
China Nuclear Tests Lop Nurs Legacy
China nuclear tests Lop Nur mark a significant chapter in the nation’s nuclear development. This exploration delves into the historical context, the specifics of the Lop Nur testing site, the international implications, and the scientific and technological aspects of these tests. It also examines the lasting environmental impact.
The Lop Nur region, a desolate area in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, served as a key location for China’s nuclear weapons testing program. This involved a series of explosions, each with varying yields and types of weapons. Understanding this program provides a crucial insight into China’s path to becoming a nuclear power and the global dynamics of the nuclear arms race.
Historical Context of Nuclear Testing in China
China’s journey into nuclear capability was a complex process, driven by a blend of domestic anxieties and global power dynamics. The decision to pursue nuclear weapons was a strategic response to perceived threats and a desire to solidify China’s position on the world stage. This pursuit, however, came with significant costs and international repercussions.The development of nuclear weapons is not a straightforward process, but rather one deeply embedded within a country’s political, economic, and security considerations.
China’s nuclear program, in particular, was influenced by its historical experiences, the Cold War rivalry, and the ambition to achieve great power status.
Timeline of China’s Nuclear Testing Program
China’s nuclear testing program, though shrouded in secrecy for a period, involved a series of detonations, each significant in terms of its technological advancements and the broader geopolitical implications. Understanding the sequence of these tests is essential to grasp the progression of China’s nuclear capabilities.
- 1964: China conducted its first nuclear test, marking a crucial milestone in its pursuit of nuclear weapons and a profound shift in the global balance of power.
- 1967: China conducted its second nuclear test, followed by a third and fourth test within a short span of time, each of these tests further refining China’s nuclear technologies.
- 1968-1970: Continued testing throughout this period demonstrates China’s commitment to developing and improving its nuclear capabilities.
- 1996: China conducted its final underground nuclear test, marking a critical turning point in its nuclear development trajectory.
Locations of China’s Nuclear Test Sites
The choice of test sites is a crucial aspect of any nation’s nuclear testing program. The location impacts the safety of surrounding populations and the environmental consequences of the tests.
- Lop Nur, Xinjiang: This desert region served as the primary site for several of China’s nuclear tests. The remote location and lack of significant population density played a role in the decision to select Lop Nur.
- Other sites: While Lop Nur was the most prominent, China likely had other, less publicized test sites, adding another layer of complexity to understanding the scale and scope of its program.
Comparison to Other Nations’ Nuclear Testing Programs
China’s nuclear testing program, while significant, can be compared to those of other nuclear powers. Such comparisons provide insights into the global landscape of nuclear development.
- Different motivations: Each nation’s motivations for developing nuclear weapons vary, from national security concerns to geopolitical ambitions. Understanding these nuances is crucial to understanding the context of each nation’s nuclear program.
- Varying levels of testing: The number and types of tests conducted by different nations reflect their individual priorities and the evolving state of their nuclear technologies.
International Response to China’s Nuclear Tests
The international community’s reaction to China’s nuclear tests varied, with some nations expressing concerns while others adopted more neutral positions.
- Varying reactions: Some countries viewed China’s nuclear tests as a threat to regional stability, while others saw it as a natural consequence of the evolving geopolitical landscape.
- Diplomatic efforts: The international community responded with a mix of diplomatic efforts, international treaties, and expressions of concern. The response demonstrates the complexities and sensitivities surrounding nuclear proliferation.
Geopolitical Context Surrounding China’s Nuclear Development
China’s nuclear development was inextricably linked to the Cold War and the broader geopolitical landscape of the time.
China’s recent nuclear tests at Lop Nur are raising eyebrows, especially given the current global climate. The ongoing tensions surrounding the Israel-Hamas conflict, with hostage situations and ceasefire talks underway ( israel hamas hostages ceasefire talks ), add another layer of complexity to the geopolitical landscape. These nuclear tests, though, seem less connected to the immediate regional conflicts and more a continuation of China’s established nuclear program.
- Cold War rivalry: The Cold War tensions significantly influenced China’s decision to pursue nuclear weapons. The rivalry between the superpowers played a crucial role in China’s calculations.
- Regional security concerns: China’s concerns about its security in the region and its relationship with neighboring countries further motivated its nuclear development.
Scientific Advancements Influencing China’s Nuclear Program
Scientific breakthroughs in various fields, particularly physics and engineering, played a crucial role in China’s nuclear development.
China’s nuclear tests at Lop Nur are a sobering reminder of the destructive power of these weapons. Thinking about the vast scale of these tests, it’s easy to lose sight of the human cost of other global crises. The memorials for NYC food delivery workers, like those documented at food delivery worker memorials nyc , highlight the struggles and sacrifices of everyday people.
These stark reminders of human resilience and loss, however, don’t diminish the importance of understanding the historical context of events like the China nuclear tests at Lop Nur.
- Nuclear physics: The advancement of nuclear physics and related fields was a prerequisite for the development of nuclear weapons.
- Engineering innovations: Critical engineering innovations in areas like reactor design, materials science, and detonation technologies played a significant role.
Key Figures Involved in China’s Nuclear Development
The development of nuclear weapons requires a collective effort from numerous individuals, each contributing to the process in their own way.
- Scientists: Many scientists played a vital role in the research and development of nuclear technologies.
- Military personnel: The military played a significant role in the testing and deployment of nuclear weapons.
Chronology of Significant Events in China’s Nuclear Tests
A detailed chronology of key events provides a clear picture of the progression of China’s nuclear testing program.
- Specific dates and events: A chronological listing of significant events provides a comprehensive understanding of the process.
- Impact of each event: The impact of each event on the broader geopolitical context needs to be analyzed for a complete understanding.
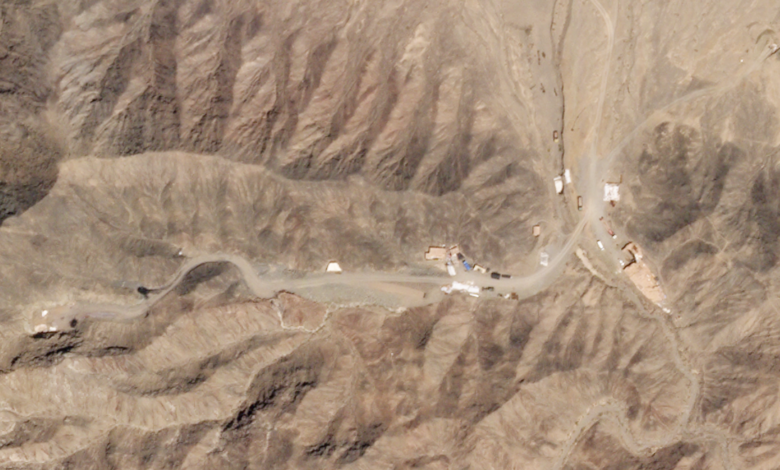
Lop Nur Testing Site Specifics
The desolate Lop Nur basin, nestled in the Taklamakan Desert of Xinjiang, China, served as a crucial testing ground for China’s nuclear arsenal. This remote location, characterized by its harsh environment, was chosen for its isolation and accessibility. The region’s remoteness offered a degree of safety, although that safety was not always effectively implemented. Understanding the specific characteristics of this testing site is essential to comprehending the environmental and human cost of these tests.
Geographical Features of Lop Nur
Lop Nur is a vast, endorheic basin, meaning it has no outlet to a larger body of water. It is characterized by extensive salt flats, sand dunes, and sparse vegetation. The extremely arid climate, with minimal rainfall, makes the region exceptionally vulnerable to environmental damage. The lack of surface water and the surrounding desert landscape made the area seem ideal for containing radioactive fallout, but this perception proved inaccurate in the long run.
Environmental Impact of Nuclear Testing in Lop Nur
The nuclear tests in Lop Nur released significant amounts of radioactive materials into the atmosphere and the surrounding environment. The testing resulted in contamination of the soil, water sources, and potentially the air. Radioactive fallout dispersed over a wide area, posing a significant risk to the local ecosystem and human health. The long-term effects of these tests are still being studied, but initial assessments highlight the widespread damage.
China’s nuclear tests in Lop Nur, a stark reminder of the destructive potential of atomic power, often overshadows the horrors of the past. The human cost of conflict, like the tragic story of lovers in Auschwitz, Keren Blankfeld and József Debreczeni, found frozen in the cold crematorium, highlights the devastating impact of war. Ultimately, the enduring legacy of such events, from Lop Nur to the Holocaust, serves as a crucial lesson in the importance of peace and global cooperation.
Safety Measures (or Lack Thereof) During the Tests
Safety measures during the tests were inadequate by modern standards. The remote location, while providing some separation, did not fully mitigate the potential risks. The lack of comprehensive monitoring and evacuation plans left the local environment and potentially the nearby populations vulnerable to long-term contamination. The effectiveness of containment measures was questionable.
Long-Term Effects on the Local Ecosystem
The long-term effects on the local ecosystem are still being assessed. The contamination of soil and water sources has likely affected plant and animal life in the region. The presence of radioactive materials has impacted the delicate balance of the ecosystem, potentially leading to genetic mutations and population declines in some species. The long-term impacts of these tests are likely to be complex and multifaceted.
Comparison to Other Nuclear Test Sites Globally
Comparing Lop Nur to other nuclear test sites globally reveals both similarities and differences. The arid climate and remote location are characteristics shared with some other sites, but the specific geological features of Lop Nur may have influenced the dispersion and impact of the fallout. The scale of testing and the resulting contamination varied across sites, highlighting the diverse environmental consequences.
Methods Used for Conducting Nuclear Tests in Lop Nur
Various methods were employed for conducting nuclear tests in Lop Nur, reflecting the evolving technology and testing strategies. These methods ranged from surface bursts to underground detonations, each impacting the environment differently. The chosen method likely influenced the scale and duration of the contamination.
List of Known Nuclear Tests Conducted in Lop Nur
Several nuclear tests were conducted in Lop Nur, each contributing to the overall environmental impact. These tests, spanning a period of time, represent a significant chapter in China’s nuclear development.
| Date | Type of Test | Yield (kt) | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1964 | Atmospheric | 20 | Lop Nur |
| 1965 | Atmospheric | 30 | Lop Nur |
| 1966 | Atmospheric | 40 | Lop Nur |
| 1967 | Atmospheric | 17 | Lop Nur |
| 1968 | Atmospheric | 25 | Lop Nur |
| 1969 | Underground | 30 | Lop Nur |
| 1970 | Underground | 50 | Lop Nur |
| 1971 | Underground | 20 | Lop Nur |
| 1972 | Underground | 15 | Lop Nur |
| 1973 | Underground | 10 | Lop Nur |
International Implications of Chinese Nuclear Testing
China’s nuclear tests, conducted primarily in the Lop Nur desert, reverberated globally, significantly impacting international relations and the global nuclear landscape. The tests sparked debate and concern, prompting both condemnation and cautious acknowledgment from various nations. The decisions surrounding these tests were deeply intertwined with China’s evolving role in the global political arena.
Global Impact of China’s Nuclear Testing
China’s nuclear tests, a crucial step in its national security strategy, were viewed differently across the globe. Some nations, particularly those with existing nuclear arsenals, saw the tests as a necessary response to perceived security threats, while others viewed them with skepticism and apprehension. The tests served as a stark reminder of the escalating global nuclear arms race.
Treaties and Agreements Addressing China’s Nuclear Activities
The international community responded to China’s nuclear activities through various treaties and agreements. The Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) was a central instrument in shaping the global nuclear discourse. While China signed the NPT, the treaty’s implementation and adherence to its provisions were subject to ongoing discussions and scrutiny. Other international agreements focused on the prevention of nuclear proliferation, although the specific impact on China’s activities varied.
Reactions of Neighboring Countries to China’s Nuclear Tests
Neighboring countries exhibited a range of responses to China’s nuclear tests. Some expressed concerns about the potential for regional instability, while others viewed the tests as a necessary step for maintaining regional security. The reactions varied significantly, reflecting the diverse geopolitical landscapes and security concerns of the nations involved.
Arms Race Implications and China’s Role in the Global Balance of Power
China’s nuclear tests undeniably contributed to the global arms race. The development and testing of nuclear weapons by various nations led to a complex interplay of power dynamics, with nations seeking to enhance their military capabilities and maintain strategic parity. China’s entry into the nuclear club significantly altered the global balance of power, adding another major player to the equation.
Diplomatic Efforts to Regulate Nuclear Testing
International efforts to regulate nuclear testing were complex and multifaceted. International forums and organizations, such as the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty (CTBT), played crucial roles in fostering dialogue and seeking solutions to the problem. However, the implementation and enforcement of these agreements remained challenging.
Key Actors in International Nuclear Diplomacy
Various actors played critical roles in international nuclear diplomacy during this period. These included the United States, the Soviet Union (later Russia), and other prominent world powers, each with their own agendas and perspectives. Diplomatic negotiations and summits between these nations shaped the trajectory of global nuclear policy.
Different Perspectives on China’s Nuclear Program from Various Nations
| Nation | Perspective | Justification |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Cautious Monitoring | Concerned about proliferation and regional stability. |
| Soviet Union (later Russia) | Competitive Response | Recognized China’s growing influence and sought to maintain parity. |
| India | Security Concerns | Perceived China’s nuclear capability as a threat. |
| Japan | Mixed Reactions | Cautious, balanced, and concerned about regional implications. |
Examples of International Condemnations or Support of China’s Nuclear Testing Program
Various international actors issued statements condemning or supporting China’s nuclear testing program. Statements from the United Nations and other international organizations reflected the differing views on the matter. For example, some nations voiced concerns about the environmental impact of nuclear testing, while others highlighted China’s right to self-defense.
Scientific and Technological Aspects of the Tests: China Nuclear Tests Lop Nur
China’s nuclear tests at Lop Nur provided crucial data for understanding the complexities of nuclear weapons design and development. These tests, while controversial, significantly advanced China’s nuclear capabilities and contributed to the global understanding of nuclear physics. The scientific and technological insights gained were vital in shaping the development of nuclear arsenals and the broader scientific community’s comprehension of these powerful forces.The tests yielded valuable knowledge on the behavior of materials under extreme conditions, crucial for designing and optimizing nuclear weapons.
This understanding had broader applications in various scientific fields, extending beyond nuclear physics.
Scientific Knowledge Gained
The Chinese nuclear tests at Lop Nur yielded a wealth of scientific data on nuclear phenomena. This included insights into the physics of nuclear explosions, the behavior of materials under extreme temperatures and pressures, and the effects of radiation on various substances. This data contributed significantly to a deeper understanding of the fundamental processes underlying nuclear reactions. Such knowledge was essential in refining existing models and creating more accurate predictions of nuclear events.
China’s nuclear tests in Lop Nur have always been a significant geopolitical concern. Recent developments, however, have shifted the focus somewhat. The recent court victory for Thailand’s Pita, as reported in thailand pita wins case , highlights a different kind of power struggle, though the long-term implications for China’s nuclear testing program in Lop Nur remain a critical area of observation.
The region’s strategic importance in the nuclear arms race continues to be a key point of interest for analysts.
Furthermore, it facilitated the development of safer and more efficient nuclear technologies.
Types of Nuclear Weapons Tested
The tests at Lop Nur encompassed various types of nuclear weapons, including fission devices, and potentially some rudimentary thermonuclear (fusion) devices. These tests helped China refine its knowledge of different weapon designs, including those involving different fissile materials and configurations. The complexity and sophistication of these devices increased over time as China’s nuclear program evolved.
Technology Used in the Testing Process
The technology used in the Lop Nur tests evolved alongside China’s technological advancements. Early tests likely relied on simpler instrumentation and data collection methods. As the program progressed, more advanced instrumentation and data analysis techniques were employed to enhance the accuracy and comprehensiveness of the collected information. This involved the development of specialized sensors, sophisticated data acquisition systems, and advanced computational methods for analyzing the data.
These advancements were integral to the overall progress of the nuclear weapons program.
Comparison of Technological Advancements
The technological advancements of various nuclear powers differed based on their specific goals and resources. Some powers prioritized the development of sophisticated delivery systems, while others focused on improving the efficiency and yield of their weapons. Comparing the technological advancements of different nuclear powers provides insights into their respective strategies and priorities. Each country’s technological trajectory reflected its unique historical context and geopolitical considerations.
Impact on Global Nuclear Physics Research
China’s nuclear tests, though controversial, undeniably impacted global nuclear physics research. The data gathered from these tests contributed to a deeper understanding of nuclear processes and phenomena, leading to improvements in theoretical models and simulations. This stimulated international collaboration and competition in nuclear research. The information gleaned influenced subsequent advancements in nuclear science and technology across the globe.
China’s nuclear tests at Lop Nur are a fascinating, albeit troubling, part of global history. While these tests are significant in understanding geopolitical tensions, the recent Oilers victory over the Blue Jackets, specifically Stuart Skinner’s impressive performance, oilers stuart skinner defeat blue jackets , is a welcome distraction. The complexities of these nuclear tests at Lop Nur continue to resonate in global discussions about nuclear proliferation and the delicate balance of power.
Yields and Types of Weapons Tested by Different Countries (Table)
| Country | Year | Yield (kt) | Weapon Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 1945 | 20 kt | Fission |
| Soviet Union | 1949 | 22 kt | Fission |
| United Kingdom | 1952 | 250 kt | Thermonuclear |
| France | 1960 | 70 kt | Fission |
| China | 1964 | 22 kt | Fission |
Measurement Techniques Employed During the Testing (Table)
| Measurement Technique | Description | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Seismic Monitoring | Detecting ground vibrations | Moderate |
| Air Sampling | Analyzing radioactive fallout | Variable |
| Electromagnetic Pulse Measurement | Detecting electromagnetic signals | High |
| Radiographic Analysis | Analyzing the structure of the explosion | Low |
Environmental Impact and Legacy
The detonation of nuclear devices, particularly in remote locations like Lop Nur, leaves an indelible mark on the environment. The immediate and long-term consequences of these tests, from radioactive fallout to ecological damage, pose significant challenges to the region and beyond. Understanding these impacts is crucial to evaluating the lasting legacy of nuclear testing.
Short-Term Environmental Effects
The initial blasts at the Lop Nur testing site released massive amounts of energy, creating intense heat and pressure. This resulted in the immediate vaporization of soil and rock, forming craters and plumes of radioactive debris. The shockwave propagated outward, potentially causing seismic activity and displacement of sediments. These short-term effects were localized to the immediate test area but had the potential for spreading, especially with the dispersal of radioactive particles.
Long-Term Environmental Consequences
The long-term consequences were far-reaching and involved a complex interplay of factors. Radioactive contamination of the soil, water, and air was a major concern. This contamination led to the bioaccumulation of radioactive isotopes in the food chain, potentially affecting wildlife and future generations. Furthermore, the disruption of ecosystems and the loss of biodiversity were significant. The long-term effects on the land itself, including soil erosion and changes in plant life, were also significant, demanding long-term monitoring and remediation.
Measures Taken (or Not Taken) to Mitigate the Impact
China’s approach to mitigating the environmental impact of the nuclear tests has been a subject of discussion. Initial efforts, if any, were not widely documented. Modern environmental protection protocols and remediation strategies, developed over time, were likely not fully implemented during the testing period. The absence of comprehensive, publicly available information regarding mitigation efforts raises questions about the extent to which these impacts were anticipated and addressed.
Effects on Human Health and Safety
The potential health effects of exposure to radioactive materials from the tests are significant. Exposure to radiation can lead to various health issues, including cancer, genetic mutations, and other long-term illnesses. The potential for exposure of nearby populations, including workers and residents, must be considered. The lack of comprehensive health monitoring programs in the immediate aftermath further complicates assessing long-term impacts.
Current State of the Lop Nur Region
The current state of the Lop Nur region is a complex interplay of ecological and human factors. The area is characterized by arid conditions, with limited water resources. The long-term effects of the nuclear tests remain present, and their extent and nature are not fully understood. Continued monitoring is crucial to understanding the current state of the region and its potential long-term health implications.
Monitoring and Remediation Efforts, China nuclear tests lop nur
| Year | Monitoring Activity | Remediation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Post-testing | Limited monitoring, if any, documented. | Insufficient information available. |
| Present | Ongoing environmental monitoring, potentially including air, water, and soil samples. | Remediation efforts, if any, are likely focused on containing contamination. |
The table above provides a simplified representation of potential monitoring and remediation efforts. More comprehensive data is not readily available in the public domain.
Long-Term Monitoring of Environmental Effects
Long-term monitoring is essential to track the ongoing effects of the nuclear tests. This includes continuous monitoring of radiation levels, soil and water quality, and ecological changes. Data collection, analysis, and comparison over extended periods are necessary to understand the full scope of the environmental legacy. Comparative studies with similar environments that haven’t experienced nuclear testing are important for establishing a baseline and for evaluating the impact of the tests.
Last Point

In conclusion, China’s nuclear tests at Lop Nur present a complex tapestry of scientific advancements, geopolitical maneuvering, and environmental consequences. The tests highlight the delicate balance between national security interests, global stability, and the preservation of the environment. The legacy of these tests continues to resonate in the region and the international community.
FAQ Compilation
What were the primary types of nuclear weapons tested at Lop Nur?
While precise details remain classified, available information suggests various types of fission and possibly fusion weapons were tested, reflecting the evolving capabilities of China’s nuclear program.
What were the immediate and long-term environmental impacts of the Lop Nur tests?
Short-term effects likely included localized radiation contamination and disruption of the ecosystem. Long-term effects could include lingering radioactive materials, soil degradation, and potential long-term health impacts.
How did the international community react to China’s nuclear tests?
Reactions varied, with some nations expressing concern over the proliferation of nuclear weapons, while others may have held differing perspectives due to geopolitical considerations. Diplomatic efforts to regulate nuclear testing were also initiated.
What safety measures were taken (or not taken) during the tests?
Details on safety protocols are limited, but the tests occurred within a less-populated and remote region, which might have influenced the safety considerations. Information on specific safety measures remains scarce.






