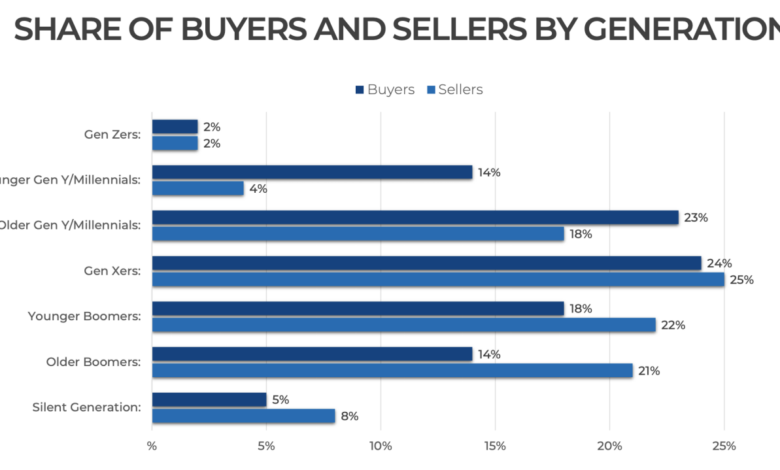
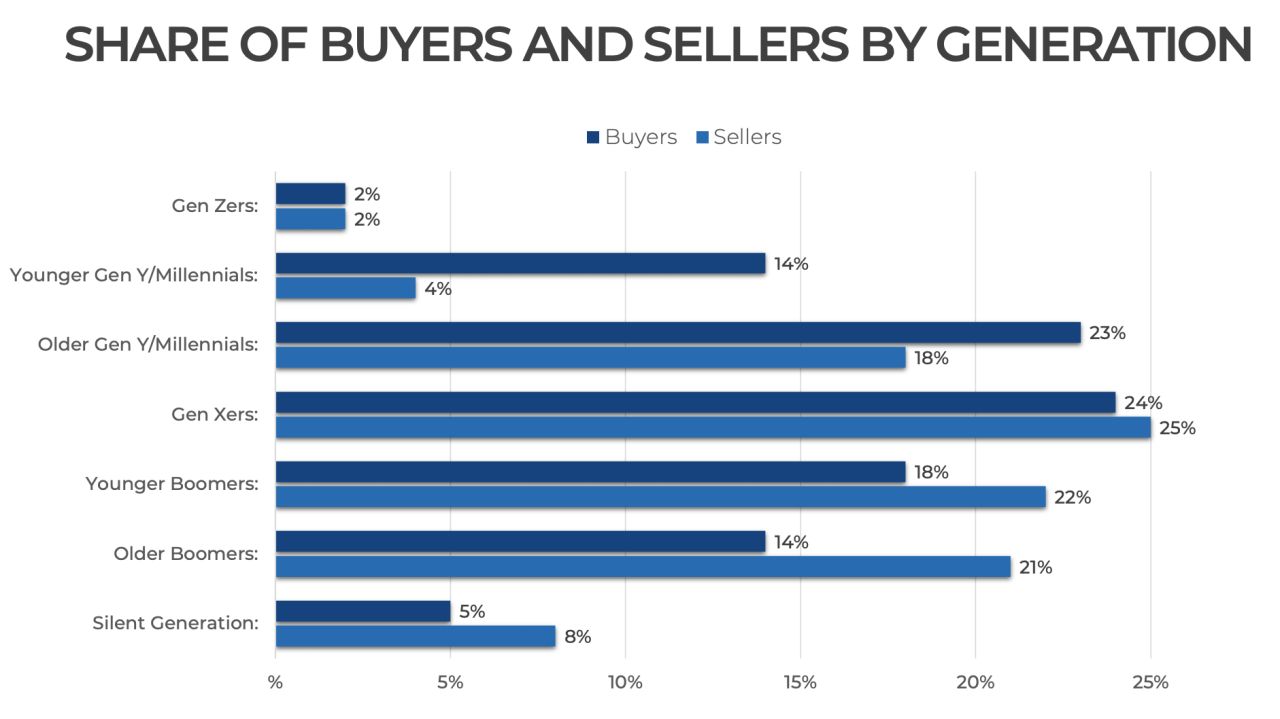
Gen Z Housing Prices A Market Overview
Housing prices Gen Z market is a critical issue facing a generation navigating a complex landscape. This article dives into the unique challenges and opportunities Gen Z faces in today’s housing market, examining affordability, preferences, and future trends. From financing hurdles to regional variations, we’ll explore the complexities of this evolving market and how it impacts this generation.
The current housing market presents both exciting possibilities and daunting obstacles for Gen Z. High interest rates and escalating prices create a financial hurdle for many, impacting their ability to enter the homeownership market. This article will examine the factors influencing these prices and how they affect Gen Z’s housing journey.
Gen Z Housing Market Overview
Gen Z, born roughly between the early 1990s and the early 2010s, is entering the homeownership phase. This generation faces unique challenges and opportunities in the housing market, shaped by factors like historically high inflation, fluctuating interest rates, and a complex economic landscape. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for Gen Z to navigate the complexities of homeownership and make informed decisions.The housing market presents both hurdles and advantages for Gen Z.
Affordability remains a significant concern, compounded by rising interest rates. However, increased inventory in some areas and a growing demand for smaller, more sustainable living spaces could potentially offer some advantages for this generation.
Current Housing Market Conditions for Gen Z
The current housing market presents a mixed bag for Gen Z. High interest rates, while impacting affordability, also influence the supply of homes available. This complex interplay of factors creates both opportunities and challenges for young adults seeking their first home. The following table highlights these conditions:
| Factor | Description | Impact on Gen Z |
|---|---|---|
| Affordability | High interest rates and rising home prices significantly limit the purchasing power of many Gen Z homebuyers. This is further exacerbated by rising living expenses. | Gen Z faces difficulty affording homes in desirable locations. They might need to consider less expensive areas or explore alternative housing options. |
| Inventory | While inventory levels fluctuate regionally, some areas show an increase in available homes. This could potentially provide more options, but also reflects a slowdown in overall housing demand. | Increased inventory might provide opportunities for more choices, but the market may not be as robust in every area, making price negotiation and securing a property more challenging. |
| Interest Rates | Historically high interest rates make mortgages more expensive, directly impacting monthly payments and affordability. These rates are a key factor in the cost of homeownership. | Higher interest rates reduce the purchasing power of Gen Z buyers. They must carefully consider the long-term financial implications of taking on a mortgage. |
Unique Challenges and Opportunities for Gen Z
Gen Z faces unique challenges compared to previous generations, including the lingering effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, which influenced both remote work and a shift in housing preferences. This generation is often more focused on sustainable living and potentially prioritizing location and community over traditional home size.Opportunities include the increasing demand for smaller homes, the rise of co-living spaces, and the potential for more readily available financing options.
These factors could lessen the financial burden and create more accessible options for first-time homebuyers.
Gen Z Demographics
Gen Z homebuyers are a diverse group. Their ages typically range from the late teens to early 30s. Location preferences vary, with some areas showing greater appeal based on employment opportunities and lifestyle factors. Income levels are typically lower than previous generations at the same stage of life, influencing their ability to afford homes.
Trends in Housing Prices and Their Impact
The overall trend in housing prices, driven by various economic factors, directly impacts Gen Z’s ability to enter the housing market. Inflation and interest rate fluctuations often create volatility in the housing market, making it more challenging to predict future price movements. The interplay between supply, demand, and financial conditions is crucial to understand the market’s dynamics.
Affordability and Financing
Gen Z faces unique challenges in the housing market, navigating a complex landscape of rising costs and financial constraints. This generation, often burdened with student loan debt and a volatile job market, finds the dream of homeownership increasingly elusive. Understanding these hurdles is crucial to developing effective solutions and policies to support Gen Z’s housing aspirations.High down payment requirements and soaring interest rates significantly hinder Gen Z’s ability to enter the housing market.
The traditional 20% down payment is often unattainable, forcing many to explore alternative options. This, coupled with the rising cost of living, makes securing a mortgage an even greater financial hurdle. Furthermore, interest rates, a critical factor in mortgage affordability, have been steadily increasing, making monthly payments less manageable for many prospective homeowners.
High Down Payment Requirements
The traditional 20% down payment requirement is a substantial barrier to homeownership for many Gen Z individuals. This large upfront cost often requires significant savings, delaying the ability to purchase a home. Many Gen Z individuals are carrying student loan debt and may be starting their careers with limited savings, making the down payment requirement a major obstacle.
Gen Z is facing some serious hurdles in the housing market, with prices skyrocketing. It’s a tough situation, especially when you consider the impressive displays of luxury at events like the Couture Didier Ludot 50th Anniversary Paris fashion show. This extravagant celebration highlights the stark contrast between the aspirational world of high fashion and the realities of affordability for a generation struggling to buy a home.
The pressure on young people to secure housing is undeniably high.
Rising Interest Rates
Increasing interest rates directly impact mortgage affordability. Higher rates translate to larger monthly payments, potentially making homeownership unaffordable for those with limited financial resources. This directly affects Gen Z, who may be less established financially and have limited financial resources compared to previous generations. For example, a $300,000 mortgage at a 7% interest rate compared to a 4% interest rate would see a significant increase in the monthly payment.
Financing Options for Gen Z
Numerous financing options exist to assist Gen Z in navigating the challenges of homeownership. These options include traditional mortgages, government-backed loans, and various assistance programs.
- Mortgages: Traditional mortgages remain a primary option, but their stringent requirements may not suit all Gen Z buyers. Different types of mortgages, such as FHA loans, VA loans, and USDA loans, offer varying down payment requirements and eligibility criteria, which can provide a suitable path to homeownership.
- Government Assistance Programs: Government programs, like the Federal Housing Administration (FHA) loans, often offer lower down payment requirements, making homeownership more accessible. The Homeownership Voucher Program and other initiatives can also provide financial assistance to eligible low-income individuals and families.
- Alternative Loans: Alternative lending options, such as those provided by non-bank lenders, may offer more flexible terms and less stringent criteria compared to traditional mortgages. However, borrowers should carefully review the terms and conditions of these options to avoid hidden fees or high interest rates.
Impact of Student Loan Debt
Student loan debt significantly impacts Gen Z’s ability to purchase a home. The substantial amount of outstanding student loan debt often reduces the amount of money available for a down payment and monthly mortgage payments. This financial burden can delay homeownership and make it harder to save for a down payment. It’s important to note that student loan debt relief programs and strategies to manage this debt are crucial to ease the financial burden and allow Gen Z to pursue homeownership.
Comparison to Previous Generations
Gen Z faces significantly higher housing costs compared to previous generations, especially considering the combination of higher interest rates and student loan debt. The increasing cost of living and the financial burdens associated with homeownership have made the process more challenging for Gen Z. For example, a 25-year-old in 2000 would have a significantly lower housing cost and student loan debt burden compared to their 2023 counterparts.
Financing Options Breakdown
| Financing Option | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Mortgage | Established process, wide availability | High down payment requirements, stringent criteria |
| FHA Loan | Lower down payment requirement, government backing | Higher interest rates, potential for more paperwork |
| VA Loan | No down payment required for eligible veterans | Limited to eligible veterans, strict eligibility requirements |
| USDA Loan | Available in rural areas, potentially lower interest rates | Geographic limitations, strict eligibility criteria |
| Alternative Loans | Potentially more flexible terms | Higher interest rates, potential hidden fees |
Housing Preferences and Needs
Gen Z, the generation born between the early 1990s and the early 2010s, is approaching homeownership with a unique set of priorities compared to previous generations. Their experiences growing up in a digitally driven world and navigating economic uncertainties shape their expectations and desires for housing. This generation is not just looking for a place to live; they’re seeking a space that reflects their lifestyle, values, and aspirations.
Understanding these preferences is crucial for real estate professionals, developers, and policymakers to cater to their needs effectively.The shift in housing preferences isn’t simply about wanting different features; it’s a fundamental change in the relationship between people and their homes. Gen Z is looking for more than just shelter; they seek spaces that enhance their lives, contribute to their communities, and align with their values, including sustainability and social responsibility.
Typical Housing Preferences
Gen Z homebuyers are often drawn to smaller, more efficient living spaces. This reflects their focus on maximizing their living space and minimizing costs, a preference shaped by economic realities and a desire for less upkeep. They are frequently drawn to urban or suburban locations with walkable access to amenities, restaurants, and public transportation. Convenience and ease of access are key.
Amenities like in-building gyms, co-working spaces, or rooftop terraces are also highly desirable, providing opportunities for social interaction and community building. The need for flexibility is also important. Many Gen Z members desire homes that can easily adapt to changing needs, whether it’s a growing family or a changing lifestyle.
Differences from Previous Generations
Gen Z differs from previous generations in their approach to homeownership. They are less focused on the traditional “American Dream” of a large, single-family home in a sprawling suburban neighborhood. Their priorities often prioritize experiences over material possessions. This translates into a desire for urban or mixed-use environments that offer a greater variety of lifestyle options. The emphasis on flexibility and adaptability is another key difference, highlighting the generation’s preference for homes that can easily adjust to changing needs.
Technology’s Influence on Housing Needs
Technology significantly impacts Gen Z’s housing preferences. Smart home technology, for instance, plays a crucial role in their choices, with features like smart thermostats, security systems, and appliances appealing to their familiarity and comfort with technology. Remote work and digital nomadism also influence their location preferences. They often prioritize access to high-speed internet and flexible living arrangements.
The digital nature of their lives often translates to a need for efficient, connected spaces.
Importance of Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Housing
Sustainability and eco-friendliness are increasingly important for Gen Z. They are acutely aware of environmental issues and seek housing options that minimize their environmental impact. Features like solar panels, energy-efficient appliances, and sustainable building materials are highly valued. The growing awareness of environmental concerns influences their choices and drives them to consider the long-term impact of their decisions.
Gen Z is facing a tough housing market, with prices skyrocketing. It’s a real struggle for young people trying to get a foothold. The incredible career of Adrian Beltre, a legendary Texas Rangers player, adrian beltre hall of fame texas rangers , is a great example of how hard work and dedication can pay off, but that doesn’t solve the current affordability crisis for the younger generation.
The current economic climate is certainly making homeownership a significant challenge for this demographic.
The desire for eco-friendly options reflects a desire for a more responsible and sustainable future.
Comparison of Housing Preferences Across Generations
| Generation | Size | Location | Amenities | Sustainability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gen Z | Smaller, more efficient spaces Emphasis on flexibility |
Urban/suburban areas with walkability, access to amenities, and public transport | Smart home technology, co-working spaces, gyms, rooftop terraces | Prioritizes sustainable materials, energy efficiency, and eco-friendly features |
| Millennials | Often larger, single-family homes in suburbs or growing urban areas | Suburbs or mixed-use areas with proximity to schools and parks | Open floor plans, outdoor spaces, and some smart home integration | Growing awareness, but not as prominent as for Gen Z |
| Gen X | Single-family homes in suburbs, or larger urban areas | Suburban neighborhoods with access to schools and community amenities | Focus on practicality and function over fancy amenities | Less prominent concern compared to Gen Z |
Impact of Economic Factors: Housing Prices Gen Z Market
Gen Z faces unique challenges in the housing market, and economic factors play a crucial role in shaping their experience. Inflation, recessionary pressures, and fluctuating construction costs directly impact their ability to save for a down payment, secure financing, and afford the rising prices of existing homes. Understanding these dynamics is vital to comprehending the complex landscape Gen Z navigates as they enter the housing market.The interplay of economic forces like inflation and recession significantly influences Gen Z’s housing aspirations.
These factors impact their ability to save, find suitable financing options, and ultimately, afford the homes they desire. Rising construction costs exacerbate these challenges, making homeownership an even greater hurdle. Government policies and supply chain disruptions further complicate the picture, creating an intricate web of influences on the Gen Z housing market.
Impact of Inflation and Recession
Inflation erodes purchasing power, making homes less affordable for Gen Z. Higher prices for essential goods and services reduce the amount of disposable income available for saving and investing, hindering their ability to accumulate the necessary funds for a down payment. Recessions, characterized by economic downturns, often lead to decreased employment opportunities and reduced income, further tightening the financial constraints on Gen Z homebuyers.
Historical examples, such as the 2008 financial crisis, demonstrate how economic downturns can significantly impact housing affordability and market stability.
Effects of Rising Construction Costs
Rising construction costs directly translate into higher home prices. This inflationary pressure on building materials, labor, and land pushes the cost of new homes beyond the reach of many, including Gen Z. Increased demand for housing, often outpacing supply, fuels these rising costs. This trend creates a vicious cycle, making homeownership more expensive and less accessible. For instance, a rise in lumber prices due to supply chain disruptions can quickly escalate the cost of a new construction project.
Impact of Government Policies
Government policies, including tax incentives, mortgage programs, and zoning regulations, significantly influence the housing market. Government subsidies for first-time homebuyers, or reduced interest rates for mortgages, can potentially ease the burden on Gen Z. Conversely, stricter lending regulations or policies that restrict housing development can limit options and increase costs. Examples of how different housing policies have affected various demographics are readily available from government and economic research institutions.
Impact of Supply Chain Disruptions
Supply chain disruptions, affecting the availability and cost of building materials, have a direct impact on housing prices. Shortages of materials, like lumber or steel, can increase costs and delay construction projects, hindering the supply of new homes. These disruptions create uncertainty and increase the price volatility of existing homes, making it harder for Gen Z to predict and plan for their housing needs.
For instance, a shortage of specific building components can result in price increases, affecting both the construction of new homes and the value of existing properties.
Interplay of Economic Factors (Flowchart)
(A visual representation of the interplay between economic factors and Gen Z’s housing market is best presented as a flowchart diagram. Unfortunately, I cannot create an image here. A visual flowchart would display the following interconnected elements: inflation, recession, construction costs, government policies, supply chain disruptions, and their combined impact on Gen Z’s ability to afford housing.)
Future Trends and Projections
Gen Z’s approach to housing is unlike any generation before them. Shaped by economic realities, technological advancements, and evolving social norms, their housing journey will likely deviate from traditional patterns. This section delves into potential future trends, exploring how technology and changing demographics will influence their housing choices.The Gen Z housing market is poised for significant evolution over the next decade.
Technological advancements and evolving social trends are reshaping the way people interact with housing, leading to new opportunities and challenges. Understanding these shifts is crucial for anyone involved in the real estate sector.
Potential Future Trends in the Gen Z Housing Market
Gen Z’s housing preferences are being shaped by a unique set of factors. Their values, priorities, and financial situations are all influencing their decisions about where and how they live. The most notable trends include a preference for urban living, flexible housing options, and a strong emphasis on sustainability.
Impact of Technology on the Gen Z Housing Market
Technology is rapidly changing the way people find, evaluate, and interact with housing. Digital tools are playing an increasingly important role in the entire process, from virtual tours and online property listings to remote payments and maintenance services.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): VR and AR technologies allow potential buyers to virtually experience a property before visiting it. This can lead to more informed decisions and a reduced reliance on physical viewings. For instance, a company like “Virtual Home Tours” is already using VR to showcase properties, allowing Gen Z to experience the space from the comfort of their own homes.
- AI-Powered Property Search: AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to match potential buyers with properties that meet their specific needs and preferences. This personalized approach can significantly improve the efficiency of the home-buying process. An example of this technology is demonstrated in “SmartPropertyFinder” which provides a curated list of properties based on user criteria.
- Smart Home Integration: Smart home technologies are becoming increasingly prevalent. Gen Z are likely to favor properties equipped with smart home features, making the home more efficient, secure, and convenient. This includes features like smart thermostats, lighting systems, and security systems.
Influence of Changing Demographics on the Gen Z Housing Market
The growing Gen Z population, combined with changing demographics and lifestyle preferences, is shaping the demand for different types of housing. The influence of cultural trends, family structures, and the desire for flexible living arrangements is shaping the future of housing for this generation.
- Shifting Family Structures: Gen Z is characterized by a greater emphasis on independent living and delaying marriage and family formation. This shift impacts the demand for smaller apartments, co-living spaces, and flexible lease terms.
- Increased Diversity: Gen Z represents a more diverse generation than previous ones, which is reflected in a broader range of housing needs and preferences. This includes a demand for culturally sensitive housing options, particularly in urban areas.
- Focus on Urban Living: Many Gen Z members are drawn to the amenities and opportunities available in urban areas. This leads to a greater demand for urban housing, with particular interest in walkable neighborhoods, public transportation access, and diverse social and cultural experiences.
Alternative Housing Options and Gen Z’s Housing Decisions
The rise of alternative housing options, such as co-living spaces and tiny homes, is significantly impacting Gen Z’s housing decisions. These options offer unique advantages, particularly in terms of affordability, flexibility, and community.
- Co-living Spaces: Co-living spaces provide a more social and communal living experience. Gen Z members may find this appealing, especially those who value social interaction and shared amenities.
- Tiny Homes: Tiny homes offer a more sustainable and affordable alternative to traditional housing. This option may appeal to Gen Z members who prioritize environmental consciousness and want to reduce their carbon footprint.
Potential Evolution of the Gen Z Housing Market (Timeline)
| Year | Trend |
|---|---|
| 2024-2025 | Increased use of digital tools and platforms for property search, virtual tours, and remote payments. |
| 2026-2028 | Rise of co-living and tiny home communities, reflecting a desire for flexibility and affordability. |
| 2029-2030 | Growing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly housing options. |
| 2031-2033 | Integration of AI-powered tools for personalized property recommendations and automated property management. |
| 2034-2036 | Further development of smart home technology and its integration into new constructions. |
Rental Market and Gen Z

Gen Z, the generation born between the mid-1990s and early 2010s, is navigating a complex and rapidly evolving rental market. The landscape is different from previous generations, shaped by economic factors, technological advancements, and shifting social priorities. This segment delves into the current state of the rental market for Gen Z, highlighting both challenges and opportunities.The rental market presents a unique set of circumstances for Gen Z.
High housing costs and the prevalence of student loan debt often make homeownership less attainable. This economic reality forces Gen Z to lean on rental options for longer periods than previous generations. Furthermore, this generation values flexibility and experiences, often prioritizing location and amenities over the permanence of homeownership.
Gen Z is facing a tough housing market, with prices soaring beyond reach for many. It’s a stark contrast to the resilience and strength demonstrated by Holocaust survivors, like those featured in Gillian Laub’s powerful portraits. Holocaust survivor portraits Gillian Laub offer a glimpse into the human spirit’s ability to endure, a valuable lesson for navigating the challenges of today’s housing market.
Ultimately, Gen Z needs support to find affordable housing options.
Rental Costs for Gen Z
Rental costs have significantly increased across many areas, placing a strain on Gen Z’s financial resources. The rise in rent prices has outpaced wage growth in numerous locations, making it more difficult for young adults to afford suitable housing. The increasing demand for rental properties in urban areas, coupled with a shortage of available units, contributes to this trend.
Gen Z is facing a tough housing market, with prices often out of reach. Navigating the complexities of securing a place to call home is definitely a challenge, but the decision of what to name a new arrival also presents a fascinating cultural discussion. For example, the intricacies of choosing a baby’s name, often involving family heritage and traditions like the selection of a surname, apellido bebe madre padre , can add another layer to the financial and social hurdles of young adulthood.
Ultimately, finding a place to live remains a major hurdle for this generation.
Comparing rental costs for Gen Z with previous generations reveals a clear difference. Gen Z often faces higher rental costs for similar living situations compared to their predecessors, exacerbating financial challenges.
Challenges Faced by Gen Z Renters
Gen Z renters face several hurdles in the current market. Limited financial resources, coupled with high rental costs, often restrict their housing options. Finding suitable, affordable housing that aligns with their lifestyle preferences and needs can be difficult. Navigating the complex processes of lease agreements, security deposits, and landlord communication adds to the challenges. Additionally, the prevalence of predatory or unethical rental practices can negatively impact Gen Z renters.
Opportunities in the Rental Market for Gen Z
Despite the challenges, opportunities exist within the rental market for Gen Z. The rise of co-living spaces, shared apartments, and flexible lease terms caters to the generation’s desire for community and adaptability. These models allow Gen Z to share costs and experiences while maintaining their autonomy. The increasing availability of online rental platforms and digital tools provides a more streamlined process for finding and securing rental accommodations.
Innovative Rental Models Appealing to Gen Z
Several innovative rental models are attracting Gen Z’s attention. These include co-living spaces, which offer social interaction and shared amenities in exchange for a lower cost per person. Short-term leases, flexible contracts, and furnished apartments are also gaining popularity. These models address the need for adaptability and ease of transition that Gen Z often prioritizes. Further, the adoption of technology in rental management, allowing for online payments and digital communication, enhances the overall experience.
“The Gen Z rental market is characterized by a strong preference for flexibility, community, and affordability. Innovations in rental models, like co-living and shared housing, are shaping the future of rental living.”
Gen Z is facing a tough housing market, with prices seemingly out of reach for many. Economic factors, like the current US economy’s growth trajectory and the ever-present geopolitical threats from North Korea, are significantly impacting the overall economic climate. This, in turn, is making it even harder for young adults to enter the housing market, and the ripple effect from us economy growth north korea threats is undoubtedly influencing the affordability of homes for this generation.
Ultimately, finding affordable housing options remains a major challenge for Gen Z.
Key Characteristics of the Gen Z Rental Market
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Flexibility | Gen Z values adaptable lease terms and options for short-term stays. |
| Community | Shared living spaces and co-living models appeal to Gen Z’s desire for social interaction. |
| Affordability | High rental costs are a major concern, influencing their choices of location and housing type. |
| Technology | Digital platforms and online tools play a significant role in their rental search and management processes. |
| Social Responsibility | Gen Z often considers eco-friendly options and socially conscious landlords when choosing a rental. |
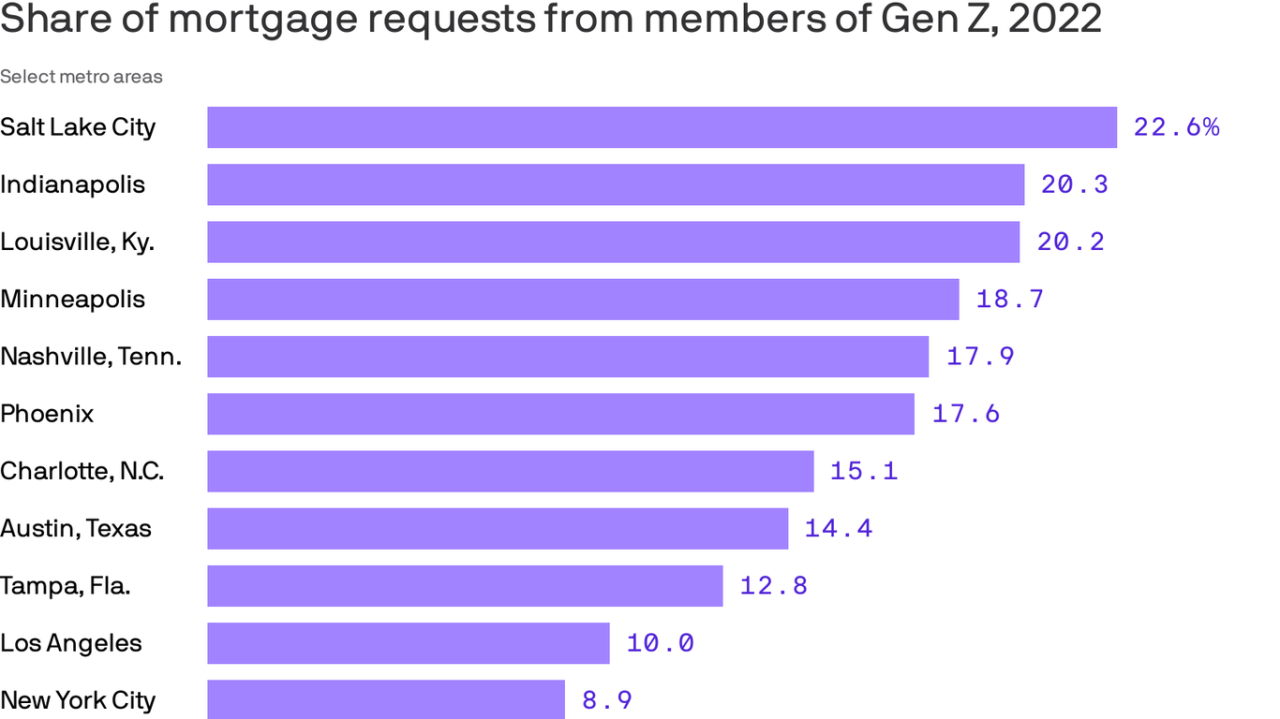
Geographic Variations
Gen Z’s approach to housing differs significantly across the US, reflecting regional economic disparities, cultural nuances, and local policies. Affordability varies dramatically, with some areas offering attractive opportunities while others present significant challenges. Understanding these regional variations is crucial for Gen Z navigating the complex housing landscape.
Regional Affordability Differences
Regional differences in housing affordability for Gen Z are stark. Coastal cities often exhibit higher housing costs, making homeownership a distant dream for many. Conversely, some mid-sized cities and rural areas offer more affordable options. This disparity in costs is a major factor influencing Gen Z’s housing choices and migration patterns. For example, the rising cost of living in California has led many young adults to seek opportunities in neighboring states with more accessible housing.
Housing Preferences Across Cities and States
Gen Z’s housing preferences vary by location. Urban dwellers often prioritize walkability, access to public transportation, and vibrant cultural experiences. Suburban residents may emphasize larger homes, private yards, and a quieter environment. Rural areas typically attract those seeking a slower pace of life, access to nature, and potentially more affordable land.
Unique Challenges and Opportunities
Specific geographic areas present unique challenges and opportunities for Gen Z homebuyers. Areas with strong job markets and affordable housing offer attractive entry points for homeownership. Conversely, regions facing economic downturns or high housing costs present significant barriers to homeownership and create different housing needs. For instance, the tech boom in the San Francisco Bay Area has made homeownership exceptionally difficult for young professionals, while other regions offer more attainable options.
Influence of Local Policies and Regulations
Local policies and regulations play a crucial role in shaping the Gen Z housing market. Zoning laws, building codes, and housing regulations significantly influence affordability and housing options. For example, stricter zoning regulations in some areas may limit the development of affordable housing options. Conversely, policies aimed at encouraging mixed-use development or incentivizing affordable housing can improve access for Gen Z.
Geographic Variations Table, Housing prices gen z market
| Region | Affordability | Unique Trends |
|---|---|---|
| Coastal Cities (e.g., San Francisco, New York) | Very High | High demand, limited supply, strong emphasis on urban living, reliance on rental markets. |
| Mid-Sized Cities (e.g., Austin, Denver) | Moderate to High | Growing job markets, increasing housing costs, potential for homeownership, diverse housing options. |
| Rural Areas (e.g., rural areas of the Midwest, Southeast) | Generally Low | Attractive to those seeking a slower pace of life, opportunities for affordable land, potential for agricultural-based careers. |
Final Review
In conclusion, the Gen Z housing market is a dynamic mix of challenges and opportunities. While high prices and financing difficulties pose significant hurdles, Gen Z’s preferences for specific amenities and locations, coupled with innovative rental models, offer potential solutions. The future of this market will likely be shaped by economic factors, technological advancements, and changing demographics. Understanding these nuances is crucial for navigating this complex market.
User Queries
What are the typical housing preferences of Gen Z?
Gen Z often prioritizes location, sustainability, and amenities. Size is sometimes less important, with a preference for more functional and adaptable living spaces. They often value modern technology integration and eco-friendly features in their homes.
How does student loan debt impact Gen Z’s ability to buy a home?
Student loan debt significantly hinders Gen Z’s ability to save for a down payment and qualify for mortgages. The high cost of education directly impacts their financial capacity to enter the housing market.
What are some innovative rental models appealing to Gen Z?
Co-living spaces, shared ownership models, and flexible lease agreements are examples of rental models gaining traction among Gen Z. These models often cater to the desire for community and affordability.
How are rising construction costs affecting Gen Z’s housing affordability?
Rising construction costs directly increase housing prices, making it harder for Gen Z to afford homes or even rent. This pressure is compounded by the limited inventory of available properties.

