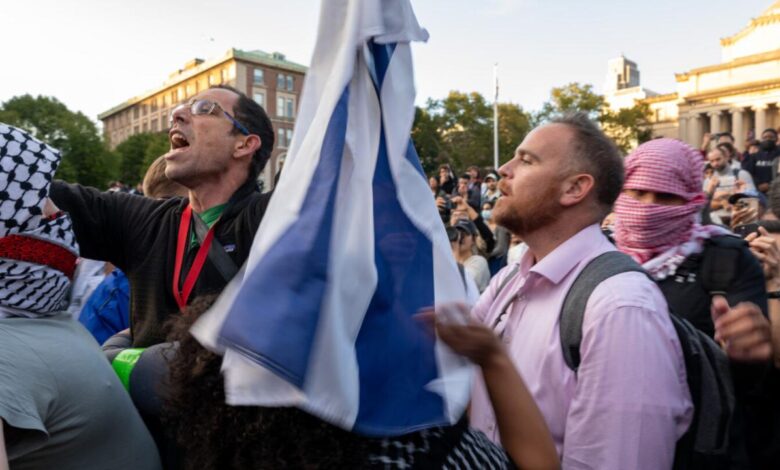

Barnard College Free Speech Israel-Hamas War Restrictions
Barnard College free speech restrictions Israel Hamas war ignite a crucial debate about balancing diverse viewpoints with campus safety. Students navigate complex political landscapes, especially regarding the Israel-Hamas conflict, while navigating established free speech policies. How do these policies address the unique challenges posed by this conflict? This exploration delves into the historical context, Barnard’s specific regulations, potential conflicts, and case studies to offer a comprehensive understanding of the issue.
This investigation examines the interplay between free speech rights, student activism, and the administration’s responsibility to foster a safe and inclusive learning environment. The complex nature of the Israel-Hamas conflict, with its passionate proponents and detractors, necessitates careful consideration of the nuances of free speech on a college campus. We explore how different perspectives are expressed and the potential restrictions that may arise.
Historical Context of Free Speech on Campus: Barnard College Free Speech Restrictions Israel Hamas War
The history of free speech on college campuses in the United States is a complex and evolving narrative, shaped by legal precedents, societal shifts, and the very nature of higher education. It’s not a static concept, but rather a dynamic interplay between the desire for open discourse and the need for order and safety within the academic environment. From the early days of universities to the present, the balance between these competing forces has been constantly renegotiated.The fundamental principle of free speech, while enshrined in the First Amendment, has always been subject to interpretation and application in diverse contexts.
This is especially true on college campuses, where the unique environment of learning and intellectual exploration necessitates careful consideration of the limitations and boundaries of expression. The legal landscape surrounding free speech on campus has evolved significantly over time, reflecting broader societal changes and legal decisions.
Early Development of Free Speech Rights
The early American universities, often founded on religious or philosophical principles, fostered a unique intellectual environment that valued open debate. However, these freedoms were not always formally codified or legally protected. The concept of academic freedom, the freedom of teachers and students to discuss and explore ideas without fear of censorship or retribution, began to emerge as a crucial element of the educational process.
The role of the university as a forum for the exchange of ideas was gaining importance.
Landmark Court Cases and Legislation
Several landmark Supreme Court cases have significantly shaped the understanding of free speech rights on college campuses.
- Tinker v. Des Moines Independent Community School District* (1969) affirmed students’ right to symbolic speech, establishing a crucial precedent for student expression.
- Hazelwood School District v. Kuhlmeier* (1988), while not directly a college case, clarified the power of school administrations to regulate student speech in school-sponsored publications. This ruling established a distinction between student speech in school-sponsored activities and student speech in non-school-sponsored forums. The evolution of these rulings, and their implications for campus life, is critical to understanding the present legal landscape.
Comparison with Public Forums
Free speech protections on college campuses differ from those in public forums. While both are important spaces for expression, the specific constraints and regulations differ significantly. Public forums, by their nature, are often subject to more extensive protections under the First Amendment, allowing for a wider range of speech. College campuses, while also crucial for expression, often operate under a more structured framework.
This structure is intended to balance freedom of expression with the educational mission and well-being of the student body. The specific characteristics of each environment need careful consideration in evaluating free speech claims.
The debate around free speech restrictions at Barnard College regarding the Israel-Hamas war is really interesting, right? It’s a complex issue with a lot of passionate opinions. Meanwhile, the recent news about Chris Young’s charges being dropped ( chris young charges dropped ) highlights the importance of fair legal processes. It makes me think about the broader implications of these kinds of discussions, especially in the context of college campuses and freedom of expression.
The Barnard situation is definitely something that deserves further consideration, and the larger context of free speech rights.
The Role of Academic Freedom
Academic freedom, the freedom of teachers and students to discuss and explore ideas without fear of censorship or retribution, is intrinsically linked to free speech on campus. It allows for critical thinking, intellectual inquiry, and the pursuit of knowledge. Academic freedom is not absolute, and its boundaries are subject to legal and institutional frameworks. It represents a critical component of the educational process, fostering the exchange of ideas and the pursuit of knowledge.
Barnard College’s recent stance on free speech regarding the Israel-Hamas war has sparked debate. It’s interesting to consider how these discussions relate to broader conversations about free expression. For example, the recent news surrounding stars like Harley Johnston, Oettinger, and Benn, as covered in this article, stars harley johnston oettinger benn highlights the complex interplay of public figures and current events.
Ultimately, the free speech restrictions at Barnard College remain a significant point of contention in the face of the ongoing war.
Table: Free Speech Protections in US States (College Campuses)
| State | Specific Protections (College Campuses) | Notable Court Cases/Legislation |
|---|---|---|
| California | Generally aligned with federal protections, with specific state laws regarding student conduct and speech. | Numerous cases interpreting the First Amendment in the context of California’s higher education institutions. |
| New York | Similar to federal standards, with emphasis on maintaining a safe and orderly learning environment. | State precedents addressing free speech rights within the context of university governance. |
| Texas | Generally aligned with federal standards, with a focus on balancing free speech with the need for a positive learning environment. | Texas-specific case law on student expression and academic freedom. |
| Florida | Protections are generally consistent with federal law, with a focus on balancing free speech rights with other legitimate institutional interests. | Court rulings in Florida addressing free speech rights on college campuses. |
| Illinois | Generally adheres to federal standards, with specific state laws concerning student conduct and speech. | Illinois cases that have shaped the interpretation of free speech on college campuses. |
This table provides a limited overview. A comprehensive analysis would require in-depth research into each state’s specific laws and court decisions. The legal landscape varies, and the specifics of each state’s approach to free speech on college campuses can differ significantly.
Barnard College’s Specific Policies
Barnard College, like many other institutions of higher learning, recognizes the importance of free speech as a cornerstone of academic discourse and a fundamental right. However, the exercise of this right must be balanced with the need to create a respectful and inclusive learning environment for all students. This balance is often complex and requires careful consideration of potential conflicts and impacts.
Barnard’s policies reflect this balancing act.Barnard College’s policies on free speech are designed to protect the right to express diverse viewpoints while simultaneously preventing disruption or harassment of the educational process. These policies aim to create an environment where open dialogue is encouraged, but where respectful communication and consideration for others are paramount. The policies are interpreted and applied within the context of the college’s commitment to inclusivity and its mission of providing a supportive and equitable learning environment for all students.
Barnard’s Free Speech Policies: A Summary
Barnard’s commitment to free expression is enshrined in its policies, which aim to strike a delicate balance between the right to express diverse viewpoints and the need for a respectful and inclusive learning environment. These policies are not simply a list of permitted or prohibited speech, but rather a framework for navigating potentially complex situations. They recognize that the exercise of free speech rights can have diverse impacts, both positive and negative.
Examples of Policy Application
Specific instances of how Barnard’s free speech policies have been applied are often case-specific and involve detailed evaluations of the context, intent, and potential impact of the expression in question. The college’s approach in these situations is guided by a careful consideration of the potential for disruption or harassment, and a commitment to fostering an environment where all students feel safe and respected.
Examples might include disciplinary action against disruptive behavior during events, or the provision of support to students who feel harassed or intimidated by the expression of certain viewpoints. These examples highlight the need for a nuanced approach to free speech on campus, considering the potential consequences and the importance of creating an environment conducive to learning for everyone.
Procedures for Challenging or Appealing Policies
Barnard College provides avenues for students, faculty, and staff to challenge or appeal decisions related to free speech policies. The precise procedures are Artikeld in the college’s relevant documents and are often reviewed by appropriate committees or panels. These procedures are designed to ensure fairness, transparency, and due process in handling complaints or appeals. Students should refer to the official college documentation for the exact procedures.
Relationship to National Trends
Barnard’s free speech policies reflect broader national trends regarding campus free speech. The increasing politicization of higher education, particularly in relation to contentious social issues, has led to a heightened awareness of the need for policies that balance free expression with inclusivity. This national trend is evident in the development and implementation of similar policies at other institutions, often involving careful consideration of factors such as the potential for disruption, the nature of the expression, and the impact on the learning environment.
Procedures for Handling Free Speech Complaints
| Type of Complaint | Procedure |
|---|---|
| Disruptive behavior during an event | Documentation of the incident by witnesses, review by the relevant office, possible disciplinary action. |
| Harassment or intimidation | Investigation by the relevant office, potential disciplinary action against the perpetrator, support for the victim. |
| Concerns about the appropriateness of an expression | Review of the expression in context, consideration of potential impact on the learning environment, dialogue with the relevant parties. |
| Appeals of disciplinary actions | Formal appeal process Artikeld in college documents, review by relevant committees, possibility of arbitration. |
The Israel-Hamas Conflict and Student Expression
The Israel-Hamas conflict, a deeply complex and emotionally charged issue, inevitably impacts campus discourse. Students bring diverse perspectives shaped by personal experiences, family backgrounds, and exposure to various media narratives. This often leads to passionate debates and sometimes, tense discussions about the conflict’s implications. Understanding these nuances is crucial for fostering a campus environment where different viewpoints can be expressed respectfully.The multifaceted nature of the conflict makes it a significant point of contention on college campuses.
Students from all walks of life, with varying levels of familiarity with the historical context, political ideologies, and personal connections to the region, will hold distinct perspectives. Navigating these differences is essential for maintaining a healthy dialogue and ensuring the safety and well-being of all students.
Different Viewpoints on Campus
Students expressing viewpoints on the conflict often fall into several categories. Some students strongly support the Israeli government’s actions, citing security concerns and historical grievances. Others align with Palestinian narratives, highlighting the issue of occupation and human rights violations. There are also students who advocate for a more nuanced perspective, emphasizing the need for a two-state solution or other peaceful resolutions.
Understanding these diverse perspectives is key to productive dialogue.
Examples of Student Expression
Student activism surrounding the conflict has taken various forms. Protests, rallies, and educational events have been common methods of expressing solidarity with either side of the conflict. Some students organize events focused on specific aspects of the conflict, like highlighting the humanitarian crisis or advocating for specific political solutions. These expressions can include speeches, presentations, discussions, and even artistic demonstrations.
Furthermore, student-run publications and social media campaigns often feature diverse viewpoints, reflecting the wide spectrum of opinions on campus.
Comparison with Other Activism
The Israel-Hamas conflict frequently generates intense student activism, comparable to other politically charged topics. However, the specific historical context and emotional investment often make this issue more complex to navigate. For instance, activism related to climate change might focus on policy changes, while activism on the Israel-Hamas conflict frequently involves deeply held personal beliefs and emotional ties to the region.
Student Perspectives Table
| Student Perspective | Key Arguments | Potential Concerns |
|---|---|---|
| Pro-Israel | Security concerns for Israel, historical grievances, and the right of self-defense. | May overlook Palestinian perspectives or be perceived as insensitive to Palestinian suffering. |
| Pro-Palestinian | Human rights violations, occupation, and the need for Palestinian self-determination. | May be seen as overly critical of Israel or fail to acknowledge Israeli concerns. |
| Neutral/Nuanced | Advocates for a two-state solution, emphasizes the need for peaceful resolution, and highlights the complexities of the conflict. | May be perceived as lacking a strong position or not taking a stance on a controversial issue. |
Potential Conflicts and Restrictions
Navigating free speech on a diverse campus like Barnard presents a complex challenge. Balancing the right to express diverse viewpoints with the need to foster a safe and inclusive environment requires careful consideration. The Israel-Hamas conflict, with its deeply held and often conflicting perspectives, amplifies these tensions. Finding a path forward necessitates a nuanced understanding of the potential conflicts that may arise and how administrators can effectively mediate them.The delicate balance between free speech and the well-being of the campus community is paramount.
Open dialogue is crucial, but so is the recognition that certain expressions may cross the line into hate speech or harassment. Understanding these boundaries is essential to maintaining a supportive environment for all students. This requires a proactive approach to identifying and addressing potential conflicts before they escalate.
Potential Conflicts Between Free Speech Rights and Campus Diversity
The inherent diversity of a campus community, including diverse viewpoints on sensitive topics like the Israel-Hamas conflict, can lead to clashes. Students holding opposing perspectives may find themselves in disagreements. Respectful dialogue is vital, but sometimes, differing opinions can escalate into hostile confrontations, impacting the learning environment for everyone.
Balancing Free Speech with the Need to Prevent Hate Speech or Harassment
Establishing clear guidelines for acceptable speech is essential to maintaining a safe and inclusive campus environment. While free speech is a fundamental right, it does not extend to expressions that promote hate speech or harassment. These forms of speech undermine the sense of belonging and safety that is essential for a thriving academic community. Campus policies should clearly delineate the difference between protected speech and prohibited conduct, ensuring that all students feel safe and respected.
Barnard College’s recent stance on free speech regarding the Israel-Hamas war is raising eyebrows. While the specifics are still unclear, it’s interesting to consider how this debate intersects with broader discussions about freedom of expression. This debate mirrors the ongoing national conversation surrounding the Carroll verdict and its implications for Haley and Trump, as seen in this CNN report.
Ultimately, the core issue at Barnard remains the tension between protecting diverse viewpoints and maintaining a safe and inclusive learning environment.
Potential Restrictions on Speech Related to the Israel-Hamas Conflict
Restrictions on speech related to the Israel-Hamas conflict are a complex issue. The conflict’s emotional intensity can easily escalate discussions, making it difficult to maintain respectful dialogue. Policies must carefully consider the potential for inflammatory rhetoric while ensuring the protection of free speech. A nuanced approach, focusing on the difference between expressing opinions and engaging in harassment, is vital.
A crucial element is the ability to distinguish between speech that incites violence and speech that simply expresses a controversial viewpoint.
The Role of Administrators in Mediating Potential Conflicts
Administrators play a critical role in mediating potential conflicts. They must be neutral facilitators, encouraging dialogue and promoting understanding. Training on conflict resolution and recognizing hate speech is crucial. Effective communication channels and readily available resources for students to report concerns are also vital. By creating a supportive environment where students feel heard and respected, administrators can help prevent conflicts from escalating.
The recent debate surrounding Barnard College’s free speech restrictions regarding the Israel-Hamas war feels incredibly disconnected from the real-world issues impacting everyday people. While the political climate surrounding the war is undoubtedly intense, it’s interesting to consider how initiatives like President Biden’s push for an infrastructure decade in Wisconsin, as detailed in this CNN article , could be seen as a different kind of response to larger societal challenges.
Ultimately, the nuanced conversation about free speech at Barnard, amidst the war, still needs a clearer focus on the needs of all students and faculty.
Table Illustrating Potential Scenarios of Conflict Resolution Regarding the Israel-Hamas Conflict on Campus, Barnard college free speech restrictions israel hamas war
| Scenario | Potential Conflict | Possible Resolution Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Student A gives a speech advocating for a specific viewpoint on the conflict that is highly critical of another group. | The speech may be perceived as inflammatory or discriminatory by some students. | Administrators could mediate a discussion with Student A and other students, encouraging respectful dialogue and outlining campus policies on hate speech. |
| Student B and Student C engage in a heated debate about the conflict that escalates into personal attacks. | The heated exchange may disrupt the campus environment and create a hostile atmosphere. | Administrators could intervene to separate the students, reminding them of campus policies on respectful discourse and encouraging them to engage in constructive dialogue. |
| A student group holds a demonstration with signs expressing a strong position on the conflict that some find offensive. | The demonstration may be seen as provocative and disruptive to the campus community. | Administrators can engage in dialogue with the student group, clarifying the campus policies on demonstrations and ensuring they do not violate any regulations. |
Case Studies of Free Speech on Other Campuses
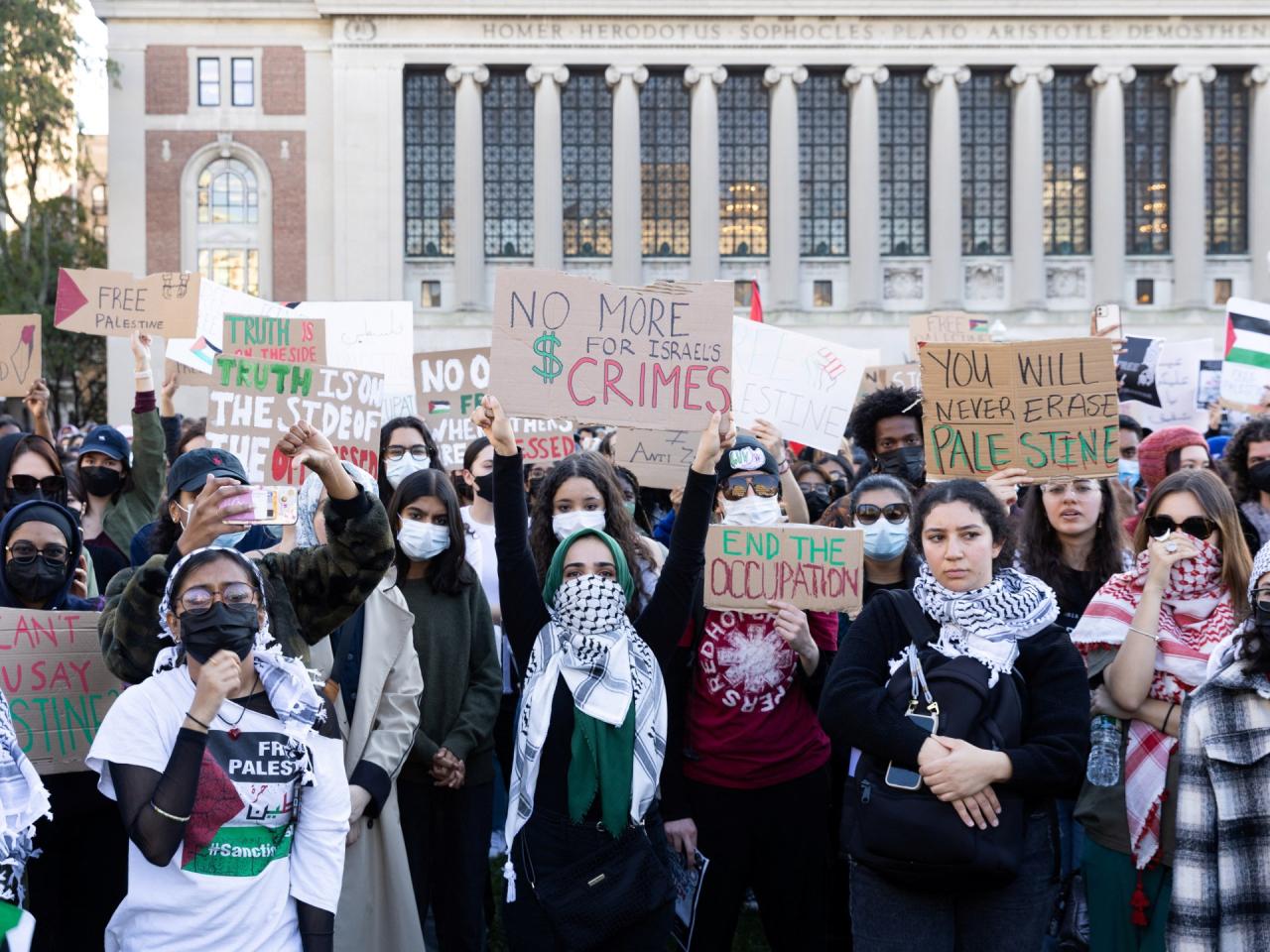

Examining how other institutions have navigated similar free speech conflicts surrounding political expression, particularly regarding the Israel-Hamas conflict, offers valuable insights for Barnard College. These case studies illuminate successful and unsuccessful strategies, providing a broader context for understanding the complexities of balancing free speech rights with the need for a respectful and inclusive campus environment. By analyzing past experiences, Barnard can potentially learn from the triumphs and pitfalls of similar institutions.Analyzing the approaches taken by other colleges and universities facing comparable free speech dilemmas provides crucial context.
Understanding the strategies used, the outcomes achieved, and the unforeseen challenges encountered allows for a nuanced examination of potential solutions and limitations.
Examples of Successful Approaches
Several universities have successfully navigated student activism related to the Israel-Hamas conflict, though not without challenges. A common thread in these successful approaches is a commitment to open dialogue, facilitated by neutral platforms for diverse viewpoints.
- Establishing Dialogue Forums: Some institutions have created dedicated spaces for student groups to engage in respectful discussion, allowing for the exchange of differing perspectives. These forums can range from structured debates to open discussion groups, aiming to foster understanding and address concerns constructively.
- Promoting Understanding Through Education: Educational initiatives play a crucial role in fostering a nuanced understanding of complex geopolitical issues. Workshops, guest speakers, and film screenings can broaden perspectives and encourage empathy. This approach acknowledges the need for students to be well-informed before engaging in passionate discussions.
- Neutral Moderation: Institutions often appoint neutral moderators or facilitators to oversee discussions, ensuring all participants feel heard and respected. This commitment to impartiality can create a more conducive environment for respectful exchange.
Examples of Unsuccessful Approaches
Unfortunately, some institutions have encountered setbacks in managing free speech conflicts related to the Israel-Hamas conflict. These instances often highlight the difficulties in balancing diverse viewpoints and maintaining a supportive campus environment.
- Suppression of Certain Voices: A key factor in unsuccessful approaches is the suppression of specific viewpoints, whether through censorship or perceived favoritism towards one side of the debate. This can create an environment where students feel their opinions are invalidated, leading to resentment and potentially more contentious interactions.
- Lack of Clear Policies: Vagueness or a lack of clearly defined policies regarding free speech and political expression can leave students and administrators uncertain about acceptable boundaries. This ambiguity can lead to misunderstandings and escalate conflicts.
- Ineffective Conflict Resolution Mechanisms: If a college lacks well-defined procedures for addressing conflicts arising from differing viewpoints, incidents may escalate quickly. A clear and efficient conflict resolution mechanism is crucial to de-escalate tense situations.
Comparative Analysis and Table
The following table summarizes successful and unsuccessful approaches observed on other campuses, offering a comparative analysis to help inform Barnard College’s policies and strategies.
| Approach | Success Factors | Failure Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Establishing Dialogue Forums | Facilitates open exchange of diverse perspectives; Fosters understanding; Creates a neutral platform | Can be challenging to manage large groups; May not effectively address deeply held beliefs |
| Promoting Understanding Through Education | Broadens perspectives; Encourages empathy; Provides students with the necessary tools to engage in nuanced discussions | Can be time-consuming; May not resonate with all students |
| Neutral Moderation | Ensures all participants feel heard and respected; Maintains an impartial environment | Can be challenging to find truly neutral moderators; May not always effectively mediate intense conflicts |
| Suppression of Certain Voices | N/A | Creates an environment where students feel their opinions are invalidated; Can lead to resentment and further conflicts |
| Lack of Clear Policies | N/A | Leaves students and administrators uncertain about acceptable boundaries; Can lead to misunderstandings and escalate conflicts |
| Ineffective Conflict Resolution Mechanisms | N/A | Allows conflicts to escalate quickly; Doesn’t provide a clear pathway for resolving disputes |
Free Speech and the Role of Student Groups
Student groups play a vital role in shaping campus discourse and advocating for free speech rights. Their involvement extends beyond simply expressing opinions; they often act as catalysts for change, initiating dialogues, and pushing for policy adjustments. Their activism can be a powerful force in creating a more inclusive and open learning environment.Student groups, whether focused on specific issues or representing broader student interests, often serve as crucial intermediaries between students and administrators.
They can channel student concerns and demands, ensuring that the voices of the student body are heard and considered. This active engagement fosters a dynamic and responsive campus environment.
Student Group Activities in Advocating Free Speech
Student groups engage in various activities to advocate for free speech rights. These range from organizing protests and rallies to writing letters to administrators and publishing articles in campus newspapers. Public forums, debates, and educational workshops also play a significant role in raising awareness and fostering dialogue on free speech issues.
- Organizing protests and rallies: These are visible forms of advocacy, drawing attention to specific issues and raising public awareness. Effective organization often includes strategic planning, outreach to campus allies, and clear communication of demands.
- Writing letters to administrators and publishing articles: Formal communication, such as letters to administrators, helps to document concerns and propose solutions. Published articles in campus newspapers or online platforms amplify these concerns and engage broader campus communities.
- Public forums, debates, and educational workshops: These interactive platforms provide opportunities for open dialogue and critical discussion, allowing different perspectives to be shared and understood. They are crucial for fostering a culture of respectful debate and understanding.
Examples of Student Group Influence on Campus Policies
Student groups have successfully influenced campus policies on various issues, including free speech. Their persistent advocacy has resulted in the establishment of clearer guidelines, improved accessibility to resources, and more inclusive environments. These changes demonstrate the power of organized student action.
- Establishment of clearer guidelines: Student groups have lobbied for more transparent and comprehensive policies regarding free speech on campus. These policies often address issues like the use of campus spaces for events, restrictions on expression, and the resolution of conflicts.
- Improved accessibility to resources: Student groups have often advocated for greater access to resources for students who wish to exercise their free speech rights, including funding for publications, printing materials, and meeting space.
- More inclusive environments: Student groups have played a significant role in creating a more inclusive environment for diverse voices and perspectives. They have organized events and initiatives aimed at promoting tolerance and respect, fostering a more welcoming campus atmosphere.
Student Group Approaches to Similar Issues on Other Campuses
Student groups on other campuses have successfully addressed similar issues regarding free speech. Their experiences provide valuable insights and best practices for similar initiatives.
- Different approaches to handling conflicts: Student groups have employed various strategies to address conflicts arising from differing viewpoints on free speech. These strategies have included facilitating dialogue, mediating disagreements, and collaborating with campus administrators to find mutually acceptable solutions.
- Success in shaping campus discourse: Examples of student groups effectively shaping campus discourse demonstrate the impact of organized student action. These examples showcase how student groups can raise awareness, initiate dialogue, and drive positive change on campus.
- Lessons learned from past campaigns: Past campaigns and experiences of student groups offer valuable lessons and best practices for future initiatives related to free speech. These experiences can provide guidance on strategies for advocacy, communication, and building support for specific causes.
Categorizing Student Groups and Their Free Speech Activities
The following table categorizes different student groups and their activities related to free speech.
| Student Group Category | Specific Activities Related to Free Speech |
|---|---|
| Academic Organizations | Organizing debates, hosting lectures, publishing journals, advocating for intellectual freedom |
| Political Organizations | Organizing protests, rallies, creating political publications, advocating for specific policies |
| Cultural Organizations | Hosting events, creating art exhibitions, promoting diverse cultural perspectives, advocating for inclusive spaces |
| Student Government | Formulating and implementing policies related to free speech, advocating for student rights, mediating conflicts |
Comparative Analysis of International Perspectives
Examining free speech rights and limitations on college campuses across the globe reveals a complex interplay of legal frameworks, cultural norms, and historical contexts. This comparative analysis highlights the variations in how different nations approach the delicate balance between protecting expression and addressing potential harms. Understanding these nuances is crucial when considering sensitive topics like the Israel-Hamas conflict on university campuses.International perspectives on free speech rights differ significantly, reflecting varying legal traditions and societal values.
The interplay of constitutional protections, statutory regulations, and cultural expectations shapes the landscape of campus discourse. This dynamic environment necessitates a nuanced understanding of how these factors interact to influence student expression.
Barnard College’s recent stance on free speech regarding the Israel-Hamas conflict has sparked debate. While the college’s position is being scrutinized, it’s important to consider the bigger picture, like how events in the snow-capped Swiss Alps, specifically the snow polo tournaments in St. Moritz, also highlight environmental concerns. The growing awareness of the impact of events like these on the environment is undeniable, especially when considering the implications for future generations, mirroring the ongoing need for discourse on freedom of expression, particularly when it comes to sensitive topics like the Israel-Hamas conflict.
snow polo st moritz climate change. The discussion surrounding Barnard’s actions regarding free speech continues to be a complex and relevant one.
Free Speech Rights in Different Countries
Different countries have different approaches to free speech, often reflecting broader societal values. Some nations emphasize individual liberties, while others prioritize social harmony or national interests. These varying perspectives impact the degree to which students can express controversial views on sensitive topics.
- In the United States, the First Amendment guarantees broad protection for freedom of speech, although limitations exist for incitement to violence or defamation. Campus speech codes often face legal challenges based on this precedent.
- European nations, while generally upholding free speech rights, may have stricter regulations regarding hate speech or expressions deemed offensive to specific groups. This often involves balancing freedom of expression with the need to protect vulnerable populations.
- Countries with authoritarian regimes may have severely restricted free speech rights, even on university campuses. Expression critical of the government or potentially disruptive to the status quo can be heavily curtailed.
Role of International Law
International law plays a limited role in dictating campus free speech policies. While international human rights instruments, such as the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, emphasize the importance of freedom of expression, their application to specific campus situations is often ambiguous. Interpretations of these rights vary, and their enforcement on university campuses is typically handled at the national or regional level.
Cultural Context and the Israel-Hamas Conflict
The expression of views on the Israel-Hamas conflict is deeply intertwined with cultural and historical contexts. Different perspectives on the conflict, rooted in varying interpretations of history, religion, and politics, may lead to diverse student opinions. Understanding these differing viewpoints is essential for fostering respectful dialogue and avoiding misunderstandings.
International Cases Related to Campus Free Speech
While readily available international cases specifically concerning campus free speech and the Israel-Hamas conflict are scarce, legal precedents regarding freedom of expression on campuses in various countries provide insights. These cases often involve student activism, protests, and debates on sensitive political issues. They demonstrate the ongoing challenges of balancing free speech rights with the potential for harm.
Table: Comparison of Free Speech Regulations
| Country | Free Speech Protections | Limitations | Cultural Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Generally broad protections under the First Amendment | Limitations on incitement to violence, defamation | Emphasis on individual liberties and expression |
| United Kingdom | Strong protection for free speech, but with limitations on hate speech | Laws addressing hate speech, discrimination | Emphasis on social cohesion and inclusivity |
| China | Limited free speech protections | Strict government control over information and expression | Emphasis on national unity and stability |
| South Africa | Strong constitutional protection for freedom of expression, but with limitations | Protection for marginalized groups | Emphasis on reconciliation and inclusivity after apartheid |
Illustrative Examples of Speech Acts
Navigating the complexities of the Israel-Hamas conflict on a college campus requires sensitivity and understanding. Student expression, while crucial for intellectual discourse, can sometimes lead to unintended consequences. The delicate balance between free speech and the need for a respectful and inclusive environment becomes particularly important when discussing highly charged political issues. This section examines potential speech acts related to the conflict and their possible impacts on the campus community.
Verbal Speech Acts
Verbal speech acts, encompassing discussions, debates, and presentations, can vary widely in tone and intent. A student might deliver a passionate speech advocating for the Palestinian cause, emphasizing the historical context of the conflict and advocating for specific policies. Conversely, another student might present a counter-argument, focusing on the security concerns of Israel and potentially invoking the concept of self-defense.
These differing perspectives can create a vibrant intellectual environment, but also potential for misunderstanding and hurt feelings.
- A student delivering a presentation on the Palestinian perspective, emphasizing human rights violations.
- A student engaging in a debate with another student, presenting a strong pro-Israel stance.
- A student sharing personal stories of family members affected by the conflict, focusing on their own experience.
Written Speech Acts
Written speech acts, including essays, posters, and online posts, play a significant role in shaping public opinion. A student might write an op-ed for the campus newspaper expressing support for a specific resolution regarding the conflict. Alternatively, another student might post inflammatory comments on social media platforms, potentially inciting conflict. These actions can be powerful tools for communication but also require careful consideration of their potential impact on the campus community.
- A student writing an op-ed for the campus newspaper advocating for a specific resolution related to the conflict.
- A student creating a flyer expressing solidarity with either Palestine or Israel, possibly using provocative imagery.
- A student posting on social media platforms, potentially using strong language or making generalizations about either side.
Visual Speech Acts
Visual speech acts, including posters, artwork, and demonstrations, often convey messages quickly and powerfully. A student might create a poster displaying images and slogans expressing solidarity with Palestine, potentially evoking strong emotional responses. Conversely, another student might create a counter-poster promoting the Israeli perspective. These visual representations can spark discussions but also risk alienating certain groups.
- A student creating a poster with images and slogans expressing solidarity with Palestine.
- A student creating a mural expressing a particular viewpoint on the conflict.
- A student organizing a demonstration on campus, either for or against specific policies or actions.
Stakeholder Responses
Different stakeholders on campus might respond to these speech acts in diverse ways. Students might engage in respectful dialogue or express concerns about the tone or content of the speech. Faculty might facilitate discussions to encourage critical thinking and understanding. Administration might intervene if the speech acts violate campus policies or create a hostile environment.
| Speech Act Type | Student Response | Faculty Response | Administration Response |
|---|---|---|---|
| Verbal Speech | Engaging in respectful debate or expressing concern about tone | Facilitating a discussion on different perspectives | Intervening if the speech violates policies or creates a hostile environment |
| Written Speech | Engaging in respectful debate or criticizing the content | Encouraging a discussion about the ideas in writing | Taking action if the writing violates policies or promotes harassment |
| Visual Speech | Discussing the message, expressing concerns about imagery | Facilitating a discussion about the symbolism and impact of the visuals | Intervening if the visuals violate policies or incite hostility |
Closure
In conclusion, the debate surrounding free speech restrictions at Barnard College, particularly concerning the Israel-Hamas conflict, highlights the intricate balance between protecting diverse viewpoints and maintaining a harmonious campus environment. This analysis underscores the importance of nuanced discussions, transparent policies, and effective conflict resolution strategies to ensure a productive and inclusive learning environment for all students. The challenges presented by this conflict mirror those faced on campuses nationwide, requiring ongoing dialogue and adaptation of policies.
Query Resolution
What are some examples of speech acts related to the Israel-Hamas conflict that could occur on campus?
Examples could include posters, social media posts, speeches, and potentially even demonstrations. The potential for heated discussions and varying interpretations of events is significant.
How does Barnard College’s policy on free speech compare to other institutions?
This analysis will explore the varying approaches to similar conflicts at other universities, examining successful and unsuccessful strategies to provide context for Barnard’s specific situation.
What role do student groups play in advocating for free speech rights at Barnard?
Student groups can act as crucial advocates, organizing discussions, protests, and potentially influencing policies to support diverse viewpoints and address specific concerns.
What are the potential conflicts between free speech rights and the need to prevent hate speech or harassment?
This is a significant tension, demanding careful consideration of how to allow for diverse expression while maintaining a safe and inclusive campus community. A nuanced approach is essential.

