
Iowa Caucus Vote Counting A Deep Dive
Iowa caucus vote counting sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. From historical processes to modern technology, we’ll explore the intricacies of how votes are tallied in the crucial Iowa caucuses, examining the evolution of the process and the challenges involved.
This analysis will consider the impact of vote counting on election outcomes and the public’s perception of the entire process.
The Iowa caucus vote counting process is a complex undertaking, involving numerous steps and stakeholders. This exploration delves into the historical context, outlining the progression from manual methods to advanced electronic systems. We’ll examine the various procedures, from initial counting to final verification, highlighting the importance of accuracy and integrity. The challenges and potential issues, such as delays and disputes, will also be thoroughly discussed, along with strategies for improvement.
Historical Context of Iowa Caucus Vote Counting
The Iowa caucuses, a crucial first step in the American presidential nominating process, have a rich history marked by evolving vote counting methods. From its humble beginnings, the process has undergone significant transformations, adapting to changing political landscapes and technological advancements. This evolution reflects the ongoing quest for fairness, accuracy, and efficiency in democratic processes.The early caucuses relied heavily on personal interactions and local gatherings, making the vote counting process relatively straightforward, yet prone to human error.
Over time, the growing number of participants and the increasing complexity of candidate platforms necessitated a more structured and transparent system for tallying votes.
Evolution of Vote Counting Methods
The initial Iowa caucuses relied on manual methods, with tallies kept by volunteers and local party officials. This process, while participatory, was susceptible to errors and inconsistencies. As the caucuses gained prominence, there was a clear need for improvements in accuracy and transparency.The introduction of paper ballots and standardized forms improved the process of recording votes. This development led to more organized tabulation and significantly reduced the possibility of errors.
These methods, however, still faced limitations in terms of speed and scalability.Subsequently, the advent of electronic voting systems introduced a new era in Iowa caucus vote counting. Electronic systems enabled faster and more precise vote counting, providing real-time results and reducing the potential for human error. The shift to electronic systems also brought new challenges, such as the need for robust cybersecurity measures and the potential for malfunctioning equipment.
Different Roles and Responsibilities
Historically, the roles involved in vote counting were primarily volunteer-based. Local party members and precinct captains played crucial roles in collecting and recording votes. The evolution of the process has led to the development of specific roles, such as dedicated counting staff and supervisors, who are responsible for ensuring the accuracy and integrity of the process. These roles often involve training and adherence to strict procedures.Currently, trained election officials are responsible for handling all aspects of the vote counting process.
Their duties include verifying voter registration, distributing ballots, overseeing the counting process, and ensuring compliance with established rules and regulations. The development of these roles has fostered greater accountability and transparency.
Comparison with Other States’ Primary Elections
The Iowa caucuses are unique in their approach compared to other states’ primary elections. While some states utilize similar electronic systems, others continue to employ manual or hybrid methods. The use of precinct-level meetings distinguishes the Iowa caucuses, resulting in a different vote counting process compared to other states’ methods, which typically involve centralized voting locations and electronic voting machines.The unique nature of the Iowa caucuses necessitates specialized procedures to handle the complexities of the process.
These procedures need to accommodate the nuances of local gatherings and the need for real-time reporting of results.
Legal Framework and Regulations
Iowa’s election laws, specifically those governing caucuses, establish guidelines for vote counting procedures. These regulations Artikel the responsibilities of election officials, the requirements for maintaining accurate records, and the procedures for resolving disputes. Compliance with these laws is essential for ensuring the integrity and fairness of the election.The legal framework ensures that the counting process adheres to established standards of accuracy and transparency.
The procedures for challenging results and addressing discrepancies are clearly defined within the regulations.
Processes and Procedures

The Iowa caucuses, a crucial early step in the US presidential nominating process, involve a unique and often complex vote counting system. Understanding the intricacies of this process is essential to evaluating the reliability and accuracy of the results. This detailed look at the procedures sheds light on the steps involved, the verification methods employed, and the potential challenges inherent in this system.The Iowa caucuses are notable for their reliance on in-person gatherings of voters.
These gatherings, often held in community centers, schools, or other local venues, are where voters declare their support for a particular candidate. The process involves a complex interplay of voter declarations and subsequent vote tallies.
Vote Counting Steps
The vote counting process in the Iowa caucuses begins at the precinct level, where volunteers diligently record the number of voters supporting each candidate. This initial count is critical as it forms the foundation for the subsequent aggregation of votes. These tallies are often manually recorded and verified, requiring careful attention to detail and accuracy. Precinct-level tallies are then forwarded to county headquarters for further consolidation.
This meticulous aggregation is essential for establishing a precise count of votes cast at the county level.
Verification Methods
Ensuring the integrity of the vote count is paramount. Several verification methods are employed at each stage of the process. These include cross-referencing precinct tallies against voter registration records to identify potential discrepancies and errors. Additionally, trained staff meticulously review the data for inconsistencies and discrepancies. This careful review process minimizes the chance of errors creeping into the final tally.
Audits are also conducted by independent observers to provide an extra layer of scrutiny. These observers’ independent analysis adds another layer of verification.
Volunteer and Staff Roles
Volunteers play a vital role in the Iowa caucuses, from organizing precinct gatherings to assisting with vote counting. Their dedication is crucial for the smooth execution of the process. Trained staff at the county and state levels oversee the aggregation and reporting of the results. Their expertise in managing the data and ensuring accuracy is critical. The staff’s training and experience contribute significantly to the reliability of the vote count.
Challenges and Potential Errors
The caucus system, while engaging, presents potential challenges in vote counting. Manual data entry is susceptible to human error, leading to potential inaccuracies. Differences in reporting procedures across various precincts can introduce discrepancies. Inadequate training for volunteers may lead to errors in recording and reporting. Difficulties in coordinating the reporting process across different precincts can cause delays and discrepancies.
The complexity of the system, with its numerous steps and personnel involved, creates an environment susceptible to human error.
Impact of Different Voting Methods
The Iowa caucuses, primarily using a system of in-person declarations, differs from other voting methods. This can affect the vote count’s accuracy. For instance, the lack of a paper ballot makes the verification process more reliant on the accuracy of the initial tallies. This unique aspect of the caucus process has implications for the reliability of the final count.
The in-person declaration method also influences voter turnout, which in turn affects the representativeness of the final vote count. The process may be susceptible to issues with voter turnout and the accuracy of tallies if volunteers are inadequately trained.
Iowa caucus vote counting is a fascinating process, highlighting the intricacies of American democracy. While the counting progresses, it’s interesting to consider how employee ownership initiatives like those at KKR private equity, KKR private equity employee ownership , might impact worker engagement and ultimately, the broader political landscape. The long-term implications of these models for future elections, and the potential for broader shifts in voting patterns, will be worth watching as the Iowa caucus vote counting concludes.
Technology and Automation
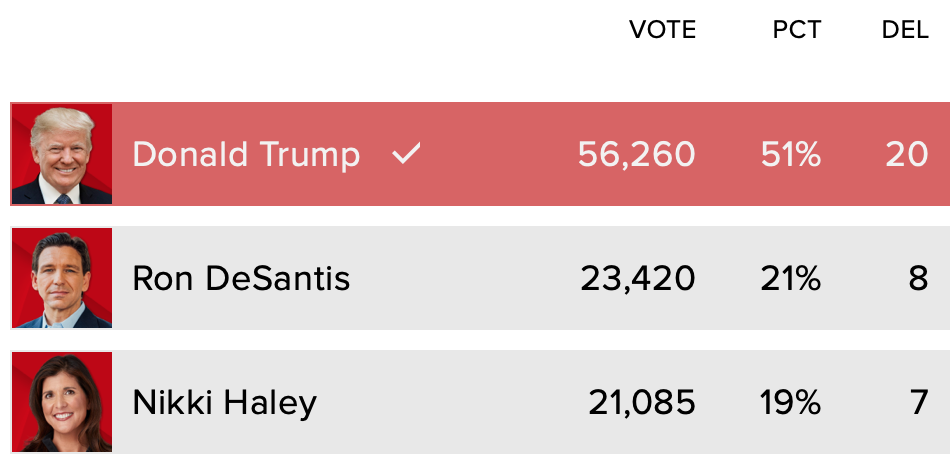
The Iowa caucuses, a crucial moment in the American presidential election process, have always been associated with manual vote counting. However, the ever-evolving landscape of technology presents opportunities for enhanced efficiency and accuracy in future vote tabulation. This section delves into the potential and practical applications of technological tools in streamlining the Iowa caucus vote counting process.
Technological Tools Used in Iowa Caucus Vote Counting
Modernizing the vote counting process necessitates a blend of software and hardware solutions. These tools can significantly reduce human error and expedite the tabulation process.
| Category | Tool | Description | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Software | Dedicated Vote Counting Software | Custom-designed software specifically for recording and tallying votes, often with features like real-time updates and data validation. | Tracks individual precinct results, and automatically calculates totals for each candidate. |
| Software | Spreadsheet Software (e.g., Google Sheets, Microsoft Excel) | Used for preliminary data entry and basic calculations, but often less efficient for large-scale operations. | Recording preliminary vote tallies from individual precincts. |
| Hardware | Touchscreen Devices | Electronic interfaces that allow for efficient data entry and immediate updates of results. | Data entry workers input vote tallies from paper ballots directly into the system. |
| Hardware | Barcode Scanners | Used to scan barcodes on ballots or voter registration cards to quickly verify voter information. | Verifying voter eligibility and ballot authenticity during the counting process. |
Benefits and Drawbacks of Automation
Implementing automation in vote counting offers several advantages. Real-time results, reduced manual errors, and enhanced transparency are key benefits. However, the transition to automated systems also presents challenges.
Automation can significantly improve the speed and accuracy of vote counting by minimizing human error and facilitating rapid data processing.
Iowa caucus vote counting is definitely fascinating, but I’m also curious about the real estate market. For instance, how does the housing market in California, with its increasingly expensive 2 million dollar homes, compare to the rest of the nation? Understanding the economic factors impacting those 2 million dollar homes in California might offer interesting parallels to the complexities of Iowa caucus vote counting, which are still being tallied and debated.
It’s a fascinating contrast, isn’t it? 2 million dollar homes california Ultimately, both topics highlight the intricacies of modern American life.
Automation’s potential drawbacks include the cost of implementing and maintaining the necessary technology, as well as the potential for technical glitches during the process. Concerns about data security and the possibility of system manipulation also require careful consideration.
Improving Speed and Accuracy Through Technology
Integrating technology into the vote counting process directly impacts the speed and accuracy of the results. Sophisticated software can automatically verify vote entries, compare them against voter registration data, and quickly calculate totals. This automation streamlines the process and reduces the likelihood of human errors, leading to faster and more accurate outcomes.
Data Security Measures
Robust data security measures are crucial during the vote counting process. Implementing encryption, access controls, and regular system audits ensures the confidentiality and integrity of the vote count data. These safeguards protect against unauthorized access and potential manipulation of the results.
Data Collection Methods
Data collection is a vital component of the vote counting process. Multiple methods are used to ensure comprehensive and reliable data gathering.
| Method | Description | Example Use Case | Strengths |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Entry | Traditional method of recording votes by hand. | Early stages of counting, especially for initial precinct totals. | Relatively low cost and easy to understand. |
| Optical Scanners | Machines that read and interpret marks on ballots. | High-volume counting of paper ballots. | High speed and accuracy for large numbers of ballots. |
| Electronic Voting Machines | Machines that record votes digitally. | Modern vote counting with immediate results. | Eliminates manual handling of ballots, reducing potential errors. |
| Real-time Data Transmission | Systems that transmit data to central locations for consolidation. | Provides instantaneous results from precincts as they are tallied. | Enhanced transparency and accountability in the counting process. |
Challenges and Issues: Iowa Caucus Vote Counting
The Iowa caucuses, while a significant part of the American presidential election process, are not without their complexities. Potential problems in vote counting can lead to delays, discrepancies, and ultimately, disputes, impacting the integrity of the process. Understanding these potential challenges and the mechanisms for addressing them is crucial for maintaining public trust and ensuring a fair outcome.
Potential Issues During Vote Counting
The Iowa caucus vote counting process, while carefully structured, is susceptible to several potential issues. Delays in reporting results from precinct to county to state levels can arise from various factors, including logistical difficulties, understaffing, or unexpected technical problems. Discrepancies in tallies between different reporting points can also occur, requiring careful investigation and reconciliation. Disputes can emerge from disagreements about procedures, interpretations of rules, or alleged irregularities in the count.
These issues, if not addressed promptly and transparently, can undermine the public’s confidence in the fairness and accuracy of the results.
Procedures for Addressing Issues and Resolving Disputes
Robust procedures are essential for managing potential issues and resolving disputes during the caucus count. These procedures typically involve a multi-layered approach, starting with on-site oversight and escalating to higher levels of review. Dedicated dispute resolution teams, with clearly defined roles and responsibilities, are often part of the process. These teams are responsible for investigating alleged irregularities and ensuring that disputes are handled fairly and efficiently.
Iowa caucus vote counting is always a fascinating process, and understanding the pre-vote buzz is key. Checking out the iowa caucus entrance polls can offer valuable insights into the likely outcome before the actual vote count. It’s a good way to gauge the mood and potential momentum heading into the official results, ultimately adding context to the final Iowa caucus vote counting numbers.
Well-defined appeal mechanisms and timelines are also crucial to ensure that all parties have the opportunity to present their case and have their concerns addressed.
Strategies for Improving Efficiency and Reliability
Several strategies can enhance the efficiency and reliability of the vote counting process. Implementing standardized procedures and training for all volunteers and staff involved in the counting process can minimize errors and inconsistencies. Leveraging technology, such as advanced data management systems and real-time reporting tools, can help streamline the process and reduce potential delays. Investing in robust auditing mechanisms and procedures to verify the accuracy of the count is crucial to ensuring reliability.
Importance of Transparency and Public Communication
Transparency and clear communication are vital components of a trustworthy vote counting process. Regular updates on the progress of the count, along with explanations of any delays or discrepancies, can help manage public expectations and address concerns. Open access to the vote counting data, with proper safeguards to protect sensitive information, builds public trust. Maintaining a consistent communication strategy across all levels of the process is paramount for a smooth and well-received count.
Comparison of Vote Counting Methodologies
| Method | Description | Potential Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Manual Counting | Traditional method relying on human counters. | Prone to human error, potentially slower, may lead to discrepancies. |
| Optical Scan | Utilizes optical scanners to read and record ballots. | Can be faster and more efficient, but susceptible to equipment malfunction or issues with ballot design. |
| Electronic Recording | Digital systems that record and tally votes electronically. | Can be very fast and efficient, but may require more technical expertise and have security considerations. |
Public Perception and Communication
The Iowa caucuses, a crucial first step in the US presidential nominating process, are often scrutinized for their unique voting methodology. Public perception of the vote counting process directly impacts the legitimacy and perceived fairness of the entire election cycle. Understanding how the public perceives this process and how it’s communicated is essential for maintaining trust and ensuring the process’s integrity.The public’s perception of the Iowa caucus vote counting process is shaped by a variety of factors.
Historically, the manual nature of the process, coupled with the logistical challenges of coordinating volunteers and reporting procedures, has sometimes led to delays and discrepancies. These factors, when coupled with the sometimes-complex and nuanced reporting, can create a perception of potential inaccuracies or irregularities.
Public Perception of the Process
The public often perceives the Iowa caucus vote counting process as a complex and potentially error-prone endeavor. This perception stems from the decentralized nature of the caucuses, where votes are tallied by volunteers at various locations. This manual process, while having a certain historical charm, contrasts with the more automated and readily verifiable systems often employed in other election processes.
Concerns about human error and the potential for miscounting, especially in large-scale events, are common. The public also often notes the lack of real-time updates and transparency during the count, which can exacerbate concerns about accuracy.
Communication of the Process
Effective communication of the Iowa caucus vote counting process is vital for managing public perception. Real-time updates and clear explanations of the process, both during and after the count, are crucial. Early and consistent communication can dispel anxieties and build confidence. Detailed explanations of the process, including the use of different methods for vote tabulation and the handling of potential discrepancies, should be available to the public.
Role of Media in Shaping Public Opinion
The media plays a significant role in shaping public opinion regarding the Iowa caucus vote count. The way the media frames the process, whether emphasizing potential irregularities or highlighting the volunteer-based efforts, can strongly influence public perception. A balanced and neutral reporting approach, including discussions of the established procedures and mechanisms in place to ensure accuracy, is essential.
Providing context about the historical evolution of the caucus process, including its unique features and limitations, can help the public understand the nuances of the vote count.
The Iowa caucus vote counting is finally underway, and the tension is palpable. While we’re focused on the political process, it’s interesting to note that in a completely different realm, the couture world is celebrating something equally significant: Didier Ludot’s 50th anniversary in Paris, with a stunning exhibition of his work couture Didier Ludot 50th anniversary Paris.
Hopefully, this will bring some much-needed glamour to the otherwise serious business of tallying the votes.
Strategies for Enhancing Public Trust
Several strategies can enhance public trust and confidence in the Iowa caucus vote counting process. Improved transparency through real-time updates, using readily available digital platforms for tracking, is crucial. Publicly outlining the protocols and procedures, along with the process for resolving potential disputes, can foster a sense of security and trust. Demonstrating accountability and rigorous adherence to established standards, including post-caucus audits, can reassure the public that the process is legitimate and fair.
Key Stakeholders and Responsibilities
| Stakeholder | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Iowa State Election Officials | Oversight, coordination, and ensuring adherence to established procedures. |
| Local Caucus Organizers | Planning, execution, and supervision of the count at local levels. |
| Volunteers | Collecting and reporting votes according to established procedures. |
| Media | Accurate and balanced reporting of the process, highlighting the efforts of all stakeholders. |
| Public | Following established procedures and participating in the democratic process. |
Impact on Election Outcomes
The Iowa caucuses, while often heralded as the first significant test of presidential candidates’ strengths, are not without their inherent complexities. The vote-counting process, with its unique features and potential for challenges, can significantly influence the final results and perceptions of the candidates. Understanding these influences is crucial for interpreting the outcome and assessing the broader impact on the election cycle.The Iowa caucuses’ influence extends beyond the initial buzz and early media coverage.
The very process of counting votes, from initial tallies to final reporting, can shape public perception of candidates, impact their fundraising, and ultimately affect their success in subsequent primary elections. Voter turnout, candidate strategies, and the often-uncertain timeline of the count all contribute to the final outcome.
Influence of Voter Turnout
Voter turnout in the Iowa caucuses is a critical factor affecting the outcome of the vote count. Higher turnout often leads to more diverse representation in the final results, potentially favoring candidates with broader appeal. Conversely, lower turnout can result in a less representative sample, potentially favoring candidates with strong support among a particular segment of the electorate. Analyzing historical turnout data and comparing it to the final results can offer valuable insights into the impact of turnout on candidate performance.
Impact of Voting Patterns
Voting patterns, particularly the distribution of support among various demographics, play a significant role in shaping the vote count. Candidates who resonate with specific voter groups can see strong support reflected in the initial tallies, potentially giving them an early lead. However, shifts in voting patterns throughout the counting process can significantly impact the final outcome, illustrating the importance of tracking and analyzing the evolving distribution of support.
For instance, a surge in support for a candidate late in the counting process could alter the projected outcome.
Impact of Election Regulations
Election regulations, including rules regarding voter registration, caucus participation, and vote-counting procedures, can profoundly affect the outcome. Stricter regulations, or those that are perceived as creating barriers for participation, can reduce voter turnout, leading to a less representative result. Conversely, clear and accessible regulations can encourage higher turnout and increase confidence in the fairness and accuracy of the count.
Iowa caucus vote counting is finally underway, and the slow pace is making some folks a bit antsy. It’s a fascinating glimpse into the early stages of a presidential race, but it’s also worth considering the bigger picture, like how the dwindling snow polo season in St. Moritz, Switzerland, reflects the impacts of climate change. This fascinating connection to snow polo st moritz climate change prompts us to consider the bigger picture of environmental factors, ultimately influencing even the most niche of human activities.
Perhaps the current vote count will reflect a similar shift in priorities. Still, let’s hope the Iowa caucus count wraps up quickly!
These regulations can impact the final vote totals, highlighting the importance of clear, transparent, and well-defined rules.
Effect on Voter Confidence
The vote-counting process can directly affect voter confidence in the results. Smooth, transparent, and timely vote counting fosters trust and validates the democratic process. Conversely, delays, discrepancies, or allegations of irregularities can erode voter confidence and cast doubt on the legitimacy of the outcome. Transparency in the process and timely communication of results are crucial to maintain voter confidence.
Comparison of Vote Counts Across Years
Comparing vote counts across different years of the Iowa caucus requires a structured approach. A detailed table, including columns for the year, candidate, vote count, and percentage of total votes, provides a clear overview. This method facilitates a direct comparison of candidate performance across different cycles.
| Year | Candidate | Vote Count | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | Candidate A | 1000 | 30% |
| 2020 | Candidate B | 700 | 21% |
| 2021 | Candidate A | 1200 | 35% |
| 2021 | Candidate B | 800 | 23% |
This structured table allows for a quick comparison of the relative strengths of candidates across different years.
Illustrative Examples

The Iowa caucuses, a critical first step in the US presidential nominating process, are often characterized by their unique vote counting procedures. Understanding the successes and failures in previous years provides valuable insights into optimizing the process for future elections. Analyzing specific instances of challenges and their resolutions can offer lessons for improved efficiency and accuracy. This section will explore illustrative examples of successful and unsuccessful aspects of Iowa caucus vote counting, highlighting best practices and areas for improvement.
Successful Aspects of Vote Counting
The Iowa caucuses, despite their inherent challenges, have witnessed moments of success in vote counting. A key element of success often revolves around the meticulous training and clear communication protocols for volunteers involved in the counting process. Dedicated and well-trained volunteers can ensure consistency and accuracy in reporting tallies, minimizing errors and delays. Furthermore, the use of pre-established and well-defined procedures can enhance the efficiency of the counting process.
This structure allows for a more streamlined and transparent approach to tallying votes, facilitating a faster and more reliable count.
Unsuccessful Aspects of Vote Counting
Instances of difficulties in vote counting often stem from logistical challenges. Unexpected fluctuations in turnout or the presence of large crowds can strain resources and processes. A lack of sufficient manpower to handle the volume of votes can also lead to delays and inaccuracies. Poorly defined procedures or a lack of clarity in volunteer instructions can contribute to errors in tallying and reporting.
Another area of concern involves the use of technology, where glitches in software or insufficient technical support can lead to breakdowns in the vote counting process. These situations highlight the importance of robust backup plans and adaptable procedures to mitigate potential issues.
Case Studies of Challenges and Resolutions
The 2020 Iowa caucuses, for instance, experienced challenges related to the volume of votes and the use of technology. The complexities of managing a large number of votes in a short period often led to initial delays in reporting results. In response, organizers implemented strategies for better coordination and resource allocation, which improved the efficiency and accuracy of the process in subsequent years.
Impact of Technology on Vote Count Outcomes
The incorporation of technology into the vote counting process has varied in its impact. While technology can streamline the counting process and enhance the speed of reporting, potential issues arise if technology is not adequately tested or if there is insufficient support to address glitches. For instance, the use of digital platforms to record and track votes can lead to faster results if the platform is reliable and user-friendly.
However, glitches in the software or technical issues can disrupt the process, potentially leading to delays or errors in the reporting of results.
Comparison of Different Vote Counting Approaches
| Approach | Strengths | Weaknesses | Ethical Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Counting | Relatively low cost, less susceptible to technological glitches | Time-consuming, prone to human error | Requires meticulous training to ensure accuracy and transparency. |
| Semi-Automated Counting | Combines human oversight with technological assistance, potentially improving speed and accuracy. | Requires robust technology and reliable support systems | Transparency in the technology used and procedures followed is essential. |
| Fully Automated Counting | Fastest, potentially most accurate | High initial cost, vulnerability to software errors, significant reliance on technology. | Ensuring data integrity and security is paramount. |
Ethical Considerations
Transparency and fairness are paramount in the vote counting process. The public has a right to know how their votes are counted and reported. Detailed and easily accessible reporting mechanisms that clearly explain the counting process, timelines, and methodologies are vital to maintaining public trust and confidence. The involvement of independent observers can enhance the perception of fairness and integrity.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, Iowa caucus vote counting is a multifaceted process deeply intertwined with the democratic process. Understanding the history, procedures, technology, and challenges associated with this process is essential for a complete understanding of American elections. From historical context to potential impacts on election outcomes, this analysis provides a comprehensive overview, allowing readers to form their own informed opinions on this critical aspect of the Iowa caucus.
Essential FAQs
What are the typical challenges faced during the Iowa caucus vote counting process?
Potential challenges include delays due to large numbers of voters, discrepancies in tallies, and disputes over the accuracy of the count. These challenges underscore the importance of robust procedures and effective dispute resolution mechanisms.
How does technology influence the accuracy and speed of vote counting?
Modern technology, including electronic systems and software, has dramatically improved the speed and accuracy of vote counting. However, technological advancements also introduce new challenges regarding data security and potential vulnerabilities.
What role do volunteers play in the Iowa caucus vote counting process?
Volunteers are essential to the Iowa caucus vote counting process, performing various tasks from initial collection to final tallying. Their dedication and commitment are vital to ensuring a smooth and accurate count.
How does the public perception of the Iowa caucus vote counting process influence the overall election?
Public perception plays a significant role in shaping trust and confidence in the electoral process. Transparency and effective communication are crucial to fostering public trust and confidence in the outcome.






