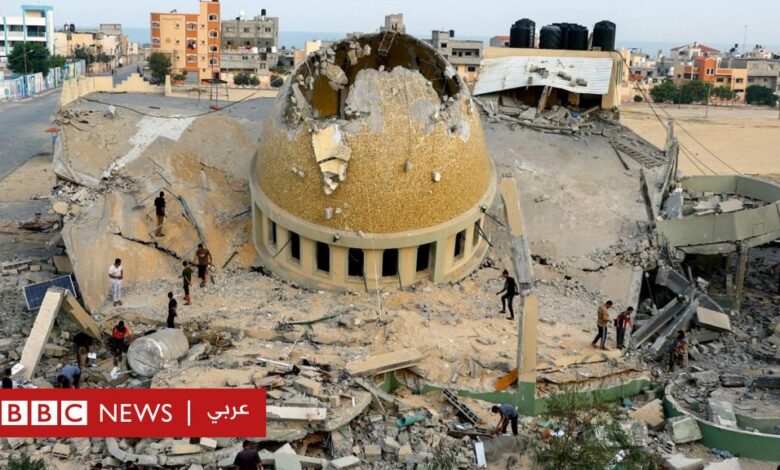
Israel Hamas Houthi Yemen News A Complex Web
Israel Hamas Houthi Yemen news paints a complex picture of interconnected conflicts. This multifaceted crisis involves the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, the actions of Hamas, the Houthi movement in Yemen, and the intricate web of regional powers caught in the middle. Understanding the history, ideologies, and current actions of these groups is crucial to grasping the nuances of this escalating situation.
The current escalation of violence has brought unprecedented humanitarian suffering to the region, highlighting the need for a comprehensive understanding of the underlying issues and potential pathways to peace. This article delves into the historical context, the roles of key players, and the interconnected nature of these conflicts, aiming to provide a clearer picture for readers.
The Israeli-Palestinian Conflict
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict, a deeply rooted and complex dispute, has shaped the geopolitical landscape of the Middle East for decades. It stems from competing claims to the same land, intertwined with historical grievances, religious significance, and political aspirations. This conflict has witnessed numerous cycles of violence and attempts at peace, leaving a lasting impact on the region and the international community.
Historical Overview
The conflict’s roots lie in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with the rise of Zionist aspirations for a Jewish homeland in Palestine, a region then largely inhabited by Arabs. The Balfour Declaration of 1917, supporting a Jewish national home in Palestine, marked a significant turning point, setting the stage for future tensions. The British Mandate for Palestine, established after World War I, further complicated matters, exacerbating existing tensions between the Jewish and Arab communities.
The 1948 Arab-Israeli War, following the declaration of the State of Israel, resulted in widespread displacement and the creation of refugee populations on both sides. The Six-Day War of 1967 saw Israel occupy the West Bank, Gaza Strip, and the Golan Heights, leading to further escalation and the continuation of the conflict. The 1973 Yom Kippur War, and the subsequent peace accords, provided a brief period of relative calm, but the underlying issues remained unresolved.
The 1993 Oslo Accords, while promising, ultimately failed to deliver a lasting peace agreement. These are just some of the major historical events that shaped the conflict.
Israeli Perspective
Israelis generally view the conflict through the lens of security concerns and the right to self-determination. They often emphasize the historical connection of Jews to the land and the need to protect their state from threats. The establishment of Israel is seen as a fulfillment of historical aspirations and a response to centuries of persecution. The need for security and the perceived threat from Palestinian militants are often cited as justification for Israeli policies.
Palestinian Perspective
Palestinians view the conflict as a struggle for self-determination and an end to occupation. They emphasize the historical presence of Arab communities in the region and the loss of land and displacement caused by the establishment of Israel. The occupation of Palestinian territories and the denial of their right to statehood are central grievances. The ongoing Israeli presence in the occupied territories is seen as a violation of international law and a significant obstacle to peace.
Role of External Actors
The United States, as a key supporter of Israel, has played a significant role in mediating the conflict. The UN, through various resolutions and peacekeeping missions, has attempted to promote peace and address humanitarian issues. Other international actors, such as the European Union and Arab nations, have also played varying roles in the conflict’s evolution.
Current State and Recent Escalations
The conflict remains unresolved, with ongoing violence and tensions. Recent escalations, including periods of heightened violence, underscore the fragility of the situation and the difficulty in reaching a lasting peace. Efforts at negotiation have yielded limited results, and a consensus on the future of the conflict remains elusive.
Impact on Regional Stability
The conflict has had a profound impact on regional stability, often fueling tensions and instability in the surrounding area. The presence of armed groups, political divisions, and the humanitarian crisis in the Palestinian territories have created a volatile environment that can easily spill over into neighboring countries.
Key Figures Involved
| Name | Role | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Golda Meir | Prime Minister of Israel | Instrumental in the 1967 Six-Day War |
| Yasser Arafat | Palestinian Liberation Organization leader | Key figure in Palestinian negotiations |
| Shimon Peres | Prime Minister of Israel | Instrumental in the Oslo Accords |
Comparison of Israeli Political Parties
| Political Party | Stance on Peace Process | Stance on Settlements | Stance on Security |
|---|---|---|---|
| Likud | Generally cautious, emphasizing security | Favor expansion and maintenance | Prioritizes defense and military strength |
| Labor | More amenable to negotiations | Generally against further expansion | Seeks a balance between security and peace |
| Meretz | Strongly supportive of a two-state solution | Opposes settlement expansion | Prioritizes de-escalation and peace |
The Hamas Role: Israel Hamas Houthi Yemen News
Hamas, an Islamist Palestinian political and military organization, plays a significant role in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and regional dynamics. Its history, ideology, and actions have shaped the landscape of the conflict for decades. Understanding Hamas’s motivations and objectives is crucial to comprehending the current crisis and potential pathways forward.Hamas’s ideology is rooted in a strict interpretation of Islamic law and a commitment to the establishment of an Islamic state in Palestine.
This ideology significantly influences its policies and actions, often leading to clashes with other political factions and the Israeli government.
History and Ideology of Hamas
Hamas emerged from the socio-political landscape of the 1980s, gaining significant traction amidst Palestinian dissatisfaction with the existing political structures. Its founding principles are deeply embedded in the Palestinian struggle for self-determination and the creation of an independent Palestinian state. The organization’s commitment to resistance against Israeli occupation and the establishment of an Islamic Palestinian state are central to its ideology.
Hamas’s Objectives and Goals
Hamas’s primary objectives include the liberation of all Palestinian territories, the establishment of an independent Palestinian state with East Jerusalem as its capital, and the dismantling of the Israeli occupation. These goals are often intertwined with its religious and political ideology. Furthermore, Hamas aims to represent Palestinian interests and resist perceived Israeli encroachment.
Hamas’s Relationship with Other Regional Actors
Hamas maintains complex and sometimes adversarial relationships with other regional actors. Its ties with various groups, including those in the wider Arab world and some international groups, often depend on shared goals and mutual interests. These relationships can shift based on evolving political circumstances and regional conflicts.
Hamas’s Military Capabilities and Tactics
Hamas possesses a substantial military wing, responsible for carrying out military operations and acts of resistance. Their military capabilities and tactics are often characterized by an emphasis on unconventional warfare, including the use of rockets, tunnels, and suicide attacks. This approach reflects the limitations of direct confrontation with the Israeli military.
Comparison of Hamas’s Tactics to Other Armed Groups in the Region
Hamas’s tactics, like those of other armed groups in the region, often involve guerrilla warfare and asymmetric warfare strategies. However, the specific tactics and approaches may vary depending on the group’s objectives and the specific circumstances of the conflict. These tactics often involve exploiting terrain advantages and relying on a network of support to carry out operations.
Hamas’s Key Actions and Statements Since the Recent Escalation
| Date | Action/Statement |
|---|---|
| October 7, 2023 | Hamas launched a large-scale attack on Israel, resulting in numerous casualties and widespread conflict. |
| October 7-present | Hamas has continued to engage in military operations and negotiations with Israel. |
Key Sources of Funding and Support for Hamas
| Source | Description |
|---|---|
| Foreign Donors | Hamas receives funding from various sources, including individuals, groups, and states. |
| Charitable Donations | Donations from individuals and organizations worldwide. |
| Palestinian Community | The Palestinian community, particularly in the Gaza Strip, contributes to Hamas’s funding and support. |
The Houthi Role in Yemen
The Houthi movement, rooted in Zaydi Shia Islam, has profoundly reshaped Yemen’s political landscape and destabilized the region. Their rise to power, coupled with their complex relationship with regional actors, has led to a protracted conflict with devastating consequences for Yemen’s population and regional stability. Understanding their origins, objectives, and military capabilities is crucial to comprehending the ongoing crisis.
Origins and Ideology of the Houthi Movement, Israel hamas houthi yemen news
The Houthi movement emerged from the Zaydi Shia community in northern Yemen. Historically, Zaydism has coexisted with other religious and political groups in the country, although tensions have existed at various times. The Houthi movement, tracing its roots back to the early 2000s, gained momentum by leveraging grievances related to socioeconomic disparities and perceived marginalization. Their ideology blends Zaydi religious interpretations with a nationalist agenda.
The group’s leadership has emphasized a vision of restoring Yemen’s sovereignty and combating perceived foreign interference.
Houthi Objectives and Goals
The Houthi movement’s objectives are multifaceted and include establishing a government that aligns with their interpretation of Islamic law. They aim to reshape Yemen’s political structure, often challenging existing power dynamics. The control of key resources, such as ports and infrastructure, has been a significant goal to achieve economic dominance.
Houthi Relationship with Other Regional Actors
The Houthi movement’s relationship with other regional actors is marked by complex and often conflicting interests. They have engaged in a proxy war with Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates (UAE), who support the internationally recognized Yemeni government. The group’s alliance with other armed groups in the region, particularly Iran, has also been a source of contention.
Houthi Military Capabilities and Tactics
The Houthi movement possesses a well-equipped and motivated military force, including armed groups. They have utilized guerrilla warfare tactics effectively in mountainous terrain, and have also employed ballistic missiles and drones, which have been a major component of their military strategy. Their military tactics have varied and evolved in response to the changing circumstances of the conflict.
Impact on Yemen’s Stability and Humanitarian Crisis
The Houthi conflict has severely damaged Yemen’s infrastructure, creating a profound humanitarian crisis. The war has led to a massive displacement of civilians and widespread poverty. The lack of access to essential services and food security has exacerbated the crisis, leading to significant loss of life.
Impact on Regional Trade Routes and Security
The Houthi conflict has significantly affected regional trade routes, particularly those in the Red Sea and the Bab el-Mandeb Strait. Disruptions to maritime traffic have impacted global trade and security. The movement’s actions have raised concerns about regional instability and the potential for escalation.
Factions Within the Yemeni Conflict
| Faction | Description | Key Objectives |
|---|---|---|
| Houthi Movement | Armed group primarily based in northern Yemen, with Zaydi Shia ideology. | Establishing a government aligned with their interpretation of Islamic law, controlling resources, and combating perceived foreign interference. |
| Internationally Recognized Yemeni Government | The government recognized by the UN, based in Aden. | Maintaining sovereignty and restoring the country’s stability. |
| Southern Separatists | Groups advocating for the independence of Southern Yemen. | Securing greater autonomy or independence from the north. |
| Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP) | A regional branch of Al-Qaeda. | Establishing a caliphate, often targeting the Yemeni government and other groups. |
The Interconnectedness of Conflicts
The seemingly disparate conflicts in Israel-Palestine, Hamas’ actions, and the Houthi conflict in Yemen are deeply intertwined. These conflicts are not isolated events but rather manifestations of a complex web of regional grievances, power struggles, and historical tensions. Understanding the interconnectedness is crucial for comprehending the escalating humanitarian crises and the potential for wider regional instability. The underlying factors fueling these conflicts often overlap, creating a volatile environment prone to escalation.The Israeli-Palestinian conflict, rooted in historical claims and competing aspirations for self-determination, has been a persistent source of regional tension.
Hamas, a Palestinian Islamist organization, has engaged in armed conflict with Israel, while also playing a significant role in the ongoing political and social landscape of Palestine. The Houthi conflict in Yemen, stemming from a complex mix of political grievances and sectarian tensions, has been exacerbated by external interference and regional rivalries. These interwoven threads create a dangerous cycle of violence and instability.
Connections Between the Conflicts
The conflicts are interconnected through various factors. Regional powers often exploit these conflicts for their own geopolitical interests, exacerbating tensions and hindering potential peaceful resolutions. For example, the supply of weapons and funding to various armed groups can contribute to the escalation of violence, further entrenching the conflict. Shared grievances and historical narratives also connect the struggles.
The sense of injustice and the quest for self-determination are prevalent themes across these conflicts, influencing the motivations and actions of the involved parties.
Role of Regional Powers
Regional powers, including Iran and Saudi Arabia, have been accused of playing a significant role in fueling the conflicts through direct and indirect support for armed groups. These interventions often exacerbate the existing tensions, making a peaceful resolution more difficult. Their influence is not just military; it extends to financial and political support, further deepening the regional divisions and complicating efforts toward de-escalation.
Humanitarian Crises
The humanitarian crises in Israel, Palestine, and Yemen are starkly different in their specific manifestations, yet share common threads of displacement, loss of life, and the breakdown of essential services. In Israel, the focus is on the immediate aftermath of attacks, including the urgent need for medical aid and shelter. In Palestine, the long-term impact of decades of conflict, including the blockade and limited access to resources, creates a persistent humanitarian challenge.
Yemen faces a devastating humanitarian crisis, compounded by years of conflict and a crippling blockade, leading to widespread famine and disease.
Potential for Regional Escalation
The potential for regional escalation is significant. The complex interplay of regional powers, coupled with the ongoing conflicts, creates a high risk of further violence and instability. Historical precedents of regional conflicts spreading demonstrate the danger of inaction and the need for a comprehensive approach to conflict resolution.
Impact on Regional Refugee Populations
| Conflict | Affected Countries | Estimated Refugee Population | Impact on Host Countries |
|---|---|---|---|
| Israeli-Palestinian | Israel, Palestine, surrounding countries | Millions (varying estimates based on time period) | Strain on resources, infrastructure, and social services in neighboring countries. |
| Houthi conflict in Yemen | Yemen, surrounding countries | Millions (varying estimates based on time period) | Significant strain on resources and stability in neighboring countries, leading to humanitarian crises. |
The table above highlights the considerable impact of these conflicts on regional refugee populations. The displacement of people leads to humanitarian crises, further destabilizing the region and creating new challenges for neighboring countries.
Different Viewpoints on Peaceful Resolution
Various perspectives exist on how these conflicts might be resolved peacefully. Some advocate for diplomatic solutions, emphasizing the need for negotiations and international mediation. Others call for a complete restructuring of the regional power dynamics to address the root causes of conflict. International cooperation, including humanitarian aid and support for peacebuilding efforts, is a crucial element in any approach toward sustainable resolution.
News and Media Coverage
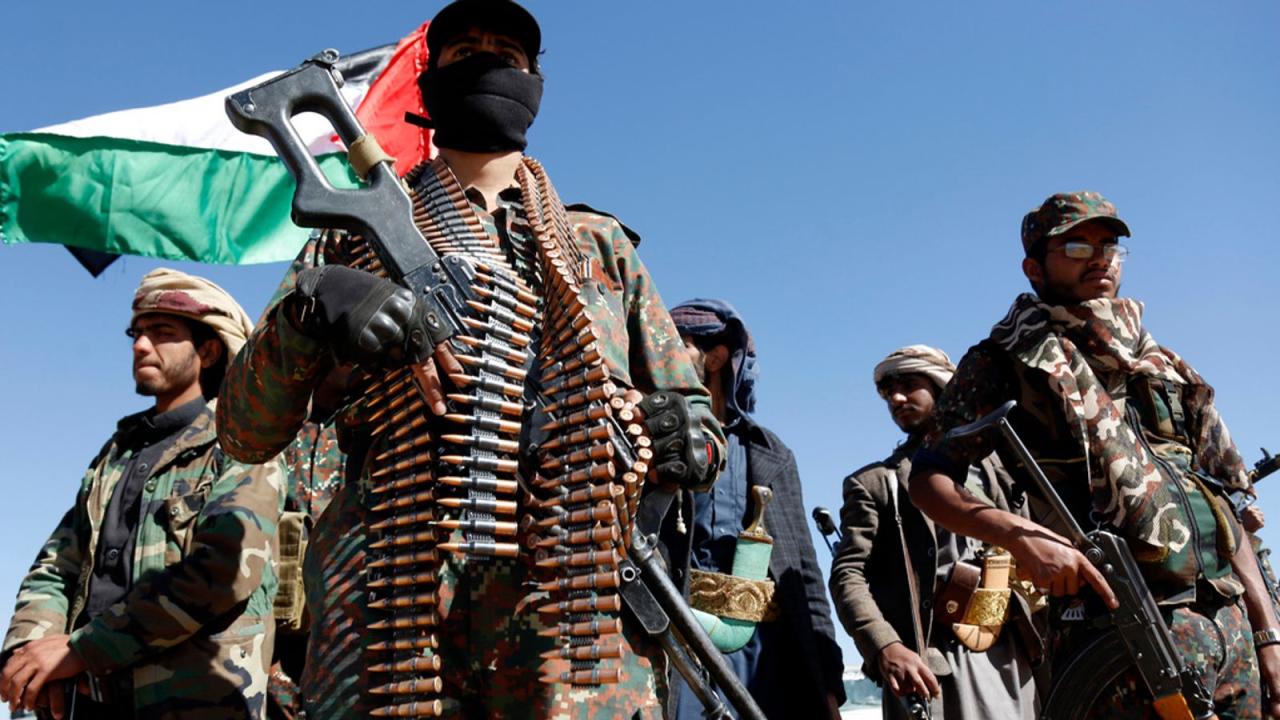

The global media landscape plays a crucial role in shaping public perception of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, the Hamas actions, the Houthi conflict in Yemen, and their interconnected nature. News coverage, whether through traditional media or social media platforms, significantly influences public opinion and can exacerbate tensions. Understanding the different perspectives presented and the potential biases inherent in these narratives is vital for a nuanced understanding of these complex events.News outlets often frame these conflicts through various lenses, reflecting their own political leanings and editorial priorities.
This can lead to biased reporting, where certain aspects of the story are highlighted while others are downplayed or ignored. It’s crucial to recognize these biases and seek out diverse sources of information to develop a comprehensive picture.
Overview of News Coverage
News coverage surrounding the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, the Hamas role, the Houthi role in Yemen, and their interconnectedness has been extensive and often intense. Major news organizations, both international and regional, have dedicated significant resources to reporting on these events. The coverage varies considerably in tone and emphasis, depending on the outlet’s perspective. Some focus on the immediate humanitarian crisis, others on the political maneuvering of key players.
This diversity in approach can be confusing for the average viewer.
Potential Biases in Reporting
News outlets often operate with inherent biases, whether intentional or unintentional. These biases can manifest in several ways, including selective reporting, framing, and the choice of language. For instance, some outlets may focus heavily on Israeli security concerns while downplaying Palestinian grievances, or vice versa. The selection of specific experts quoted and the use of particular imagery can also shape public perception.
It’s essential to critically examine the source and context of news reports to evaluate potential biases.
Different Perspectives in News Outlets
Different news outlets present distinct perspectives on the conflicts. Some outlets may emphasize the Israeli narrative, highlighting security concerns and actions taken to protect civilians. Others may focus on the Palestinian perspective, emphasizing the human cost of the conflict and the perceived injustices. Similarly, some news sources might emphasize the role of Hamas or the Houthis, while others may focus on broader regional or geopolitical implications.
Understanding these contrasting viewpoints is vital to forming a balanced opinion.
Social Media’s Role in Information and Misinformation
Social media platforms have become crucial avenues for disseminating information, both accurate and inaccurate, about the conflicts. The speed and reach of social media make it a powerful tool for spreading narratives and influencing public opinion. However, the same speed and reach also facilitate the rapid spread of misinformation and propaganda. The lack of fact-checking and the ease with which false information can be shared online pose significant challenges in distinguishing truth from falsehood.
Role of Propaganda and Disinformation
Propaganda and disinformation play a significant role in shaping public perception of the conflicts. Actors involved, whether governments, political groups, or individuals, often employ these tactics to manipulate public opinion, mobilize support, or damage their opponents’ reputations. This includes the use of fabricated stories, selective editing of images and videos, and targeted social media campaigns. The spread of disinformation often exploits existing tensions and anxieties, making it more effective.
Table of News Sources
| Source Category | Examples | Potential Biases |
|---|---|---|
| International News Agencies | Reuters, Associated Press, AFP | Often considered more objective but can still reflect the perspectives of the countries they report from. |
| Major International News Outlets | BBC, CNN, The New York Times | May lean towards specific political perspectives, often reflecting the values and priorities of their regions. |
| Regional News Outlets | Al Jazeera, Middle Eastern newspapers | May reflect the regional political climate and concerns. |
| Social Media Platforms | Twitter, Facebook, YouTube | High potential for the spread of misinformation and propaganda due to the lack of fact-checking. |
Illustrative Examples
The interwoven conflicts in the Middle East, particularly the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, the Hamas actions, and the Houthi insurgency in Yemen, are marked by a series of significant incidents. Understanding these events, their context, and consequences is crucial to comprehending the complex dynamics at play. Analyzing specific examples illuminates the strategies employed by different actors and the devastating impact on civilian populations.
Specific Incidents and Actions
Numerous incidents highlight the escalation of violence and the devastating impact on civilian populations. The targeting of civilian infrastructure, such as hospitals and schools, is a recurring theme in these conflicts. For example, the 2023 Hamas attacks on Israeli targets demonstrated a deliberate strategy to inflict widespread casualties and damage. The subsequent Israeli response, while aiming to neutralize Hamas capabilities, resulted in significant collateral damage in Palestinian territories, causing further suffering and displacement.
Similarly, the Houthi attacks on Saudi Arabian oil facilities highlight the potential for regional destabilization and the broader implications of these conflicts.
Contextual Factors Surrounding Incidents
The context surrounding these incidents is crucial for understanding their motivations and consequences. Political tensions, historical grievances, and economic disparities often fuel these conflicts. The Israeli-Palestinian conflict, rooted in competing claims to the land, has endured for decades. The rise of Hamas, often perceived as a political and military organization, has further complicated the situation. The Houthi conflict in Yemen is intricately linked to broader political and socioeconomic issues, including the struggle for power and control over resources.
Consequences of Incidents
The consequences of these incidents are often devastating, encompassing loss of life, displacement, and the destruction of vital infrastructure. The impact on civilian populations is profound, creating humanitarian crises and long-term challenges for recovery. The conflict’s economic ramifications are equally significant, disrupting trade, hindering development, and exacerbating poverty in affected regions. For example, the 2023 attacks and retaliations caused widespread displacement and damage, impacting both Israel and Palestine.
Types of Weapons Used
| Type of Weapon | Description | Conflict Context |
|---|---|---|
| Rockets and Missiles | Various types of rockets and missiles, ranging from short-range to long-range, have been used in the conflicts. | Often used in attacks on populated areas and infrastructure. |
| Small Arms | Standard firearms, including rifles and pistols, are widely used. | Used in close-quarters combat and targeted attacks. |
| Heavy Artillery | Mortars and other heavy artillery pieces. | Capable of inflicting significant damage to buildings and infrastructure. |
| Air-Launched Munitions | Missiles and bombs dropped from aircraft. | Used in targeted strikes and for suppressing enemy forces. |
Strategies and Tactics
The conflicts showcase various strategies and tactics employed by different parties. Hamas, for instance, utilizes a combination of guerilla warfare tactics and urban warfare strategies. Israel employs precision strikes and air power, while the Houthis utilize both conventional and unconventional warfare methods, including attacks on critical infrastructure. The effectiveness of these strategies often depends on the specific circumstances and the political and military context.
Humanitarian Aid Efforts
Humanitarian aid efforts play a vital role in alleviating the suffering caused by these conflicts. Organizations such as the United Nations and various non-governmental organizations (NGOs) provide crucial assistance to displaced populations, offering food, shelter, and medical care. These efforts, however, often face significant challenges in reaching those in need due to the ongoing conflict and security concerns.
For instance, access to besieged areas in Yemen has been severely restricted, impeding the delivery of vital aid.
Closing Notes
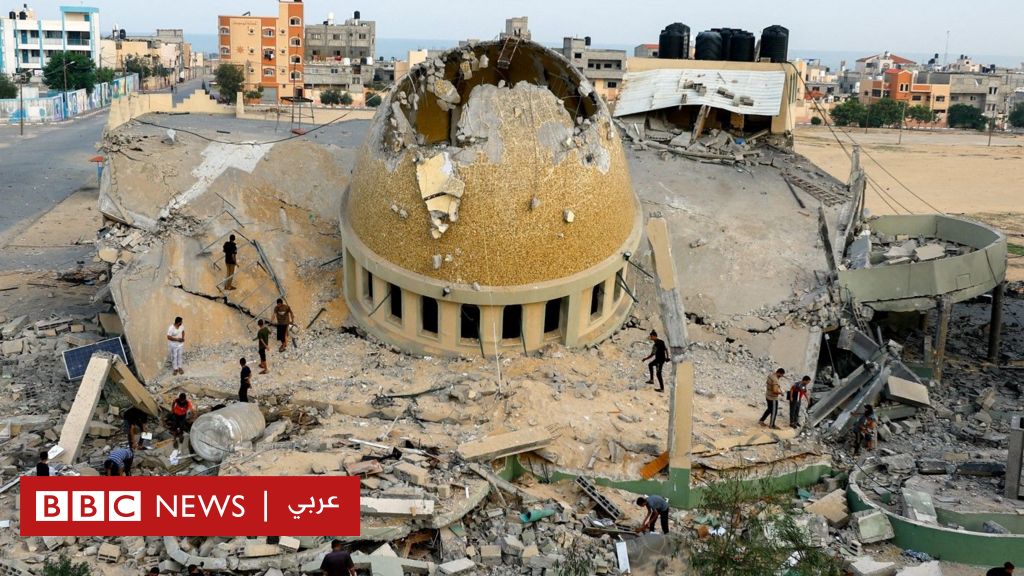

In conclusion, the interconnected conflicts in Israel, Palestine, and Yemen present a formidable challenge to regional stability. The humanitarian crisis is undeniable, and the potential for further escalation is a significant concern. While finding a peaceful resolution is a daunting task, exploring different viewpoints and understanding the complex interplay of actors is essential for fostering dialogue and potentially paving the way toward a more peaceful future.
This complex web of conflict requires a nuanced approach to understanding, and further investigation is warranted.
Questions Often Asked
What is the current status of negotiations between Israel and Palestine?
Unfortunately, there are no significant active negotiations between Israel and Palestine reported recently, despite ongoing efforts by international actors. The situation remains highly volatile and unpredictable.
What are the key differences between Hamas and other Palestinian factions?
Hamas’s ideology is distinct, emphasizing an Islamic approach to Palestinian liberation, often differing from the more secular or moderate stances of other Palestinian groups.
How does the conflict in Yemen affect regional trade routes?
The Houthi conflict has disrupted key trade routes in the region, impacting vital shipping lanes and causing economic hardship for surrounding countries.
What is the role of the United States in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict?
The US has historically played a significant role as a mediator and supporter of Israel, although its approach has varied across administrations. Recent efforts at mediating have been limited.