
Utility Bills Clean Energy Savings
Utility bills clean energy is a growing concern for many households and businesses. This exploration dives into the intricate relationship between energy consumption, clean energy sources, and how these choices impact your monthly expenses. We’ll examine various clean energy options, from solar panels to wind turbines, and analyze their impact on your utility bills, alongside practical strategies to reduce costs.
From understanding the components of your utility bill to exploring government incentives, this guide will provide a comprehensive overview. Discover how adopting clean energy solutions can not only benefit your wallet but also contribute to a healthier planet.
Introduction to Utility Bills and Clean Energy
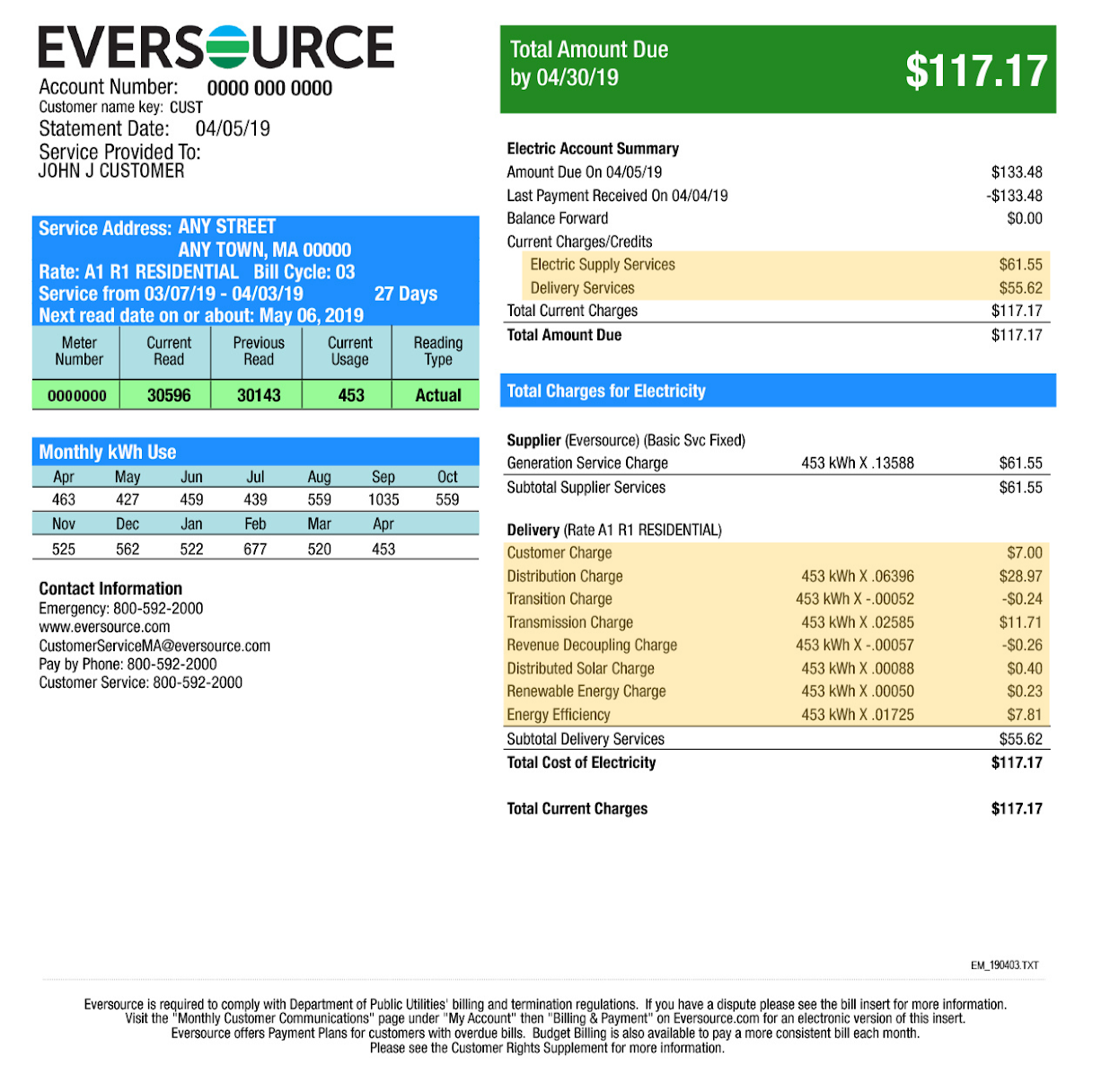
Utility bills are a necessary expense for most households, but understanding their components and potential savings is crucial. These bills often include charges for electricity, natural gas, water, and potentially other services. Knowing the breakdown of costs allows for better budgeting and potentially significant long-term savings. Clean energy sources, such as solar and wind power, offer a path toward reduced reliance on traditional fossil fuel-based utilities and lower utility bills.
This shift to cleaner energy sources is increasingly attractive due to both environmental benefits and cost savings.The transition to clean energy can be a significant step toward sustainability and financial well-being. Understanding how clean energy alternatives impact utility bills is key to making informed decisions about energy consumption and investments.
Lowering utility bills is a top priority, and clean energy solutions are key. Recent discussions about the future of energy have highlighted the need for sustainable options, like solar and wind power. This, coupled with celebrity endorsements like those from stars Harley Johnston, Oettinger, and Benn, highlights the growing awareness of the importance of clean energy.
Ultimately, everyone benefits from a transition to sustainable energy sources, and lower utility bills are just one of the many advantages.
Utility Bill Components and Costs
Utility bills vary depending on location, usage, and specific service providers. Common components include base charges, usage-based fees (kilowatt-hours for electricity, cubic feet for natural gas), and sometimes taxes and surcharges. Understanding these components helps consumers grasp the factors driving their bill totals.
Clean Energy Sources and Their Characteristics
Clean energy sources are characterized by their minimal environmental impact, often utilizing renewable resources. Solar power harnesses sunlight to generate electricity, while wind power utilizes wind turbines to convert kinetic energy into electricity. Hydropower relies on water flow, and geothermal energy taps into the Earth’s internal heat. These sources have significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuel-based energy generation.
Utility bills are a constant concern, especially when we’re trying to embrace cleaner energy options. It’s great to see how teams like the Steelers are making strides in the energy sector, not just on the field, but by hiring a new offensive coordinator, Arthur Smith. Hopefully, this innovative approach translates into more efficient and sustainable energy practices for everyone, ultimately bringing down those utility bills in the long run.
Relationship Between Utility Bills and Clean Energy Adoption
The adoption of clean energy sources can directly impact utility bills. For example, households investing in solar panels can reduce their reliance on grid electricity, leading to lower monthly bills. While initial investments can be substantial, long-term savings can be substantial.
Table: Utility Bill Components and Clean Energy Alternatives
| Bill Component | Cost Breakdown | Clean Energy Alternative | Savings Potential |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base Charge (Electricity) | A fixed monthly fee, regardless of usage. | Solar panels, potentially reducing or eliminating reliance on grid electricity. | Significant savings over time, especially if solar panels generate more electricity than consumed. |
| Usage-Based Fees (Electricity) | Cost per kilowatt-hour (kWh) of electricity consumed. | Energy efficiency measures (e.g., LED lighting, smart thermostats), reducing electricity consumption. | Savings from reduced energy consumption. |
| Natural Gas Usage | Cost per cubic foot (cf) of natural gas consumed. | Switching to propane or biogas for heating, depending on local availability. | Savings potential depends on energy costs and efficiency of the clean alternative. |
| Water Usage | Cost per unit of water consumed. | Water-efficient appliances and fixtures, reducing water consumption. | Savings through reduced water usage and potential rebates for water-efficient equipment. |
| Taxes and Surcharges | Applicable local and state taxes on utility services. | No direct clean energy alternative to reduce these costs. | Savings are indirectly linked to reducing overall consumption and reliance on utilities. |
Types of Clean Energy Sources
Harnessing clean energy sources is crucial for a sustainable future and mitigating the effects of climate change. This transition is not just about environmental responsibility; it also impacts our utility bills in significant ways. Understanding the different types of clean energy and their implications is key to making informed decisions about our energy consumption and investment choices.
Solar Energy
Solar energy, harnessed from the sun’s rays, is a remarkably abundant and consistent source of power. Photovoltaic (PV) panels convert sunlight directly into electricity, while concentrated solar power (CSP) systems use mirrors to focus sunlight to heat a fluid, generating steam to drive turbines. The environmental impact of solar energy is generally positive, with minimal greenhouse gas emissions during operation.
However, the manufacturing process of solar panels can have a small environmental footprint, requiring careful consideration of raw materials and recycling practices. Installation costs for solar systems vary depending on factors such as system size, location, and local incentives. Ongoing maintenance is relatively low, primarily focused on cleaning panels and occasional inspections.
Wind Energy
Wind energy harnesses the kinetic energy of wind to generate electricity. Wind turbines, often grouped in wind farms, convert wind’s energy into electricity. The environmental impact of wind energy is largely positive, with no greenhouse gas emissions during operation. However, concerns exist regarding the visual impact on landscapes and the potential impact on bird and bat populations.
Careful siting and design considerations are essential to minimize these impacts. Initial installation costs for wind farms can be substantial, and ongoing maintenance involves regular inspections and repairs of turbines.
Hydropower
Hydropower harnesses the energy of flowing water to generate electricity. Dams capture water’s potential energy, releasing it through turbines to create electricity. The environmental impact of hydropower varies depending on the size and design of the dam. Large dams can significantly alter river ecosystems, impacting fish migration and water flow patterns. Smaller-scale hydro projects can have a smaller environmental footprint.
Construction costs for hydropower plants can be high, and ongoing maintenance includes dam upkeep and turbine repairs.
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy taps into the Earth’s internal heat to generate electricity or provide heating and cooling. Heat from deep within the Earth is used to produce steam, which drives turbines to generate electricity. Geothermal energy has a very low environmental impact during operation, producing minimal greenhouse gas emissions. However, concerns exist about potential emissions from drilling and the possibility of ground subsidence.
Installation costs for geothermal power plants can be substantial, and ongoing maintenance involves monitoring and potentially repairing geothermal wells.
Biomass Energy
Biomass energy utilizes organic matter, such as wood, agricultural residues, and municipal waste, to produce energy. Burning biomass releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, but this is considered carbon neutral if the biomass is sustainably sourced and managed. The environmental impact depends on the type of biomass used and the combustion methods employed. Installation costs for biomass plants vary depending on the size and specific fuel source.
Ongoing maintenance involves regular fuel replenishment and maintaining combustion equipment.
Comparison Table
| Source | Environmental Impact | Cost Impact | Sustainability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar | Low, minimal emissions during operation | Moderate initial cost, low ongoing maintenance | High, abundant resource |
| Wind | Low, minimal emissions during operation; potential visual and wildlife impacts | High initial cost, moderate ongoing maintenance | High, abundant resource |
| Hydro | Variable, significant impacts on river ecosystems (large dams) | High initial cost, moderate ongoing maintenance | Moderate, water availability is crucial |
| Geothermal | Low, minimal emissions during operation; potential ground subsidence | High initial cost, moderate ongoing maintenance | High, sustainable resource |
| Biomass | Variable, carbon neutral if sustainably sourced | Variable, depends on biomass type | Moderate, depends on sustainable sourcing |
Clean Energy Technologies and their impact on Utility Bills
Harnessing clean energy sources is crucial for reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and lowering utility bills. This shift towards renewable energy is driven by factors like environmental concerns, fluctuating fossil fuel prices, and the potential for significant cost savings. The adoption of clean energy technologies is rapidly transforming the energy landscape, and the benefits are becoming increasingly apparent.The various clean energy technologies available today play a vital role in achieving these goals.
From solar panels capturing sunlight to wind turbines harnessing the power of the wind, these technologies offer sustainable and cost-effective alternatives to traditional energy sources. Smart grids further optimize energy distribution and consumption, leading to improved efficiency and reduced waste. Energy storage solutions are emerging as critical components in this transition, enabling the reliable use of intermittent renewable energy sources and potentially leading to greater bill stability.
Solar Panel Technologies
Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity. Photovoltaic (PV) panels are the most common type, utilizing semiconductor materials to generate direct current (DC) electricity. The efficiency of these panels varies, with advancements constantly pushing limits. Different panel types, such as monocrystalline and polycrystalline, exhibit different efficiencies and costs. The installation of solar panels can significantly reduce electricity bills, particularly in regions with abundant sunshine.
Furthermore, many jurisdictions offer incentives and rebates to encourage residential and commercial adoption.
Wind Turbine Technologies
Wind turbines capture the kinetic energy of wind to generate electricity. Larger wind turbines, often located in remote areas, can generate substantial amounts of power. The effectiveness of wind turbines depends on consistent wind speeds. Offshore wind farms, which are positioned further out at sea, can potentially capture stronger and more consistent winds, leading to higher energy production.
However, the initial investment for wind turbine projects can be substantial. Nevertheless, the long-term cost savings and environmental benefits can often outweigh the initial capital outlay.
Smart Grid Technologies
Smart grids utilize advanced technologies to monitor, manage, and optimize energy distribution. These systems can intelligently adjust energy flow based on real-time demand and supply, reducing waste and improving overall efficiency. Smart meters allow for real-time monitoring of energy consumption, enabling users to make informed decisions to reduce their energy footprint. The integration of renewable energy sources into smart grids is crucial for a more sustainable energy future.
The implementation of smart grid technologies can lead to substantial cost savings by reducing energy loss during transmission and distribution.
Rising utility bills are a real concern, especially with the push towards clean energy. The recent faculty strike at the California State University system, highlighted in this news article , is impacting budgets across the board, and likely influencing how the state prioritizes various funding sources. Still, the shift towards clean energy solutions is crucial for long-term sustainability, and ultimately, keeping those utility bills down.
Energy Storage Solutions
Energy storage solutions are crucial for mitigating the intermittency of renewable energy sources like solar and wind. These solutions store excess energy generated during peak production periods and release it when demand is high. Different storage technologies offer varying levels of efficiency, cost, and capacity. The adoption of these solutions is essential for a stable and reliable energy supply.
Comparison of Energy Storage Solutions
| Storage Technology | Efficiency | Cost | Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium-ion Batteries | High (typically 80-95%) | Moderate to High | Variable, from small residential units to large utility-scale systems |
| Pumped Hydro | High (typically 70-85%) | High | Very Large |
| Flow Batteries | Moderate (typically 80-90%) | Moderate | Variable, often suitable for larger scale storage |
| Thermal Storage | Moderate (typically 70-85%) | Moderate | Variable, suitable for various applications |
Note: Efficiency, cost, and capacity values are approximate and can vary depending on specific technologies, scale, and location.
The table above highlights the varying characteristics of different energy storage solutions. Each technology has its own advantages and disadvantages regarding cost, efficiency, and scalability. The optimal choice for a particular application depends on the specific needs and constraints. The ongoing development and refinement of these technologies are driving down costs and improving performance, making them increasingly attractive for a broader range of applications.
Utility Bill Reduction Strategies using Clean Energy: Utility Bills Clean Energy

Harnessing clean energy sources not only reduces our environmental footprint but also presents significant opportunities to lower utility bills. This section delves into practical strategies for achieving this, emphasizing energy efficiency measures alongside clean energy adoption. By implementing these strategies, both homeowners and businesses can substantially decrease their energy consumption and related costs.
Energy Efficiency Measures
Implementing energy efficiency measures is a cornerstone of reducing utility bills, especially when combined with clean energy sources. These measures can significantly lower energy consumption without sacrificing comfort or functionality. The initial investment in energy-efficient technologies often pays for itself through reduced utility costs over time.
Energy efficiency is often the most cost-effective way to reduce utility bills.
- Insulation: Proper insulation minimizes heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. This translates to lower heating and cooling needs, directly impacting energy consumption. Adding insulation to walls, attics, and crawl spaces can substantially reduce energy waste and utility bills. For example, a well-insulated home can reduce heating costs by 20-30%.
- Smart Thermostats: Programmable or smart thermostats allow for precise temperature control based on occupancy schedules. This avoids unnecessary energy use when a home is unoccupied. These devices can adjust temperatures automatically, learning from user patterns to optimize energy consumption and minimize bills. Smart thermostats can lower energy costs by 10-15%.
- Energy-Efficient Appliances: Replacing older appliances with newer, energy-efficient models significantly reduces energy consumption. Look for appliances with Energy Star ratings, which indicate they meet strict energy efficiency standards. This can lead to considerable savings over the lifespan of the appliance. For instance, a new Energy Star refrigerator can use up to 40% less energy than older models.
Clean Energy Integration Strategies
Integrating clean energy solutions into existing infrastructure can yield significant savings. A multifaceted approach that combines energy efficiency measures with renewable energy sources is crucial for substantial bill reductions.
- Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Systems: Installing solar panels can generate electricity from sunlight, reducing reliance on the grid and lowering energy costs. The amount of savings depends on factors such as the amount of sunlight received, the size of the system, and local electricity rates. For example, a homeowner with a sizable solar PV system could see a significant portion of their electricity bill offset, or even eliminated entirely during peak sunlight hours.
Lowering utility bills with clean energy is a crucial goal, and it’s exciting to see the potential of new technologies. Considering the recent results of the New Hampshire Democratic primary, results new hampshire democratic primary , it’s clear that voters are increasingly focused on solutions for a sustainable future. Ultimately, a shift towards clean energy sources will directly impact the affordability of our utility bills for years to come.
- Wind Turbines: In areas with consistent wind conditions, wind turbines can provide a clean and sustainable energy source. The feasibility of wind turbines depends on factors like wind speed and local regulations. These systems can provide a consistent and reliable source of clean energy for both homes and businesses.
- Geothermal Energy: Utilizing the Earth’s consistent temperature for heating and cooling systems is another clean energy option. Geothermal systems offer year-round cost savings by reducing reliance on traditional heating and cooling systems. These systems are more suited for certain climates and geographical locations.
Implementation Examples
Implementing these strategies at home or in businesses can yield substantial returns.
- Homeowners: Installing solar panels, upgrading to energy-efficient windows and doors, and using smart thermostats can drastically reduce energy consumption and utility bills. Consider the return on investment when assessing the viability of different solutions.
- Businesses: Implementing energy-efficient lighting, upgrading HVAC systems, and exploring renewable energy sources like solar panels or wind turbines can significantly lower energy costs for businesses. This can have a profound impact on profitability.
Government Policies and Incentives for Clean Energy
Government policies play a crucial role in driving the adoption of clean energy solutions. These policies create a supportive environment for businesses and consumers, encouraging investment in renewable energy technologies and incentivizing the shift away from fossil fuels. The resulting benefits often extend beyond environmental protection, impacting utility bills and promoting economic growth.Government initiatives often focus on reducing the cost of clean energy technologies, making them more competitive with traditional energy sources.
These policies can also streamline permitting processes, fostering faster deployment of renewable energy projects. The impact on utility bills can be significant, as clean energy often leads to lower operating costs and potentially lower electricity rates for consumers. Consumers, in turn, are more likely to choose clean energy options when they become more accessible and affordable.
Government Incentives for Clean Energy Installations
Government incentives significantly impact the cost of clean energy installations, making them more attractive to consumers and businesses. These incentives often take the form of tax credits, rebates, or subsidies, designed to offset the initial investment costs. The specific structure and value of these incentives can vary by jurisdiction, affecting consumer choices and the overall adoption rate of clean energy.
Examples of Government Programs
A variety of government programs exist to encourage clean energy adoption. These programs provide financial assistance and support to individuals and businesses looking to install renewable energy systems. Understanding these programs can be beneficial in identifying opportunities to reduce utility bills and contribute to a cleaner energy future.
| Program Name | Eligibility Criteria | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) | Residential and commercial solar installations. Specific requirements and limitations may apply. | 30% tax credit on the cost of new clean energy equipment. This can significantly reduce the overall cost of installation. |
| State Solar Incentives | Vary by state, but typically include residential solar installations. | State-level tax credits, rebates, or grants. These can supplement federal incentives and reduce the cost further. Examples include property tax exemptions or streamlined permitting processes. |
| Local Government Programs | Vary by municipality. Some offer incentives for community solar projects or energy efficiency upgrades. | Local grants, rebates, or partnerships with utilities to promote energy efficiency and clean energy. |
Impact on Utility Bills and Consumer Choices, Utility bills clean energy
Government policies and incentives significantly influence consumer choices. When clean energy solutions become more affordable, consumers are more likely to invest in solar panels, wind turbines, or other renewable energy technologies. These choices directly affect utility bills, potentially reducing reliance on traditional energy sources and lowering electricity costs.
Potential Tax Credits, Rebates, and Subsidies
Tax credits, rebates, and subsidies play a crucial role in reducing the financial burden of adopting clean energy. They provide a direct incentive to homeowners and businesses, potentially offsetting a significant portion of the installation costs. For instance, the federal investment tax credit (ITC) for solar energy installations provides a substantial financial incentive, making solar power more attractive.
Consumer Behaviour and Clean Energy Adoption
Consumer attitudes and perceptions play a crucial role in the adoption of clean energy solutions. Understanding these factors is essential for policymakers and energy providers to design effective strategies that encourage wider adoption and ultimately contribute to a more sustainable future. Individual choices about energy sources are often influenced by a complex interplay of economic, environmental, and social factors.Consumer perceptions of clean energy technologies often hinge on factors such as perceived cost, reliability, and ease of implementation.
The perceived value of clean energy in terms of its environmental benefits and potential for future savings also plays a significant role. This understanding allows for the development of targeted communication strategies that effectively address these concerns and promote a more positive outlook towards clean energy.
Factors Influencing Consumer Decisions
Consumer decisions regarding clean energy solutions are shaped by various interconnected factors. These factors include:
- Cost and affordability: The upfront investment required for clean energy technologies, such as solar panels or energy-efficient appliances, is often a primary concern for consumers. Government incentives, financing options, and potential long-term savings can significantly influence decisions.
- Perceived reliability and performance: Concerns about the reliability and consistency of clean energy sources, particularly intermittent sources like solar and wind, are sometimes a barrier to adoption. Addressing these concerns through robust infrastructure development and energy storage solutions is crucial.
- Ease of installation and maintenance: The complexity of installing and maintaining clean energy systems can deter potential adopters. Streamlining installation processes, offering readily available maintenance services, and providing clear user instructions can significantly enhance the appeal of these technologies.
- Environmental consciousness: Growing awareness of environmental issues and a desire to contribute to a sustainable future motivates many consumers to choose clean energy options. Education and awareness campaigns can play a pivotal role in fostering this motivation.
- Social norms and peer influence: Positive experiences and recommendations from friends, family, or community leaders can significantly impact consumer decisions. Promoting successful adoption stories and creating a supportive social environment can encourage broader adoption.
- Government policies and incentives: Government regulations, tax credits, rebates, and other incentives can significantly influence the cost and accessibility of clean energy technologies, thereby encouraging adoption.
Successful Consumer Adoption Strategies
Several successful strategies have been employed to promote clean energy adoption among consumers. These include:
- Public awareness campaigns: Raising public awareness about the benefits of clean energy and its impact on the environment can motivate individuals to consider adopting these technologies. Educational materials, social media campaigns, and community events can all play a vital role.
- Financial incentives and rebates: Government subsidies and tax credits for clean energy installations can reduce the upfront cost and make these technologies more accessible to a wider range of consumers.
- Demonstrations and pilot programs: Allowing consumers to experience clean energy technologies firsthand through demonstrations and pilot programs can build trust and confidence in these solutions.
- Community engagement and partnerships: Involving local communities in clean energy initiatives and fostering partnerships between businesses, governments, and consumers can create a supportive environment for adoption.
Impact of Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns have a demonstrable impact on clean energy adoption. Effective campaigns often utilize a multi-faceted approach, combining various communication channels and targeting specific demographics. For instance, campaigns highlighting the environmental benefits of clean energy and the potential cost savings for consumers have proven effective in promoting adoption. By emphasizing the positive impacts of clean energy, these campaigns can foster a more favorable perception of these technologies and ultimately encourage their wider use.
Case Studies of Clean Energy and Utility Bill Reductions
Real-world examples demonstrate the significant potential for clean energy to reduce utility bills. These case studies highlight successful implementations, showcasing the tangible benefits and paving the way for wider adoption. From residential homes to commercial businesses, the transition to clean energy can translate into substantial cost savings.These case studies explore the various technologies, strategies, and results achieved by different entities, providing concrete data points and detailed accounts of the implementation process.
This allows for a deeper understanding of how clean energy solutions can impact financial well-being while contributing to environmental sustainability. Specific cost savings figures and implementation details will be presented.
Residential Case Study: The Smith Family
The Smith family, located in a suburban area of California, implemented a comprehensive clean energy strategy. Their primary focus was on solar photovoltaic (PV) panels. They installed a system with a capacity of 5kW, enough to power their home during peak hours. The installation process involved careful assessment of roof space, sunlight exposure, and electrical infrastructure. Initial investment costs totaled $15,000, which included equipment, installation, and permits.
- After a year of operation, the Smiths realized a significant reduction in their monthly electricity bills. They saved an average of $100 per month, demonstrating a return on investment (ROI) within the first few years of operation.
- Their experience highlights the long-term cost-effectiveness of solar energy, surpassing the initial investment costs in a relatively short period. The monthly savings are consistent and predictable.
Commercial Case Study: GreenGrocer
GreenGrocer, a local grocery store chain, adopted a combination of energy-efficient technologies to reduce its energy footprint and utility bills. They installed LED lighting throughout their stores, implemented energy-efficient refrigeration systems, and optimized HVAC controls. In addition, they partnered with a local utility provider to explore time-of-use tariffs.
Rising utility bills are a real concern for many, and clean energy solutions are definitely a part of the conversation. However, the recent results from the Iowa caucus, where trump voters iowa caucus showed strong support, highlight a potential divide on the best approach to energy policy. Ultimately, finding affordable and sustainable energy options is crucial for everyone, regardless of political leanings.
- These measures resulted in a 20% decrease in their overall energy consumption and a consequent 15% reduction in utility bills annually.
- GreenGrocer’s strategy illustrates the effectiveness of combining multiple clean energy technologies. The comprehensive approach not only lowered energy costs but also improved the store’s operational efficiency.
Summary Table of Case Studies
| Case Study | Technologies Used | Cost Savings (USD/Year) | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smith Family | 5kW Solar PV Panels | $1,200 | Suburban California |
| GreenGrocer | LED Lighting, Energy-Efficient Refrigeration, HVAC Optimization, Time-of-Use Tariffs | $15,000 | Local Grocery Store Chain |
Last Word
In conclusion, embracing clean energy isn’t just environmentally responsible; it can significantly reduce your utility bills. By understanding the various clean energy sources, technologies, and government incentives available, you can make informed decisions that save money and promote a sustainable future. This exploration provides a clear path toward greener living and lower energy costs. Ultimately, taking control of your energy consumption is key to a brighter tomorrow.
Popular Questions
What are some common components of a utility bill?
Typical utility bills include charges for electricity, gas, water, and sometimes sewage. Costs often depend on usage, rates, and applicable taxes.
How can I find out about local government incentives for clean energy?
Contact your local utility company or government agencies for information about rebates, tax credits, and other incentives for clean energy installations. Local energy offices are a good resource.
What are the long-term costs of installing solar panels?
Initial installation costs can be substantial, but long-term savings from reduced electricity bills can offset these costs significantly. Solar panel efficiency and maintenance should also be considered.
What is the difference between solar and wind energy?
Solar energy harnesses sunlight, while wind energy utilizes wind patterns. Solar panels are often suited for residential use, while wind farms are more commonly associated with large-scale projects. Both offer substantial savings in the long run.

