Iceland Is Living in Our Future A Look Ahead
Iceland is living in our future, showcasing innovative societal models, technological advancements, and environmental sustainability. This exploration delves into Iceland’s unique approach to these critical areas, highlighting their potential impact on global trends and future practices. From their groundbreaking renewable energy initiatives to their forward-thinking social structures, Iceland provides a compelling glimpse into a more sustainable and equitable future.
Iceland’s approach to resource management, social equality, and environmental protection offers valuable lessons for the world. This post will delve into the specifics, examining their current practices, contrasting them with other developed nations, and considering their potential for global influence.
Icelandic Societal Models
Iceland, a small island nation in the North Atlantic, boasts a unique blend of societal structures. Its relatively homogenous population, coupled with a strong emphasis on social responsibility and environmental consciousness, has shaped a distinct model that merits examination. This model offers valuable insights into potential pathways towards a more sustainable and equitable future.Iceland’s economic model is predominantly market-driven, yet it incorporates significant social safety nets and government intervention to ensure equitable distribution of wealth.
This approach, combined with a robust social welfare system, aims to create a society where economic success is balanced with social well-being. Environmental considerations are deeply ingrained in Icelandic culture and policy, reflecting a profound connection to the land and its resources.
Economic Models
Iceland’s economy is diversified, relying on sectors such as fishing, tourism, and technology. While reliant on natural resources, Iceland actively seeks to transition towards a more sustainable and renewable energy-based economy. Government support for innovation and research plays a crucial role in fostering this transition. Icelandic businesses are increasingly exploring opportunities in renewable energy technology, demonstrating a forward-thinking approach to long-term economic viability.
Social Values
Icelandic society is characterized by a strong emphasis on social equality and inclusivity. A high degree of social trust and civic engagement contributes to a supportive and collaborative environment. The nation has made strides in gender equality, with women holding prominent positions in various fields. A strong emphasis on education and personal development further contributes to a well-rounded and informed citizenry.
Environmental Policies
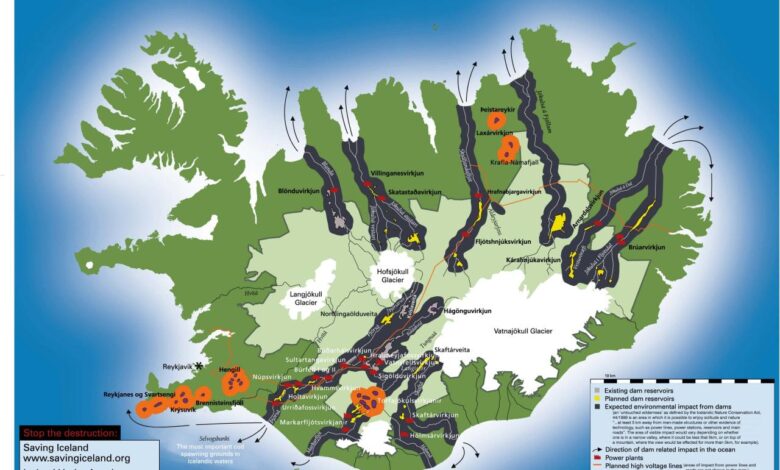
Iceland’s environmental policies are internationally recognized for their progressive nature. Iceland has established ambitious targets for renewable energy generation, aiming to reduce its carbon footprint significantly. Stringent regulations regarding waste management and pollution control contribute to a cleaner environment. Iceland’s commitment to protecting its unique natural landscapes and biodiversity underscores a deep respect for the environment. Examples include the development of geothermal power plants and investments in hydropower projects.
Specific Initiatives
Icelandic initiatives addressing sustainability and social equality include:
- Renewable Energy Initiatives: Iceland leverages its geothermal resources to generate significant amounts of renewable energy, setting an example for other nations seeking to transition away from fossil fuels.
- Social Safety Nets: Iceland’s robust social welfare system provides universal healthcare and education, ensuring basic needs are met for all citizens. This fosters social mobility and reduces inequality.
- Gender Equality Policies: Iceland has consistently ranked high in gender equality indicators, with strong policies and programs aimed at achieving equal opportunities for women and men.
Comparison with Other Developed Nations
Compared to other developed nations, Iceland stands out for its proactive approach to sustainability. While other countries have made progress, Iceland’s commitment to renewable energy and environmental protection is often more pronounced. However, the social safety nets and emphasis on social equality vary across developed nations, reflecting diverse cultural and historical contexts. The balance between economic growth and environmental protection remains a challenge for all developed countries.
Potential Global Impacts
Iceland’s approach to resource management, particularly its successful integration of renewable energy sources, holds significant potential for influencing global practices. Its example could inspire other nations to adopt more sustainable and equitable economic models. The country’s innovative approach to waste management and environmental protection could serve as a blueprint for other countries facing similar challenges. The emphasis on social equality and civic engagement within Icelandic society could also be seen as a model for promoting social cohesion in other parts of the world.
Resource Management Influence
Iceland’s commitment to responsible resource management, including its focus on renewable energy, could significantly influence future global practices. Its experience in managing geothermal and hydro resources, as well as its policies regarding sustainable fishing practices, could provide valuable lessons for other nations seeking to balance economic development with environmental protection.
| Societal Aspect | Iceland’s Approach | Comparison with another nation (e.g., Norway) | Potential Future Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Economic Model | Market-driven with strong social safety nets | Norway’s reliance on oil and gas, though with a social safety net | Inspiration for more balanced models globally, promoting sustainability alongside economic growth |
| Environmental Policies | Ambitious targets for renewable energy, stringent regulations | Norway’s focus on renewable energy and sustainability | Potential for global adoption of more sustainable practices, particularly in energy production |
| Social Values | Strong emphasis on social equality and inclusivity | Varying degrees of social equality across developed nations | Influence on global discussions and policies promoting social equity and cohesion |
Technological Advancements in Iceland: Iceland Is Living In Our Future
Iceland, a land of fire and ice, is rapidly becoming a global leader in innovative technologies, particularly in the realm of sustainable energy. This forward-thinking approach is deeply intertwined with the nation’s unique geological features and unwavering commitment to environmental responsibility. The nation’s pioneering efforts in renewable energy are not only shaping its own future but also offering valuable lessons and potential solutions for the world.Iceland’s diverse technological advancements are driven by a strong commitment to sustainability, making it a model for other nations striving to reduce their environmental footprint.
The country’s inherent advantages, including abundant geothermal resources and a wealth of hydro power, are being leveraged to develop and implement cutting-edge technologies that contribute to a greener future.
Renewable Energy Innovations
Iceland’s rich geothermal resources are a cornerstone of its renewable energy infrastructure. Harnessing these resources through innovative technologies ensures a stable and sustainable energy supply. The nation is at the forefront of geothermal power generation, demonstrating its ability to convert heat from the Earth’s interior into usable energy. This includes developing advanced geothermal power plants and efficient heat exchange systems.
Hydropower, another significant renewable energy source, is also being optimized through modern technologies, enhancing efficiency and minimizing environmental impact.
Geothermal Power Applications
Iceland’s geothermal power plants are a prime example of harnessing renewable energy. These plants utilize the heat from the Earth’s interior to generate electricity and provide heating for homes and businesses. The nation’s infrastructure has evolved to accommodate these innovations, ensuring widespread access to this sustainable energy source. Examples include the Hellisheiði geothermal power plant, which showcases advanced technologies for efficient energy extraction and distribution.
The country’s focus on district heating systems further exemplifies the utilization of geothermal energy for heating purposes, minimizing reliance on fossil fuels and maximizing energy efficiency.
Iceland’s sustainable energy practices are a glimpse into our future, showcasing how we can power our world responsibly. Thinking about how Chita Rivera’s incredible career trajectory, documented in detail on chita rivera key moments career , highlights the importance of resilience and innovation in achieving success, mirroring the pioneering spirit of Iceland’s eco-friendly approach. This forward-thinking attitude is key to a sustainable future for all, and Iceland’s example should inspire us all to embrace similar methods.
Other Innovative Sectors
Iceland is also a leader in developing cutting-edge technologies beyond renewable energy. The nation’s commitment to technological advancement extends to sectors like advanced materials, biotechnology, and even space exploration. These innovations are helping to shape Iceland’s future by creating new industries, fostering economic growth, and contributing to the nation’s overall well-being.
Global Implications
Iceland’s technological advancements have the potential for significant global implications. The country’s success in harnessing renewable energy resources could inspire other nations to adopt similar strategies. The development of sustainable technologies, including those for geothermal energy and hydropower, can contribute to a global transition towards cleaner energy sources, ultimately reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change. Iceland’s innovations also offer solutions for sustainable infrastructure development and resource management.
| Technology | Iceland’s Application | Global Impact | Future Outlook |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geothermal Power | Generating electricity and district heating | Reduced reliance on fossil fuels, decreased greenhouse gas emissions | Further development of advanced geothermal systems, wider adoption by other countries |
| Hydropower | Utilizing rivers and waterfalls for energy generation | Clean energy alternative, reduced carbon footprint | Integration with other renewable sources, optimized water management |
| Advanced Materials | Developing sustainable building materials | Reduced environmental impact of construction, decreased waste | Growth in the construction sector, innovative applications in other industries |
| Biotechnology | Developing sustainable agricultural practices and food production | Improved food security, reduced environmental impact of farming | Enhanced efficiency in agriculture, potential for biofuel production |
Sustainability Goals
Iceland’s commitment to sustainability is exemplified in its integration of various technologies. The country is actively using technology to achieve its environmental goals. For example, smart grids are being implemented to manage energy distribution more efficiently, and advanced sensors are used to monitor and optimize geothermal power plant operations. This comprehensive approach demonstrates a strong commitment to sustainability and provides a model for other nations to follow.
Iceland’s Environmental Sustainability
Iceland, a land of fire and ice, boasts a unique approach to environmental stewardship. Historically shaped by its harsh climate and reliance on natural resources, Iceland has developed a strong commitment to sustainability, reflected in its policies and practices. This commitment is not merely a recent trend but a deeply ingrained part of Icelandic identity. The nation recognizes that its economic prosperity and social well-being are inextricably linked to the health of its environment.Iceland’s dedication to environmental protection stems from a multifaceted understanding of the interconnectedness between nature and human society.
Iceland’s stunning landscapes and renewable energy solutions are a glimpse into our future. The recent Oilers victory, with Stuart Skinner’s stellar performance against the Blue Jackets, a testament to hockey’s enduring appeal , highlights the exciting innovations that are shaping our world. Ultimately, Iceland’s sustainable model is a compelling example of how we can build a greener and more resilient tomorrow.
The island nation has recognized the long-term benefits of sustainable practices, not only for its own citizens but also for the global community. This proactive approach has resulted in a model that other countries can learn from and potentially adapt.
Historical and Current Environmental Policies
Iceland’s environmental policies have evolved over time, reflecting changing societal values and scientific understanding. Early policies focused primarily on resource management and conservation. More recently, there’s been a strong emphasis on mitigating climate change and promoting ecological balance. Current policies are characterized by a comprehensive approach encompassing renewable energy, waste management, and biodiversity protection. Iceland’s constitution also acknowledges the importance of environmental protection, fostering a strong legal framework for sustainability.
Strategies for Mitigating Climate Change
Iceland’s commitment to combating climate change is evident in its significant investment in renewable energy sources. The country has successfully transitioned a substantial portion of its energy production to hydropower, geothermal power, and increasingly, wind power. This commitment to renewable energy is not only beneficial for the environment but also economically viable. Iceland’s innovative approach to climate change mitigation serves as a model for other nations seeking to reduce their carbon footprint.
Strategies for Promoting Ecological Balance
Iceland’s environmental policies aim to maintain a delicate ecological balance. The country has implemented strict regulations on pollution and habitat destruction. Iceland’s approach to ecological balance is proactive and comprehensive, recognizing that environmental protection requires ongoing vigilance and adaptation to changing conditions. This proactive stance is further demonstrated by the significant investment in research and development related to environmental sustainability.
Key Environmental Initiatives
Iceland has consistently placed a high priority on environmental protection, with several key initiatives driving this commitment.
- Renewable Energy Transition: Iceland’s shift away from fossil fuels and towards hydropower, geothermal, and wind power is a cornerstone of its sustainability strategy.
- Waste Management: The country’s comprehensive waste management system, including recycling programs and landfill minimization, significantly reduces environmental impact.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Iceland has established numerous protected areas to safeguard its unique flora and fauna, ensuring the preservation of ecosystems.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Iceland actively monitors and researches climate change impacts, developing strategies to adapt and reduce emissions.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Iceland promotes sustainable agricultural practices, reducing the environmental footprint of food production.
Potential for Inspiration and Adoption
Iceland’s environmental model holds significant potential for inspiring other nations. The country’s strong policies and effective implementation of sustainable practices demonstrate the feasibility of transitioning to a low-carbon economy. The combination of strong political will, supportive public opinion, and significant investment in research and development has been instrumental in shaping Iceland’s environmental model. Countries facing similar challenges can learn from Iceland’s experiences and adapt its strategies to their specific contexts.
Examples of Adaptable Practices, Iceland is living in our future
- Waste Management: Iceland’s successful recycling programs and waste reduction strategies can be adopted and adapted by other nations, particularly those with similar waste generation profiles.
- Renewable Energy: Iceland’s pioneering use of geothermal and hydropower as primary energy sources provides a compelling example of a renewable energy transition. This model can inform similar efforts in other countries with suitable geothermal or hydropower potential.
Future Trends in Iceland

Iceland, a nation renowned for its breathtaking landscapes and innovative spirit, is poised for exciting developments in the decades to come. The country’s unique blend of natural resources, progressive social policies, and burgeoning technological advancements will shape its future trajectory, potentially influencing global trends in sustainability and innovation. These developments promise both challenges and opportunities, requiring careful consideration and proactive planning.Iceland’s current strengths, such as its commitment to renewable energy and strong social safety nets, will likely be further amplified.
However, adapting to evolving global dynamics, including shifts in economic landscapes and environmental pressures, will be critical for Iceland’s continued success.
Potential Developments in Iceland’s Social Sphere
Iceland’s robust social safety net and progressive policies will likely continue to be a cornerstone of its societal structure. This includes access to quality healthcare, education, and social services. Further, the emphasis on gender equality and inclusivity is expected to remain a key element of Icelandic society. Population growth and aging demographics will necessitate adjustments to social infrastructure and policies.
Potential Developments in Iceland’s Economic Sphere
Iceland’s economy is diversified, with tourism playing a significant role. The continued development of sustainable tourism practices, alongside the expansion of the renewable energy sector, is anticipated. Further, innovation in sectors like biotechnology and advanced manufacturing will likely become increasingly important. These developments are closely tied to global trends in sustainability and technology. Iceland’s proximity to other Scandinavian countries and its geographical position in the North Atlantic are key elements in shaping its economic prospects.
Potential Developments in Iceland’s Environmental Sphere
Iceland’s commitment to environmental sustainability is likely to intensify. The country’s reliance on renewable energy sources, particularly geothermal and hydroelectric power, will likely remain central. The development of sustainable aquaculture practices and the management of its vast natural resources will be crucial. Further, adapting to the effects of climate change, such as rising sea levels and glacial melt, will require proactive strategies.
Comparison with Similar Nations
Iceland shares similarities with other Nordic countries in its emphasis on social welfare, environmental protection, and technological innovation. However, Iceland’s unique geographical location and resource base will shape its specific trajectory. Comparing Iceland’s future with nations like Norway, Sweden, and Finland will offer valuable insights into potential paths and challenges. The global competitiveness of these nations in similar sectors will also be relevant to Iceland’s strategy.
Iceland’s sustainable practices are often cited as a glimpse into our future, but the complex reality of global supply chains is highlighted by issues like drug imports, particularly between Canada and Florida. For instance, recent reports on drug imports Canada Florida show the intricate web of international trade and its potential vulnerabilities. Ultimately, Iceland’s focus on renewable energy and resource management still offers a compelling model for a more sustainable future.
Potential Impacts on the World Stage
Iceland’s advancements in renewable energy, sustainable tourism, and social welfare could serve as a model for other nations seeking to create more sustainable and equitable societies. Iceland’s successful adaptation to climate change and resource management could influence international policies and practices.
| Potential Trend | Societal Impact | Environmental Impact | Global Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Expansion of renewable energy | Increased job opportunities, lower energy costs, improved air quality | Reduced carbon emissions, conservation of natural resources | Potential for global leadership in renewable energy technology |
| Development of sustainable tourism | Increased revenue, preservation of cultural heritage | Reduced environmental impact of tourism, responsible resource use | Potential for more sustainable tourism models globally |
| Technological advancements in aquaculture | Improved food security, economic diversification | Reduced environmental footprint of aquaculture, efficient use of resources | Potential for more sustainable food production models globally |
| Adaptation to climate change | Resilient infrastructure, enhanced preparedness | Mitigation of climate change impacts, reduced vulnerability | Examples of effective adaptation strategies for other countries |
Icelandic Cultural Influence
Icelandic culture, deeply rooted in its unique history and environment, possesses a profound capacity to inspire future global values and behaviors. Its emphasis on sustainability, social responsibility, and well-being offers valuable lessons for navigating the challenges of the 21st century. The nation’s artistic and storytelling traditions provide a rich tapestry of potential influence on global narratives and trends.Icelandic culture, shaped by centuries of isolation and a harsh, yet beautiful, natural environment, has fostered a strong sense of community and a deep respect for nature.
This ethos is reflected in numerous aspects of Icelandic life, providing a blueprint for sustainable living.
Iceland, with its unique and often extreme environment, feels like a glimpse into our potential future. The recent cancellation of the Indiana University Samia Halaby exhibition, unfortunately highlighting a growing trend of cultural suppression , makes me think even harder about how we’re shaping our future. Perhaps, in some ways, Iceland’s stark beauty and resilience mirror the challenges we’ll face, reminding us that a sustainable future needs open minds and diverse perspectives.
We need to learn from the past to build a better future, just as Iceland’s landscapes offer us a lesson in adaptability.
Sustainability and Social Responsibility in Icelandic Culture
Icelandic traditions emphasize interconnectedness with nature and a sense of responsibility for the environment. This isn’t merely a modern concept; it’s deeply embedded in their historical and cultural fabric. Traditional Icelandic practices, like resource management and respect for the land, often predate modern environmental awareness. The enduring emphasis on communal values further reinforces a sense of shared responsibility.
Iceland’s otherworldly landscapes, seemingly plucked from a futuristic movie, are a glimpse into our potential future. Think of the stunning volcanic activity and geothermal energy, a parallel to the themes explored in the recent Godzilla Oppenheimer Heron Boy hype, where nature’s power meets human creation. Ultimately, Iceland’s resilience and innovative energy solutions show us a pathway towards a sustainable future, one that we can all hopefully learn from.
- Respect for the natural environment: Traditional Icelandic farming practices, fishing methods, and resource utilization demonstrate a sophisticated understanding of the need for sustainable resource management. These practices prioritize long-term well-being over short-term gains, highlighting a cultural value system that aligns closely with modern sustainability goals.
- Social responsibility and communal values: Icelandic society emphasizes social responsibility and communal values. These values are reflected in the strong social safety nets and cooperative spirit present in Icelandic communities. This interconnectedness fosters a sense of shared responsibility, contributing to a more equitable and sustainable society.
Influence on Global Approaches to Well-being
Iceland’s emphasis on well-being extends beyond material wealth. The nation’s commitment to mental health initiatives, mindfulness practices, and a strong social safety net are influential models for global well-being strategies.
- Mental health initiatives: Iceland’s proactive approach to mental health, incorporating preventative measures and accessible support systems, can be a valuable model for other nations. The nation’s focus on mental health as a crucial aspect of overall well-being can inspire global efforts to promote mental health and reduce the stigma surrounding it.
- Emphasis on holistic well-being: Iceland’s culture often prioritizes a holistic approach to well-being, considering the interconnectedness of physical, mental, and social health. This holistic perspective can serve as a powerful framework for global health initiatives.
Icelandic Artistic Expressions and Future Trends
Icelandic artistic expressions, from literature and music to visual arts, often reflect the nation’s unique cultural values and environmental awareness. These expressions can shape future trends in art and storytelling.
- Reflection of cultural values: Icelandic art frequently portrays themes of nature, resilience, and social responsibility. This focus on core values can influence global artistic trends, moving away from purely commercial or superficial narratives towards more meaningful and impactful expressions.
- Influence on storytelling and narrative: Icelandic sagas and folklore, rich in themes of resilience and social responsibility, can inspire global storytelling and narrative. These narratives, emphasizing sustainability and communal values, can create impactful stories that shape global perspectives.
Iceland’s Role in Global Challenges
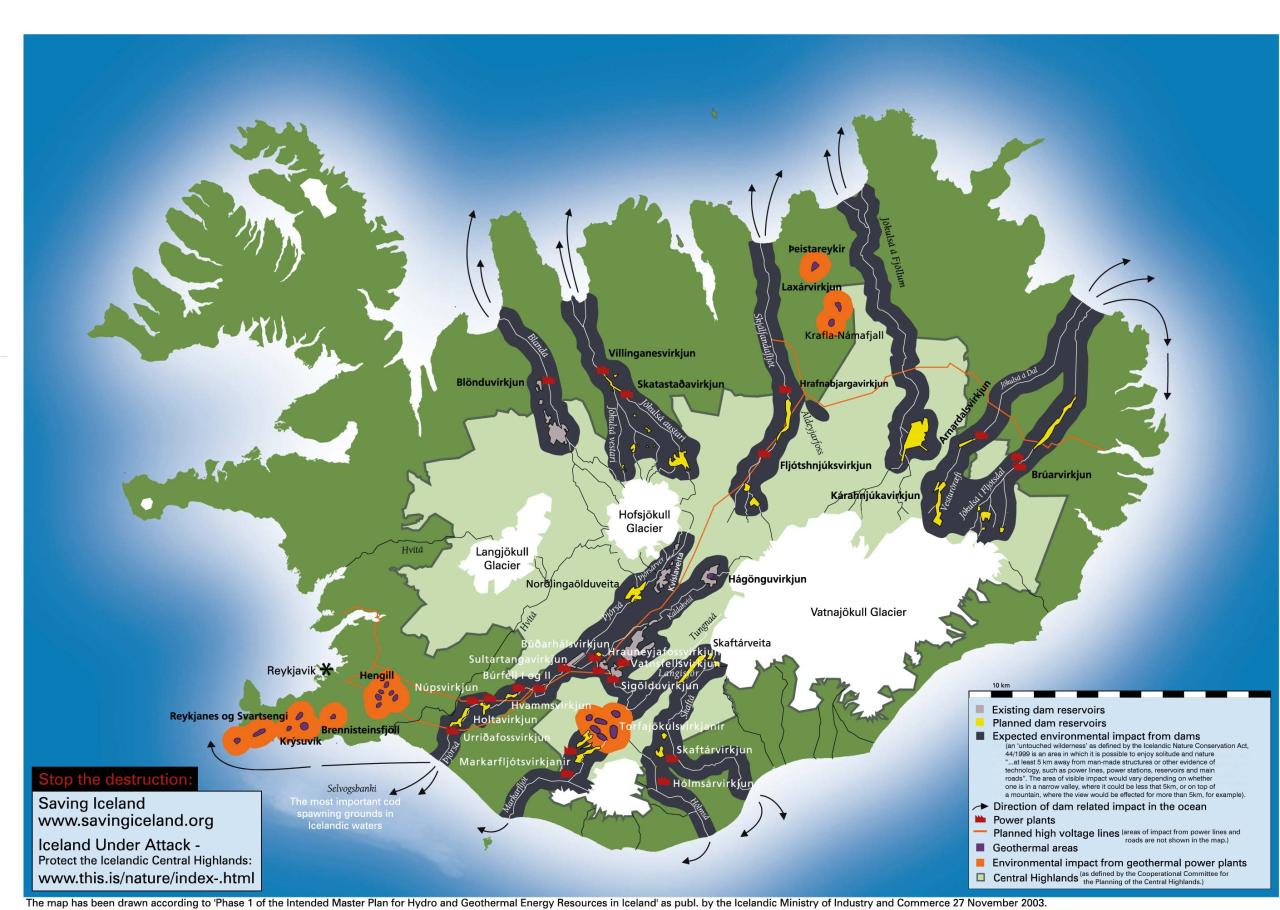
Iceland, a land of stark beauty and resilient spirit, offers a unique perspective on navigating global challenges. Its geographically isolated position, coupled with a strong commitment to environmental sustainability and social well-being, allows it to serve as a valuable model for other nations. This exploration delves into Iceland’s approach to addressing climate change, resource management, and social equity, highlighting its potential to inspire global change and international collaboration.Iceland’s approach to global challenges is rooted in its unique combination of natural resources, advanced technological capabilities, and a deep-seated commitment to social progress.
This approach is not simply a response to global concerns but rather an integral part of Iceland’s national identity and long-term vision.
Addressing Climate Change
Iceland’s commitment to mitigating climate change is evident in its proactive renewable energy policies. Hydropower and geothermal energy are fundamental components of the Icelandic energy sector, significantly reducing reliance on fossil fuels. This transition is not just economically beneficial; it also sets a benchmark for other nations seeking to decarbonize their economies. Iceland’s experience demonstrates that a transition to renewable energy is not only possible but also economically viable, particularly when coupled with innovative technologies.
For example, Iceland’s geothermal energy plants are often integrated into broader community development projects, showcasing the potential for sustainable economic growth.
Resource Management Practices
Iceland’s approach to resource management prioritizes sustainability. Careful planning and responsible exploitation of natural resources, including fisheries and geothermal energy, ensure long-term viability. The country’s emphasis on sustainable fishing practices, including quotas and regulations, has contributed to the healthy state of its marine ecosystems. These examples showcase how responsible resource management is essential for ensuring the longevity of both natural and economic systems.
Iceland’s approach to resource management is an example of how nations can prioritize both economic growth and environmental protection.
Promoting Social Equity
Iceland has a strong tradition of social equity, exemplified by progressive social policies. High levels of gender equality, comprehensive social safety nets, and strong emphasis on education contribute to a society where opportunities are more equally distributed. This commitment to social equity is reflected in Iceland’s policies, including robust support for families and affordable childcare. The country’s success in achieving high levels of social equity demonstrates that social progress and economic prosperity are not mutually exclusive.
International Collaborations
Iceland’s engagement in international collaborations extends across various sectors, including climate change initiatives and resource management. The country actively participates in international forums and initiatives, sharing its knowledge and expertise with other nations. Examples of these collaborations include participation in international agreements on climate change, sharing best practices in renewable energy development, and exchanging expertise on sustainable fisheries management.
These collaborations underline Iceland’s commitment to working with other nations to address global challenges.
Iceland as a Model for Global Partnerships
Iceland’s approach to global challenges provides a valuable template for future partnerships. The country’s unique blend of natural resources, technological prowess, and social policies positions it as a potential model for other nations. By embracing innovative approaches to resource management and social equity, Iceland can inspire international cooperation and pave the way for a more sustainable and equitable future for all.
Iceland’s commitment to international collaborations and its willingness to share best practices are key factors in its potential to become a model for future global partnerships.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, Iceland’s commitment to sustainability, technological innovation, and social well-being paints a compelling picture of a future we can strive for. Their successes, challenges, and potential for inspiring global change are explored in detail. By understanding Iceland’s journey, we can better envision a more sustainable and equitable world. The tables included offer concrete examples and comparisons, highlighting the potential for other nations to learn and adapt.
Common Queries
What are some specific examples of Iceland’s sustainability initiatives?
Iceland boasts a robust renewable energy sector, primarily utilizing geothermal and hydropower. They’ve also implemented ambitious waste management programs, focusing on recycling and minimizing landfill use. Specific examples are detailed in the article.
How does Iceland’s approach to social equality differ from other developed nations?
Iceland’s strong emphasis on gender equality, social safety nets, and community engagement sets it apart. The article compares their societal models to other developed nations and highlights the unique aspects of their approach.
What are the potential risks or limitations of Iceland’s model?
While Iceland’s model offers many benefits, challenges like population density and resource limitations could hinder their ability to scale some initiatives. The article acknowledges these potential constraints.
Can Iceland’s model be replicated in other nations?
While Iceland’s model is unique, its core principles – sustainability, social responsibility, and innovation – can be adapted and implemented in other countries. The article provides analysis of how Iceland’s approaches can inspire global change.






