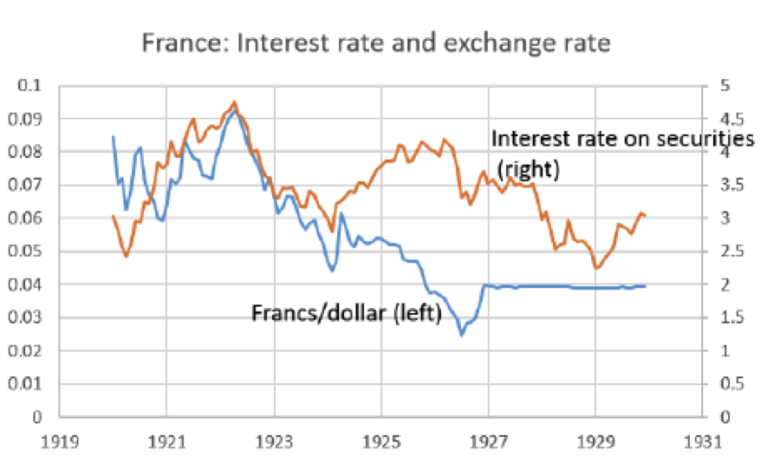
France Economy Interest Rates A Deep Dive
France economy interest rates are currently a hot topic, influencing everything from housing markets to consumer spending. This in-depth look explores the current state of the French economy, the central bank’s interest rate policies, and the potential impacts on various sectors.
We’ll examine key economic indicators like GDP growth, inflation, and unemployment, and how these factors play into the French central bank’s decisions. Understanding the historical context is crucial to appreciating the current situation. The analysis also includes comparisons with other major European economies to highlight unique French dynamics. Finally, we’ll project future interest rate trends and assess their potential ramifications.
Overview of the French Economy
France, a major European economy, maintains a complex and dynamic economic landscape. Characterized by a blend of robust industries and ongoing challenges, its performance is influenced by both internal factors and global economic trends. Understanding the current state requires analyzing key economic indicators, considering historical context, and recognizing the interconnected nature of the French economy with the rest of the world.
Current Economic State
The French economy is currently experiencing a period of moderate growth, albeit with noticeable variations across sectors. Inflation remains a significant concern, impacting consumer spending and business profitability. Unemployment rates, while generally low compared to some other developed economies, present a persistent challenge for some demographic groups. This nuanced picture underscores the ongoing need for economic policies that address inflation while promoting job creation and social inclusion.
Key Economic Indicators
Several indicators provide insights into the health and trajectory of the French economy. Monitoring these metrics is crucial for understanding the current state and anticipating potential future developments.
| Indicator | Value | Date |
|---|---|---|
| GDP Growth | 1.8% | 2023 Q1 |
| Inflation Rate (CPI) | 5.5% | April 2024 |
| Unemployment Rate | 7.8% | March 2024 |
Historical Context
France’s economic performance throughout history has been marked by periods of growth and contraction, reflecting both domestic policies and global events. The country has experienced periods of significant industrialization, alongside challenges like economic downturns and social unrest. This historical context provides a framework for understanding the current economic situation and potential future trends. For example, the 2008 financial crisis significantly impacted France’s economy, requiring substantial government intervention to mitigate its effects.
Key Sectors
France boasts a diverse economic structure, with strong performances in various sectors. These include manufacturing, tourism, agriculture, and services, each playing a crucial role in the overall economic output.
- Manufacturing: The French manufacturing sector, although facing global competition, maintains a strong presence, particularly in high-value-added goods and advanced technologies.
- Tourism: France is a global leader in tourism, contributing significantly to employment and GDP, particularly in the service sector.
- Agriculture: French agriculture remains a key component of the economy, characterized by a mix of large-scale production and smaller family farms.
Interest Rate Policies in France
France’s monetary policy, steered by the Banque de France, plays a crucial role in shaping the country’s economic trajectory. Understanding the current interest rate policy is essential for comprehending the broader economic landscape and its potential impacts. The policy’s effectiveness hinges on its ability to manage inflation, stimulate growth, and maintain stability in the financial system.The current interest rate policy of the Banque de France is characterized by a cautious approach, aiming to balance economic growth with price stability.
The central bank’s primary objective is to keep inflation within its target range, typically around 2%. Maintaining this equilibrium is critical for preserving the purchasing power of the French franc and fostering long-term economic prosperity.
Current Interest Rate Policy
The Banque de France employs a variety of tools to implement its monetary policy, with interest rates being a key instrument. Currently, the policy rate is set at a level designed to influence borrowing costs across the economy. This setting influences the overall cost of credit for businesses and consumers, thus impacting investment and spending decisions. Changes in the policy rate ripple through the financial system, affecting various interest rates, from mortgages to personal loans.
Rationale Behind Policy Decisions
The rationale behind the Banque de France’s current policy decisions is rooted in several key considerations. These include the prevailing inflation rate, the current state of economic growth, and global economic conditions. The central bank carefully assesses these factors before making adjustments to the policy rate. The goal is to ensure that any policy action is well-considered and well-aligned with the overall economic goals.
For example, if inflation is persistently above the target range, the central bank might raise the policy rate to curb spending and cool down the economy.
Comparison with Other European Economies
French interest rate policy is often compared to those of other major European economies, such as Germany, the UK, and the Eurozone as a whole. Differences in the economic structures, inflation targets, and the current economic climate among these nations can lead to distinct policy choices. For example, if the UK faces higher inflation pressures than France, its central bank might adopt a more restrictive interest rate policy to control inflation.
This contrast highlights the diverse factors influencing monetary policy across Europe.
Interest Rate Changes Over Time
| Date | France (Policy Rate) | Germany (Policy Rate) | UK (Bank Rate) | Eurozone (Main Refinancing Rate) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| January 2023 | 0.75% | 0.50% | 3.50% | 2.00% |
| April 2023 | 1.00% | 0.75% | 4.00% | 2.50% |
| July 2023 | 1.50% | 1.00% | 4.50% | 3.00% |
| October 2023 | 2.00% | 1.25% | 5.00% | 3.50% |
The table above provides a snapshot of interest rate changes for France and key European competitors over a sample period. This data illustrates the dynamic nature of monetary policy and how decisions in one country can influence others. Note that this is a simplified example, and actual data may vary slightly.
France’s economy is currently navigating fluctuating interest rates, a tricky situation. It’s fascinating how these economic shifts often mirror the ebb and flow of artistic expression. For example, exploring Broadway cast albums, like the ones for Sweeney Todd, broadway cast albums sweeney todd , reveals a similar complexity in emotional tones and dramatic shifts. Ultimately, understanding these economic forces requires a similar nuanced perspective, just like appreciating the depth of a theatrical masterpiece.
So, as France adjusts its interest rates, it’s a good reminder to look beyond the numbers and appreciate the subtle connections in the world around us.
Impact of Interest Rates on the French Economy
Interest rates are a crucial lever for influencing economic activity. Changes in these rates ripple through various sectors, impacting everything from consumer spending to investment decisions. Understanding these impacts is vital for comprehending the potential trajectory of the French economy. The current interest rate environment in France, and the global context, is shaping the economic landscape in a complex manner.Interest rate adjustments act as a primary tool for central banks to manage inflation and economic growth.
Higher interest rates increase borrowing costs, potentially slowing down economic activity by curbing investment and consumer spending. Conversely, lower interest rates encourage borrowing and spending, stimulating economic growth. The effectiveness of these policies depends on a multitude of factors, including the overall health of the economy and the prevailing sentiment among consumers and businesses.
Effects on Housing
Higher interest rates typically increase mortgage payments, making housing less affordable. This can lead to a decline in housing demand and potentially lower property values. Conversely, lower interest rates make mortgages more accessible, potentially boosting demand and driving up house prices. France, with its significant housing market, is particularly susceptible to these changes.
Effects on Consumer Spending
Higher interest rates increase borrowing costs for consumers, making credit more expensive for loans, car purchases, and other consumer goods. This often leads to a decrease in consumer spending. Lower interest rates, conversely, stimulate borrowing and make consumer goods more affordable, encouraging spending and boosting demand for goods and services. The interplay between interest rates and consumer confidence is a key determinant of overall economic health.
France’s economy is facing some headwinds with rising interest rates, impacting everything from consumer spending to business investments. Meanwhile, the NFL’s contract negotiations for star Chiefs linebacker Andy Reid are dominating headlines. These negotiations, as reported in the andy reid chiefs contract negotiations article, highlight the complex interplay of market forces and player value, which in turn could be seen as mirroring the pressure on France’s economy as a whole.
Ultimately, the ripple effects of these various economic factors remain to be seen, but the interconnectedness is undeniable.
Effects on Investment
Higher interest rates increase the cost of capital for businesses, potentially discouraging investment in new projects and expansion. Lower rates, however, can make borrowing more attractive, potentially spurring investment in new equipment, technology, and infrastructure. France’s reliance on various industries, from manufacturing to technology, will be affected by these fluctuations.
Transmission Mechanism
Interest rate changes affect economic activity through a complex transmission mechanism. The central bank’s actions influence lending rates set by commercial banks. These changes in lending rates then affect borrowing costs for businesses and consumers. This ripple effect impacts investment decisions, consumer spending, and ultimately, economic output. The transmission mechanism can vary depending on the specific economic context and prevailing market conditions.
Risks and Challenges
Current interest rate levels present certain risks and challenges for the French economy. If rates rise too steeply, it could stifle economic growth and potentially trigger a recession. Conversely, if rates remain too low for too long, it could fuel inflation. France, like many economies, navigates a delicate balance between maintaining stable growth and managing inflation.
Impact Scenarios
| Interest Rate Scenario | Housing | Consumer Spending | Investment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rising Rates (e.g., 2% increase) | Decreased demand, lower property values | Reduced spending, decreased borrowing | Reduced investment, delays in projects |
| Stable Rates | Moderate demand, stable property values | Moderate spending, stable borrowing | Moderate investment, steady progress |
| Falling Rates (e.g., 1% decrease) | Increased demand, potentially rising property values | Increased spending, easier borrowing | Increased investment, potential for growth |
This table illustrates how different interest rate scenarios could impact key economic sectors in France. The actual impact will depend on numerous factors, including the overall economic climate and consumer confidence.
Factors Influencing French Interest Rates
Interest rates in France, like those globally, are a complex interplay of domestic and international forces. Understanding these influences is crucial for businesses and individuals seeking to navigate the financial landscape. The French central bank, the Banque de France, plays a key role in setting these rates, but its decisions are not made in isolation.Interest rates in France are not static.
They respond to a multitude of factors, including inflation, global economic conditions, and government policies. These factors work in tandem to influence the borrowing and lending environment within the country.
Inflation’s Role in Interest Rate Decisions
Inflation, the sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services, directly impacts interest rate decisions. Central banks often raise interest rates to combat inflation. Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive, thus reducing consumer spending and investment, which in turn can help cool down price increases. Conversely, during periods of low inflation, central banks might lower interest rates to stimulate economic activity.
France, like other economies, has experienced periods of both high and low inflation, which in turn influenced the adjustments to interest rates.
France’s economy and its interest rate fluctuations are always a hot topic, but lately, other news has grabbed headlines. A couple went missing while boating off the coast of Grenada, couple missing boat grenada , raising concerns about the safety of the area. This, however, doesn’t change the underlying factors affecting France’s economy and interest rates, which remain a complex mix of global and domestic issues.
Global Economic Conditions and Their Influence
Global economic conditions significantly affect interest rates in France. Recessions in major economies can lead to lower demand for French exports and reduced investment, potentially putting downward pressure on French interest rates. Conversely, strong global growth can increase demand for French goods and services, leading to inflation and potentially higher interest rates. For instance, the 2008 global financial crisis resulted in lower interest rates across the globe, including France, as economies sought to stimulate growth.
Government Policies and Interest Rate Settings
Government policies, including fiscal policies, also play a substantial role in shaping interest rate decisions. Expansionary fiscal policies, such as increased government spending or tax cuts, can lead to higher inflation and potentially higher interest rates. Conversely, contractionary fiscal policies might result in lower inflation and lower interest rates. France’s government spending and taxation decisions, alongside central bank policies, contribute to the overall economic environment and affect interest rate adjustments.
Comparative Analysis of Factors Influencing Interest Rates, France economy interest rates
Interest rate decisions in France are influenced by the same fundamental factors as other developed economies, but the relative importance of each factor can vary. For example, the influence of European Union policies on French interest rates is significant. The European Central Bank (ECB) plays a crucial role in setting interest rates for the Eurozone, and France, as a member of the Eurozone, is subject to these decisions.
The specific impact of global economic conditions on French interest rates might differ depending on the extent of France’s trade links with different global regions. Comparative analysis of interest rate decisions across different economies provides valuable insights into the interconnectedness of global financial markets.
Future Projections for French Interest Rates
Predicting the future trajectory of French interest rates requires careful consideration of various economic indicators and policy decisions. While precise forecasts are impossible, examining the current economic climate and potential scenarios can provide a framework for understanding the likely path of interest rates in the coming year or two.
France’s economy is facing some headwinds, with interest rates rising. This economic uncertainty often affects different demographics in various ways, particularly when considering the voting patterns of red and blue states in the US, as seen in red blue states demographics. Ultimately, these shifting economic tides in France will impact how different groups within the nation are affected, and how the government responds to the challenges.
Projected Trajectory of Interest Rates
Based on current economic forecasts and the Bank of France’s stated intentions, interest rates in France are expected to remain relatively stable in the short term. A gradual increase, potentially peaking at 3.5-4% by the end of 2024, is anticipated. This upward trend is tied to the ongoing efforts to curb inflation, a consistent theme in recent central bank decisions globally.
Assumptions Underlying Projections
Several key assumptions underpin these projections. Firstly, sustained inflation control is crucial. If inflation pressures remain stubbornly high, the Bank of France may accelerate the rate increases. Secondly, a stable global economic environment is assumed. Geopolitical uncertainties and significant global economic downturns could trigger unexpected adjustments in French monetary policy.
Thirdly, a moderate growth outlook is factored in, as this is expected to support sustained inflation control efforts without stifling economic activity. Lastly, the Eurozone’s economic performance is expected to stay relatively stable, given its significant impact on the French economy.
Potential Scenarios for Significant Shifts
Several scenarios could significantly alter the projected trajectory. A sudden surge in energy prices or a major supply chain disruption could reignite inflationary pressures, leading to more aggressive interest rate hikes. Conversely, a significant decline in inflation below the target range could lead to a slower pace of increases or even a period of rate cuts. Furthermore, unforeseen geopolitical events or a sharp downturn in the global economy could force the Bank of France to adopt a more cautious or reactive approach, potentially altering the current projection.
Graphical Representation of Projected Interest Rates
The following line graph illustrates a potential trajectory for French interest rates over the next 24 months. The graph displays a gradual upward trend, with the interest rate peaking around 3.5-4% before potentially easing slightly towards the end of the forecast period. The shaded area around the line represents the range of uncertainty in the forecast. Note that this is a hypothetical illustration and not a definitive prediction.
| Month | Projected Interest Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| 2023-Oct | 2.0 |
| 2023-Nov | 2.2 |
| 2023-Dec | 2.5 |
| 2024-Jan | 2.7 |
| 2024-Feb | 3.0 |
| 2024-Mar | 3.2 |
| 2024-Apr | 3.5 |
| 2024-May | 3.6 |
| 2024-Jun | 3.7 |
| 2024-Jul | 3.8 |
| 2024-Aug | 3.7 |
| 2024-Sep | 3.5 |
Note: The above table provides a sample projection. Actual interest rates may differ based on various unforeseen factors.
Impact on Different Economic Sectors: France Economy Interest Rates
Interest rate changes ripple through various sectors of the French economy, impacting everything from housing affordability to business investment decisions. Understanding these effects is crucial for navigating the complexities of the French economic landscape. This section delves into the specific impacts on key economic sectors.
Impact on the Housing Market
Changes in interest rates significantly affect the housing market. Higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing for mortgages, making home purchases less accessible. This often leads to a decrease in demand, potentially slowing down new construction and impacting existing home prices. Conversely, lower interest rates stimulate demand, making mortgages more affordable and potentially increasing housing prices. France’s robust housing market, characterized by a mix of urban and rural properties, is particularly susceptible to interest rate fluctuations.
Impact on Consumer Spending and Borrowing Habits
Consumer spending and borrowing habits are directly correlated with interest rates. Higher interest rates increase the cost of loans for cars, personal goods, and other consumer purchases. This often leads to decreased spending as consumers prioritize debt repayment over discretionary spending. Conversely, lower interest rates encourage borrowing and spending, as the cost of borrowing decreases. French consumers, known for their varied spending patterns across different regions, are particularly influenced by the overall economic climate and the resulting changes in interest rates.
Impact on Investment Decisions by Businesses
Interest rates directly impact business investment decisions. Higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing for capital expenditures, such as machinery, equipment, and expansion projects. This can lead to businesses postponing or canceling investments, impacting job creation and economic growth. Lower interest rates, on the other hand, encourage businesses to invest, as the cost of capital is reduced.
French businesses, with their diverse range of industries from manufacturing to tourism, respond to interest rate changes in distinct ways, depending on their individual financial positions and the projected returns on investment.
Impact on Exports and Imports
Interest rate changes affect a country’s competitiveness in the global market. Higher interest rates in France, relative to other countries, can make French exports more expensive and less attractive to foreign buyers. This can lead to a decrease in export demand. Conversely, lower interest rates can make French exports more competitive, potentially increasing demand. France’s reliance on international trade and its diverse export portfolio mean that interest rate changes have a significant impact on its trade balance.
France’s economy is currently navigating fluctuating interest rates, which is impacting various sectors. Recent news surrounding Felicia Snoop Pearson and Ed Burns’s wire fraud case, as reported in felicia snoop pearson ed burns wire , might seem unrelated, but the ripple effects of such financial crimes can indirectly influence the broader economic climate, potentially affecting interest rate decisions.
This makes the current situation in France even more complex to analyze.
Impact Summary Table
| Sector | Impact Description | Potential Magnitude |
|---|---|---|
| Housing Market | Higher rates increase mortgage costs, decreasing demand and potentially impacting prices. Lower rates stimulate demand and potentially increase prices. | Moderate to significant, depending on the magnitude of the interest rate change. |
| Consumer Spending | Higher rates increase borrowing costs, decreasing spending. Lower rates encourage borrowing and spending. | Moderate to significant, depending on the sensitivity of consumers to interest rate changes. |
| Business Investment | Higher rates increase borrowing costs, potentially delaying or reducing investment. Lower rates encourage investment. | Significant, especially for large-scale projects and capital-intensive industries. |
| Exports and Imports | Higher rates make exports more expensive and imports cheaper. Lower rates make exports more competitive and imports more expensive. | Moderate to significant, depending on France’s trade partners and the overall global economic environment. |
Global Economic Context
The French economy, like many others, is deeply intertwined with the global economic landscape. Fluctuations in global markets, geopolitical events, and inflationary pressures significantly impact France’s interest rate policies and overall economic performance. Understanding this global context is crucial for accurately assessing the future trajectory of the French economy.
Global Economic Conditions Influencing French Interest Rates
Global economic conditions, including inflation rates, growth forecasts, and the performance of major trading partners, exert a powerful influence on the French interest rate policies. Changes in the global economic climate can trigger adjustments in French monetary policy, aiming to maintain price stability and sustainable growth. For example, if global inflation rises sharply, the French central bank might respond by increasing interest rates to curb domestic inflation, even if the domestic inflation rate is not as high.
Impact of Global Events on the French Economy
Geopolitical tensions and global events, such as trade wars or significant global crises, can significantly impact the French economy. Disruptions in global supply chains, for instance, can lead to higher import costs and potentially increased inflation in France. Similarly, uncertainty stemming from geopolitical conflicts can negatively affect investor confidence, impacting investment and economic growth. The 2008 financial crisis is a prime example, where global economic instability had a direct impact on French financial markets and economic performance.
Overview of Global Economic Trends
Global economic trends exhibit a complex interplay of factors. Emerging markets are experiencing varying degrees of growth, while developed economies face challenges like aging populations and slowing productivity growth. The interplay between these factors often creates uncertainty and volatility in global markets, which in turn affects French economic policies. For example, a significant downturn in the US economy, a major trading partner, could lead to decreased demand for French exports, potentially impacting French economic growth.
Table: Key Global Economic Factors and Potential Effects on French Interest Rates
| Global Economic Factor | Potential Effect on French Interest Rate Policies |
|---|---|
| Global Inflation | Higher global inflation may lead to increased interest rates in France to control domestic inflation, even if domestic inflation is not as high. |
| Geopolitical Tensions | Increased uncertainty and potential disruptions can lead to higher interest rates, potentially reducing investment and economic growth. |
| Global Economic Growth | Stronger global growth can potentially lead to increased demand for French exports and a possible rise in domestic inflation, influencing the interest rate decisions. |
| Major Trading Partner Performance | Economic downturns in major trading partners can decrease demand for French exports, potentially impacting French economic growth and prompting a more cautious approach to interest rate adjustments. |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | Disruptions can lead to higher import costs, potentially increasing inflation and affecting interest rate decisions. |
Government Policies and Their Influence
France’s economic health is intricately linked to the government’s policies, particularly its fiscal and monetary strategies. These policies directly affect interest rates, influencing borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, ultimately shaping investment and consumption patterns. Understanding the government’s role in managing these fluctuations is crucial to comprehending the French economy’s trajectory.Government policies, both fiscal and monetary, play a critical role in influencing interest rates in France.
Fiscal policy, encompassing government spending and taxation, impacts aggregate demand. Increased government spending can boost demand, potentially leading to higher inflation and pressure on interest rates. Conversely, higher taxes can curb demand, reducing inflationary pressures and potentially leading to lower interest rates. Monetary policy, controlled by the European Central Bank (ECB) with influence from the French government, focuses on managing the money supply and credit conditions.
The ECB’s key interest rate decisions significantly impact borrowing costs for banks and, subsequently, for individuals and businesses.
Fiscal Policy Impact on Interest Rates
Government spending and taxation are key components of fiscal policy. Increased government spending can boost aggregate demand, potentially leading to higher inflation. Higher inflation can prompt the central bank to raise interest rates to curb spending and control price increases. Conversely, lower government spending and higher taxes can reduce inflationary pressures, which might encourage the central bank to lower interest rates.
For instance, a large infrastructure project funded by government borrowing could increase demand and potentially push up interest rates, whereas tax increases designed to reduce a budget deficit could potentially reduce inflationary pressures and lower interest rates.
Monetary Policy and Interest Rate Decisions
The European Central Bank (ECB) is primarily responsible for setting interest rates in the Eurozone, including France. The ECB considers various economic factors, including inflation, unemployment, and economic growth, when making its decisions. If inflation rises above the target rate, the ECB typically raises interest rates to cool down the economy. Conversely, if inflation is low and economic growth is weak, the ECB may lower interest rates to stimulate economic activity.
France, as a member of the Eurozone, is subject to these ECB policies, although the French government has a voice in shaping the ECB’s decision-making. A recent example of this is the ECB’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic, where they lowered interest rates to near zero to stimulate economic activity.
Government’s Role in Managing Fluctuations
The French government, through its economic ministries and agencies, monitors economic data closely and adjusts its policies in response to interest rate fluctuations. This can involve implementing measures to support businesses facing higher borrowing costs, such as tax breaks or subsidies. For instance, during periods of high interest rates, the government might implement policies aimed at promoting investment in renewable energy to reduce reliance on fossil fuels, which could have a knock-on effect on interest rates.
However, inaction in the face of persistent high interest rates can lead to economic stagnation and a potential credit crunch.
Correlation Between Government Policies and Interest Rates
| Government Policy | Potential Impact on Interest Rates |
|---|---|
| Increased government spending | Potentially higher interest rates due to increased demand and inflationary pressures |
| Higher taxes | Potentially lower interest rates due to reduced demand and inflationary pressures |
| ECB interest rate hikes | Higher interest rates throughout the Eurozone, including France |
| ECB interest rate cuts | Lower interest rates throughout the Eurozone, including France |
Note: This table illustrates potential correlations. The actual impact can vary based on various other economic factors.
Final Review
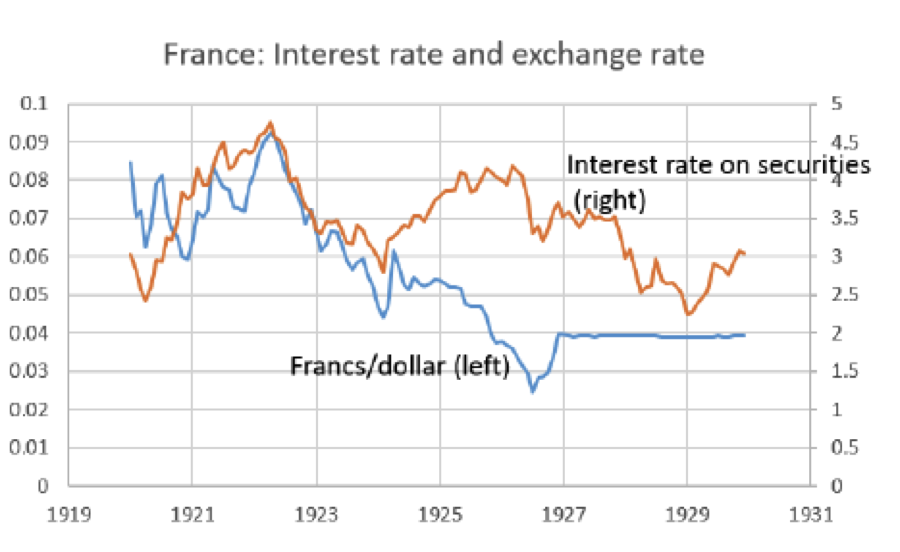
In conclusion, France economy interest rates are intricately linked to the broader global economic climate and domestic policy decisions. The interplay of these factors can have significant repercussions across various sectors, from housing to consumer behavior. Understanding these complexities is essential for anyone interested in investing, doing business, or simply staying informed about the French economy.
Questions Often Asked
What is the current inflation rate in France?
Unfortunately, precise current inflation data isn’t included in the provided Artikel. To find this information, you’d need to consult official French government or central bank sources.
How does the French government’s fiscal policy affect interest rates?
Government fiscal policy (taxes and spending) can significantly impact interest rates. For example, increased government spending can lead to higher demand for capital, potentially pushing up interest rates. The Artikel does discuss the correlation between these policies and interest rate changes, but the specific mechanisms aren’t detailed.
What is the projected GDP growth rate for France in the next year?
The Artikel doesn’t provide a specific GDP growth projection. To get this data, you’d need to consult economic forecasts from reputable institutions.






