Chile Wildfires A Global Warming Crisis
Chile wildfires global warming is a pressing issue, highlighting the devastating impact of climate change on the South American nation. The escalating frequency and intensity of these fires are directly linked to rising global temperatures, altered weather patterns, and a complex interplay of human factors. This post delves into the historical context, the role of global warming, the devastating impacts, and potential mitigation strategies.
From the arid landscapes of central Chile to the towering Andes, these wildfires are leaving an indelible mark. Understanding the science behind these events, the human cost, and the possible solutions is critical to preventing future disasters and protecting vulnerable communities.
Introduction to Chilean Wildfires
Chile, a country with a diverse geography and climate, has a long history of wildfires, shaped by a combination of natural and human factors. The recent intensification of these events is a significant concern, demanding a deeper understanding of the contributing elements to prevent future devastation. The impact of these fires extends beyond the immediate loss of property and life, encompassing wider ecological and socioeconomic consequences.The escalating frequency and severity of wildfires in Chile underscore the need for a comprehensive analysis of the factors driving these events.
Understanding the interplay between natural geographical predispositions and human activities is critical to developing effective mitigation strategies. The examples of past major wildfire events serve as potent reminders of the potential scale of the threat and the importance of proactive measures.
The devastating Chilean wildfires are a stark reminder of the devastating impacts of global warming. Witnessing the scale of the destruction is truly heartbreaking, and the loss of life and livelihoods is deeply unsettling. It’s easy to feel helpless in the face of such overwhelming events, and that’s why stories like “Grief is for people” Sloane Crosley offer a vital space to process these feelings.
Ultimately, though, these tragedies highlight the urgent need for collective action to combat climate change and prevent future disasters.
Historical Overview of Wildfires in Chile
Chile has experienced wildfires throughout its history, with varying degrees of intensity and impact. Historical records, though not always comprehensive, reveal patterns of fire activity linked to seasonal changes and weather conditions. Indigenous communities and early settlers have adapted to and managed wildfires as part of the landscape, though the intensity and frequency have changed significantly in recent decades.
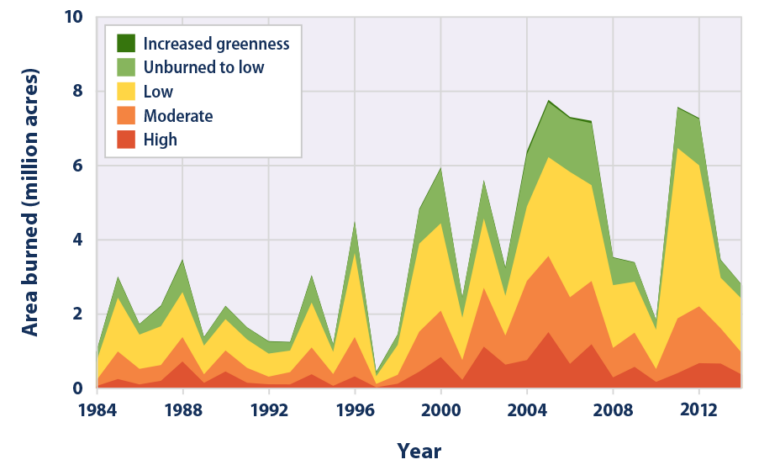
Recent Trends in Wildfire Frequency and Intensity, Chile wildfires global warming
Recent decades have witnessed a noticeable increase in the frequency and intensity of wildfires in Chile. This trend correlates with rising global temperatures and altered weather patterns. Satellite data and ground observations provide evidence of more extensive burn areas and longer fire seasons. Analysis of these trends helps understand the changing wildfire landscape and informs proactive measures.
Geographical Factors Contributing to Wildfire Risk in Chile
Chile’s diverse topography and climate play a significant role in determining wildfire risk. The country’s long, narrow shape, combined with varied elevations and vegetation types, creates diverse microclimates, making some regions more susceptible to fire than others. Dry, arid regions, particularly in central and northern Chile, are prone to intense wildfires due to their low humidity and high temperatures.
Human Factors Influencing Wildfire Occurrence
Human activities significantly contribute to the occurrence and spread of wildfires in Chile. Land use changes, such as deforestation for agriculture or urbanization, increase the amount of flammable vegetation. Furthermore, careless disposal of cigarettes or campfires, as well as electrical malfunctions, can easily spark devastating fires. Uncontrolled or inadequate maintenance of power lines, and lack of public awareness about fire safety practices are further exacerbating the problem.
Examples of Past Major Wildfire Events in Chile and Their Impact
Several significant wildfires have impacted Chile in recent years. The 2017 wildfires in the central region, for example, devastated vast areas of forest and agricultural land, displacing communities and causing significant environmental damage. These events highlight the profound and multifaceted effects of wildfires on Chilean society and its environment.
Global Warming’s Role in Chilean Wildfires
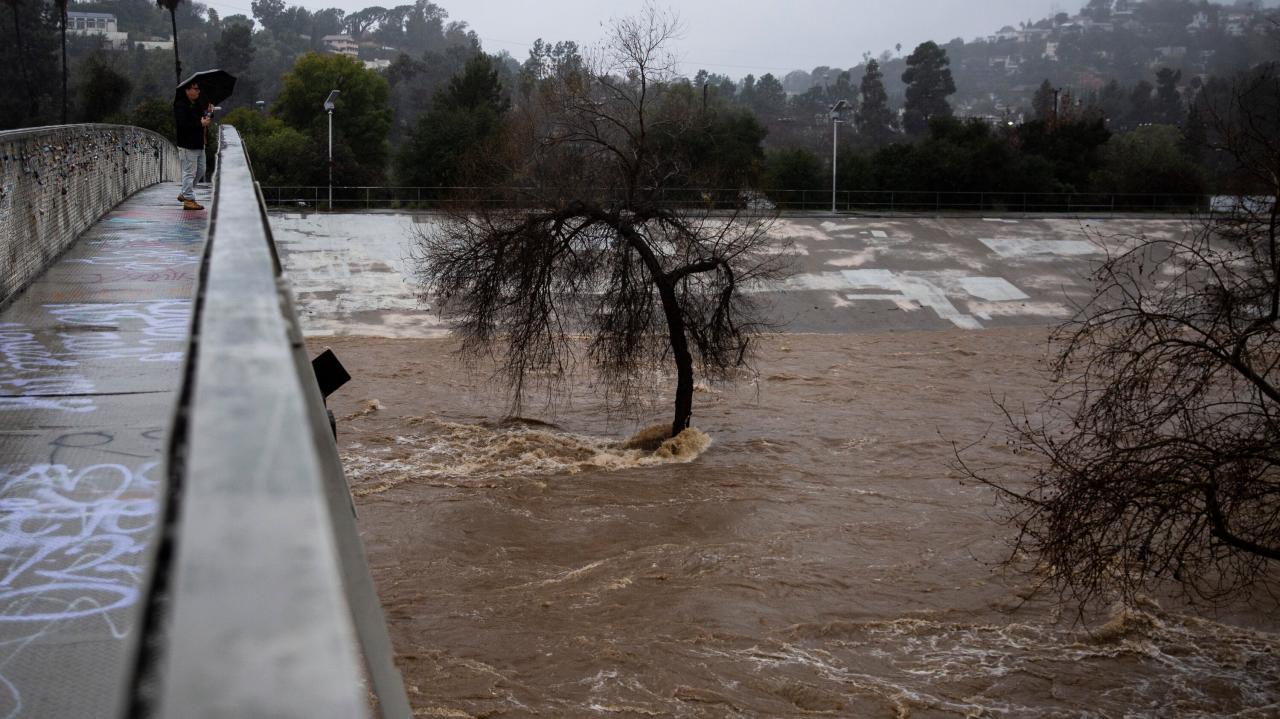

The devastating Chilean wildfires of recent years have underscored the alarming connection between human-induced climate change and increased wildfire risk. These infernos, fueled by extreme weather conditions, highlight the urgent need to understand the complex interplay between global warming and the escalating threat of these catastrophic events. Understanding the specific mechanisms through which climate change exacerbates wildfire conditions is crucial to mitigating future risks and developing effective strategies for preparedness and response.Global warming is significantly increasing the likelihood and intensity of wildfires in Chile, as well as globally.
The relentless rise in global temperatures is altering weather patterns, leading to drier conditions, higher temperatures, and longer periods of drought, all of which are key ingredients for wildfire ignition and propagation. This intensified wildfire risk presents a serious threat to human life, property, and the environment.
Mechanisms of Climate Change Exacerbating Wildfire Conditions
Climate change fuels wildfires through several interconnected mechanisms. Warmer temperatures increase evapotranspiration rates, leading to drier vegetation that acts as highly flammable fuel. Prolonged periods of drought further deplete soil moisture, making the landscape even more susceptible to ignition and rapid spread. Increased frequency and intensity of high-temperature heat waves contribute to a heightened risk of ignition and hinder firefighting efforts.
Stronger winds, a consequence of altered atmospheric circulation patterns, can fan flames, spreading fires over vast areas with devastating speed.
Evidence Linking Global Temperature Increases to Wildfire Patterns in Chile
A growing body of scientific research establishes a correlation between rising global temperatures and increased wildfire activity in Chile. Analysis of historical wildfire data shows a clear trend of increasing fire frequency and severity in regions experiencing higher temperatures and altered precipitation patterns. Studies often highlight a statistically significant relationship between rising global temperatures and the observed rise in wildfire activity in Chile.
For example, a study published in the journalNature Climate Change* found a strong correlation between rising global temperatures and increased wildfire risk in the Mediterranean region, a pattern also observable in Chilean ecosystems. This correlation is further strengthened by observed changes in precipitation patterns and altered vegetation.
Chile’s recent wildfires are a stark reminder of the devastating impact of global warming. While the tragedy in Chile is heartbreaking, it’s important to also consider the current geopolitical landscape. The Netanyahu hostage deal in Rafah, as reported in netanyahu hostage deal rafah , highlights the complex interplay of global crises. These crises, unfortunately, often overshadow the long-term effects of climate change, but the Chilean wildfires underscore the urgency of addressing global warming.
The interconnectedness of these issues cannot be ignored.
Altered Weather Patterns Contributing to Wildfires
The following weather patterns directly contribute to wildfire risk in Chile:
- Drought: Extended periods of drought significantly reduce soil moisture, making vegetation extremely dry and highly flammable. This dryness creates an environment primed for wildfire ignition and rapid spread, as seen in numerous recent Chilean wildfires.
- High Temperatures: Elevated temperatures increase the risk of ignition and intensify the burning process. Higher temperatures can lead to rapid evapotranspiration rates, reducing soil moisture and making vegetation more susceptible to fire. High temperatures also reduce the effectiveness of firefighting efforts.
- Strong Winds: Strong winds can rapidly spread embers and flames over vast distances, exacerbating the fire’s intensity and making it challenging to contain. This is a crucial factor in the devastating spread of many Chilean wildfires.
- Changes in Precipitation Patterns: Altered precipitation patterns, such as reduced rainfall or increased rainfall intensity, can result in prolonged periods of dryness and contribute to the buildup of highly flammable vegetation, increasing the risk of wildfires.
Projected Future Impact of Climate Change on Chilean Wildfire Risk
Climate change projections indicate a further increase in the frequency, intensity, and geographic extent of Chilean wildfires. Scientists predict that global warming will continue to intensify the aforementioned factors, leading to a higher likelihood of catastrophic wildfire events. Increased frequency of extreme weather events, such as heat waves and droughts, is anticipated to further exacerbate the risk. The projected future impact suggests a need for enhanced wildfire preparedness and mitigation strategies in Chile.
For instance, increased investment in early warning systems, proactive vegetation management, and improved fire suppression capabilities are essential to minimizing the impact of future wildfires.
Impacts of Chilean Wildfires
The devastating Chilean wildfires, fueled by climate change, have inflicted profound and multifaceted damage. Beyond the immediate spectacle of flames engulfing landscapes, the consequences ripple through ecosystems, communities, and economies. Understanding these impacts is crucial for effective disaster response and long-term recovery strategies.
Immediate Environmental Impacts
The immediate aftermath of wildfires brings a complex cocktail of environmental consequences. Smoke plumes, often extending hundreds of kilometers, significantly degrade air quality. Fine particulate matter, released during the combustion process, poses serious health risks to residents and wildlife. Respiratory illnesses, cardiovascular problems, and even premature death can result from prolonged exposure to polluted air. The intense heat and flames directly impact biodiversity.
Plant life, including native flora, is destroyed, while countless animals lose their habitats and food sources. Many species face extinction risks due to the loss of critical ecosystems. This rapid biodiversity loss can trigger cascading effects throughout the food web, leading to long-term ecological imbalances.
Social and Economic Consequences for Affected Communities
Wildfires have devastating impacts on the social and economic well-being of affected communities. Homes are destroyed, livelihoods are disrupted, and psychological trauma can persist for years. The loss of homes and belongings disrupts families’ lives, creating hardship and potentially causing displacement. Farmers, who rely on agricultural land for their livelihoods, often face catastrophic crop losses. The loss of livestock further compounds the economic hardship.
Moreover, the wildfires often disrupt critical infrastructure, including transportation routes and communication systems. This disruption creates a challenge for providing aid and support to the impacted areas.
Long-Term Effects on Infrastructure, Agriculture, and Tourism
The long-term effects of wildfires are profound and pervasive. Damaged infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and power lines, requires extensive repair and reconstruction, placing a substantial financial burden on communities and governments. The recovery process can take years. Agriculture, a vital sector in many Chilean communities, is severely affected by the loss of fertile land and the disruption of agricultural cycles.
Re-establishing productive farmland requires significant time and investment. Tourism, a crucial source of income for many areas, is significantly impacted by the destruction of natural landscapes. The recovery of tourist attractions often involves substantial ecological restoration and investment. Reputational damage can linger for years, affecting the area’s attractiveness to visitors.
Human Cost of Chilean Wildfires
The human cost of Chilean wildfires is immeasurable. Loss of life is a tragic consequence, and the psychological scars on survivors and their families are enduring. The health impacts, ranging from respiratory problems to mental health issues, affect individuals and communities for extended periods. The loss of livelihoods and homes, coupled with the disruption of daily life, creates profound social and economic hardship.
These impacts can have a long-lasting effect on the affected population, necessitating long-term support and recovery strategies.
Mitigation Strategies for Chilean Wildfires
Chile’s devastating wildfires underscore the urgent need for proactive mitigation strategies. These strategies must address the root causes, enhance preparedness, and foster community resilience to prevent future catastrophic events. A multifaceted approach combining preventative measures, improved warning systems, and sustainable land management is crucial for safeguarding Chile’s ecosystems and communities.Effective mitigation requires a comprehensive understanding of the interplay between climate change, land management practices, and human activities.
By implementing robust preventative measures, Chile can significantly reduce the likelihood and impact of future wildfires.
Preventing Future Wildfires
Strategies to prevent future wildfires encompass a range of actions focusing on land management, fuel reduction, and responsible human behavior. Effective prevention involves addressing the underlying causes of wildfire risk. This includes proactive measures to reduce flammable materials in forested areas and along vulnerable ecosystems, promoting sustainable forest management practices, and encouraging responsible use of fire in rural areas.
- Fuel Reduction: Implementing controlled burns, prescribed fires, and mechanical thinning to reduce the amount of dry vegetation and forest litter is vital. This can create a safer environment by reducing the fuel load available for wildfire ignition. This technique has proven effective in many regions, demonstrating a measurable reduction in fire intensity and spread.
- Sustainable Land Management: Promoting practices like reforestation and afforestation with fire-resistant species can help create natural barriers to wildfire spread. Additionally, careful planning and implementation of logging practices can reduce the risk of unintended ignitions.
- Responsible Human Behavior: Educating the public about the risks associated with open flames, campfires, and discarded cigarettes is crucial. Strict regulations on outdoor burning and clear communication about fire danger levels are essential to minimizing human-caused ignitions.
Improving Early Warning Systems and Response Protocols
A robust early warning system is essential for timely evacuation and response efforts. This includes enhancing monitoring systems, developing advanced predictive models, and improving communication infrastructure.
- Advanced Monitoring Systems: Utilizing a combination of satellite imagery, weather data, and ground-based sensors to detect and track potential fire outbreaks can improve the accuracy and speed of warnings. This includes installing sensors in high-risk areas to provide real-time data.
- Predictive Modeling: Developing advanced predictive models to forecast fire behavior and potential spread can help authorities plan for evacuation routes and resource allocation. This includes incorporating data on wind patterns, topography, and vegetation types into the models.
- Improved Communication Infrastructure: Ensuring reliable communication channels for alerts, evacuations, and coordination among emergency responders is essential. This includes investing in radio networks, mobile apps, and other technologies to facilitate rapid communication.
Sustainable Land Management Practices
Sustainable land management practices are crucial for reducing wildfire risk and promoting ecosystem resilience. These practices are vital for the long-term sustainability of forest ecosystems and include careful forest management, sustainable grazing practices, and the use of fire-resistant vegetation.
- Controlled Burns: Implementing controlled burns at specific times of the year and under favorable conditions can reduce fuel loads and promote healthy forest ecosystems. This practice is not without risk, but when managed effectively, it can dramatically lower the potential for wildfires.
- Sustainable Grazing Practices: Proper grazing management can help control the spread of invasive species, improve the health of grasslands, and reduce the risk of wildfire ignition.
- Reforestation and Afforestation: Planting fire-resistant species can create natural barriers to wildfire spread and help to restore damaged ecosystems.
Community Engagement and Preparedness
Community engagement and preparedness are critical components of wildfire mitigation. This involves educating residents about wildfire risks, promoting evacuation plans, and training on fire safety procedures.
- Community Education Programs: Providing workshops and educational materials to residents about wildfire risks, prevention, and preparedness measures is crucial. This includes educating communities on how to recognize signs of potential wildfires and how to respond appropriately.
- Evacuation Planning: Developing clear evacuation plans and procedures for communities at risk of wildfire is essential. This involves identifying evacuation routes, assembly points, and communication protocols.
- Fire Safety Training: Training community members on fire safety procedures, including how to safely use and maintain fire-related equipment, is essential. Practical exercises can help familiarize residents with the appropriate actions during a wildfire emergency.
Comparison of Wildfire Prevention Methods
| Method | Description | Effectiveness | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Controlled Burns | Planned burning of vegetation to reduce fuel load. | High, if managed properly | Moderate |
| Mechanical Thinning | Removal of vegetation through mechanical means. | High | High |
| Reforestation with Fire-Resistant Species | Planting trees that are resistant to wildfire. | Moderate to High, long-term | Moderate |
| Public Education Campaigns | Raising awareness about wildfire risks and prevention. | Moderate to High, dependent on community engagement | Low |
International Cooperation and Support
Chile, a nation frequently facing the devastating impact of wildfires, relies heavily on international support during these crises. The scale of these events often surpasses the capacity of Chilean resources, necessitating the intervention of global partners. This aid manifests in various forms, from financial assistance to the sharing of expertise.International collaboration plays a vital role in bolstering Chile’s capacity to manage wildfires.
This support extends beyond immediate response, aiming to enhance long-term preparedness and resilience against future events. The spirit of solidarity shown by international partners demonstrates the global recognition of wildfire risks and the need for collaborative solutions.
Role of International Organizations
International organizations, such as the United Nations and various regional bodies, play a crucial role in coordinating international aid efforts during wildfire emergencies. Their expertise in disaster response and their ability to mobilize resources across borders are essential. These organizations often facilitate the provision of technical assistance and financial support to affected communities, helping them rebuild and recover.
Financial and Technical Aid to Affected Communities
International assistance often involves providing financial resources to affected communities. This funding can be used to rebuild homes, restore infrastructure, and support economic recovery. Technical aid encompasses expertise in wildfire management, providing training to local personnel and facilitating the implementation of improved fire prevention and suppression strategies. This includes the provision of equipment and technology.
Exchange of Knowledge and Expertise on Wildfire Management
The exchange of knowledge and expertise on wildfire management is crucial for improving fire prevention and response strategies. International experts often share their knowledge and experience in areas like fire behavior modeling, risk assessment, and early warning systems. This knowledge sharing strengthens the overall capacity of Chilean wildfire management agencies.
Comparison of International Response Strategies to Wildfire Disasters
Different countries and international organizations may employ varied strategies in response to wildfire disasters. Some prioritize rapid financial aid, while others focus on long-term infrastructure improvements and community resilience building. The effectiveness of each strategy often depends on the specific context of the wildfire event and the needs of the affected communities. A tailored approach that considers the particularities of each disaster is crucial for optimizing the impact of international support.
Examples of International Assistance Provided to Chile During Past Wildfire Events
| Country | Type of Aid | Amount (Approximate) | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Firefighting personnel, equipment (e.g., helicopters, specialized tools), and financial grants | USD 100,000-500,000 (depending on the event) | Provided immediate support for fire suppression, aided in containing the spread of the fire, and assisted with the recovery of affected areas. |
| Canada | Firefighting personnel, specialized equipment, and training | USD 50,000-250,000 (depending on the event) | Provided crucial support during the most challenging phases of the wildfire, including rapid deployment of personnel and advanced equipment. |
| Australia | Technical expertise in wildfire management, sharing of best practices, and training programs | Variable, often in-kind contributions | Strengthened Chile’s wildfire management capacity through the exchange of knowledge and expertise, enhancing the nation’s preparedness for future events. |
| European Union | Financial aid for reconstruction, and technical assistance for wildfire risk mitigation | USD 200,000-1,000,000 (depending on the event) | Supported long-term recovery efforts by providing financial assistance for infrastructure rehabilitation and training in wildfire risk management. |
Illustrative Examples of Chilean Wildfires
Chile, a country with breathtaking landscapes, is tragically vulnerable to devastating wildfires. These fires, often fueled by extreme weather conditions, have left a trail of destruction, impacting communities and ecosystems. Understanding these events provides valuable insights into the interplay of human activities, environmental factors, and the consequences of climate change.
The 2022-2023 Wildfire Season
The 2022-2023 wildfire season in Chile was particularly intense, exceeding previous records in terms of both the number and severity of fires. This period saw a significant increase in fire activity, with multiple large-scale blazes erupting across the country, primarily in the central and southern regions. These fires highlighted the vulnerability of the Chilean ecosystems to extreme weather events.
The Chilean wildfires, a devastating consequence of global warming, are truly heartbreaking. It’s hard to comprehend the scale of the destruction, and the loss of life and livelihoods. Meanwhile, the recent NYC shooting on the D train, as reported by CNN , highlights the complexities of modern urban life and the urgent need for solutions to prevent further tragedies.
While these events are vastly different, both situations underscore the fragility of our world and the urgent need for action on climate change.
Geographical and Meteorological Conditions
The geographic factors contributing to the fires included a combination of dry, dense vegetation, often found in forests and grasslands. This fuel load, coupled with the aridity typical of the Chilean climate, created an extremely flammable environment. Meteorological conditions, including strong winds and high temperatures, further exacerbated the situation, rapidly spreading flames across vast areas. These events often occur during periods of extended drought, where the combination of factors leads to a high fire risk.
Long-Term Impacts on the Affected Region
The 2022-2023 wildfires had devastating long-term impacts on the affected regions. Loss of biodiversity, including the destruction of unique plant and animal species, was substantial. The loss of habitats resulted in a disruption of the ecosystem’s natural processes. Moreover, the fires caused significant damage to infrastructure, including homes, roads, and critical utilities. The recovery process for these regions has been lengthy and complex, involving extensive efforts in rebuilding communities and restoring the environment.
The economic repercussions are substantial and extend beyond the initial damage, affecting tourism, agriculture, and other related industries.
The recent Chilean wildfires are a stark reminder of the devastating impacts of global warming. While international attention is understandably focused on critical issues like the Biden-Israel-Hamas cease fire situation, biden israel hamas cease fire , these environmental disasters are a constant and crucial concern. The Chilean crisis highlights the urgent need for global action on climate change, a problem that transcends political boundaries.
Challenges Faced in Responding to the Wildfire
Responding to these wildfires presented significant challenges. The sheer scale of the fires, often spanning vast areas, made it difficult to contain them effectively. Limited resources, including personnel and equipment, proved insufficient to combat the rapid spread of flames. Difficult terrain, including mountainous regions and dense vegetation, further complicated firefighting efforts. Moreover, coordinating resources across multiple agencies and jurisdictions was a significant logistical challenge.
The rapid spread and unpredictability of the fires often led to evacuation orders, displacing thousands of people and requiring robust emergency response protocols.
Survivor Statement
“The fire came so quickly. We had no time to react. Everything we owned, our home, our memories, everything was gone in a matter of hours. It’s a trauma that will never leave us.”
Anonymous wildfire survivor.
Future Trends and Projections: Chile Wildfires Global Warming
The escalating frequency and intensity of wildfires in Chile, inextricably linked to global warming, necessitate a forward-looking approach to risk management. Predicting future trends allows for proactive measures to mitigate the devastating impacts on ecosystems, communities, and the economy. Accurate projections, grounded in climate modeling and historical data, are crucial for developing effective adaptation strategies.Climate models consistently predict an increase in both the frequency and intensity of wildfires in Chile over the coming decades.
These projections are based on the expected rise in temperatures, shifts in precipitation patterns, and increased atmospheric dryness, all contributing factors to a more flammable environment. This trend is not unique to Chile; similar patterns are observed globally, highlighting the urgent need for international collaboration and adaptation strategies.
Projected Frequency and Intensity of Wildfires
Climate models suggest a significant increase in the frequency and intensity of wildfires in Chile, particularly in regions with existing high-risk factors. These models are based on various scenarios, incorporating factors such as greenhouse gas emissions, land-use changes, and weather patterns. This increase in fire risk will affect various regions differently, depending on factors like terrain, vegetation type, and existing infrastructure.
Understanding these regional variations is critical for targeted mitigation efforts.
Chile’s recent wildfires are a stark reminder of the devastating effects of global warming. While these tragedies are heartbreaking, it’s important to remember that there are ways to find moments of joy and community even amidst crisis. This weekend, check out the subway weekend Jose LaSalle for a fun, local event. It’s a welcome distraction from the serious issues, but it’s crucial to understand that events like these don’t negate the need for continued action to combat global warming and protect our planet.
Potential Strategies to Adapt to Future Wildfire Risk
Adapting to the increasing wildfire risk requires a multi-pronged approach. Strategies should focus on improved early warning systems, enhanced fire suppression capabilities, and proactive land management practices. This includes developing robust early warning systems that utilize satellite imagery, weather forecasts, and fire detection networks. Effective suppression strategies rely on a combination of personnel, equipment, and strategic resource allocation.
Further, proactive land management, such as controlled burns and vegetation management, is crucial for reducing fuel loads and creating defensible space around communities and critical infrastructure.
Need for Long-Term Planning and Preparedness
Long-term planning and preparedness are essential for mitigating the impact of future wildfires. This involves community engagement, developing evacuation plans, and investing in resilient infrastructure. Communities need to be actively involved in understanding and responding to wildfire risks, including preparedness measures such as developing evacuation routes and practicing emergency procedures. Infrastructure, such as homes, roads, and utility lines, must be designed with wildfire resistance in mind.
Public education and awareness campaigns are critical to promoting understanding and preparedness.
Potential Impacts of Wildfires on Specific Ecosystems
Wildfires have profound and varied impacts on Chile’s diverse ecosystems. Forests, grasslands, and wetlands each experience unique consequences, including loss of biodiversity, soil erosion, and disruptions to hydrological cycles. The impacts on wildlife populations are equally significant, with some species facing habitat loss, food scarcity, and increased mortality. Furthermore, the effects on water quality and availability can have cascading impacts on the region’s overall ecological health.
Predicted Wildfire Risk Zones in Chile (Next Decade)
| Region | Predicted Risk Level | Mitigation Efforts | Projected Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Central Valley | High | Enhanced fire prevention measures, improved early warning systems, and increased fire suppression resources. | Significant damage to agricultural land, loss of biodiversity, and potential displacement of communities. |
| Southern Andes | Medium | Controlled burns, improved forest management practices, and community-based wildfire preparedness programs. | Loss of native vegetation, potential impacts on water resources, and disruption to wildlife habitats. |
| Northern Patagonia | Low | Monitoring and early warning systems to detect potential fires. | Reduced impacts on ecosystems, but potential for rapid spread in specific conditions. |
| Araucanía Region | Very High | Comprehensive fire management plan, including controlled burns and community involvement in fire prevention and preparedness. | High risk of large-scale fires, extensive habitat loss, and potential impacts on water quality. |
Last Point
In conclusion, Chile wildfires global warming underscores the urgent need for international cooperation, sustainable land management, and proactive community engagement. The future of Chile’s ecosystems, economies, and communities hangs in the balance. By understanding the interconnectedness of global warming and wildfire risk, we can work together to build resilience and protect this beautiful nation for generations to come.
FAQ Resource
What are the most common human factors contributing to Chilean wildfires?
Agricultural practices, deforestation, and careless disposal of materials are often significant contributors to wildfire occurrences in Chile. Poor land management practices, including inadequate fire breaks, also increase the risk.
How does international cooperation play a role in mitigating wildfire risks?
International organizations can provide crucial support through financial aid, technical expertise, and the sharing of best practices in wildfire management. This collaborative effort strengthens preparedness and response capabilities.
What are some examples of short-term impacts of Chilean wildfires?
Immediate impacts include severe air pollution, loss of biodiversity, damage to infrastructure, and disruption of daily life for affected communities.
What are some long-term strategies for preventing future wildfires?
Long-term strategies include sustainable land management practices, improved early warning systems, enhanced community preparedness, and promoting responsible land use policies.






