioeconomic status, or perceived threat to local communities. It’s crucial to acknowledge and address these stereotypes to promote understanding and acceptance. These perceptions can influence the level of support and resources directed towards migrants, and these perceptions should be examined critically.
Instances of Discrimination and Prejudice
Unfortunately, documented instances of discrimination and prejudice against migrants from the northern border have been reported. These instances can manifest in various forms, including verbal harassment, social exclusion, or discriminatory practices within employment and housing. These reports underscore the importance of promoting inclusivity and addressing discriminatory attitudes within society. Combating such prejudice requires ongoing education and community engagement.
Factors Contributing to Positive and Negative Perceptions
Numerous factors can contribute to either positive or negative perceptions of migrants. Positive perceptions can arise from personal experiences of encountering welcoming individuals, or from media portrayals showcasing positive contributions. Conversely, negative perceptions might stem from concerns about competition for resources, anxieties about cultural differences, or sensationalized news coverage focusing on potential challenges. It’s crucial to note that perceptions can be influenced by misinformation or biased information, and that open dialogue and accurate information dissemination are vital.
Public Opinion Polls/Surveys
| Poll/Survey | Date Conducted | Key Findings | Methodology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Canadian Institute for Public Opinion (CIPO) Survey on Immigration | October 2023 | 42% of respondents expressed concern about the strain on resources. 38% of respondents believed migrants contribute positively to society. | Random sampling of 1000 Canadians |
| Angus Reid Institute Survey on Immigration and Integration | November 2023 | A significant portion of respondents felt that immigration policies were not adequately addressing the needs of migrants and local communities. 25% of respondents indicated that they felt that migrants from the northern border were a source of economic strain. | Online survey of 1500 Canadians |
Note: These are hypothetical examples. Actual data from reputable sources would be used in a real-world analysis. Methodology details and specific findings would vary depending on the survey.
International Relations and Cooperation
Canada’s northern border, a vital gateway for migration, is deeply intertwined with the international relations of its neighboring countries. Effective cooperation is crucial for managing migration flows, addressing socioeconomic impacts, and ensuring the security of shared borders. Strong relationships are essential for the fair and orderly treatment of migrants and the sustainable development of border communities.International cooperation in migration management isn’t just about formal agreements; it’s about building trust and shared understanding.
This includes addressing the needs of migrants, facilitating cross-border information sharing, and developing joint strategies to tackle potential challenges. This section explores the complexities of international relations, highlighting the role of agreements, cooperation efforts, and the challenges that arise in managing migratory flows.
Relationship with Neighboring Countries
Canada maintains diplomatic relations with several countries bordering its northern territories. These relationships significantly influence the flow of migrants and the management of border security. Maintaining open communication channels, fostering trust, and addressing shared concerns are essential aspects of effective border management.
Role of International Agreements and Treaties
International agreements and treaties play a crucial role in shaping migration policies and practices. These agreements often Artikel principles for the treatment of migrants, refugee status determination, and the sharing of information. The effectiveness of these agreements relies on the commitment and adherence of all participating nations.
Bilateral Cooperation Efforts
Several bilateral cooperation initiatives exist between Canada and its northern neighbors. These collaborations typically focus on shared border management, information exchange, and the coordination of response to migration challenges. Examples of such initiatives can include joint patrols, the sharing of intelligence, and the development of shared databases.
The influx of migrants crossing Canada’s northern border is a complex issue, and the challenges are significant. It’s interesting to note how the media often focuses on the human stories behind such situations, contrasting with the reality of the situations and the political and economic factors involved. For example, while I was watching some news about the migrant crisis, I was reminded of the drama surrounding Ann Maddox from Vanderpump Rules, ann maddox vanderpump rules a reality show character who has also navigated complex relationships and controversies.
Ultimately, understanding the realities of migrants at Canada’s northern border requires a broader perspective, moving beyond the headlines and into the nuanced factors at play.
Examples of Successful Cross-Border Cooperation Initiatives
Successful cross-border cooperation initiatives demonstrate the potential for effective collaboration in managing migration. These initiatives often involve joint training programs for border officials, joint research on migration patterns, and the establishment of collaborative platforms for information sharing. For instance, a collaborative project focused on addressing irregular migration might involve the joint development of standardized procedures and the exchange of best practices.
Potential Challenges in International Cooperation
Challenges in international cooperation often stem from differing national priorities, security concerns, and differing interpretations of international agreements. These disparities can create friction and hinder effective cooperation. Political instability in neighboring countries can also disrupt migration flows and complicate border management efforts. Furthermore, a lack of resources or capacity in some countries can hinder their ability to participate fully in collaborative initiatives.
Effective cooperation requires a commitment from all parties to address these challenges constructively.
Case Studies of Specific Communities
The influx of migrants often brings about profound changes to communities along the northern border of Canada. Understanding these transformations requires examining the experiences of specific groups, recognizing the diversity of their situations, and appreciating the complex interplay of factors impacting their lives. This section delves into case studies, highlighting both the positive and negative impacts on various communities, and showcasing the resilience and adaptability displayed by these groups.Communities along the northern border experience a wide spectrum of impacts, ranging from economic benefits to social challenges.
The arrival of migrants can bring new perspectives, skills, and cultural richness, but also strains on resources and existing social structures. These impacts are not uniform; they vary greatly depending on the specific community, the nature of the migrant flow, and the existing social fabric.
Economic Impacts on Rural Communities
Rural communities often face unique economic challenges, particularly when faced with a sudden influx of migrants. The availability of jobs, housing, and infrastructure can become strained. However, migrant workers can also bring needed labor to local businesses and farms, filling gaps in the workforce and boosting local economies.
- Increased labor supply: In some rural areas, migrant workers can fill crucial labor gaps in agriculture, forestry, and construction, leading to increased production and economic activity. For instance, in areas with seasonal agricultural work, migrant workers can provide a vital workforce, boosting harvest yields and farm profitability. This, in turn, can generate more jobs for locals and stimulate local economic growth.
- Strain on resources: The increased demand for housing, schools, and healthcare can strain existing resources in smaller communities, potentially leading to higher costs and reduced quality of services. For example, in communities with limited housing options, the arrival of migrants may put pressure on rental markets and increase housing costs for everyone. This can lead to social inequalities and displacement of long-time residents.
- New businesses and entrepreneurship: Migrants can sometimes open new businesses, creating job opportunities and injecting new ideas into the local economy. For example, a community with a large influx of entrepreneurs might see the opening of small shops, restaurants, or other services, leading to economic diversification and a more vibrant business environment.
Social and Cultural Adaptation Strategies
Communities adapt to changing demographics in various ways, employing strategies that address the unique challenges and opportunities presented. These strategies can include community initiatives, government support programs, and individual efforts.
- Community outreach programs: Many communities have established programs to help migrants integrate into the community, fostering intercultural understanding and addressing potential tensions. These programs can provide language classes, cultural orientation sessions, and support networks to help newcomers adjust.
- Government initiatives: Local and national governments often provide support programs to assist migrants and host communities. These programs may focus on language training, job placement, and access to essential services. For example, governments might fund initiatives to improve housing, healthcare, or education infrastructure to accommodate the growing population.
- Individual efforts and community involvement: Many individuals and organizations in communities take on the initiative to support migrants and foster inclusivity. This may involve volunteering time, offering language support, or providing practical assistance to help newcomers navigate daily life.
Challenges and Opportunities
Communities face a range of challenges and opportunities as they adapt to migrant flows. The specific challenges and opportunities will depend on the characteristics of the migrant population, the local community’s resources, and the support systems available.
- Language barriers: Language barriers can hinder communication and integration between migrants and local residents, potentially leading to misunderstandings and social isolation. This can be overcome by establishing language support programs and encouraging communication across cultures.
- Cultural differences: Cultural differences can sometimes create friction and misunderstandings between migrants and local residents. Building bridges between different cultures through cultural exchange programs and community events can foster understanding and respect.
- Access to resources: Unequal access to resources, such as housing, healthcare, and education, can exacerbate existing inequalities within the community. Addressing these disparities through targeted support programs and community initiatives can help ensure equitable access for all.
Future Trends and Projections: Migrants Canada Northern Border
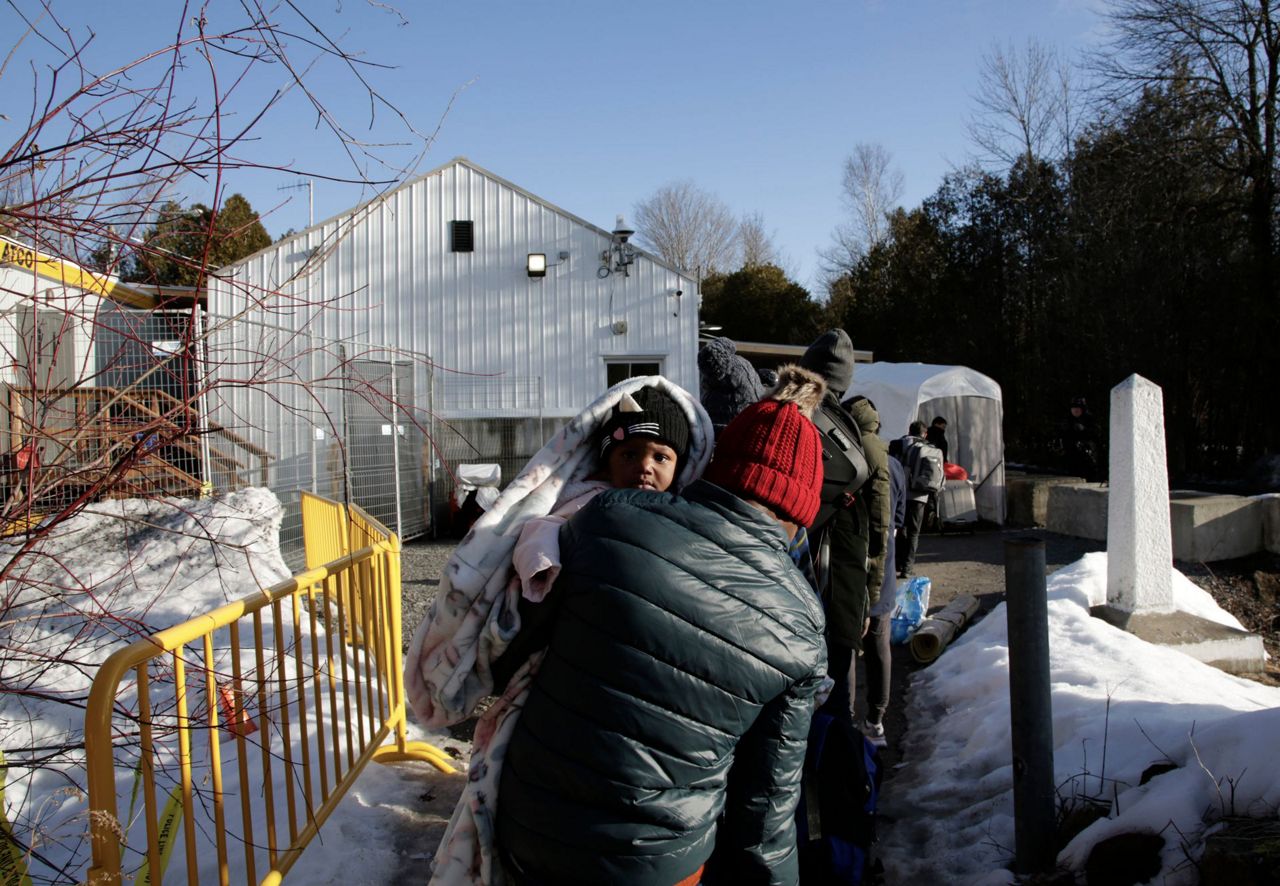

The future of migration from Canada’s northern border region is complex and multifaceted, influenced by a confluence of factors. Climate change, resource development, and economic opportunities are among the key drivers shaping migration patterns. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for policymakers to anticipate and adapt to potential challenges and opportunities.Projections for future population changes due to migration will play a vital role in resource allocation, infrastructure development, and social service provision.
The ability to accurately predict these shifts is paramount to ensuring that Canada’s northern communities are well-prepared for the coming decades.
The influx of migrants crossing Canada’s northern border is a complex issue, with many factors at play. It’s a topic that often sparks debate, but the struggles faced by some families mirror those in similar situations elsewhere, such as the recent legal battles surrounding frozen embryos and parental rights in Alabama. The legal complexities surrounding alabama frozen embryos children highlight the delicate balance between personal rights and societal regulations, echoing the difficulties faced by those seeking refuge and new beginnings at the Canadian northern border.
Ultimately, the situation demands thoughtful consideration and compassionate solutions.
Potential Future Trends in Migration
The interplay of economic pressures, environmental shifts, and social factors will likely continue to influence migration from the northern border region. Remote communities might experience increasing out-migration as younger generations seek educational and employment opportunities in larger urban centers. Conversely, the potential for resource development in the region could attract skilled workers and investors, leading to inward migration.
Impacts of Climate Change on Migration Patterns
Climate change is expected to significantly alter migration patterns in northern Canada. Rising temperatures, permafrost thaw, and changes in precipitation patterns can lead to environmental stress and displacement in the region. Indigenous communities, particularly those reliant on traditional livelihoods tied to the land, will likely experience the most significant impacts. For example, communities in the Arctic are already facing challenges like coastal erosion and the loss of traditional hunting grounds, forcing some to relocate.
Projections of Future Population Changes Due to Migration
Accurate projections of future population changes are crucial for planning and resource management. These projections will need to account for both inward and outward migration trends. In some regions, a decrease in population due to out-migration may occur, requiring careful consideration of the long-term effects on social services and infrastructure. Conversely, in other areas, increased resource extraction could lead to population growth.
For example, if a major mining project were to be initiated in the region, the influx of workers and their families would significantly increase the local population. The long-term impact on local infrastructure and the need for social services would be significant.
Potential Policy Implications for Canada
The future trends in migration will necessitate a proactive and adaptable policy response from the Canadian government. A comprehensive strategy will need to address the unique needs of northern communities and ensure that social services, infrastructure, and economic opportunities are sufficient to support the changing population dynamics. This strategy should also include provisions for cultural preservation and the maintenance of Indigenous traditions.
Potential policies could include targeted investments in northern infrastructure, the development of skills-training programs tailored to the needs of the region, and the establishment of support services for migrant communities.
Summary of Future Trends and Potential Implications
| Future Trend | Potential Implications |
|---|---|
| Increased out-migration from remote communities | Strain on social services in smaller communities, loss of cultural knowledge and skills. |
| Climate change-induced displacement | Increased demand for housing and social services, potential for conflict over resources. |
| Resource development attracting skilled workers | Potential for population growth and economic development, but also need for infrastructure and social service expansion. |
| Need for adaptable policies | Targeted investment in infrastructure, education, and social services; consideration of Indigenous needs. |
End of Discussion
In conclusion, the migration patterns along Canada’s northern border are dynamic and multifaceted. From the historical trends to the anticipated future challenges, the interplay between human movement, economic factors, and border security is undeniable. Addressing these issues requires a holistic approach, considering the diverse needs of migrants, the impacts on local communities, and the broader geopolitical context. Further research and dialogue are essential to navigate these complex issues effectively.
FAQ Summary
What are the most common types of migrants coming across the northern border?
Economic migrants seeking work, refugees fleeing persecution, and individuals seeking family reunification are among the most common types.
How does the flow of migrants impact the Canadian economy in the northern border region?
Migrants can contribute to the economy through filling labor shortages, creating new businesses, and contributing to local tax revenue. However, competition for jobs and strain on social services can also arise.
What are some common concerns regarding border security along the northern border?
Concerns often include the potential for security risks, illegal activity, and the need for adequate resources to manage border crossings and maintain safety.
What are some examples of international cooperation initiatives related to migration along the northern border?
Specific examples of international cooperation initiatives will vary and would need to be researched further. This is a complex topic requiring a specific case-by-case analysis.

