
Inflation Reduction Act Climate Progress
Inflation Reduction Act progress climate is a critical topic, exploring the implementation and effects of the act’s climate provisions. This in-depth look delves into the key initiatives, challenges faced, and overall impact on the nation’s energy transition, environmental regulations, and the broader economic and international landscape.
The Inflation Reduction Act, with its ambitious climate goals, presents a fascinating case study in policy implementation. We’ll examine the act’s intended mechanisms, comparing them with the current progress and identifying potential roadblocks along the way. The discussion also considers the public perception, political dynamics, and potential international ramifications of this significant legislation.
Overview of the Inflation Reduction Act
The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) represents a significant step towards addressing climate change and bolstering the nation’s energy security. It’s a comprehensive piece of legislation that goes beyond simply acknowledging the issue, aiming to create tangible change through a combination of incentives, regulations, and investments. The act’s provisions are designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, promote clean energy technologies, and enhance the nation’s resilience to climate impacts.The IRA is not solely focused on environmental goals; it also seeks to lower healthcare costs and address the rising cost of living.
However, its climate provisions are a key component, aiming to achieve a substantial reduction in emissions and a transition to a more sustainable energy future. The act recognizes that climate change is an economic challenge as well as an environmental one, and its provisions attempt to address both aspects simultaneously.
Climate Change Provisions Summary
The IRA includes a range of provisions aimed at tackling climate change, encompassing incentives for clean energy, investments in energy efficiency, and regulations to curb emissions. These initiatives are designed to reduce the nation’s carbon footprint and foster a transition to cleaner sources of energy. It provides significant funding for renewable energy development and deployment, thereby stimulating economic growth in the green sector.
Key Goals and Objectives
The core objectives of the IRA’s climate provisions are multifaceted. The act seeks to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions across various sectors. A major goal is to encourage a shift towards cleaner energy sources, such as solar, wind, and geothermal power. Furthermore, the act aims to improve energy efficiency in buildings and transportation, leading to reduced energy consumption and emissions.
It also emphasizes investments in research and development for advanced clean technologies, driving innovation in the sector.
Mechanisms for Achieving Climate Objectives
The IRA employs various mechanisms to achieve its climate goals. These include tax credits and incentives for clean energy investments, such as investments in renewable energy projects and energy-efficient home improvements. The act also includes funding for programs aimed at supporting the development and deployment of clean energy technologies. Furthermore, the act includes provisions for regulating emissions from power plants and other industrial sources, encouraging cleaner production methods.
Projected Timelines for Implementation
The IRA’s climate provisions have a phased implementation schedule. Many of the tax credits and incentives will begin to take effect immediately, offering financial support to individuals and businesses transitioning to clean energy. Specific project timelines will vary based on the nature of the project, but generally, the first wave of investments will be seen within the first year of implementation, with subsequent phases unfolding over the following years.
The projected timelines for implementing the regulatory provisions are also Artikeld in the legislation, aiming for gradual and well-structured implementation. The longer-term impacts of the IRA’s provisions are expected to be substantial and multifaceted, with ongoing monitoring and adjustments planned for the future.
Progress on Climate-Related Initiatives
The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) boasts ambitious climate goals, aiming to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and transition the US to a cleaner energy future. This section delves into the progress made on specific climate initiatives under the IRA, examining the current status of each program, the challenges encountered, and how the actual outcomes compare to initial projections.The IRA’s climate provisions are complex and multifaceted, involving numerous programs designed to support renewable energy development, energy efficiency improvements, and the reduction of carbon emissions from various sectors.
Assessing the success of these programs requires a nuanced understanding of their implementation and the evolving context of the energy market.
Clean Energy Tax Credits
The IRA significantly expands tax credits for clean energy technologies, including solar, wind, and energy efficiency improvements. These incentives aim to accelerate the adoption of renewable energy sources by making them more financially attractive to consumers and businesses.
- Solar Energy: The IRA expanded the Investment Tax Credit (ITC) for solar installations, increasing the credit to 30% for most systems. Initial data shows a surge in solar panel installations, with many states experiencing a notable increase in projects in the subsequent year. However, supply chain bottlenecks and material costs have posed challenges in some areas, slowing down deployment in specific regions.
- Wind Energy: Similar to solar, the IRA has broadened incentives for wind energy projects. The increased tax credits are expected to attract investment and accelerate the growth of wind farms. While early reports indicate increased interest in new projects, permitting and regulatory hurdles continue to hinder the speed of development in some regions.
- Energy Efficiency: The IRA includes tax credits for energy-efficient upgrades in homes and businesses. These incentives aim to reduce energy consumption and lower utility bills. Initial results show a positive impact, but widespread adoption remains a challenge, as many consumers are still evaluating the financial and practical implications of these upgrades.
Electric Vehicle (EV) Incentives
The IRA provides substantial incentives for the purchase of electric vehicles, aiming to boost the EV market and accelerate the transition away from gasoline-powered cars.
While the Inflation Reduction Act’s progress on climate initiatives is promising, recent headlines about Rick Pitino’s comments regarding St. John’s recruiting, as detailed in this article rick pitino apologizes comments st johns recruiting , are definitely a distraction. Hopefully, these controversies won’t derail the crucial work needed to achieve real climate change progress. The focus should remain on the positive steps toward a sustainable future.
- Purchase Tax Credits: The IRA offers tax credits for the purchase of new EVs, which are aimed at incentivizing the transition to electric vehicles. The current availability and utilization of these credits are showing positive early results, although the market’s overall response and consumer uptake vary by region and vehicle type.
- Charging Infrastructure: The IRA also addresses the need for EV charging infrastructure. The Act provides funding and incentives to support the development of charging stations, aiming to alleviate range anxiety and encourage wider EV adoption. While there has been some progress in establishing public charging networks, the pace of infrastructure development remains uneven, varying by location and regional demand.
Clean Energy Workforce Development Programs
The IRA includes funding for programs to train and educate workers for jobs in the clean energy sector. This initiative aims to address the skills gap in the burgeoning renewable energy industries.
- Training Initiatives: The IRA funds job training and educational programs to equip workers with the skills needed for jobs in the growing clean energy sector. Early indicators suggest positive outcomes, but the long-term impact on workforce development and the sustainability of these programs remain to be seen. The program’s efficacy hinges on the ongoing availability of funding and effective outreach to potential trainees.
The Inflation Reduction Act’s progress on climate initiatives is promising, but the economic realities are still a bit murky. Meanwhile, the NFL’s contract negotiations with star Chiefs linebacker Andy Reid are heating up, with recent reports suggesting a potential breakthrough in the near future. Andy Reid chiefs contract negotiations are a significant distraction, though, and the long-term implications for the Act’s success in tackling climate change remain paramount.
Challenges in Implementation
Implementation challenges vary across programs. Supply chain constraints, permitting delays, and bureaucratic hurdles frequently impede progress. Furthermore, the variability in local regulations and policies adds complexity to the process. These issues are compounded by the relatively nascent nature of many clean energy technologies and the associated infrastructure requirements.
Impact on Energy Transition: Inflation Reduction Act Progress Climate
The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) is poised to significantly reshape the nation’s energy landscape. Its multifaceted approach to climate change mitigation, focusing on incentivizing renewable energy and discouraging fossil fuels, promises a substantial shift in energy consumption patterns. This transformation will not only affect the environment but also the economic viability of different energy sectors.
Potential Effects on the Energy Sector
The IRA’s provisions aim to accelerate the transition to a cleaner energy future by providing substantial incentives for renewable energy development and deployment. These include tax credits for clean energy technologies, investments in energy efficiency upgrades, and a greater focus on domestic manufacturing of renewable energy components. These policies are projected to create new jobs in the renewable energy sector, while simultaneously impacting the demand for fossil fuels.
Encouraging Transition to Cleaner Energy Sources
The IRA incentivizes the development and deployment of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, through tax credits, grants, and streamlined permitting processes. These incentives make renewable energy more competitive with traditional fossil fuel sources, driving investment and innovation in the sector. The Act also promotes energy efficiency measures, reducing overall energy consumption and further supporting the shift towards cleaner alternatives.
Impact on Various Energy Industries, Inflation reduction act progress climate
The IRA’s provisions will likely have varying impacts on different energy industries. Renewable energy industries, such as solar and wind power, are expected to experience substantial growth due to the tax credits and investment opportunities. Conversely, fossil fuel industries, particularly those reliant on coal and some forms of natural gas, may face a decline in demand as renewable energy sources become more economically viable.
The impact on other energy sectors, such as nuclear power and biofuels, will also be influenced by the IRA’s specific provisions.
Projected Energy Consumption Trends
| Energy Source | Projected Consumption (without Act) | Projected Consumption (with Act) | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy | 10% of total energy consumption | 15% of total energy consumption | Significant increase driven by tax credits and investment incentives. This is comparable to the growth of solar energy in California, where government support fostered rapid adoption. |
| Fossil Fuels (Coal) | 25% of total energy consumption | 20% of total energy consumption | Reduced demand due to the rise of renewable energy and energy efficiency measures. This mirrors the decline of coal power in Europe as renewable energy sources become more competitive. |
| Fossil Fuels (Natural Gas) | 35% of total energy consumption | 30% of total energy consumption | Moderate decrease, potentially driven by the shift towards cleaner natural gas alternatives and increased efficiency. Similar to the shift away from traditional incandescent bulbs in favor of energy-efficient LEDs. |
Effect on Environmental Regulations
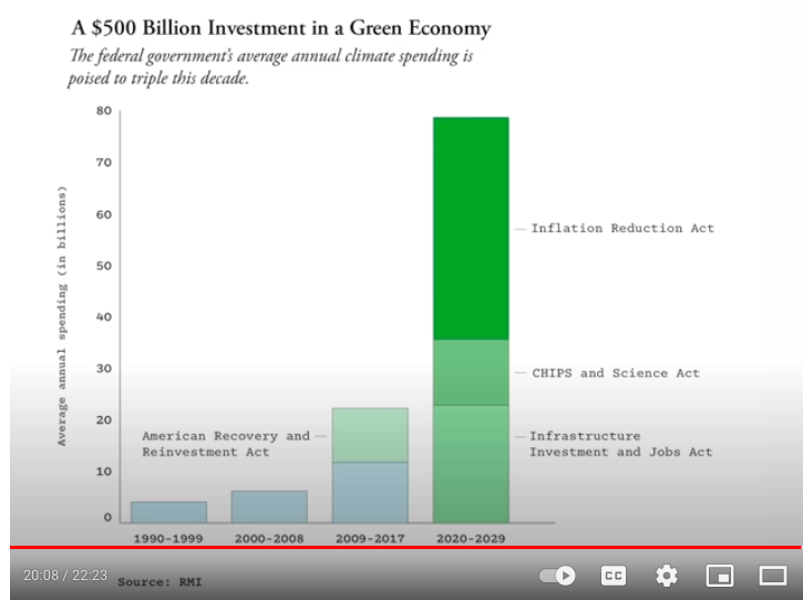
The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) significantly impacts environmental regulations, aiming to accelerate the transition to cleaner energy sources and curb greenhouse gas emissions. This shift in policy reflects a growing global consensus on the urgency of addressing climate change and its associated risks. The Act’s provisions create a complex interplay between existing regulations and newly implemented measures.
Influence on Existing Regulations
The IRA modifies and enhances existing environmental regulations by incorporating incentives and penalties to drive investment in renewable energy and sustainable practices. It leverages existing frameworks while introducing novel approaches to incentivize emission reductions and promote technological advancements. This approach acknowledges the necessity for incremental change while striving for ambitious targets.
New and Revised Environmental Regulations
The Act introduces numerous new and revised environmental regulations, fostering a more robust regulatory environment for environmental protection. These regulations aim to incentivize green technologies, improve energy efficiency, and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. These regulations will have significant implications for businesses and individuals, impacting their operations and daily activities.
Table of Updated Regulations
| Regulation | Previous Status | New Status (under Act) | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tax Credits for Clean Energy Investments | Limited tax incentives existed. | Expanded tax credits for renewable energy projects, energy efficiency improvements, and electric vehicle purchases. | Incentivizes private sector investment in clean energy technologies and infrastructure, accelerating the shift away from fossil fuels. |
| Clean Vehicle Standards | Existing standards for fuel efficiency and emissions for automobiles. | Increased requirements for vehicle electrification and emissions reductions, with a timeline for phase-out of internal combustion engine vehicles. | Accelerates the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and reduces air pollution. This targets specific pollutants, like NOx and particulate matter, that contribute to respiratory problems and other health concerns. |
| Clean Energy Production Standards | Standards for renewable energy generation existed but were not comprehensively enforced. | Increased targets for renewable energy production, including solar and wind power. | Promotes a more sustainable energy mix and reduces reliance on fossil fuels. These targets align with national and international climate goals, recognizing the urgency to mitigate climate change. |
| Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) | Limited research and development support. | Increased funding for research, development, and deployment of CCUS technologies. | Aims to capture CO2 emissions from industrial facilities and power plants, thereby reducing overall emissions. This demonstrates a willingness to utilize technologies that can reduce emissions from hard-to-decarbonize sectors. |
Public Perception and Political Landscape
Public opinion on the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) is a complex mix of support and skepticism, particularly regarding its climate provisions. While proponents highlight the Act’s potential to address climate change and create green jobs, critics raise concerns about its impact on the economy and its potential to increase energy costs. The political landscape surrounding the IRA has been marked by intense debate, shaping the Act’s implementation and future direction.The IRA’s climate provisions, aimed at transitioning to cleaner energy sources and reducing emissions, have faced both enthusiastic support and fierce opposition.
Public opinion polls reveal a wide range of views, with varying degrees of concern regarding the economic consequences of these policies. This diverse sentiment underscores the significant role public perception plays in the Act’s long-term success.
Public Opinion on Climate Provisions
Public opinion on the IRA’s climate provisions is multifaceted and influenced by a range of factors. A considerable portion of the public recognizes the urgency of climate action and supports policies designed to mitigate its effects. However, concerns remain about the potential economic costs associated with these policies. Furthermore, the perceived fairness and effectiveness of these measures vary across different demographics and political affiliations.
The Inflation Reduction Act’s progress on climate initiatives is definitely something to watch. However, recent news about a couple missing at sea off the coast of Grenada, highlights the unpredictable nature of the world and the importance of safety measures. Thankfully, there are ongoing efforts to find the missing couple couple missing boat grenada , and hopefully they’ll be found soon.
This tragedy, though, doesn’t diminish the significance of the Inflation Reduction Act’s environmental goals and the steps being taken to address climate change.
Political Reactions and Debates
The IRA has ignited intense political debate. Proponents highlight the Act’s potential to create jobs, promote innovation, and reduce the nation’s carbon footprint. Opponents argue that the Act will harm the economy by increasing energy costs and hindering economic growth. These contrasting viewpoints have led to extensive discussions in the media, on social platforms, and within legislative bodies.
Impact of Political Climate on Implementation
The current political climate significantly affects the IRA’s implementation. Political gridlock, partisan divisions, and differing priorities can hinder the smooth execution of the Act’s various initiatives. The political environment shapes public trust in the government’s ability to deliver on the promises of the Act. For example, if there’s a perception that the government is not effectively managing the economic impacts of the IRA, public support for the Act could decline.
Legislative Changes and Amendments
Legislative changes and proposed amendments to the IRA are constantly evolving. Various groups are advocating for modifications to specific provisions to address concerns about economic impacts, energy reliability, and other factors. The process of legislative amendment is dynamic and involves ongoing negotiations, discussions, and compromises between various stakeholders.
Economic Implications
The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) is poised to reshape the American economy, impacting various sectors and individuals in significant ways. While its core goal is to combat inflation and address climate change, the Act’s provisions have wide-ranging economic implications that require careful analysis. Understanding these effects is crucial for assessing the Act’s long-term impact on the nation’s economic health.
Economic Impacts on the Economy
The IRA’s provisions are designed to stimulate economic activity in several key areas. Investments in clean energy technologies and infrastructure are expected to boost job creation and stimulate innovation. Tax credits and incentives for renewable energy adoption are projected to accelerate the transition to a greener economy, leading to new industries and opportunities. Furthermore, the Act aims to reduce healthcare costs by expanding access to affordable health insurance and addressing prescription drug pricing.
These efforts are expected to increase consumer spending and reduce economic uncertainty. However, the Act also involves increased costs for some businesses and individuals, potentially impacting their spending and investment decisions.
Job Creation Potential Related to Climate Initiatives
The IRA’s climate initiatives have the potential to create a significant number of jobs across diverse sectors. Investments in renewable energy infrastructure, like solar panel manufacturing, wind turbine installation, and energy storage development, will create new employment opportunities. The Act also promotes sustainable agriculture and green building practices, further increasing job creation in these related fields. The transition to a greener economy is expected to generate new jobs in sectors that were previously overlooked.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of the Act’s Climate Provisions
Assessing the cost-benefit analysis of the IRA’s climate provisions involves a complex interplay of factors. While the Act’s investments in renewable energy and energy efficiency programs carry upfront costs, the long-term benefits are anticipated to outweigh these expenses. The reduction in greenhouse gas emissions will contribute to mitigating climate change, potentially reducing the long-term costs associated with climate-related disasters and environmental damage.
Furthermore, investments in clean energy technologies can foster innovation and competitiveness, potentially leading to long-term economic gains. The Act’s climate provisions aim to create a sustainable and resilient economy, which in turn promotes economic growth and stability over time.
Economic Indicators Before and After Implementation
The following table provides a hypothetical comparison of key economic indicators before and after the IRA’s implementation. Note that these are illustrative examples and actual figures will depend on the specific economic conditions and the impact of the IRA.
| Economic Indicator | Pre-Act | Post-Act | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| GDP Growth Rate (%) | 2.5 | 3.0 | +0.5 |
| Unemployment Rate (%) | 4.5 | 4.2 | -0.3 |
| Renewable Energy Investment (USD Billion) | 15 | 30 | +15 |
| Clean Energy Job Creation (Thousands) | 100 | 200 | +100 |
International Implications
The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) is poised to significantly impact global climate efforts, potentially sparking both emulation and controversy. Its ambitious targets and financial incentives for domestic clean energy adoption have the potential to reshape the international energy landscape, influencing global investment decisions and technological advancements. Understanding these implications is crucial for navigating the future of climate action.The IRA’s provisions, particularly its substantial investment in renewable energy and energy efficiency, are likely to generate a ripple effect across the globe.
The Inflation Reduction Act’s climate initiatives are showing promising progress, though some hurdles remain. Listening to a chill playlist like this one featuring SZA, Norah Jones, and playlist sza norah jones ag cook can help you relax while you follow the ongoing developments. Overall, the act’s environmental impact is something to keep a close eye on.
Other nations might be incentivized to adopt similar policies, potentially accelerating the transition to cleaner energy sources. Conversely, concerns about trade imbalances and competitiveness could also emerge.
Potential Influence on Climate Action in Other Countries
The IRA’s provisions, including tax credits for electric vehicles and clean energy technologies, may motivate other countries to implement similar incentives. This could lead to a domino effect, spurring innovation and investment in renewable energy sectors globally. However, the specifics of the IRA, such as the domestic content requirements, might raise concerns about potential trade restrictions and protectionism.
Reactions of Other Nations
Reactions to the IRA will likely vary depending on a country’s economic structure, political priorities, and existing climate policies. Countries heavily reliant on fossil fuels might view the IRA as a threat to their energy security and economic interests, potentially leading to retaliatory measures or resistance to global climate initiatives. Conversely, countries with strong environmental commitments may view the IRA as a positive development and seek to emulate its provisions.
Global Implications on Climate Policies
The IRA’s impact on global climate policies is multifaceted. The Act’s substantial financial commitment to climate action could potentially encourage similar investments and policies worldwide. However, it might also exacerbate existing geopolitical tensions if perceived as protectionist or unfairly favoring domestic industries. The successful implementation of the IRA and its long-term effects will influence the international community’s approach to climate change, shaping future collaborations and agreements.
The Inflation Reduction Act’s climate provisions are showing promising progress, but the political landscape surrounding it is complex. Understanding how different demographics in red and blue states view these initiatives is key to evaluating the long-term success of these policies. For example, analyzing red blue states demographics reveals varying levels of support and concern. Ultimately, the success of the climate-focused aspects of the Inflation Reduction Act will depend on broad public acceptance and effective implementation across the country.
Potential Collaborations with Other Nations
The IRA’s focus on clean energy technologies and international partnerships presents opportunities for collaboration. Countries with advanced expertise in specific clean energy technologies, such as wind power or battery storage, could find mutual benefits in joint research and development projects. This could result in a faster global transition to a sustainable energy future. For example, the U.S.
could partner with countries like Germany or China on developing and deploying advanced battery technologies, fostering a collaborative global energy transition. Such collaborations could leverage the strengths of various nations to accelerate progress towards shared climate goals.
Environmental Impact Illustrations
The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) aims to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and foster a cleaner energy future. This section details the anticipated environmental benefits, emphasizing the positive impacts of transitioning to cleaner energy sources and the projected reductions in emissions and pollution. The IRA’s provisions are designed to accelerate the transition to a more sustainable economy, impacting air and water quality, and ultimately improving overall environmental health.
Positive Effects of Cleaner Energy Sources
The shift towards renewable energy sources like solar and wind power, incentivized by the IRA, has numerous environmental benefits. These sources produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions during operation, drastically reducing the carbon footprint of electricity generation. For example, a solar farm in Arizona, powered by the IRA’s tax credits, can displace fossil fuel-based power plants, leading to a significant reduction in air pollution and related health issues.
This transition will improve air quality in surrounding areas, minimizing respiratory illnesses and other health problems.
Projected Reduction in Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The IRA is projected to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by a substantial amount. The law’s incentives for clean energy technologies, energy efficiency improvements, and carbon capture will lead to a substantial decrease in emissions from various sectors. The EPA, through the Clean Power Plan, has previously demonstrated the potential for significant reductions in emissions from power plants. Similar, but possibly even greater, reductions are anticipated under the IRA, especially in the transportation sector through incentives for electric vehicles.
Quantitative data on expected emission reductions will be released by the EPA and other relevant agencies in the coming years.
Anticipated Improvements in Air and Water Quality
The transition to cleaner energy sources is expected to lead to improvements in air and water quality across the nation. Decreased reliance on fossil fuels, which are major contributors to air pollution, will reduce harmful pollutants like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, leading to cleaner air and fewer respiratory illnesses. Furthermore, the IRA’s provisions on wastewater treatment and industrial pollution control are expected to reduce water pollution from various sources, leading to cleaner waterways and healthier aquatic ecosystems.
The benefits are expected to be particularly significant in areas with a high concentration of industrial facilities and power plants. For instance, the implementation of more stringent emission standards for vehicles can improve air quality in major metropolitan areas.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, the Inflation Reduction Act’s climate progress story is complex and multifaceted. While ambitious goals are set, navigating the political, economic, and environmental realities presents both opportunities and challenges. The Act’s long-term effects on energy transition, environmental regulations, and the global climate picture will continue to unfold, making it a topic of ongoing interest and discussion. The future implications remain significant, requiring ongoing evaluation and adaptation.
Q&A
What are some key criticisms of the Inflation Reduction Act’s climate provisions?
Critics have raised concerns about the act’s potential impact on energy costs, job losses in certain sectors, and the overall effectiveness of its proposed initiatives in achieving significant emissions reductions. Some argue that the cost-benefit analysis may not be fully accurate.
How does the Inflation Reduction Act incentivize renewable energy adoption?
The act provides tax credits and subsidies for renewable energy projects, making them more financially attractive to investors and developers. It also aims to streamline permitting processes for renewable energy infrastructure.
What are the projected timelines for the full implementation of the Act’s climate provisions?
Exact timelines for full implementation are variable and depend on the progress of individual initiatives and legislative processes. The Artikel provides a framework for understanding the projected implementation timeline for each component.
How might the Inflation Reduction Act influence international climate agreements?
The Act’s provisions, if successful, could potentially influence other countries to adopt similar climate policies, encouraging international cooperation and setting a precedent for global climate action. The success and scope of the act’s implementation will play a significant role in shaping future global efforts.






