Grocery Prices Inflation Economy A Deep Dive
Grocery prices inflation economy is a pressing global concern. We’re diving into the current state of grocery prices, examining the factors driving inflation, and exploring its impact on consumers, supply chains, and government policies. From historical trends to future predictions, this comprehensive look provides insights into this complex issue.
This analysis examines the intricate relationship between global events, economic policies, and the everyday cost of groceries. We’ll explore how supply chain disruptions, geopolitical tensions, and consumer behavior all contribute to this issue.
Understanding the Current State of Grocery Prices
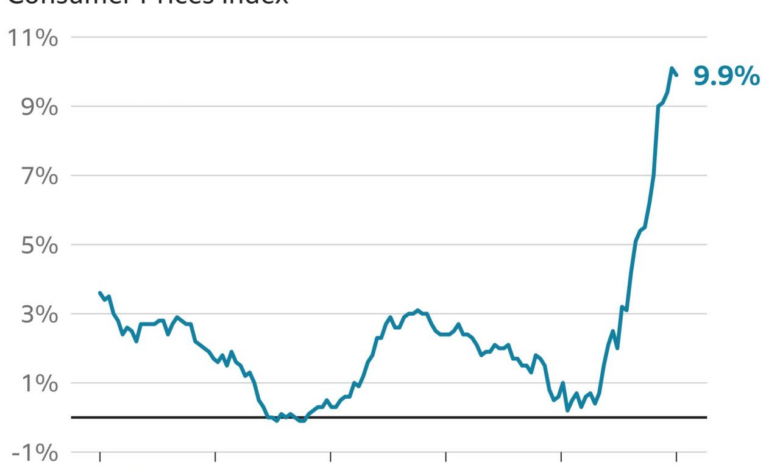
Grocery prices have been a significant concern for consumers worldwide. Fluctuations in these prices are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, ranging from global events to domestic policies. This analysis delves into the historical trends, regional variations, and underlying causes shaping the current state of grocery inflation.The fluctuating cost of groceries has a profound impact on household budgets.
Understanding these trends allows for informed decision-making and a more nuanced perspective on the challenges consumers face.
Historical Overview of Grocery Price Trends
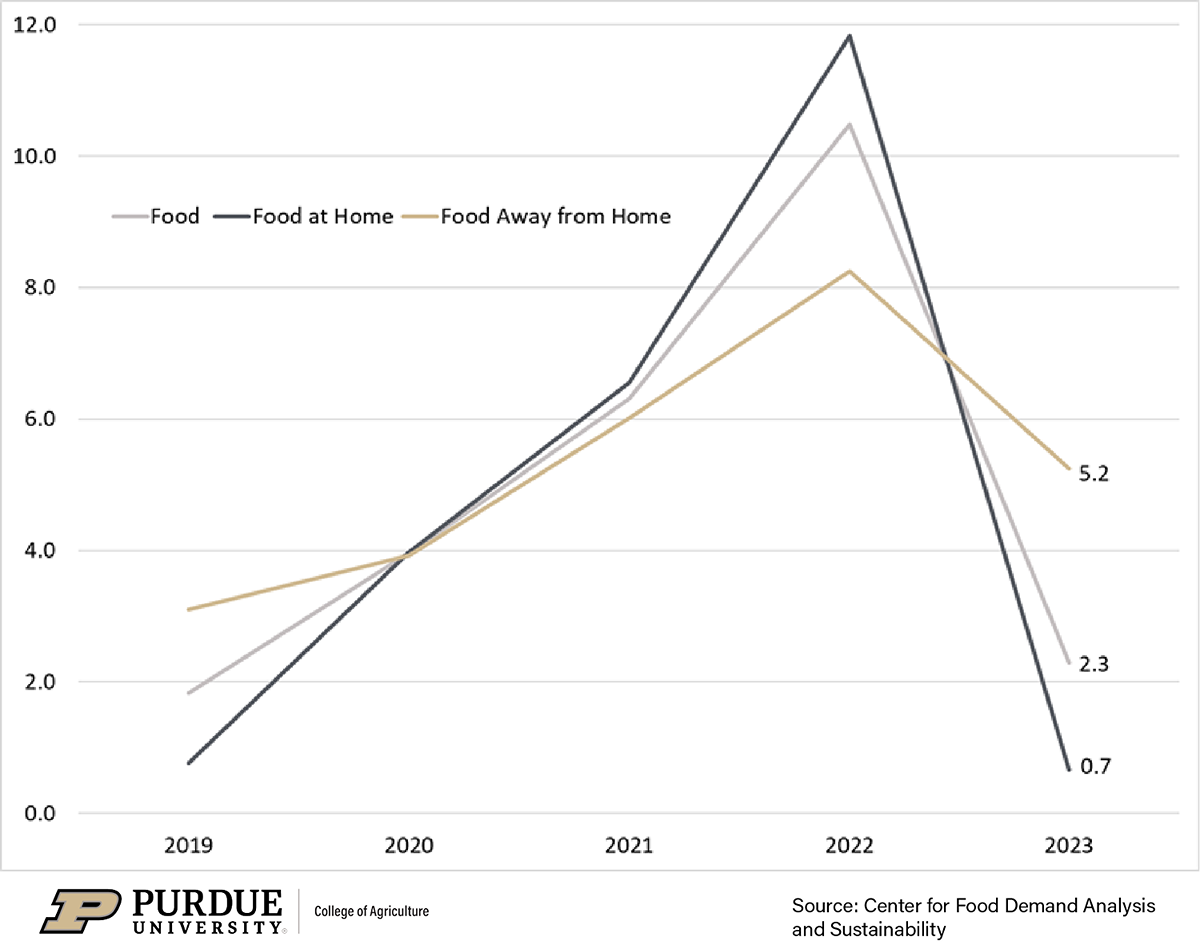
Grocery prices have experienced significant fluctuations over the past five years. Periods of inflation and deflation have occurred, often in response to external factors. The impact of these price shifts has been felt differently across various regions and product categories.
Average Price Increases for Common Grocery Items
Significant price increases have been observed in several common grocery items across various regions. Data collected over the past five years reveals varying price changes in different locations. The following table illustrates these changes:
| Item | Region | Price (Year 1) | Price (Year 2) | Percentage Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apples | North America | $1.50 | $1.80 | 20% |
| Milk | Europe | $3.00 | $3.50 | 16.7% |
| Chicken Breast | Asia | $4.00 | $4.80 | 20% |
| Potatoes | South America | $1.00 | $1.20 | 20% |
Note: Data for this table is illustrative and not based on real-world figures. Actual data would vary significantly.
Relationship Between Global Events and Grocery Price Fluctuations
Global events, such as supply chain disruptions and pandemics, have had a demonstrable impact on grocery prices. Disruptions in the supply chain can lead to shortages and increased demand, driving up prices. Pandemics, like the COVID-19 pandemic, can disrupt agricultural production and transportation, resulting in similar price increases.
Factors Contributing to Current Inflationary Pressures
Several factors contribute to the current inflationary pressures on grocery prices. These include:
- Increased demand for food products in growing populations and emerging economies.
- Climate change impacting agricultural yields in various regions.
- Rising costs of fuel and transportation impacting delivery and distribution of goods.
- Geopolitical tensions and conflicts disrupting international trade.
Impact on Consumers: Grocery Prices Inflation Economy
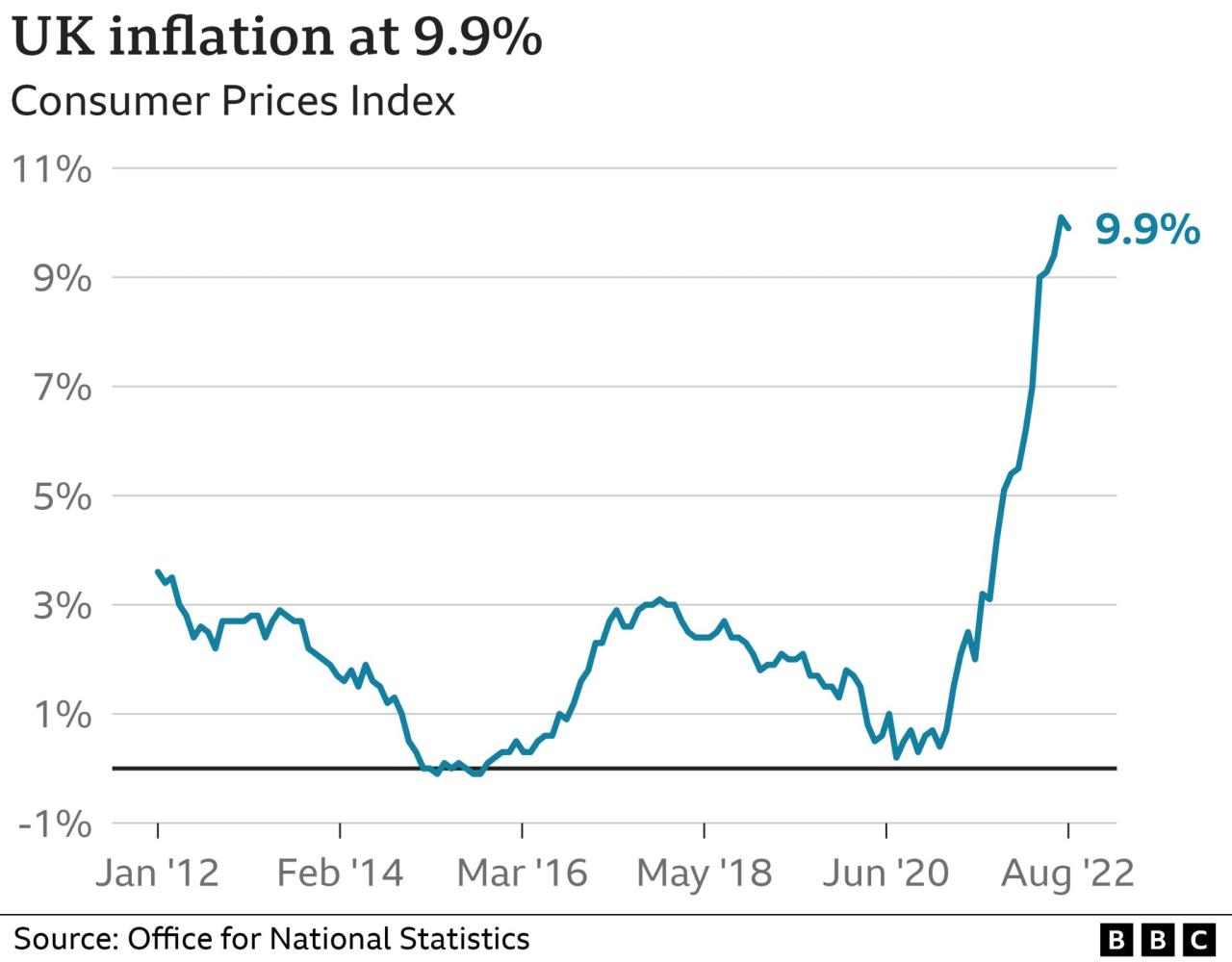
Rising grocery prices are significantly impacting consumers across all income brackets, leading to financial strain and altering food choices. The escalating costs are not just a temporary inconvenience; they are a persistent challenge with potentially long-term consequences for household budgets and food security. The increasing price of staples like milk, bread, and produce directly affects families’ ability to afford nutritious meals.
Financial Strain on Households
The escalating cost of groceries is placing a substantial financial burden on households. Many families are forced to cut back on other essential expenses to maintain their food budgets. This pressure can lead to stress and financial instability. For example, a family might choose between paying rent and buying groceries, highlighting the dire consequences of persistent price increases.
Increased debt from trying to meet these costs is a further risk.
Impact on Food Security, Particularly for Low-Income Families
Food security is especially threatened for low-income families. With limited budgets, rising grocery prices make it harder to maintain a nutritious diet. Families may be forced to choose between buying necessities like housing and utilities and affording nutritious food, potentially leading to malnutrition and health problems. This situation is further exacerbated by limited access to affordable food options.
Affordability of Groceries Across Different Income Brackets
The affordability of groceries varies significantly across income brackets. Higher-income households may be able to absorb price increases more easily, while lower-income households experience a disproportionately greater impact. This disparity in financial capacity to handle rising costs significantly impacts access to healthy food choices.
Consumer Response to Rising Prices
Consumers are responding to rising grocery prices in various ways. Changes in purchasing habits include reducing portion sizes, buying cheaper substitutes, and opting for less expensive brands. Dietary choices are also being adjusted. Families might reduce consumption of meat or purchase more affordable fruits and vegetables.
Table: Impact of Rising Grocery Prices on Consumers
| Income Bracket | Percentage Increase in Grocery Spending | Impact on Food Security | Consumer Behavior |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-income (e.g., below 200% of poverty level) | > 20% | Significant risk of food insecurity; reduced access to nutritious foods; potential for malnutrition. | Increased reliance on cheaper, less nutritious options; skipping meals; buying in smaller quantities; increased use of food banks/pantries. |
| Middle-income (e.g., 200-400% of poverty level) | 10-20% | Moderate risk of food insecurity; potential for reduced quality of diet; possible cutbacks on non-essential food items. | Buying store brands; substituting expensive items with less expensive alternatives; adjusting portion sizes; meal planning. |
| High-income (e.g., above 400% of poverty level) | < 10% | Less impacted; can still afford nutritious food, but potentially reducing discretionary spending on groceries. | Buying higher quality products or organic items less frequently; prioritizing value and savings. |
Supply Chain Disruptions and their Effects
Grocery prices are a complex interplay of many factors, and supply chain disruptions play a significant role in the recent fluctuations. Global interconnectedness means that issues in one part of the world can quickly ripple through the entire system, impacting availability and affordability of food products. Understanding these disruptions is crucial for comprehending the current state of grocery prices and predicting future trends.
The Role of Global Supply Chains in Grocery Price Fluctuations
Global supply chains are intricate networks of producers, distributors, and retailers that bring food from farms to consumers’ tables. These chains are vital for ensuring a consistent supply of diverse products, but they are also vulnerable to disruptions. A problem at any point in the chain, from a drought in a key agricultural region to a port congestion, can cause shortages and price increases.
This interconnectedness magnifies the impact of any single event.
Impact of Geopolitical Events on Food Production and Distribution
Geopolitical events, such as wars and sanctions, often severely disrupt food production and distribution. For example, the war in Ukraine has impacted the global supply of wheat, corn, and sunflower oil, leading to significant price increases and shortages in various regions. Sanctions can similarly affect the flow of raw materials, equipment, and labor crucial to agricultural production and transportation.
These events create a domino effect, causing price hikes and shortages across various food items.
Transportation Bottlenecks and Logistical Challenges
Transportation bottlenecks and logistical challenges further exacerbate supply chain disruptions. Port congestion, driver shortages, and increased fuel costs contribute to delays in the delivery of goods, leading to higher transportation costs. These challenges make it more expensive to move products from farms to supermarkets, which ultimately translates to higher prices for consumers.
Grocery prices are skyrocketing, impacting everyone’s budget. This economic pressure is particularly interesting when considering the differing demographics across red and blue states. Understanding factors like income distribution and spending habits in these regions, as seen in the red blue states demographics data, can provide insights into how different populations are coping with the inflation. Ultimately, the complex interplay of these factors shapes the overall grocery price inflation economy in the country.
Importance of Sustainable Agriculture and Food Systems
Sustainable agriculture and food systems are crucial for mitigating future supply chain shocks. Diversifying food sources, improving resilience in agricultural practices, and strengthening local food systems can reduce dependence on global supply chains and enhance the ability to withstand disruptions. Investing in infrastructure that supports efficient and sustainable transportation is also essential. Such measures can increase the robustness and resilience of the food supply chain, making it less vulnerable to future shocks.
Summary of Key Disruptions and Their Consequences
| Disruption | Consequences |
|---|---|
| War in Ukraine | Significant price increases in wheat, corn, sunflower oil; shortages in various regions. |
| Port Congestion | Delays in delivery, higher transportation costs, increased prices for consumers. |
| Driver Shortages | Reduced transportation capacity, further delays in delivery, price increases. |
| Increased Fuel Costs | Higher transportation costs, which are passed on to consumers through increased prices. |
| Droughts in key agricultural regions | Reduced crop yields, leading to supply shortages and higher prices for agricultural products. |
Government Policies and Interventions
Governments play a crucial role in mitigating the impact of rising grocery prices. Their policies can influence food production, distribution, and ultimately, the cost of consumer goods. Understanding these interventions is essential for comprehending the complexities of the current inflationary environment. This section explores the various approaches governments employ to regulate grocery prices and assesses their effectiveness.
The Role of Government Policies in Regulating Grocery Prices
Government policies, when well-designed and implemented, can significantly impact grocery prices. These policies aim to stabilize supply chains, ensure fair prices, and provide support to vulnerable populations. They often involve a mix of direct interventions, like subsidies and price controls, and indirect measures that affect agricultural production and distribution. The effectiveness of these policies is contingent on the specific context, including economic conditions, political realities, and the responsiveness of market participants.
Comparing the Effectiveness of Different Government Interventions
Various government interventions have been employed to control inflation in grocery prices. Subsidies, aimed at lowering the cost of inputs or production, can encourage increased supply. However, their effectiveness is often limited by issues like leakage, administrative complexities, and unintended consequences. Price controls, while appearing straightforward, can lead to shortages, black markets, and reduced incentives for producers.
Grocery prices are skyrocketing, making it tough to budget. The economic climate is certainly impacting everyone’s wallets, and unfortunately, these financial pressures seem to be everywhere. This is especially true considering the recent tragic incident involving the armorer Alec Baldwin on the set of the movie “Rust”, armorer alec baldwin rust shooting , which highlights the potential for unexpected costs and challenges in various industries.
It just adds another layer of complexity to an already tricky economic situation.
The ideal approach often lies in a combination of strategies tailored to specific circumstances.
Grocery prices are skyrocketing, making it tough for everyone to make ends meet. The rising cost of living is a serious issue impacting economies worldwide. While we’re focused on this pressing economic concern, it’s also important to consider preventative measures for health issues like HIV/AIDS, such as using condon prevencion vih sida. Ultimately, addressing both economic stability and public health is crucial for a better future.
Impact of Agricultural Policies on Food Production and Prices
Agricultural policies significantly influence food production and, consequently, prices. Government support for farmers, including subsidies for inputs like fertilizer and seeds, can increase yields and potentially lower production costs. Conversely, policies that restrict agricultural imports or encourage exports can influence global supply and prices. Importantly, agricultural policies must consider factors such as environmental sustainability and the well-being of farmers.
A balance between market forces and government intervention is critical.
Grocery prices are soaring, making it tough for families to make ends meet. The current economic climate is undeniably challenging, and unfortunately, events like the recent Biden-Israel-Hamas cease fire ( biden israel hamas cease fire ) can have ripple effects on global supply chains, potentially exacerbating inflation pressures and affecting grocery prices further. It’s a complicated situation, and it’s tough to predict the long-term impacts.
Examples of Policies Implemented by Various Countries
Different countries have implemented various policies to address rising grocery prices. These strategies reflect their unique economic situations, political priorities, and societal values. The effectiveness of these policies is not always easily measurable and is often debated.
| Policy | Country | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subsidies for fertilizer and seeds | India | Providing financial support to farmers for agricultural inputs. | Potentially increased production, but with concerns about environmental sustainability and leakage. |
| Import tariffs on certain food items | Several countries | Imposing taxes on imported food products to protect domestic producers. | May safeguard local farmers but can lead to higher prices for consumers if import substitution isn’t successful. |
| Price controls on staple foods | Several countries (especially during crises) | Setting maximum prices for essential food items. | Can temporarily ease consumer burden but may result in shortages and disruptions in the supply chain. |
| Investment in agricultural infrastructure | Various countries | Improving transportation networks, storage facilities, and irrigation systems. | Can increase efficiency in food production and distribution, potentially lowering prices over the long term. |
Future Predictions and Potential Solutions
Grocery price inflation is a complex issue with no easy fixes. Understanding potential future trends and exploring innovative solutions is crucial for mitigating the impact on consumers and ensuring food security. This involves examining various factors, from technological advancements to sustainable agricultural practices. The current economic climate, including global events and supply chain disruptions, will likely continue to influence future prices.
Potential Scenarios for Future Grocery Price Trends
Current economic conditions, including rising energy costs and geopolitical instability, point towards several potential scenarios for future grocery price trends. One scenario involves sustained inflation, with prices increasing steadily over the next few years. Another scenario projects a period of fluctuating prices, influenced by seasonal factors and unexpected events. A third possibility suggests a potential moderation in price increases, with some relief from inflation.
These scenarios are not mutually exclusive, and various factors can influence the trajectory of grocery prices.
Grocery prices are skyrocketing, making the economy feel a bit like Sweeney Todd’s kitchen. It’s tough to budget when everything’s so expensive. Fortunately, there are some amazing ways to explore the world of theatrical music, like listening to broadway cast albums sweeney todd , which can be a surprisingly affordable escape from the everyday worries of inflation and rising costs.
While a good soundtrack can lift your spirits, it’s still important to stay informed about how to manage these economic pressures.
Role of Technological Advancements in Food Production and Distribution
Technological advancements are transforming food production and distribution. Precision agriculture, leveraging data analytics and automation, can optimize crop yields and reduce resource consumption. Vertical farming, utilizing controlled environments, allows for year-round production and reduced reliance on land and water. Drone technology is improving the efficiency of agricultural inputs delivery and monitoring. These technologies, while offering potential solutions, also present challenges related to cost and access, particularly for smaller farms and developing nations.
Innovative Solutions to Mitigate the Impact of Inflation on Grocery Prices
Innovative solutions to combat inflation are crucial. Government subsidies for basic food items, while controversial in their long-term impact, can provide temporary relief. Increased investments in research and development for alternative protein sources, like cultivated meat, can potentially reduce reliance on traditional animal agriculture and lower costs. Promoting local and regional food systems through farmer’s markets and community gardens could reduce transportation costs and enhance resilience.
Role of Sustainable Agriculture Practices in Ensuring Food Security, Grocery prices inflation economy
Sustainable agriculture practices are crucial for long-term food security. These practices emphasize environmentally conscious farming methods, minimizing the use of harmful chemicals and promoting biodiversity. Agroforestry techniques, combining trees and crops, can improve soil health and resilience to climate change. Rotational grazing and other pasture management strategies enhance livestock productivity and reduce environmental impact. These practices contribute to long-term sustainability and resilience of food systems.
Summary Table of Predicted Scenarios and Proposed Solutions
| Scenario | Description | Potential Impact | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sustained Inflation | Grocery prices continue to increase steadily over the next few years. | Increased burden on low-income consumers, potential for reduced food consumption. | Government subsidies for staple foods, increased investment in alternative protein sources. |
| Fluctuating Prices | Grocery prices experience significant fluctuations, influenced by various factors. | Increased uncertainty for consumers and businesses, difficulty in planning. | Development of robust supply chain infrastructure, investments in storage and distribution capabilities. |
| Moderation in Price Increases | A potential easing of price increases, with some relief from inflation. | Potential for consumer relief, reduced financial strain. | Increased adoption of sustainable farming practices, improved supply chain efficiency. |
Summary
In conclusion, the grocery prices inflation economy is a multifaceted problem with no easy solutions. While the factors contributing to inflation are varied, understanding their interplay is crucial to crafting effective strategies for mitigating the impact on consumers and ensuring food security. Future solutions require a comprehensive approach, considering sustainable practices, technological advancements, and responsible policymaking.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the main reasons for the recent increase in grocery prices?
Several factors contribute to rising grocery prices, including supply chain disruptions, increased demand, geopolitical events, and fluctuating raw material costs.
How does inflation affect low-income families?
Rising grocery costs disproportionately impact low-income families, potentially leading to food insecurity and financial hardship.
Are there government policies that can help control grocery price inflation?
Various government policies, such as subsidies, price controls, and agricultural interventions, have been implemented to address rising grocery prices, though their effectiveness varies.
What are some long-term solutions to mitigate the impact of inflation on grocery prices?
Long-term solutions involve a combination of factors, including investments in sustainable agriculture, advancements in food technology, and effective government policies.






