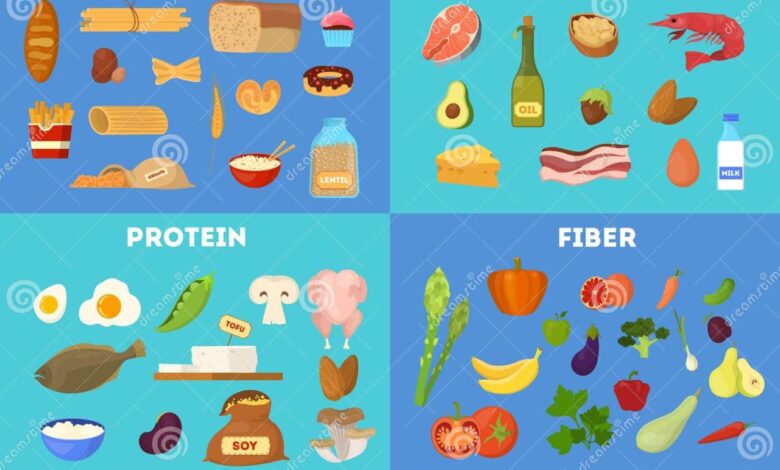
Mediterranean Diet Protein Fiber A Guide
Mediterranean diet protein fiber is a powerful combination for a healthy lifestyle. This guide explores the key aspects of incorporating protein and fiber-rich foods into a Mediterranean diet, showcasing their benefits for overall well-being.
We’ll delve into the fundamental principles of the Mediterranean Diet, highlighting the crucial role of protein and fiber. From understanding the different protein sources to exploring the importance of fiber in digestion, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge to make informed choices about your diet.
Introduction to the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean Diet, far from being a fad, is a time-tested approach to healthy eating rooted in the culinary traditions of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea. It emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods and promotes a lifestyle rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. This approach has been linked to numerous health benefits, making it a compelling choice for those seeking a sustainable and enjoyable path to well-being.The Mediterranean Diet is not just about food; it’s a holistic lifestyle that encourages regular physical activity, social connection, and mindful eating.
Its principles extend beyond specific foods to encompass a balanced and enjoyable way of life.
Core Principles of the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean Diet’s strength lies in its simplicity and emphasis on natural foods. It encourages a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and healthy fats. Portion control and mindful eating play crucial roles in its success. It also advocates for regular physical activity and social connection, emphasizing the importance of a balanced lifestyle.
Key Dietary Components
This dietary approach is characterized by several key components. The foundation is built on whole, unprocessed foods, including fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These are often consumed in larger quantities than other food groups. Legumes, nuts, and seeds are also prominent, offering fiber and healthy fats. Olive oil is the primary source of fat, replacing other unhealthy sources.
Moderate consumption of fish, poultry, and dairy is encouraged. Red meat is consumed less frequently.
- Fruits and vegetables:
- Whole grains:
- Legumes and nuts:
- Olive oil:
- Fish and poultry:
- Dairy and eggs:
- Red meat:
A plethora of colorful fruits and vegetables are integral to the Mediterranean Diet. They provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, promoting overall health and well-being.
Whole grains, like whole wheat bread, brown rice, and quinoa, offer complex carbohydrates and fiber, crucial for sustained energy and digestive health.
Legumes (beans, lentils) and nuts (almonds, walnuts) are excellent sources of protein and fiber, contributing to satiety and a healthy gut microbiome.
Extra virgin olive oil is the cornerstone of healthy fats in the Mediterranean Diet, offering monounsaturated fats linked to heart health.
Fish, especially oily fish like salmon and tuna, are incorporated regularly for their omega-3 fatty acids. Poultry, in moderation, provides lean protein.
Dairy products, like yogurt and cheese, and eggs are consumed in moderation.
Red meat consumption is kept to a minimum, emphasizing lean protein sources from other components.
Relationship to Overall Health
Numerous studies have linked the Mediterranean Diet to a reduced risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Its emphasis on plant-based foods, healthy fats, and moderate protein intake contributes to overall well-being and a healthier lifestyle. The lifestyle element of social interaction and physical activity further reinforces its positive impact on health.
Comparison to Other Diets
| Dietary Approach | Key Focus | Allowed Foods | Restricted Foods |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mediterranean Diet | Plant-based foods, healthy fats, moderate protein | Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, olive oil, fish, poultry, dairy (in moderation), eggs | Processed foods, red meat (limited), refined grains, sugary drinks |
| DASH Diet | Lowering blood pressure | Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, low-fat dairy, lean protein | Saturated and trans fats, sodium, red meat |
| Ketogenic Diet | High fat, very low carbohydrate | Healthy fats, lean protein, non-starchy vegetables | Carbohydrates, sugars, most fruits |
Protein Sources in the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean Diet, renowned for its heart-healthy benefits, emphasizes whole foods and lean protein sources. This approach prioritizes sustainable eating habits, contributing to overall well-being. A crucial aspect of this diet revolves around the types of proteins consumed, particularly those rich in fiber. Understanding these protein sources provides insight into how to optimize the nutritional value of your meals while enjoying the flavors of the Mediterranean.Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues, maintaining a healthy immune system, and regulating various bodily functions.
The Mediterranean Diet intelligently integrates diverse protein sources, promoting satiety and a balanced intake of nutrients. The emphasis on plant-based proteins and lean animal sources creates a holistic approach to dietary health.
Common Protein Sources
A variety of protein-rich foods are fundamental to the Mediterranean Diet. These include fish, poultry, legumes, and dairy products. Each category contributes unique nutrients and benefits to the overall diet.
- Fish: A significant component of the Mediterranean Diet, fish, particularly oily fish like salmon, tuna, and mackerel, are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids. These essential fats play a vital role in maintaining cardiovascular health and brain function. Examples of fish-based meals include grilled tuna salad with a lemon-herb dressing, baked salmon with roasted vegetables, or a Mediterranean fish stew.
Focusing on Mediterranean diet protein fiber is a fantastic way to nourish your body, and Gordon Ramsay’s innovative approach to cooking, as seen in his show Gordon Ramsay next level chef , highlights the power of fresh, high-quality ingredients. Learning how to incorporate lean protein sources and fiber-rich vegetables into your meals can lead to amazing results, mirroring the healthy eating principles of the Mediterranean diet.
- Poultry: Lean poultry, such as chicken and turkey, provide high-quality protein without excessive fat. They can be prepared in various ways, including grilled, baked, or roasted. Incorporating poultry into the diet can be done through dishes like chicken souvlaki with Greek salad, or roasted turkey with Mediterranean vegetables.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent sources of plant-based protein and dietary fiber. They are versatile ingredients, easily incorporated into soups, stews, salads, and even dips. For example, lentil soup, hummus, or falafel are delicious and nutritious Mediterranean dishes that highlight the versatility of legumes.
- Dairy Products: Yogurt, cheese, and milk, when consumed in moderation, contribute to the protein intake. Greek yogurt, feta cheese, and goat cheese are commonly used in Mediterranean cuisine and are rich in protein and calcium.
Nutritional Benefits
Each protein source offers unique nutritional benefits. Fish provides omega-3 fatty acids crucial for heart health. Poultry offers lean protein without excessive saturated fat. Legumes are a powerhouse of fiber and plant-based protein, aiding digestion and promoting satiety. Dairy products, consumed in moderation, contribute calcium and other essential nutrients.
Protein and Fiber Comparison
The table below illustrates the approximate protein and fiber content in various Mediterranean protein sources. These values can vary depending on preparation methods and specific food items.
| Protein Source | Approximate Protein (grams/100g) | Approximate Fiber (grams/100g) | Example Dishes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salmon | 20-25 | 0-1 | Grilled salmon with roasted vegetables, salmon patties |
| Chicken Breast | 30 | 0 | Chicken souvlaki, chicken salad |
| Lentils | 25 | 8-10 | Lentil soup, lentil salad |
| Chickpeas | 19 | 7-8 | Hummus, falafel, chickpea stew |
| Greek Yogurt | 10-15 | 0-2 | Yogurt with fruit, tzatziki |
Fiber Content and Sources
The Mediterranean Diet isn’t just about delicious food; it’s a lifestyle that emphasizes whole, unprocessed ingredients. A significant component of this wholesome approach is the abundance of dietary fiber. Fiber plays a crucial role in digestive health, satiety, and overall well-being, contributing to the diet’s renowned health benefits. This crucial element fuels the body’s natural processes and keeps you feeling full and energized.Fiber acts as a crucial building block for digestive health, promoting regularity and preventing constipation.
Focusing on Mediterranean diet protein fiber is crucial for a healthy lifestyle. It’s interesting to note how this relates to recent events, like the Thailand Pita’s win in a recent case, thailand pita wins case , which highlights the importance of balanced diets. Ultimately, prioritizing protein fiber within the Mediterranean diet remains key for sustained well-being.
It also aids in maintaining a healthy weight by promoting feelings of fullness, reducing the urge for excess calorie intake. Furthermore, soluble fiber can lower cholesterol levels, while insoluble fiber helps regulate bowel movements. This intricate interplay of fiber types contributes significantly to the Mediterranean Diet’s reputation for promoting long-term health.
Types of Dietary Fiber
The Mediterranean Diet boasts a variety of fiber-rich foods, each contributing unique benefits. Dietary fiber is broadly categorized into two main types: soluble and insoluble. Soluble fiber dissolves in water, forming a gel-like substance that can help lower cholesterol and blood sugar levels. Insoluble fiber, on the other hand, does not dissolve in water and aids in promoting regularity and preventing constipation.
Both types of fiber are essential for optimal digestive health.
High-Fiber Foods in the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean Diet emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods, which naturally contain high levels of fiber. These foods are integral to maintaining a healthy lifestyle and are readily available and affordable. A wide range of vegetables, fruits, legumes, and whole grains contribute significantly to the fiber content of the Mediterranean Diet.
- Vegetables: Leafy greens like spinach, kale, and arugula are excellent sources of both soluble and insoluble fiber. Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts also provide a good amount of fiber, alongside other important vitamins and minerals. Root vegetables like carrots, beets, and sweet potatoes contribute to the overall fiber intake.
- Fruits: Fruits like apples, pears, berries, and figs are packed with both soluble and insoluble fiber. The fiber in these fruits contributes to healthy digestion and helps regulate blood sugar levels. The natural sweetness and vibrant colors of these fruits make them a delightful addition to any meal.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent sources of fiber, protein, and essential nutrients. These legumes are a cornerstone of Mediterranean cuisine, offering a wide range of flavor profiles and nutritional benefits. They can be incorporated into soups, stews, salads, or enjoyed as a side dish.
- Whole Grains: Whole wheat bread, pasta, and brown rice are excellent sources of fiber, providing sustained energy and promoting healthy digestion. The use of whole grains in the Mediterranean Diet adds a substantial amount of fiber to the daily intake. These grains are also rich in other essential nutrients.
Protein-Fiber Combinations
The Mediterranean diet, renowned for its health benefits, emphasizes the importance of balanced meals. A key aspect of this balance lies in the strategic combination of protein and fiber. This synergy creates a satisfying and sustained feeling of fullness, which can aid in weight management and contribute to overall well-being. The combination also helps regulate blood sugar levels, promoting better metabolic health.Combining protein and fiber in meals is a cornerstone of the Mediterranean diet’s effectiveness.
These nutrients work together to slow down digestion, preventing blood sugar spikes and promoting a more gradual release of energy. This controlled release of nutrients contributes to sustained satiety, preventing overeating and promoting better management of hunger.
Common Protein-Fiber Combinations
The Mediterranean diet excels in naturally combining protein and fiber. Legumes, for instance, are a fantastic source of both, providing a complete protein source in addition to ample fiber. Similarly, fish, poultry, and eggs, when paired with vegetables and whole grains, form another excellent protein-fiber combination. These diverse options offer a wide range of nutrients, supporting a healthy and varied diet.
Mediterranean Dishes with Protein-Fiber Synergy
Many traditional Mediterranean dishes naturally incorporate both protein and fiber. A hearty lentil soup, rich in fiber from the lentils and vegetables, can be a satisfying and nutritious meal. Grilled fish, accompanied by a side of roasted vegetables and whole-wheat bread, offers a protein-rich main course with substantial fiber intake. Similarly, a plate of hummus and whole-wheat pita bread, a popular Mediterranean snack, provides both protein and fiber.
These examples demonstrate the ease with which these nutrients can be combined in flavorful and fulfilling meals.
Focusing on Mediterranean diet protein fiber is crucial for a healthy lifestyle. However, ethical considerations, like those surrounding the purchase of “stranger letters,” stranger letters purchase ethics , should also be considered. Ultimately, understanding both the nutritional value of protein fiber in the Mediterranean diet and the ethical implications of certain purchases will empower healthier choices overall.
Example Table of Protein-Fiber Content in Mediterranean Recipes
| Recipe | Protein (grams) | Fiber (grams) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lentil Soup | 15 | 12 | A hearty and filling soup, rich in both protein and fiber. Lentils are a complete protein source. |
| Grilled Fish with Roasted Vegetables | 25 | 8 | Fish offers lean protein, while roasted vegetables contribute significant fiber. Whole-wheat bread can further increase fiber intake. |
| Hummus and Whole-Wheat Pita | 5 | 7 | A popular Mediterranean snack that provides both protein (from chickpeas in hummus) and fiber (from whole-wheat pita). |
| Chicken with Quinoa and Steamed Broccoli | 30 | 10 | Lean protein from chicken combined with the fiber-rich quinoa and vegetables creates a complete meal. |
Note: The protein and fiber content in the table are approximate and may vary depending on the specific ingredients and preparation methods.
Health Benefits of Protein and Fiber
The Mediterranean Diet, renowned for its heart-healthy qualities, owes much of its nutritional prowess to the abundant protein and fiber it provides. These essential nutrients are not just important for feeling full and satisfied; they play a vital role in numerous bodily functions, contributing to overall well-being and supporting a healthy lifestyle. The synergistic effect of these nutrients is key to understanding the diet’s profound impact on health.The Mediterranean Diet’s emphasis on whole, unprocessed foods naturally leads to higher protein and fiber intake.
This is crucial for optimal health outcomes, as these nutrients are integral to maintaining stable blood sugar levels, supporting gut health, and promoting satiety.
Satiety and Weight Management
Adequate protein intake promotes feelings of fullness and reduces cravings. Protein takes longer to digest than carbohydrates, thus keeping you feeling satisfied for a longer period. This is further enhanced by the presence of fiber. Fiber, also being slow to digest, adds bulk to the diet, contributing to a sense of fullness and reducing the likelihood of overeating.
The combined effect of protein and fiber in the Mediterranean Diet creates a natural appetite-regulating mechanism. This contributes to weight management by preventing excessive caloric intake and encouraging a healthier relationship with food.
Blood Sugar Regulation
Both protein and fiber play a critical role in maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Protein slows the absorption of carbohydrates, preventing rapid spikes in blood glucose. Fiber also slows down the rate at which sugars are released into the bloodstream. This gradual release of sugar helps prevent blood sugar fluctuations, a common concern for individuals with diabetes or those looking to maintain healthy blood glucose levels.
The Mediterranean Diet’s focus on whole grains, legumes, and lean protein sources naturally supports this process.
Gut Health Support, Mediterranean diet protein fiber
The high fiber content in the Mediterranean Diet is paramount for a healthy digestive system. Fiber acts as a prebiotic, feeding beneficial gut bacteria. This fosters a thriving gut microbiome, which plays a crucial role in digestion, immunity, and overall health. Protein also contributes to gut health, as it supports the growth and function of the intestinal lining, further enhancing the gut’s ability to absorb nutrients and maintain a healthy environment.
The diverse array of fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains in the Mediterranean Diet provides a wide range of prebiotic fibers, creating a rich and diverse gut environment. This diversity is essential for a robust and healthy gut microbiome.
Speaking of healthy eating, the Mediterranean diet is rich in protein and fiber, crucial for a balanced lifestyle. It’s fascinating how these dietary choices impact overall well-being, especially considering recent developments like the Carroll verdict regarding Haley Trump. This case, as reported in carroll verdict haley trump , highlights the complexities of legal proceedings. Still, focusing on a diet rich in Mediterranean protein and fiber remains a key strategy for a healthy lifestyle, regardless of current events.
Protein and Fiber Intake Recommendations: Mediterranean Diet Protein Fiber
The Mediterranean Diet emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods, rich in both protein and fiber. Understanding appropriate intake levels is crucial for maximizing the health benefits while avoiding potential risks. This section provides guidelines for protein and fiber consumption tailored to individual needs within the context of the Mediterranean Diet.
Daily Protein and Fiber Intake Recommendations
The Mediterranean Diet promotes moderate protein intake, alongside a substantial amount of fiber. These nutrients play vital roles in satiety, digestion, and overall health. Individual needs vary significantly based on age, activity level, and overall health status. A balanced approach is essential.
Protein Intake Recommendations
Protein is crucial for building and repairing tissues. While specific protein needs vary, most adults following the Mediterranean Diet should aim for a moderate intake, typically ranging from 0.8 to 1.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. For example, a 70kg individual might consume 56 to 84 grams of protein daily. This range is not absolute, and adjustments may be needed depending on factors like physical activity.
High-protein diets may not be suitable for everyone, and should be approached cautiously.
Fiber Intake Recommendations
Dietary fiber is essential for digestive health and overall well-being. The Mediterranean Diet is naturally high in fiber, derived from fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains. Recommendations for daily fiber intake generally range from 25 to 38 grams for adults. This intake is important for promoting regularity, lowering cholesterol levels, and maintaining a healthy weight.
The Mediterranean diet is packed with protein and fiber, crucial for a healthy lifestyle. While focusing on those aspects, it’s interesting to note how the high fiber content in this diet complements the successful career of someone like Chita Rivera, who demonstrated incredible stamina and dedication throughout her career, especially considering her key moments. A balanced diet, rich in fiber and protein, is a cornerstone of a healthy lifestyle, just as a strong work ethic is for a fulfilling career.
This healthy eating pattern is clearly beneficial for long-term well-being.
Individual Variations in Recommendations
Protein and fiber requirements vary based on age and activity levels. Growing children and adolescents need more protein for growth and development. Similarly, highly active individuals, especially athletes, may require higher protein intake for muscle repair and recovery. Conversely, older adults may need adjusted protein intake to maintain muscle mass.
Age-Based Recommendations
| Age Group | Recommended Protein Intake (grams/day) | Recommended Fiber Intake (grams/day) | Important Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Children (6-12 years) | 25-35 | 20-25 | Growing bodies need adequate protein and fiber for development. |
| Adults (19-50 years) | 56-84 | 25-38 | Moderate intake is generally suitable for maintaining health. |
| Adults (51+ years) | 50-70 | 25-30 | Maintaining muscle mass and preventing age-related decline is important. |
Potential Risks of Excessive Protein or Fiber Intake
While protein and fiber are essential, excessive intake can pose risks. Consuming excessive protein can strain the kidneys and liver, potentially leading to issues in these organs. Similarly, excessive fiber intake can cause bloating, gas, and digestive discomfort. A balanced approach is crucial for optimal health.
Meal Planning and Recipes

The Mediterranean diet’s emphasis on whole, unprocessed foods, including ample protein and fiber, makes meal planning straightforward and enjoyable. This section will explore delicious and balanced Mediterranean meals, offering adaptable recipes and meal plans for diverse dietary needs. Planning meals around protein and fiber-rich foods helps in maintaining satiety and promotes overall well-being.Understanding the fundamental principles of the Mediterranean diet empowers you to create personalized meal plans that align with your individual needs and preferences.
By focusing on fresh ingredients, wholesome combinations, and mindful portion sizes, you can effortlessly incorporate this healthy eating pattern into your lifestyle.
Balanced Mediterranean Meals
A core principle of the Mediterranean diet is consuming a variety of foods. Balanced meals incorporate protein, healthy fats, complex carbohydrates, and plenty of fiber-rich vegetables and fruits. These meals offer sustained energy, support digestive health, and contribute to a sense of fullness. For example, a meal featuring grilled fish with roasted vegetables and a side of whole-wheat pasta exemplifies this balanced approach.
Protein and Fiber-Rich Meal Examples
These examples showcase how to effectively combine protein and fiber in Mediterranean meals:
- Lentil Soup with Whole-Wheat Bread: Lentils provide a complete protein source, while whole-wheat bread contributes fiber. This hearty soup is both nutritious and satisfying.
- Chicken with Roasted Vegetables and Quinoa: Grilled or baked chicken provides lean protein. Roasted vegetables, such as broccoli, carrots, and zucchini, are rich in fiber. Quinoa offers a complete protein and fiber-rich carbohydrate source.
- Baked Salmon with Asparagus and Brown Rice: Salmon is a great source of omega-3 fatty acids, protein, and vitamin D. Asparagus and brown rice add fiber and complex carbohydrates to the meal.
Adapting Recipes for Dietary Needs
The Mediterranean diet’s flexibility allows for easy adaptation to various dietary needs.
- Vegetarian Options: Substitute meat with beans, lentils, tofu, or tempeh. Increase the intake of vegetables, fruits, and whole grains. For example, a vegetarian option might include a lentil stew with a side of whole-wheat pita bread and a large salad.
- Vegan Options: Ensure all animal products are excluded. Increase the consumption of plant-based protein sources, like nuts, seeds, and legumes. A vegan meal might feature a hearty lentil soup with a side of roasted vegetables and a sprinkle of toasted pumpkin seeds.
- Gluten-Free Options: Substitute traditional wheat-based grains with gluten-free alternatives, such as brown rice, quinoa, or corn. Carefully read labels to ensure that the chosen substitutes are indeed gluten-free.
Sample Meal Plans
A variety of protein and fiber combinations can be incorporated into daily meal plans:
Example Meal Plan:| Day | Breakfast | Lunch | Dinner ||—|—|—|—|| Monday | Greek Yogurt with Berries and Nuts | Lentil Soup with Whole-Wheat Bread | Baked Salmon with Asparagus and Quinoa || Tuesday | Oatmeal with Fruit and Seeds | Chickpea Salad Sandwich on Gluten-Free Bread | Vegetarian Chili with Brown Rice || Wednesday | Scrambled Eggs with Spinach and Whole-Wheat Toast | Hummus and Vegetable Wraps | Grilled Chicken with Roasted Vegetables and Couscous || Thursday | Smoothie with Protein Powder, Fruits, and Vegetables | Quinoa Salad with Black Beans and Corn | Baked Tofu with Roasted Sweet Potatoes and Broccoli || Friday | Fruit Salad with Cottage Cheese | Mediterranean Veggie Platter with Hummus | Tuna Salad with Mixed Greens and Whole-Wheat Crackers |
This meal plan is a starting point and can be customized to meet individual needs and preferences. Adjust portion sizes and swap out meals based on personal taste. Remember to stay hydrated throughout the day.
Culinary Insights and Culture

The Mediterranean diet isn’t just about the ingredients; it’s deeply intertwined with the culture and history of the region. From the sun-drenched terraces of the Greek islands to the bustling markets of Italy, the preparation methods and the cultural significance of protein and fiber-rich foods are deeply ingrained in the fabric of Mediterranean life. Respect for seasonal produce and a focus on simple, wholesome dishes reflect a connection to the land and a celebration of fresh flavors.Traditional Mediterranean cooking often prioritizes minimal processing and emphasizes the natural flavors of ingredients.
This approach, alongside the emphasis on whole foods, contributes to the diet’s health benefits, preserving essential nutrients and promoting a balanced nutritional profile. This cultural perspective shapes how protein and fiber are sourced, prepared, and combined, creating a unique culinary tapestry.
Cultural Significance of Protein and Fiber
Mediterranean cultures have long recognized the importance of protein and fiber in their diets. These nutrients are not just fuel for the body; they are central to social gatherings, family traditions, and celebrations. Dishes featuring protein and fiber often play a significant role in communal meals, reflecting the importance of shared experiences and family bonding. The emphasis on fresh, local ingredients underscores a connection to the land and the seasons, a practice that resonates with the values of the region.
Traditional Preparation Methods
Different Mediterranean countries have distinct traditional preparation methods for protein and fiber-rich foods, often reflecting regional ingredients and culinary traditions.
- Greece: Greek cuisine frequently employs slow-cooking methods, like braising and stewing, to tenderize meats and vegetables. These methods extract maximum flavor and preserve the nutrients in the ingredients. Soups and stews, particularly those featuring legumes and vegetables, are staples in the Greek diet, demonstrating the importance of both protein and fiber in the daily meal.
- Italy: Italian cuisine is renowned for its diverse preparation methods. Pasta dishes, a staple in Italian cooking, often combine protein sources like legumes, fish, or meat with substantial amounts of vegetables. The emphasis on fresh ingredients and simple preparations allows the natural flavors to shine through, ensuring the nutritional value of the ingredients is retained. From the hearty minestrone soup to the flavorful pasta e fagioli, the Italian diet highlights the combination of protein and fiber.
- Spain: Spanish cuisine features a wide variety of dishes rich in protein and fiber. The use of fresh seafood, particularly fish and shellfish, is prevalent. Often, these are prepared with simple techniques, such as grilling or baking, preserving their nutritional value and natural flavors. Many traditional Spanish stews and soups are replete with legumes and vegetables, providing a balanced intake of protein and fiber.
- Turkey: Turkish cuisine incorporates a wide array of protein and fiber-rich ingredients, with many dishes featuring grilled meats and vegetables. The use of flavorful spices and herbs enhances the taste while preserving the nutritional value of the foods. The reliance on fresh ingredients, combined with simple cooking techniques, makes the Turkish diet an excellent source of protein and fiber.
Mezze platters, with their array of vegetables, dips, and protein-rich spreads, highlight the balance in a traditional Turkish meal.
Impact on Nutritional Value
The traditional preparation methods employed in Mediterranean countries significantly impact the nutritional value of protein and fiber-rich foods. Slow-cooking methods, for instance, break down tough fibers, making them easier to digest. The use of fresh ingredients and simple techniques minimizes nutrient loss, maximizing the nutritional benefits.
Protein and Fiber Combinations in Mediterranean Dishes
The Mediterranean diet is renowned for its skillful combinations of protein and fiber sources, showcasing the cultural appreciation for balanced meals.
- Greek Moussaka: This layered dish combines ground meat or eggplant with a flavorful tomato sauce, creating a satisfying combination of protein and fiber. The inclusion of vegetables and the slow-cooking method ensures that the nutritional value is preserved.
- Italian Pasta e Fagioli: This hearty soup features pasta, beans, and vegetables. The combination of carbohydrates, protein, and fiber provides a complete and balanced meal.
- Spanish Paella: This vibrant dish often includes seafood, vegetables, and rice, providing a rich source of protein, fiber, and essential nutrients. The variety of ingredients ensures a balanced and flavorful meal.
- Turkish Kebab: This dish often features grilled meats or vegetables, accompanied by various salads and sides. The inclusion of both protein and fiber-rich vegetables contributes to a balanced and flavorful meal.
Illustrative Examples of Protein-Fiber Combinations
The Mediterranean diet, renowned for its health benefits, emphasizes a harmonious balance of nutrients. Protein and fiber are crucial components, working synergistically to promote satiety, regulate blood sugar, and support overall well-being. This section provides illustrative examples of how these nutrients are naturally combined in delicious Mediterranean dishes.Protein and fiber, when paired effectively, create a powerful duo for satiety and sustained energy throughout the day.
They contribute to digestive health, manage blood sugar levels, and support overall bodily functions. The following examples showcase these combinations within traditional Mediterranean recipes.
Protein and Fiber Combinations in Mediterranean Dishes
A variety of protein and fiber combinations exist within Mediterranean cuisine, making it a complete and satisfying diet. The dishes below highlight the rich tapestry of these nutrient-dense components.
| Dish | Protein Source | Fiber Source | Preparation Method & Nutritional Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grilled Fish with Roasted Vegetables | Fresh white fish (e.g., cod, sea bass) | Assorted Mediterranean vegetables (e.g., zucchini, bell peppers, eggplant, tomatoes) | Fish is grilled over medium heat, ensuring minimal fat. Vegetables are roasted with olive oil, herbs, and spices. This method retains the natural flavors and nutrients of the ingredients. The combination is low in saturated fat and high in essential nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals. The fiber from vegetables promotes healthy digestion, while the protein from the fish supports muscle repair and growth. |
| Lentil Soup with Whole Wheat Bread | Lentils | Whole wheat bread and vegetables in the soup | Lentils are simmered in a flavorful broth with chopped vegetables like carrots, celery, and onions. The addition of whole wheat bread provides a substantial source of complex carbohydrates and fiber. This hearty soup is a complete protein source and provides sustained energy. The fiber content aids in digestion and regulates blood sugar levels. |
| Chickpea Salad with Quinoa | Chickpeas | Quinoa | Chickpeas are mashed with fresh herbs, lemon juice, and olive oil for a vibrant salad. Quinoa, a complete protein source, adds a nutty flavor and texture. This salad is packed with plant-based protein, fiber, and healthy fats. The fiber from quinoa and chickpeas contributes to digestive health, while the protein supports satiety. |
| Greek Salad with Feta Cheese | Feta cheese | Cucumber, tomatoes, olives, and red onion | This classic salad combines crumbled feta cheese with fresh vegetables and olives. The feta cheese provides a rich source of protein, while the vegetables and olives offer various fibers. The preparation involves simple combining and dressing with olive oil and herbs. The combination is rich in antioxidants and supports cardiovascular health. The protein from feta and the fiber from the vegetables are excellent for maintaining a healthy gut. |
Last Point
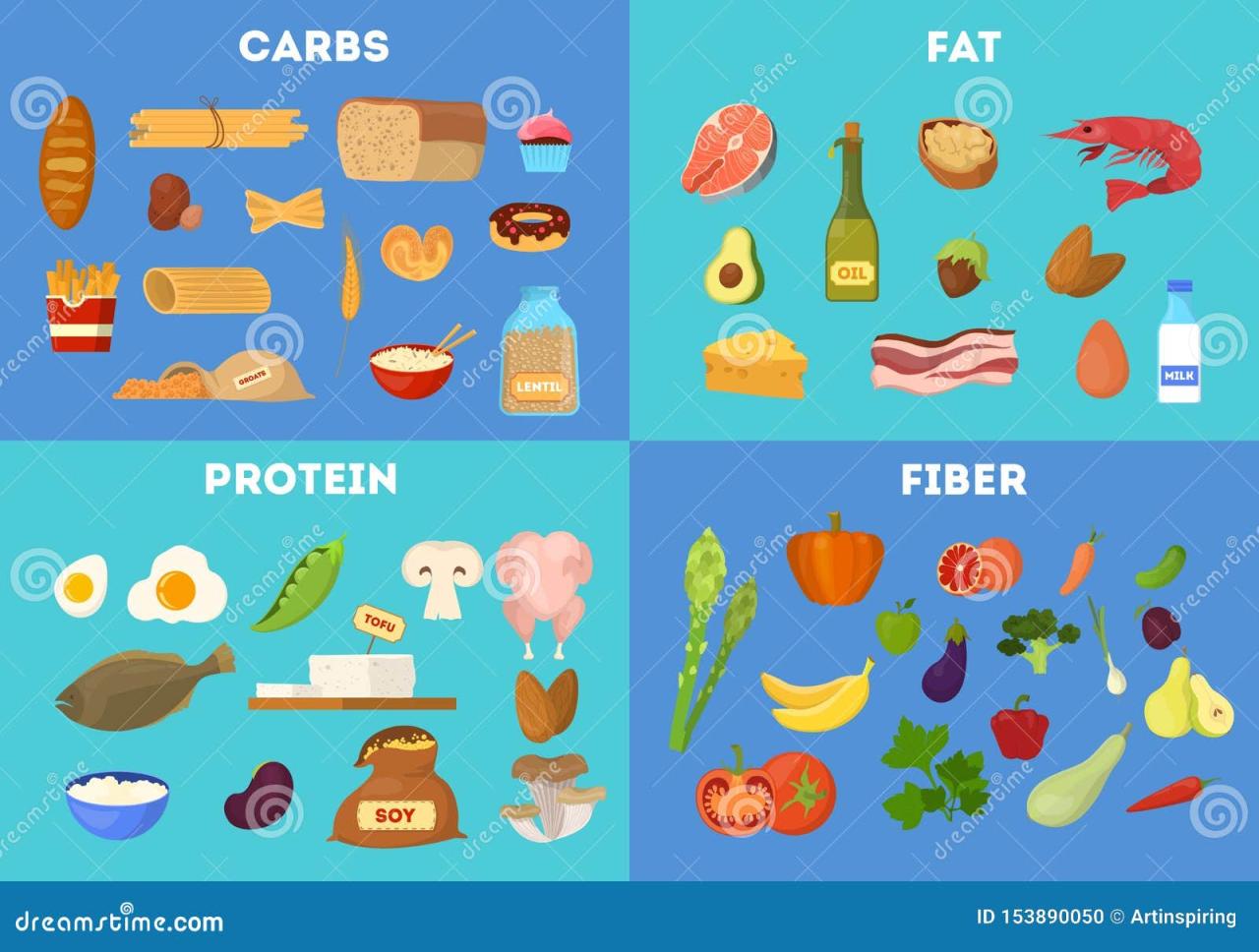
In conclusion, the Mediterranean diet’s emphasis on protein and fiber offers a delicious and nutritious path to better health. By understanding the sources, combinations, and benefits, you can personalize your dietary approach and reap the rewards of a balanced and flavorful lifestyle. The combination of protein and fiber is key to maximizing the positive impact of the Mediterranean diet on your overall health and well-being.
FAQ
What are some good vegetarian protein sources in the Mediterranean diet?
Legumes like chickpeas, lentils, and beans are excellent sources of plant-based protein and fiber. They are commonly used in Mediterranean dishes, providing both protein and fiber.
How much protein and fiber should I aim for daily?
Daily recommendations vary based on individual needs like age and activity level. Consulting a registered dietitian or healthcare professional can help determine the right amount for you.
Are there any potential risks of consuming too much fiber?
While fiber is essential, excessive intake can sometimes lead to digestive discomfort. Gradually increasing fiber intake and ensuring adequate water consumption can help mitigate this.
What are some simple ways to increase protein and fiber in my meals?
Adding a side of vegetables or legumes to your meals can significantly increase your fiber intake. Using beans in stews or incorporating lentils into soups are simple ways to boost both protein and fiber.

