
Dobbs Roe Wade States A Deep Dive
Dobbs Roe Wade States: This in-depth exploration delves into the landmark Supreme Court decision that overturned Roe v. Wade, analyzing its historical context, legal arguments, state responses, impact on access to abortion, and the potential future of abortion rights. We’ll examine the ripple effects this decision has had on individuals, communities, and the nation as a whole.
The decision to overturn Roe v. Wade has sparked significant debate, with passionate arguments on both sides. This article provides a balanced overview, exploring the historical precedent, legal justifications, and the diverse reactions across the country. We will also examine the complex and evolving landscape of abortion rights in the United States.
Historical Context of Roe v. Wade
The landmark 1973 Roe v. Wade Supreme Court decision fundamentally reshaped the legal landscape surrounding abortion in the United States. This ruling, which established a woman’s constitutional right to an abortion, sparked intense debate and continues to be a contentious issue today. Understanding the historical context of Roe v. Wade is crucial to comprehending the ongoing legal and societal battles over reproductive rights.The Supreme Court’s decision in Roe v.
Wade hinged on the interpretation of the Fourteenth Amendment’s Due Process Clause. The Court argued that this clause protects a woman’s right to privacy, including the right to make decisions about her own body and reproductive health. This interpretation of privacy as a fundamental right was pivotal in establishing the right to abortion.
Legal Reasoning and Impact of Roe v. Wade
The Supreme Court, in Roe v. Wade, established a trimester framework for regulating abortion access. In the first trimester, the state could not prohibit abortion. In the second trimester, the state could regulate abortion in ways reasonably related to maternal health. In the third trimester, the state could prohibit abortion except when necessary to save the life or health of the mother.
This framework aimed to balance the state’s interest in protecting potential life with the woman’s right to privacy.
Differing Legal Interpretations of the Fourteenth Amendment
The Fourteenth Amendment’s Due Process Clause has been subject to various interpretations throughout history. The Court in Roe v. Wade drew on earlier precedents that recognized a right to privacy as inherent in the Constitution. However, dissenting opinions argued that the right to privacy should not be extended to abortion. Different justices had different views on the extent to which the Constitution protects individual autonomy and the balance between individual rights and state interests.
Societal Context Surrounding Roe v. Wade
The 1970s saw a burgeoning women’s rights movement advocating for greater equality and autonomy. Societal attitudes toward abortion were evolving, with increasing support for a woman’s right to choose. However, significant opposition existed from religious and anti-abortion groups. This societal tension played a critical role in shaping the political climate leading up to and following the Roe v.
Wade decision.
Early Challenges to Roe v. Wade and Their Outcomes
Following the Roe v. Wade decision, several legal challenges emerged, aiming to limit or overturn the ruling. Some challenged the trimester framework, arguing it was overly broad or lacked sufficient clarity. Other challenges sought to impose more stringent regulations on abortion access. The outcomes of these cases often depended on the specific regulations challenged and the prevailing legal and societal context.
Comparison of Legal Arguments in Roe v. Wade and Later Cases
| Case | Argument in Favor of Abortion Rights | Argument Against Abortion Rights | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Roe v. Wade (1973) | A woman’s right to privacy, encompassing reproductive decisions, outweighs the state’s interest in regulating abortion until the point of viability. | The state has a compelling interest in protecting potential life from the moment of conception. | Established a trimester framework for regulating abortion access. |
| Planned Parenthood v. Casey (1992) | Reaffirmed the right to abortion, but introduced the “undue burden” standard. | States can enact regulations that do not create a substantial obstacle to a woman seeking an abortion. | Modified the trimester framework and upheld the right to abortion. |
| Gonzales v. Carhart (2007) | A woman’s right to choose, including late-term abortion procedures, should be protected. | The state has a compelling interest in protecting potential life at all stages of pregnancy. | Upheld a federal law banning certain late-term abortions. |
The Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization Decision: Dobbs Roe Wade States
The landmark Supreme Court decision in
The Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization ruling has significantly impacted reproductive rights across many states. It’s a complex issue with a lot of varied opinions, and thinking about the human cost of such decisions really makes you pause. For instance, exploring the powerful work of Holocaust survivor portraits, like those by Gillian Laub, holocaust survivor portraits gillian laub , sheds light on the enduring impact of loss and the fight for fundamental rights.
Ultimately, the ripples of the Dobbs decision continue to shape the future of reproductive freedom in the United States.
- Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization* fundamentally altered the landscape of abortion rights in the United States. Overturning the nearly 50-year-old
- Roe v. Wade* precedent, the ruling shifted the authority to regulate abortion to individual states, sparking widespread debate and protests. This decision has far-reaching implications for women’s reproductive freedom and the balance of power between federal and state governments.
The core issue in
- Dobbs* revolved around the constitutionality of a Mississippi law restricting abortion after 15 weeks of pregnancy. This case presented a direct challenge to the fundamental right to abortion established in
- Roe v. Wade*. The Court’s decision to overturn
- Roe* had profound implications for the legal status of abortion nationwide.
Legal Arguments Presented in Dobbs, Dobbs roe wade states
The legal arguments in
- Dobbs* focused on the interpretation of the Fourteenth Amendment’s Due Process Clause. The central contention was whether the right to an abortion is a fundamental right protected by the Constitution. Opponents of
- Roe* argued that the right to abortion was not deeply rooted in the nation’s history and tradition, thus not deserving of constitutional protection. Conversely, supporters of
- Roe* maintained that the right to abortion was a fundamental right, essential to women’s equality and autonomy.
Supreme Court’s Reasoning in Overturning Roe v. Wade
The Supreme Court, in its majority opinion, reasoned that the right to abortion was not a constitutionally protected right. The Court explicitly rejected the “undue burden” standard established in
- Planned Parenthood v. Casey* and concluded that the states have the authority to regulate or prohibit abortion. The majority opinion emphasized the importance of returning the issue of abortion regulation to the political process, where it can be addressed through democratic means. The Court asserted that the decision in
- Roe v. Wade* had been wrongly decided and that the issue of abortion should be decided by the states. The Court argued that the Constitution does not guarantee a right to abortion and that the states have the authority to regulate or prohibit abortion.
Dissenting Opinions and Justifications
The dissenting justices argued that the majority opinion’s decision undermined the principle of stare decisis, which is the legal doctrine of adhering to precedent. They maintained thatRoe v. Wade* had been the settled law of the land for nearly five decades and that overturning it would create instability and uncertainty in the legal system. They also argued that the decision would disproportionately harm women, particularly those in states with restrictive abortion laws.
The dissenters emphasized the importance of individual liberty and the right to privacy, arguing that the right to an abortion is a fundamental component of these rights. They highlighted the potential for significant negative impacts on women’s health and economic well-being.
Legal Precedents Cited in the Majority Opinion
The majority opinion in
The Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization ruling is definitely a hot topic, impacting reproductive rights across states. Meanwhile, the Steelers are shaking things up on the field with their new offensive coordinator hire, Arthur Smith. This new hire signals a fresh approach to the team’s offensive strategy, and it’s interesting to see how these seemingly disparate events connect in the broader societal landscape, as the debate around reproductive rights continues.
- Dobbs* cited various legal precedents, including cases related to the Fourteenth Amendment’s Due Process Clause and the relationship between the federal government and state governments. These precedents were used to support the argument that the right to abortion was not a fundamental right protected by the Constitution. Crucially, the majority opinion distinguished
- Roe v. Wade* from other precedents, arguing that the prior decision lacked historical support and was fundamentally flawed in its reasoning.
Summary Table of Arguments for and Against Overturning Roe v. Wade
| Argument | Supporting
|
Opposing
The Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization ruling has understandably sparked a lot of debate about reproductive rights in various states. While that’s a serious issue, it’s worth considering how events like the snow polo tournaments in St. Moritz are also being impacted by climate change, as highlighted in this fascinating article about snow polo st moritz climate change. Ultimately, these interconnected issues show how societal shifts and environmental concerns are deeply intertwined, even in seemingly disparate areas like sports and reproductive rights in the US.
|
Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Constitutional Basis | The right to abortion is not deeply rooted in the nation’s history and tradition, and thus not protected by the Constitution. | The right to abortion is a fundamental right, protected by the Fourteenth Amendment’s Due Process Clause. | This highlights the differing interpretations of constitutional principles. |
| State’s Rights | States have the authority to regulate or prohibit abortion, returning the issue to the political process. | Federal protection of abortion rights prevents states from enacting unduly restrictive laws. | This touches on the balance of power between federal and state governments. |
| Impact on Women | Overturning
|
Overturning
|
This focuses on the potential societal impact of the decision. |
| Historical Precedent | *Roe v. Wade* was wrongly decided and lacks historical support. | *Roe v. Wade* has been the settled law of the land for nearly 50 years and should be upheld. | This addresses the importance of precedent in legal interpretation. |
State Responses to the Dobbs Decision
The Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization decision fundamentally altered the landscape of abortion access in the United States, prompting a complex and varied response from individual states. States have been tasked with balancing the constitutional rights of individuals with the political and moral considerations surrounding abortion. This has led to a range of legislative and legal actions, from enacting restrictive measures to bolstering protections for reproductive rights.Following the Dobbs decision, states have taken a variety of approaches to regulating abortion, reflecting a spectrum of political and moral views.
These approaches have led to significant legal challenges and ongoing court battles. The ensuing legal landscape has been marked by both the enactment of new laws and the legal challenges mounted against them.
Varying State-Level Responses
States have responded to the Dobbs decision in a multitude of ways, enacting laws that either restrict or protect abortion access. These responses demonstrate a significant division in the nation regarding the legality and availability of abortion.
- Restrictive Laws: Several states swiftly enacted stringent regulations or outright bans on abortion, aiming to curtail or eliminate abortion access within their borders. These laws often imposed restrictions on the gestational age at which abortions could be performed, mandated specific procedural requirements, and/or required parental consent or notification for minors seeking abortions. Examples include gestational limits and mandatory waiting periods.
- Protective Laws: Conversely, some states have enacted measures to safeguard abortion access, aiming to maintain or enhance the availability of abortion services. These states often focused on protecting existing abortion clinics and procedures, ensuring access to necessary medical resources, and establishing protocols for maintaining healthcare standards. States may have codified abortion rights into their laws, ensuring these rights are upheld by state courts.
Comparison of State Approaches
The approaches taken by different states demonstrate a significant divergence in political and moral viewpoints on abortion. Some states prioritize the protection of fetal life, enacting laws that place stringent limitations on abortion access. Other states prioritize the right to bodily autonomy and reproductive freedom, implementing measures that protect and expand abortion access.
- Differing Legal Standards: States have applied different legal standards to abortion restrictions, leading to discrepancies in the level of protection afforded to abortion access. Some states have established broader protections based on a right to privacy, while others have relied on more narrowly defined restrictions.
- Different Levels of Regulation: States vary in the extent of regulation they impose on abortion providers and facilities. This difference is directly correlated to the level of restriction or protection being enacted. Some states may maintain existing laws and guidelines, while others implement stringent new restrictions.
Legal Challenges and Court Rulings
The Dobbs decision has sparked numerous legal challenges to state abortion laws. These challenges often revolve around the constitutionality of the laws in question and their potential impact on fundamental rights.
- Constitutional Arguments: Legal challenges to state abortion laws often invoke the Fourteenth Amendment’s Due Process Clause and its implications for bodily autonomy and reproductive rights. Plaintiffs may argue that certain restrictions violate these fundamental rights.
- Judicial Review: Courts are tasked with reviewing the constitutionality of these laws, examining their impact on individual rights and their potential to create inequalities. The legal processes involved can take time, and outcomes can be varied, depending on the jurisdiction.
Table of State Laws and Legal Challenges
| Category of State Laws | Examples of Laws | Legal Challenges | Court Rulings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Restrictive Abortion Laws | Gestational limits, mandatory waiting periods, parental consent requirements | Violation of bodily autonomy, undue burden on women seeking abortions | Mixed results, depending on the specific law and jurisdiction. Some laws have been temporarily blocked, while others have been upheld. |
| Protective Abortion Laws | Codification of abortion rights, protection of abortion providers, ensuring access to medical resources | Challenges to the constitutionality of these laws, arguing that they infringe on the rights of individuals or entities opposed to abortion. | Mixed results, with ongoing litigation concerning the scope and reach of these laws. |
Impact on Access to Abortion
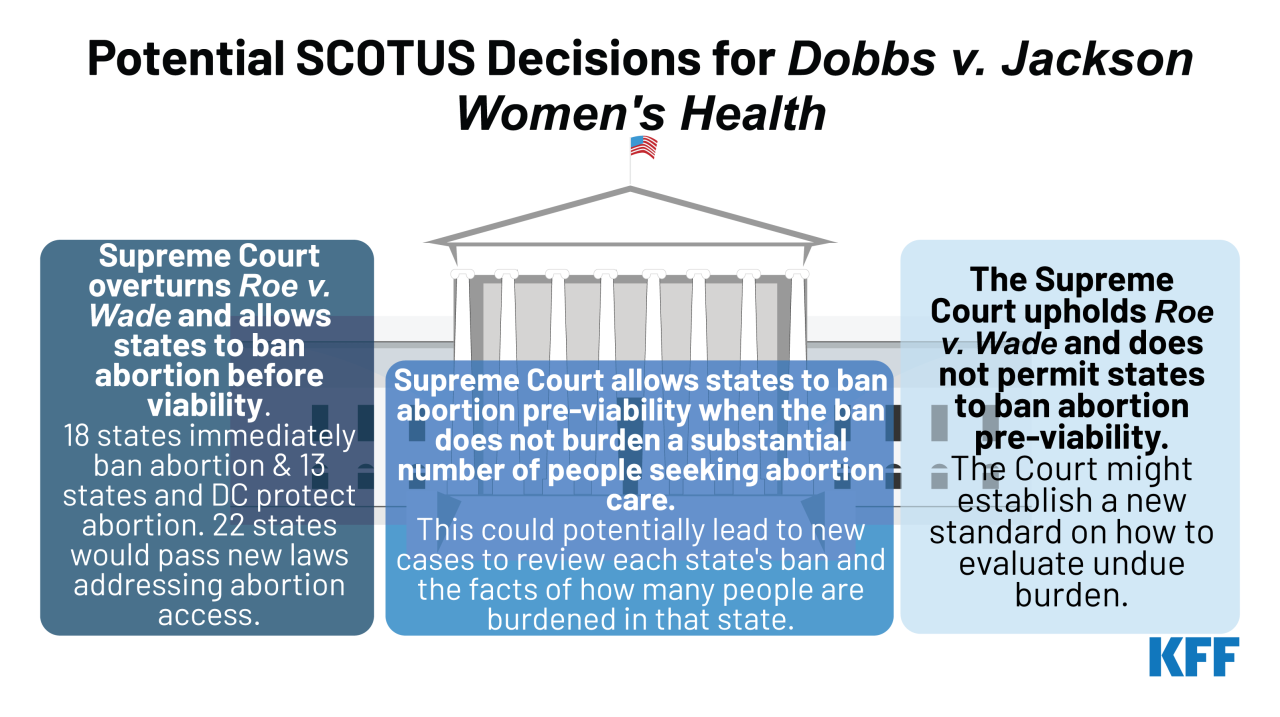
The Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization decision fundamentally reshaped the landscape of abortion access in the United States, shifting power from the federal level to individual states. This shift has led to a patchwork of laws and regulations, creating stark differences in access to abortion services across the country. The decision’s impact extends beyond legal frameworks, affecting individuals’ lives, communities, and the overall health of the nation.The implications of the ruling are far-reaching, impacting various demographic groups differently.
Women of color, low-income individuals, and those geographically isolated often face disproportionate barriers to accessing abortion care. The decision has also triggered significant political debate and social unrest, highlighting the deeply held beliefs and values surrounding reproductive rights.
Current Landscape of Abortion Access
The states are now the primary arbiters of abortion laws, leading to significant disparities in access across the country. Some states have enacted near-total bans, while others have maintained relatively liberal access to abortion services. This creates a complex and challenging situation for individuals seeking reproductive healthcare. The practical implications of these state-level variations are profound, influencing travel patterns, financial burdens, and the overall health of women and families.
Effects on Different Demographics
The Dobbs decision has significantly impacted various demographics in the United States. For example, low-income individuals often face greater challenges in traveling to states where abortion is legal. The financial burden of travel, lodging, and childcare can be insurmountable for many. Similarly, women of color often experience additional obstacles due to systemic inequalities. Their access to transportation, financial resources, and support networks may be limited, further hindering their ability to access abortion care.
Stories of Affected Individuals and Communities
The stories of individuals and communities affected by the decision highlight the human cost of this legal shift. Many have shared personal accounts of the emotional distress and practical challenges they face navigating the new legal landscape. These stories underscore the need for equitable access to reproductive healthcare and the importance of supporting those who are struggling to maintain control over their own bodies and futures.
For instance, a young woman from a rural community may have to travel hundreds of miles to access an abortion clinic, facing significant financial and logistical hurdles.
Practical Implications of State-Level Abortion Laws
State-level abortion laws have significant practical implications for individuals seeking reproductive healthcare. These implications include:
- Travel burdens: Individuals may need to travel to another state for abortion services, leading to financial and logistical challenges.
- Financial strain: The cost of travel, lodging, and childcare can be prohibitive for many individuals, especially those with limited resources.
- Potential for increased health risks: In some cases, the distance to access care may increase the potential for complications and delays, potentially affecting health outcomes.
- Increased emotional distress: Navigating the complex legal landscape and the emotional implications of restricted access can lead to considerable stress and anxiety.
Differences in Abortion Access Across Regions and States
The following table illustrates the differences in abortion access across various regions and states, showing a range of situations from near-total bans to continued legal access.
| Region/State | Abortion Access Status | Key Restrictions (if any) | Impact on Affected Populations |
|---|---|---|---|
| States with near-total bans | Limited or no access | Often include gestational limits, mandatory waiting periods, or restrictions on providers | Increased financial and logistical barriers, potential health risks for individuals seeking care |
| States with legal access | Continued availability | May have some regulations but are generally less restrictive | Relatively easier access for those seeking reproductive healthcare services |
| States with restrictions | Access with limitations | May have gestational limits, mandatory counseling, or restrictions on providers | Varied access based on specific regulations |
| Rural vs. Urban areas | Significant disparity | Rural areas often have fewer clinics and providers, increasing travel distances | Rural populations face greater access barriers due to geographic isolation and limited resources |
Future of Abortion Rights
The Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization decision has irrevocably altered the landscape of abortion rights in the United States. The future trajectory of these rights hinges on a complex interplay of legal challenges, legislative efforts, and the ever-shifting political and social climate. Understanding these factors is crucial to predicting the potential outcomes and the strategies required to protect and expand access to abortion services.The legal landscape surrounding abortion rights is dynamic and contested.
The Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization ruling significantly impacted abortion access across various states. It’s fascinating to see how these legal battles often intersect with other compelling narratives, like the journey of a celebrated actress like Chita Rivera. Her career, full of iconic performances and key moments, is a testament to the human spirit and resilience, detailed in this piece chita rivera key moments career.
Ultimately, the implications of the Dobbs decision on women’s rights and healthcare remain a pivotal discussion point in American society.
Future legal battles will likely focus on the interpretation of state laws and the constitutionality of various restrictions. The scope of these challenges could range from specific regulations on abortion procedures to the broader question of a state’s authority to control access to reproductive healthcare.
Potential Legal Challenges and Legislative Efforts
Legal challenges to abortion restrictions will undoubtedly continue. These challenges may target the constitutionality of state laws, arguing that they violate the Fourteenth Amendment’s due process clause or other fundamental rights. Conversely, legislative efforts to restrict abortion access will likely include stricter regulations on abortion providers, such as mandatory waiting periods or mandatory counseling. These efforts may also include measures that limit access to abortion services based on gestational age.
Role of Political and Social Factors
Political and social factors play a pivotal role in shaping the future of abortion rights. Public opinion polls, advocacy campaigns, and the political agenda of elected officials will significantly influence the legal and legislative trajectory of abortion rights. The composition of the judiciary, particularly the Supreme Court, will also exert considerable influence. Social movements, both in support of and against abortion rights, will continue to exert pressure on elected officials and shape public discourse.
For example, the success of abortion rights advocates in some states, coupled with ongoing public debates and legal challenges, will influence the future of access.
Potential Strategies to Protect Abortion Access
Protecting abortion access will require a multifaceted approach. Legal challenges to restrictive state laws will remain a crucial component of this strategy. Furthermore, grassroots activism and public awareness campaigns are essential to galvanize support for abortion rights. Building coalitions among various advocacy groups and engaging in legislative advocacy at the state and federal levels are critical for shaping policy.
Additionally, supporting and strengthening abortion providers is essential to ensure the continuity of services.
Comparison of Strategies
Strategies for preserving and expanding abortion access differ significantly from those aimed at restricting access. Advocates for abortion access will emphasize the right to bodily autonomy, focusing on legal challenges, legislative advocacy, and public awareness campaigns to counter restrictions. In contrast, opponents of abortion access will emphasize the moral status of the fetus, focusing on legislative measures, legal challenges, and public awareness campaigns to restrict abortion.
Potential Scenarios for the Future of Abortion Rights
| Scenario | Description | Implications for Access | Potential Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increased Restrictions | State legislatures enact increasingly restrictive abortion laws, potentially leading to outright bans in many states. | Significant reductions in abortion access, potentially forcing individuals to travel long distances or seek unsafe procedures. | Strengthen legal challenges to restrictive laws; mobilize public support for abortion access; bolster funding for abortion providers and legal aid organizations. |
| Continued Litigation and Legal Challenges | Legal battles continue over the constitutionality of state abortion laws, with the Supreme Court potentially weighing in on key cases. | Uncertainty regarding access, with varying levels of access across states, and potentially temporary shutdowns of abortion clinics. | Develop comprehensive legal strategies; build strong alliances between legal organizations and advocacy groups; focus on building a strong legal defense. |
| Increased Access in Some States | Some states may pass legislation expanding access to abortion, possibly offering financial assistance or eliminating barriers. | Increased access in specific areas, potentially creating a patchwork of policies across the nation. | Advocate for pro-choice legislation at the state level; provide support to organizations working to expand access in specific regions; focus on legislative victories. |
| National Legislation | Congress passes a federal law that establishes national standards for abortion access, either restricting or expanding it. | Significant shift in the national landscape for abortion access, with uniform or more defined regulations nationwide. | Engage in national legislative advocacy; work with organizations dedicated to federal policy reform; mobilize support across the nation. |
Societal Impact
The Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization decision has ignited a profound and multifaceted societal impact, exposing deep-seated divisions and anxieties about fundamental rights, bodily autonomy, and the role of government in personal decisions. The decision’s reverberations extend far beyond the legal realm, influencing political discourse, social movements, and the lived experiences of countless individuals.The decision has exacerbated existing societal tensions, creating a stark divide between those who believe in the right to choose and those who advocate for the protection of fetal life.
This polarization has impacted political discourse, making compromise on abortion rights challenging and potentially shaping future policy debates.
Social and Political Divisions
The Dobbs decision has dramatically widened the chasm between pro-choice and pro-life advocates. This division is reflected in public opinion polls, political activism, and the ongoing legal battles surrounding abortion access. The differing interpretations of fundamental rights and the role of government in regulating personal choices have contributed to the intensity of the debate. Pro-choice advocates emphasize bodily autonomy and reproductive freedom, while pro-life advocates prioritize the moral status of the fetus and the protection of potential life.
The Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization ruling has sparked a lot of debate about abortion access in various states. It’s interesting to consider how such significant legal changes impact the fabric of a society, and how figures like Adrian Beltre, a Texas Ranger legend and now Hall of Famer, also contribute to the narrative of a state’s identity.
Adrian Beltre’s hall of fame career with the Texas Rangers reminds us of the diverse threads that make up the story of the American landscape. Ultimately, the Dobbs decision continues to influence the direction of conversations about women’s rights and reproductive freedom across the states.
Potential Impact on Women’s Health and Equality
The implications for women’s health and equality are significant. Restricting access to abortion can disproportionately affect marginalized communities, leading to higher maternal mortality rates, limited educational and economic opportunities, and heightened risk of violence. Women in underserved areas may face insurmountable barriers to accessing necessary healthcare services. The potential for increased financial strain and social isolation also warrants concern.
Public Reactions to the Dobbs Decision
Public reactions to the Dobbs decision have been varied and intense. Demonstrations, protests, and rallies have been held across the nation, expressing support for or opposition to the ruling. Social media has also played a significant role in amplifying these reactions, creating a complex tapestry of viewpoints and arguments. Some individuals celebrated the decision, while others mourned the loss of reproductive rights and expressed fears about the future.
These varied responses highlight the profound emotional and societal impact of the decision.
Role of Activism and Advocacy Groups
Activism and advocacy groups have been instrumental in shaping the conversation surrounding abortion rights. Organizations dedicated to protecting or opposing abortion rights have mobilized their members and resources to engage in advocacy efforts, lobbying, and community outreach. Their actions have contributed significantly to the public discourse, influencing public opinion and policy decisions. The sustained activism of both sides reflects the deep-seated conviction and the intensity of the debate.
Comparison of Societal Impact: Roe v. Wade and Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization
| Aspect | Roe v. Wade (1973) | Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization (2022) | Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public Opinion | Public opinion was divided but the ruling fostered a sense of legal stability and relative acceptance of abortion as a right. | Public opinion became highly polarized, creating a stark divide between pro-choice and pro-life supporters. | The Roe decision led to relative stability in the legal landscape, while the Dobbs decision triggered heightened social and political polarization. |
| Political Impact | The ruling led to political debate but did not cause a complete fracture in the political spectrum. | The ruling sparked significant political divisions and potentially shaped future policy debates. | Roe v. Wade did not create a complete political rift, while Dobbs potentially impacted future political outcomes. |
| Impact on Women’s Health | The decision was believed to improve access to healthcare and reduce maternal mortality in some areas. | Potential for increased maternal mortality and disparities in healthcare access, especially in underserved communities. | Roe v. Wade had potential positive impacts on women’s health, while Dobbs potentially poses risks. |
| Social Activism | There were advocacy efforts, but they weren’t as widely seen as the post-Dobbs movement. | Both pro-choice and pro-life activism intensified, significantly impacting public discourse and political lobbying efforts. | Dobbs generated a significant increase in both sides’ activism, whereas the Roe v. Wade era saw some activism but not as widespread. |
Epilogue

In conclusion, the Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization decision has irrevocably altered the landscape of abortion rights in the United States. The varying state responses, the practical implications for access, and the ongoing legal battles highlight the deeply divisive nature of this issue. This article has sought to provide a comprehensive understanding of the legal, social, and political factors at play, acknowledging the complexities and uncertainties that lie ahead for the future of abortion rights.
FAQs
What were the key arguments in the Dobbs decision?
The majority opinion in Dobbs argued that the Constitution does not confer a right to abortion, and that the decision should be left to individual states. Dissenting opinions emphasized the importance of bodily autonomy and the precedent set by Roe v. Wade.
How have different states reacted to the Dobbs decision?
States have responded with a wide range of measures, from enacting restrictive abortion laws to protecting abortion access. Some states have completely banned abortions, while others have maintained broad access. The legal landscape is constantly evolving as challenges and court rulings continue to shape the future of abortion rights in specific states.
What are the potential future legal challenges to abortion rights?
Future challenges could involve legislative efforts at the federal level to codify abortion rights, or to restrict them further. Legal battles are anticipated as the ongoing debate and judicial interpretations continue to develop.
What is the impact of the Dobbs decision on women’s health?
The decision has raised concerns about potential negative impacts on women’s health, especially in states with restrictive abortion laws. Access to healthcare and potential disparities in care quality are key factors to consider.






