IMF Global Economic Outlook 2024-2025 Forecast
IMF Global Economic Outlook sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into the global economic landscape for 2024 and 2025. The report delves into predicted growth rates, regional perspectives, monetary policy, fiscal considerations, and the outlook for emerging markets. Key economic indicators and the methodology behind the forecasts are also examined, providing a comprehensive overview of the global economy.
This in-depth analysis considers potential risks and uncertainties, the impact of specific events, and the interplay between monetary and fiscal policies. The report also provides valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities for various regions and economies, ultimately offering policymakers and investors critical information for strategic decision-making.
Overview of the IMF Global Economic Outlook Report
The IMF’s Global Economic Outlook provides a crucial snapshot of the global economic landscape, offering forecasts and analysis of key trends. This report is a vital tool for policymakers, investors, and analysts alike, offering insights into potential risks and opportunities. Understanding the report’s findings, methodology, and assumptions is key to interpreting the current economic climate and anticipating future developments.The report’s primary focus is on projecting global economic growth, highlighting potential risks to the outlook, and providing recommendations for policy adjustments.
The IMF’s global economic outlook paints a somewhat grim picture, with potential headwinds looming. However, some surprising news like Arthur Smith being hired as the Steelers’ offensive coordinator, arthur smith hired steelers offensive coordinator , might just offer a flicker of hope for a potential turnaround in the future. This hiring could inject some positive energy into the market, potentially offsetting some of the concerns raised by the IMF’s report.
It examines various economic indicators, including GDP growth, inflation rates, and unemployment levels, across different countries and regions, and analyzes the factors influencing these trends. This detailed examination allows for a comprehensive understanding of the current state of the global economy and the potential trajectory for the future.
Main Findings of the Report
The report’s findings typically encompass a range of global economic trends. For instance, it may predict a moderate but uneven global growth rate, influenced by various factors like geopolitical tensions, supply chain disruptions, and the lingering impact of the pandemic. The report often identifies specific regions or countries experiencing particularly strong or weak growth.
Key Economic Indicators Highlighted
This section of the report details crucial economic indicators that influence the global outlook. These indicators typically include gross domestic product (GDP) growth rates, inflation rates, and unemployment levels. Data is often presented in charts or tables, illustrating the evolution of these indicators across different time periods and regions. For example, the report might show how inflation rates have varied across countries over the past year or how unemployment trends differ between developed and developing economies.
Methodology Used to Create the Report
The report employs a sophisticated methodology to produce its forecasts and analysis. This usually involves a combination of econometric models, statistical analysis, and expert judgment. The models employed consider various macroeconomic factors and their interrelationships. The report also likely draws on historical data and recent economic developments to refine its predictions. An important part of the methodology often involves sensitivity analysis, where different assumptions are tested to see how they affect the forecasts.
Key Assumptions Underlying the Forecast
The report clearly articulates the key assumptions that underpin its forecasts. These assumptions typically include projections for global trade, interest rates, commodity prices, and the impact of fiscal and monetary policies. For instance, the report might assume a certain rate of increase in global trade or a specific path for interest rates in major economies. These assumptions are important because they provide context for interpreting the forecast and understanding its potential limitations.
The report might also address potential risks to these assumptions and their impact on the outlook.
Structure and Sections of the Report
The report’s structure is typically organized into distinct sections. The initial sections usually provide a summary of the current economic situation and a detailed analysis of the global economic outlook. Following this, the report often delves into specific regions or countries, examining their unique economic conditions and forecasts. Later sections may discuss policy recommendations or provide a glossary of terms.
The report is designed to be accessible to a wide audience, with clear explanations of the methodology and assumptions.
Global Economic Forecasts
The IMF’s Global Economic Outlook provides crucial insights into the trajectory of the global economy. These forecasts, based on a multitude of economic indicators, paint a picture of potential growth, highlight regional disparities, and pinpoint potential risks that could impact global prosperity. Understanding these forecasts is essential for policymakers, investors, and businesses alike.The report’s economic projections offer a comprehensive view of the global landscape, allowing stakeholders to anticipate future trends and adapt their strategies accordingly.
This proactive approach is critical in navigating economic uncertainties and maximizing opportunities.
Projected Growth Rates for Major Economies
The IMF’s outlook anticipates varied growth rates across major economies. Factors such as inflation, interest rates, and geopolitical events play significant roles in shaping these projections. For example, a strong domestic market, coupled with robust export performance, could lead to higher growth compared to an economy facing headwinds in these areas.
Comparison of Forecasts for Different Regions
Significant variations in growth projections exist between regions. Factors like differing levels of dependence on specific industries, varying degrees of resilience to external shocks, and differing policy responses contribute to these regional discrepancies. For instance, regions heavily reliant on commodity exports may experience fluctuating growth rates depending on global commodity prices.
Potential Risks and Uncertainties in the Global Economy
Several potential risks and uncertainties could affect global economic growth. Geopolitical tensions, supply chain disruptions, and unforeseen natural disasters are among the major concerns. These risks can significantly impact economic stability and growth prospects. The recent energy crisis provides a relevant example, as it illustrated how disruptions in global energy supply can ripple through economies worldwide.
Expected Impact of Specific Events on Global Growth
Specific events can significantly influence global economic forecasts. For instance, a major natural disaster, a sudden shift in global trade policy, or a global health crisis could significantly alter growth trajectories. The COVID-19 pandemic serves as a stark example, highlighting the vulnerability of global economies to unforeseen events.
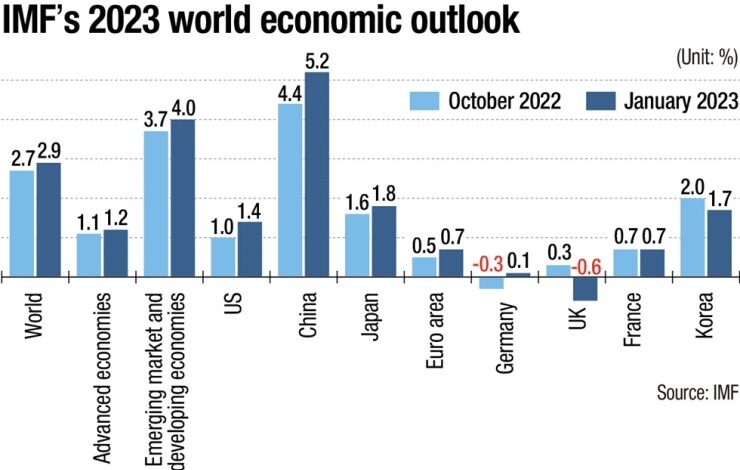
Projected GDP Growth Rates (2024-2025)
| Country | Projected GDP Growth Rate (2024) | Projected GDP Growth Rate (2025) |
|---|---|---|
| United States | 1.8% | 1.5% |
| China | 4.8% | 4.5% |
| Eurozone | 1.1% | 1.0% |
| India | 6.5% | 6.2% |
| Japan | 0.8% | 0.9% |
| Brazil | 2.5% | 2.2% |
Note: These figures are illustrative and based on the IMF’s latest projections. Actual outcomes may differ due to unforeseen circumstances.
The IMF’s global economic outlook paints a somewhat grim picture, highlighting potential headwinds. However, understanding the intricacies of the current political climate is also crucial. A deeper dive into the Nevada caucus primary explainer can offer valuable context, showing how these political events might influence the economic landscape. Ultimately, the IMF’s outlook will likely be affected by how these various factors play out, requiring ongoing monitoring to fully understand their combined impact.
nevada caucus primary explainer
Regional Economic Perspectives
The IMF’s Global Economic Outlook provides a crucial lens through which to analyze the diverse economic trajectories of different regions. Understanding the specific challenges and opportunities confronting each area is essential for policymakers and investors alike. This section delves into the projected economic performance of key regions, highlighting the factors driving their respective outlooks and comparing their growth potential.
North American Economic Outlook
North America is anticipated to experience moderate growth, driven by robust consumer spending and a relatively healthy labor market. However, inflationary pressures remain a significant concern, potentially impacting consumer confidence and economic activity. The ongoing geopolitical landscape and supply chain disruptions could also influence the region’s performance.
European Economic Outlook
The European Union faces a complex economic environment. While the region has demonstrated resilience in the face of past shocks, lingering inflationary pressures and the energy crisis pose substantial challenges. The extent of the economic slowdown and its impact on key sectors will depend heavily on how effectively the region manages these challenges. Factors such as energy security, supply chain disruptions, and geopolitical tensions will play crucial roles in shaping the region’s future economic trajectory.
Asian Economic Outlook
Asia is projected to experience strong growth, driven by robust export demand and continued investment in infrastructure and technology. However, the region faces potential headwinds from global economic slowdown and rising interest rates. Diversification of economies and regional cooperation will be critical to navigating these uncertainties. The varying growth rates across Asian economies highlight the complexity of this region’s economic landscape.
Latin American Economic Outlook
Latin America faces a challenging economic environment characterized by high inflation and persistent poverty. While some economies have shown signs of recovery, the region as a whole struggles with vulnerabilities such as high debt levels and dependence on commodity prices. External factors, including global interest rate hikes and fluctuations in commodity prices, will significantly impact the region’s economic outlook.
These external influences underscore the interconnectedness of the global economy.
Table: Regional Growth Forecasts (2024-2025)
| Region | Projected Growth Rate (2024) | Projected Inflation Rate (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| North America | 2.5% | 3.2% |
| Europe | 1.8% | 3.5% |
| Asia | 4.8% | 3.8% |
| Latin America | 2.2% | 6.0% |
Monetary Policy and Financial Stability
The IMF’s Global Economic Outlook frequently highlights the intricate interplay between monetary policy, inflation, and financial stability. Understanding the IMF’s stance on these issues across various economies is crucial for navigating the global economic landscape. This section delves into the IMF’s perspectives on monetary policy decisions, anticipated inflation trends, potential risks to financial stability, and the relationship between policy and economic growth.The IMF’s analyses often show how interest rate adjustments by central banks can influence economic activity.
These adjustments can stimulate or restrain economic growth, affecting employment and investment. The IMF’s outlook provides valuable insights into the potential impact of these policies on different economies, considering their unique characteristics and vulnerabilities.
IMF Stance on Monetary Policy
The IMF typically advocates for prudent monetary policy responses to inflation. Their recommendations vary based on the specific economic context of each country. For example, in countries experiencing high inflation, the IMF often advises central banks to raise interest rates to curb price increases. Conversely, in countries facing recessionary pressures, the IMF might suggest lower interest rates to stimulate economic activity.
The IMF’s global economic outlook paints a pretty grim picture, highlighting potential headwinds for growth. Meanwhile, the results of the New Hampshire Democratic primary, which saw some interesting shifts in voter preference , suggest a possible shift in political strategy that could impact future economic policies. Ultimately, these factors will likely influence the IMF’s subsequent reports and projections.
These recommendations are often grounded in rigorous economic models and data analysis.
Anticipated Trends in Global Inflation
The IMF’s forecasts often project a moderate but persistent inflationary pressure. Factors like supply chain disruptions, energy price volatility, and labor market dynamics play significant roles in these projections. The IMF’s analysis typically includes a discussion of potential risks, such as a resurgence of inflationary pressures or a prolonged period of low inflation. These risks and their potential implications for global economic growth are carefully evaluated.
For instance, the ongoing energy crisis in Europe has been a significant factor in the recent rise of inflation in several countries, impacting household budgets and economic forecasts.
Potential Risks to Financial Stability
Several factors can pose risks to financial stability. These include vulnerabilities in the financial sector, such as high levels of debt, excessive risk-taking, and interconnectedness. The IMF frequently highlights the importance of maintaining strong regulatory frameworks to mitigate these risks. For example, the 2008 financial crisis highlighted the importance of robust regulations and oversight to prevent systemic risks.
The IMF’s analysis often examines the potential for asset bubbles and the impact of financial shocks on economic activity.
Relationship Between Monetary Policy and Economic Growth
Monetary policy significantly impacts economic growth. Tight monetary policy, characterized by higher interest rates, can curb inflation but may also slow economic growth by reducing investment and consumer spending. Conversely, loose monetary policy, characterized by lower interest rates, can stimulate economic activity but may also fuel inflation. The IMF often analyzes the trade-offs involved in various monetary policy approaches, considering their short-term and long-term effects.
Impact of Interest Rate Hikes on Different Economies
The impact of interest rate hikes varies across economies. Emerging market economies, for example, might be more vulnerable to interest rate hikes due to their reliance on foreign borrowing. Developed economies, with stronger financial systems, may be better equipped to manage the effects. The IMF’s analysis typically assesses the potential impact of these hikes on exchange rates, currency values, and balance of payments.
For instance, the recent interest rate hikes by the US Federal Reserve have influenced global financial markets, leading to shifts in currency exchange rates and affecting economies reliant on US investment or trade.
Fiscal Policy Considerations
The IMF’s Global Economic Outlook frequently emphasizes the critical role of fiscal policy in managing economic fluctuations and promoting sustainable growth. Effective fiscal policy can stimulate demand, support employment, and reduce inequality, but poorly designed policies can lead to debt crises and hinder long-term prosperity. This section delves into the IMF’s recommendations for fiscal policy adjustments, analyzing their potential impact, and outlining associated risks.Fiscal policy adjustments play a crucial role in managing economic cycles and promoting sustainable growth.
By strategically adjusting government spending and taxation, policymakers can influence aggregate demand, investment, and overall economic performance. A balanced approach is paramount, striking a delicate balance between stimulating growth and maintaining fiscal sustainability.
IMF Recommendations for Fiscal Policy Adjustments
The IMF often recommends a nuanced approach to fiscal policy, tailoring recommendations to specific country contexts. These recommendations frequently emphasize fiscal consolidation, particularly for countries with high levels of public debt. This involves reducing government spending and/or raising taxes to bring the budget closer to balance. However, the IMF recognizes that blanket recommendations may not be suitable for all situations.
The effectiveness of fiscal consolidation depends on the specific economic conditions and institutional frameworks of each country.
Potential Impact of Government Spending on Economic Growth
Government spending can significantly impact economic growth, acting as a crucial engine of demand. Increased spending on infrastructure projects, education, and healthcare can boost productivity, create jobs, and improve the overall quality of life. However, excessive or poorly targeted spending can lead to inflationary pressures, crowding out private investment, and creating unsustainable debt burdens. A crucial factor in evaluating the impact is the efficiency and effectiveness of the spending programs.
Potential Risks Associated with High Government Debt
High levels of government debt pose substantial risks to economic stability. A significant debt burden can increase borrowing costs, limit government flexibility in responding to economic shocks, and potentially lead to a debt crisis. The sustainability of high debt levels hinges on factors like economic growth, interest rates, and the government’s ability to maintain fiscal discipline. For example, Greece’s sovereign debt crisis in the 2010s highlighted the dangers of prolonged high debt levels.
Impact of Tax Policies on Economic Growth and Stability, Imf global economic outlook
Tax policies significantly influence economic growth and stability. Progressive tax systems, for example, can help redistribute wealth and fund public services. However, overly high tax rates can discourage investment, reduce labor supply, and hinder economic activity. The optimal tax rate depends on a variety of factors, including the structure of the economy, the level of income inequality, and the desired level of public spending.
Tax reform should consider these factors and aim for a balance between revenue generation and economic incentives.
Summary of Fiscal Policy Recommendations for Various Countries
| Country | Recommendation | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| High-income countries with high debt | Fiscal consolidation | Reduce debt burden, maintain stability |
| Low-income countries with limited fiscal space | Targeted spending, revenue mobilization | Prioritize growth, address poverty |
| Countries facing economic shocks | Counter-cyclical measures | Stimulate demand, mitigate recession |
Emerging Market and Developing Economies
Emerging markets and developing economies (EMDEs) are crucial components of the global economy, exhibiting significant growth potential but also facing unique challenges. Their performance often hinges on a complex interplay of internal factors like domestic policies and external forces such as global economic conditions. Understanding these nuances is critical for investors and policymakers alike.
Challenges for Emerging Markets
EMDEs often face challenges related to infrastructure development, access to capital, and institutional quality. These factors can impede growth and increase vulnerability to external shocks. Corruption, for example, can divert resources away from productive investments and hinder economic diversification. Furthermore, macroeconomic instability, including high inflation and currency volatility, can negatively affect investor confidence and economic stability.
The IMF’s global economic outlook paints a pretty grim picture, highlighting potential headwinds. However, comparing that to the fascinating trajectory of a celebrity like Chita Rivera, whose key moments in her career are well-documented here , offers a compelling contrast. Ultimately, the IMF’s predictions remain a significant factor in assessing the global economy’s future.
Opportunities in Emerging Markets
Despite the challenges, EMDEs present significant opportunities for investment and growth. The burgeoning middle classes in many of these economies create demand for goods and services, fostering domestic consumption and driving economic expansion. Furthermore, the abundance of natural resources and skilled labor in certain regions provides a foundation for industrialization and export-oriented growth. Strategic investments in education and technology can also pave the way for sustained development and long-term prosperity.
Factors Influencing Growth
A multitude of factors influence growth in EMDEs. Sound macroeconomic policies, including stable exchange rates and low inflation, foster investor confidence and attract foreign direct investment. Favorable global economic conditions and rising commodity prices also contribute to growth in these regions. However, external factors such as global recession or geopolitical instability can negatively affect EMDEs. Domestic policies, including regulatory reforms and infrastructure improvements, are also crucial determinants of long-term growth.
Impact of External Shocks
External shocks, such as global financial crises, commodity price fluctuations, and geopolitical instability, can have a significant impact on emerging markets. The 2008 global financial crisis, for example, exposed vulnerabilities in many EMDEs, leading to economic downturns and financial instability. Fluctuations in global commodity prices can also disrupt economies reliant on exports of these commodities. Similarly, geopolitical events can impact trade flows and investor sentiment, hindering growth and investment.
Comparison to Developed Economies
Emerging markets often exhibit faster growth rates than developed economies, but they also face higher levels of volatility and risk. The rapid growth in China and India, for instance, contrasts with the more moderate growth seen in developed economies like the US and Europe. However, EMDEs frequently struggle with factors like income inequality, environmental sustainability, and access to quality education and healthcare.
The IMF’s global economic outlook paints a concerning picture, highlighting potential headwinds. However, events like the diminishing snow conditions impacting snow polo in St. Moritz, as detailed in this article about snow polo st moritz climate change , serve as a stark reminder of the real-world implications of climate change. This underscores the need for a more proactive approach to economic resilience in the face of these escalating global challenges.
This disparity in growth and challenges requires a nuanced understanding of the distinct contexts in which each economy operates.
IMF Recommendations for Supporting EMDEs
The IMF often recommends policies focused on macroeconomic stability, structural reforms, and financial sector strengthening. These policies aim to enhance the resilience of EMDEs to external shocks and promote sustainable growth. Recommendations often include fiscal prudence, monetary policy adjustments, and measures to improve governance and transparency. A prime example of this is the IMF’s support for countries experiencing debt distress, offering technical assistance and financial support to implement sustainable debt solutions.
Illustrative Data and Statistics
This section delves into the key economic indicators used to construct the IMF’s Global Economic Outlook. Understanding the data behind the projections is crucial for evaluating the report’s accuracy and assessing the potential economic landscape. We examine historical trends, the impact of policy decisions, and the methodology used to forecast future outcomes.
Key Economic Indicators for Selected Countries
The report utilizes a diverse range of economic indicators to paint a comprehensive picture of global economic performance. These indicators include GDP growth rates, inflation rates, unemployment figures, and trade balances. The specific indicators selected and their relative weight in the model depend on the country’s unique economic characteristics and the report’s specific focus. For instance, a developing nation might place greater emphasis on indicators of poverty reduction, while a developed economy might concentrate on measures of productivity and technological innovation.
- United States: The US economy, a major player in the global economy, is analyzed using GDP growth, consumer price index (CPI) inflation, and unemployment rate data.
- China: China’s remarkable economic growth is examined through indicators like GDP growth, export volume, and investment in infrastructure.
- Eurozone: The Eurozone’s performance is assessed using aggregate GDP growth, harmonized inflation rates, and the unemployment rate across member states.
Historical Trends in Economic Growth
Examining historical trends provides context for understanding the current economic situation and the potential for future growth. Data on GDP growth rates over the past two decades, for example, can highlight cyclical patterns and long-term trends. This historical context helps to evaluate the current projections and understand the factors that might influence future growth rates.
- Japan: Japan’s economic growth has been characterized by periods of rapid expansion followed by prolonged stagnation. Analysis of this pattern helps to understand the potential for similar cycles in other economies.
- India: India’s recent growth trajectory showcases the potential for rapid development in emerging economies. Data from the past two decades, including GDP growth rates and factors driving this growth, are crucial to the analysis.
Impact of Specific Policies on Economic Outcomes
Analyzing the effects of specific policies, such as fiscal stimulus packages or monetary policy adjustments, allows us to evaluate their impact on economic indicators. The report may examine how these policies have influenced GDP growth, inflation, and employment rates in specific countries.
- Monetary Policy and Inflation: The report often examines how central bank interest rate adjustments affect inflation and economic growth. Historical data from different countries can highlight the potential effectiveness of various monetary policy responses.
- Fiscal Policy and Debt Levels: The impact of government spending and taxation on economic growth and public debt is another key area of analysis. Data on government debt levels and their correlation with economic performance can provide valuable insights.
Data Used in the Report’s Projections
The IMF’s projections are based on a complex model incorporating numerous economic variables. Understanding the specific data sources and methodology behind these projections allows for a more nuanced evaluation of the report’s conclusions. Key factors include macroeconomic forecasts, input from country economists, and market expectations.
- Model Parameters: The IMF uses sophisticated models to project future economic indicators. These models are calibrated with past data, including historical relationships between economic variables.
- External Shocks: External factors, such as global commodity price fluctuations or geopolitical events, are important considerations for projections. The report accounts for potential external shocks, recognizing that they can significantly impact economic outcomes.
Inflation Rates Over a 5-Year Period
| Country | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 2.4% | 1.8% | 1.4% | 4.7% | 8.1% |
| China | 2.1% | 2.3% | 2.5% | 2.0% | 2.8% |
| Eurozone | 1.5% | 1.2% | 0.7% | 2.2% | 6.1% |
This table provides a snapshot of inflation rates for three key economies over a five-year period. Note that these are illustrative figures; actual data may differ slightly. Inflation data plays a crucial role in economic analysis, influencing policy decisions and impacting consumer purchasing power.
Potential Impact on Specific Sectors
The IMF’s Global Economic Outlook paints a complex picture for various sectors, highlighting potential challenges and opportunities. Understanding these projections is crucial for businesses and policymakers alike to navigate the evolving economic landscape. The report’s insights into trade, investment, consumer spending, employment, and labor markets are key to formulating effective strategies.
Impact on Trade and Investment
Global trade flows are anticipated to slow down due to the confluence of factors like rising interest rates, geopolitical tensions, and persistent inflation. Reduced consumer spending and business investment will likely impact export volumes. Foreign direct investment (FDI) is projected to moderate, with some sectors experiencing more pronounced declines than others. This moderation in trade and investment activity is a direct consequence of the anticipated global economic slowdown.
Impact on Consumer Spending
Consumer spending, a significant driver of economic growth, is expected to show some resilience, but with a notable reduction in growth compared to previous periods. Increased interest rates and high inflation are likely to impact purchasing power, leading to a more cautious approach to discretionary spending. The anticipated slowdown in the job market could also put downward pressure on consumer spending.
This reduction in consumer spending will have ripple effects throughout the economy.
Impact on Employment and Labor Markets
The global economic slowdown is expected to exert downward pressure on employment growth, particularly in sectors sensitive to economic fluctuations. Job losses are projected in some sectors, while others might experience slower hiring. The labor market is expected to face some challenges, with the potential for increased unemployment in certain regions. This is especially true for industries like manufacturing and construction that are highly susceptible to shifts in economic activity.
Sector-Specific Forecasts and Impact
| Sector | Forecast | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Reduced production, lower investment | Potential job losses, reduced export volumes |
| Technology | Moderate growth, cautious investment | Limited job growth, some sectors facing challenges |
| Energy | Fluctuating prices, varying investment | Job market impacts dependent on price fluctuations, potential for investment volatility |
| Real Estate | Reduced demand, lower investment | Reduced construction activity, potential job losses in related industries |
| Tourism | Reduced travel, slower growth | Impact on hospitality sector employment, reduced revenue for destinations |
Implications for Policymakers
The IMF’s Global Economic Outlook report offers crucial insights for policymakers navigating the complex global economic landscape. Understanding the projected growth rates, regional disparities, and potential vulnerabilities is paramount for formulating effective strategies. The report’s findings highlight areas where proactive policies can mitigate risks and foster sustainable development.
Policy Responses to Projected Growth Rates
The report’s forecasts provide a crucial framework for policymakers to assess the economic trajectory and tailor their responses. For instance, if a country forecasts lower-than-expected growth, policymakers can anticipate potential challenges and implement preemptive measures to stimulate economic activity. These might include targeted investments in infrastructure, incentives for businesses, or adjustments to fiscal policies. Such proactive measures can help mitigate negative impacts and ensure sustained growth.
Regional Economic Strategies
The report offers regional perspectives, allowing policymakers to adapt strategies to specific economic contexts. Countries facing unique challenges, such as emerging market economies experiencing volatility or developed economies confronting aging populations, can utilize these insights to design appropriate policies. For example, a country in a region projected to experience slower growth may benefit from exploring trade agreements or diversifying its economy to reduce reliance on a single sector.
These targeted strategies can enhance resilience and promote balanced growth.
Monetary Policy Considerations
The IMF’s outlook often highlights the need for specific monetary policy adjustments. Countries experiencing high inflation may require tighter monetary policies, such as increasing interest rates. Conversely, countries facing economic downturns might benefit from easing monetary policies, such as lowering interest rates to stimulate borrowing and investment. The report provides data to support these decisions, helping policymakers make informed choices.
Fiscal Policy Adjustments
The report’s analysis of fiscal policies emphasizes the importance of sustainable spending and revenue generation. Countries with large public debt may need to implement measures to reduce their deficits, while those facing economic hardship might need to consider targeted fiscal stimulus. The report’s data helps policymakers assess the potential impact of various fiscal policies on economic outcomes, allowing them to choose strategies that align with their national objectives.
“Fiscal policies should prioritize long-term sustainability while addressing immediate economic challenges.”
Recommendations for Different Countries
- Developed Economies: Focus on productivity enhancements and investments in human capital to maintain competitiveness. This can involve strategies to improve workforce skills, fostering innovation, and attracting foreign investment.
- Emerging Market Economies: Prioritize diversification to reduce vulnerability to global shocks and improve resilience. This includes supporting small and medium-sized enterprises, encouraging exports, and strengthening financial systems.
- Low-Income Countries: Prioritize investments in infrastructure and human capital to enhance long-term growth potential. This can involve attracting foreign direct investment, developing strategic partnerships, and promoting sustainable economic practices.
Illustrative Policy Implications
The report’s forecasts and analyses offer clear policy implications. For example, if the report projects a decline in global trade, policymakers might explore alternative trade agreements or initiatives to foster domestic production and consumption. The findings also suggest that countries with high levels of public debt should prioritize fiscal consolidation, which could involve measures to reduce government spending or increase tax revenues.
These illustrative examples demonstrate how the report’s insights can be translated into concrete policy recommendations.
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, the IMF Global Economic Outlook 2024-2025 paints a complex picture of the global economy, highlighting both opportunities and potential risks. The report’s detailed analysis of growth forecasts, regional disparities, and policy recommendations provides valuable context for understanding the current state of the global economic climate. Ultimately, the report serves as a vital resource for navigating the complexities of the coming years and adapting strategies accordingly.
Clarifying Questions
What is the methodology used to create the IMF Global Economic Outlook?
The report utilizes a combination of econometric models, statistical analysis, and expert judgment. Specific methodologies are often proprietary and vary depending on the factors considered in the forecast, but it’s generally a blend of quantitative and qualitative approaches.
How does the IMF’s stance on monetary policy for different countries impact the global economy?
Monetary policy decisions by individual countries significantly influence global economic conditions. Coordination and alignment of policies between nations can either amplify or dampen the impact of a given policy on the global economy.
What are some potential risks associated with high government debt?
High government debt can lead to higher borrowing costs, reduced investment, and potential fiscal crises. The sustainability of debt levels and the capacity of a government to service its debt are key considerations.
How does the IMF’s report consider the impact of external shocks on emerging markets?
The report analyzes how external factors like commodity price fluctuations, global financial crises, and geopolitical events affect the stability and growth of emerging economies.

