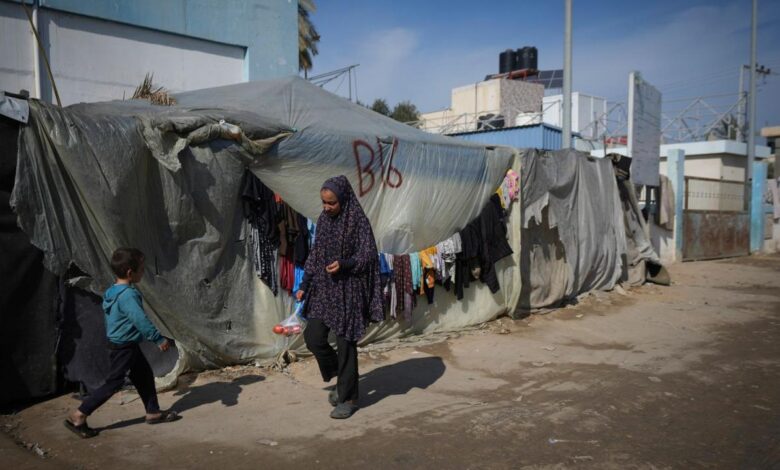
Israel-Gaza Cease-Fire A Complex Analysis
Israel gaza cease fire – Israel-Gaza cease-fire: A delicate truce hangs in the balance, with the aftermath demanding careful consideration of humanitarian, economic, and geopolitical implications. This analysis delves into the historical context, immediate aftermath, and long-term implications of this significant event, exploring the intricate negotiations, international responses, and efforts towards humanitarian aid and reconstruction.
The latest cease-fire agreement, reached after a period of intense conflict, marks a crucial moment for both Israelis and Palestinians. Understanding the terms, motivations, and concessions made by each side is vital for evaluating the potential for lasting peace. This overview also explores the diverse perspectives and public opinions surrounding the agreement, offering a nuanced understanding of the complexities involved.
Historical Context
The recent Israel-Gaza cease-fire is the latest chapter in a long and complex history between Israel and Palestine. Understanding the roots of this conflict requires examining decades of significant events, conflicts, and agreements that have shaped the region. This historical overview will provide context for the current situation and illuminate the enduring challenges in reaching lasting peace.
Timeline of Significant Events
This timeline Artikels key events leading up to the latest cease-fire, highlighting the escalating nature of the conflict. The events are presented chronologically to illustrate the progression and interconnectedness of various actions.
The Israel-Gaza cease-fire is a significant development, but it’s still a complex situation. Meanwhile, news out of Grenada is concerning, with a couple missing after their boat capsized. This tragic event, like the ongoing tensions in the Middle East, highlights the unpredictable nature of life and the human cost of conflict, which sadly seems to be the constant backdrop to the Israel-Gaza cease-fire negotiations.
couple missing boat grenada Hopefully, a peaceful resolution will soon be reached in both regions.
- 1948 Arab-Israeli War: This conflict marked the establishment of Israel and resulted in displacement and significant loss of life. It fundamentally altered the demographic landscape of the region and laid the groundwork for future tensions.
- 1967 Six-Day War: Israel’s victory in this war led to the occupation of the West Bank, Gaza Strip, and the Golan Heights. This occupation became a central point of contention in the conflict.
- 1993 Oslo Accords: These landmark agreements aimed at establishing a Palestinian state alongside Israel, offering a glimmer of hope for peace. However, they were not fully implemented, and the process stalled.
- 2000s Escalation: The second Intifada and a series of retaliatory actions by both sides marked a significant escalation in violence and the breakdown of peace efforts.
- 2006 Hamas takeover of Gaza: The rise of Hamas as the dominant political force in Gaza significantly altered the political landscape and complicated peace negotiations.
- Ongoing Cycles of Violence: Repeated cycles of violence, including rocket attacks and Israeli military responses, have defined the conflict in recent years.
Major Conflicts and Agreements
Numerous conflicts and agreements have shaped the Israeli-Palestinian relationship. Examining these events reveals the complex interplay of political, social, and religious factors.
- 1948 Arab-Israeli War: This war resulted in the displacement of hundreds of thousands of Palestinians and the establishment of Israel, creating a foundational conflict that continues to this day.
- 1967 Six-Day War: The outcome of this war dramatically altered the geopolitical landscape of the region, with Israel gaining control of the West Bank, Gaza Strip, and East Jerusalem.
- Oslo Accords (1993): These agreements represented a significant attempt to establish a two-state solution, but ultimately failed to deliver a lasting peace.
- Camp David Summits: These summits, while not yielding conclusive agreements, were crucial diplomatic attempts at resolving the conflict, demonstrating the need for continued negotiation.
Evolution of the Israeli-Palestinian Conflict
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict has evolved from a simple territorial dispute to a complex political and social struggle. Several factors have contributed to this evolution.
- Land Disputes: The control and division of land between Israel and Palestine has been a constant source of contention.
- Refugee Issue: The Palestinian refugee crisis remains a critical humanitarian issue and a source of ongoing tension.
- Political and Social Factors: Political ideologies, religious beliefs, and social norms have significantly influenced the conflict.
Key Figures and Organizations
Numerous figures and organizations have played crucial roles in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Understanding their involvement is essential to grasping the dynamics of the situation.
- Yitzhak Rabin, Shimon Peres, and Yasser Arafat: These figures played pivotal roles in the peace process, although their efforts were ultimately not enough to achieve lasting peace.
- Hamas and Fatah: These Palestinian organizations have significantly influenced the political landscape of Palestine.
- Israeli Prime Ministers: Successive Israeli prime ministers have taken different stances on the conflict and peace process.
Key Dates, Events, and Outcomes of Past Cease-fires
A table summarizing past cease-fires helps to illustrate the patterns and limitations of these temporary agreements.
| Date | Event | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1970 | First Ceasefire attempt | Short-lived and ineffective |
| 2005 | Disengagement Plan | Israeli withdrawal from Gaza |
| Various dates | Other Ceasefires | Varying degrees of success, often broken due to unresolved issues |
Immediate Aftermath
The recent cease-fire in Gaza has brought a temporary respite from the violence, but the scars of the conflict remain deeply etched on the landscape and the lives of the people. The immediate aftermath is characterized by widespread devastation, economic hardship, and a complex humanitarian crisis demanding urgent attention. The challenges facing both Israel and Gaza are multifaceted, requiring coordinated international efforts to mitigate the suffering and facilitate a path toward sustainable peace.
Humanitarian Consequences
The conflict left a trail of immense suffering, with civilians bearing the brunt of the fighting. Hospitals and schools were damaged or destroyed, disrupting essential services. The loss of life and injury rates were substantial, and many were left with long-term physical and psychological trauma. Furthermore, the disruption of supply chains and access to clean water and sanitation led to outbreaks of disease, threatening the health and well-being of a vulnerable population.
The immediate priority was to provide emergency medical care, shelter, and essential supplies to the affected population.
Economic Impact
The conflict severely impacted the economies of both Israel and Gaza. Israel’s tourism sector, already susceptible to geopolitical instability, suffered significant losses due to the uncertainty and disruption. Gaza, already grappling with a protracted blockade, experienced a catastrophic economic downturn. Businesses were shuttered, agricultural production was hampered, and the already precarious economic situation deteriorated dramatically. The rebuilding process will require substantial investment and international assistance to restore essential services and infrastructure.
Displacement and Refugee Crises
The conflict caused significant displacement within both Gaza and Israel. In Gaza, a large segment of the population was displaced from their homes, creating a pressing need for temporary housing and support services. The situation in Israel was also affected by the conflict, though the scale of displacement was different. The need for relocation and the challenges of long-term resettlement will demand extensive support from both local and international aid organizations.
The recent cease-fire in Israel and Gaza is a welcome development, but the underlying issues remain complex. Effective preventative measures, like those discussed in condon prevencion vih sida , highlight the importance of proactive strategies to address broader social and health concerns. Ultimately, a lasting peace in the region requires addressing the root causes of conflict, which are far more intricate than a short-term truce.
The UNHCR and other organizations will be key in coordinating assistance and identifying long-term solutions.
Role of International Actors
International organizations, governments, and humanitarian groups played a crucial role in providing immediate relief and support during the aftermath. Their contributions ranged from delivering essential supplies to coordinating humanitarian aid efforts. The United Nations, in particular, played a vital role in coordinating relief efforts and ensuring the delivery of humanitarian assistance to those most in need. The ongoing need for international support is critical in helping both Israelis and Palestinians rebuild their lives and communities.
Impact Comparison Before and After Cease-Fire
| Sector | Before Cease-Fire | After Cease-Fire |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Functional, though strained by prior conflicts. | Severely damaged hospitals and medical facilities; shortages of essential supplies and personnel; increased need for emergency medical care. |
| Infrastructure | Varied conditions, some areas well-maintained, others facing challenges. | Extensive damage to infrastructure, including roads, water systems, and power grids. Damage to housing and community facilities. |
| Economy | Gaza’s economy was already fragile under blockade, Israel’s economy was relatively stable. | Gaza’s economy is in shambles, Israel’s economy faces uncertainty and reduced tourism. |
This table provides a basic overview of the impact before and after the cease-fire on various sectors. The extent of damage and recovery needs vary greatly across different areas and communities.
Cease-fire Terms and Negotiations
The recent Gaza cease-fire, while offering a fragile respite, highlights the complex dynamics and enduring tensions in the region. Understanding the terms of the agreement, the roles of key negotiators, and the motivations behind the accord provides crucial insight into the ongoing conflict and potential for future stability. This examination delves into the specifics of the negotiations, exploring the concessions made by both sides.The cease-fire negotiations, often conducted in secret and with varying degrees of transparency, are characterized by competing interests and entrenched positions.
Each party brings to the table a unique set of priorities, shaping the final agreement and its potential long-term impact. The agreement itself represents a temporary halt to hostilities, but it also reflects the enduring power dynamics and the ongoing need for a lasting resolution.
Cease-fire Agreement Terms
The terms of the cease-fire agreement, while not fully public, likely involved a combination of de-escalation measures, humanitarian aid provisions, and security guarantees. These are often interwoven and difficult to disentangle without access to confidential documents. However, common elements in such agreements often include restrictions on military activities, the reopening of border crossings for humanitarian aid, and the establishment of monitoring mechanisms to maintain the cease-fire.
Key Negotiators and Their Roles, Israel gaza cease fire
Identifying the precise roles of key negotiators is often challenging due to the sensitive nature of these processes. However, it is widely acknowledged that representatives from various international organizations, regional powers, and even the parties directly involved often play crucial roles. Their backgrounds and affiliations shape their perspectives and influence the eventual agreement. These individuals may include diplomats, mediators, and high-ranking officials with specific expertise in conflict resolution or regional affairs.
Motivations Behind the Agreement
The motivations behind the cease-fire agreement likely differ for each party involved. For example, the desire to reduce casualties and civilian suffering may be a primary concern for both sides. The potential for restoring stability, improving economic conditions, and gaining a strategic advantage in the long term are also likely considerations.
Concessions Made by Each Party
Determining the precise concessions made by each party is inherently difficult without access to detailed documentation. However, it is reasonable to expect that both sides made concessions to reach an agreement. These concessions could involve easing military restrictions, agreeing to certain humanitarian aid provisions, or even agreeing to some degree of mutual accountability or oversight.
Summary of Cease-fire Points
| Point | Parties Involved | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Resumption of Humanitarian Aid | International Organizations, Israel, Hamas | Agreement to allow the unimpeded flow of humanitarian aid into Gaza. This often involves negotiations on the specific routes, types of aid, and oversight mechanisms. |
| De-escalation of Military Actions | Israel, Hamas | Agreement to limit military operations in specified areas or under specific conditions. This is usually accompanied by monitoring mechanisms to ensure compliance. |
| Security Guarantees | Israel, Hamas, International Community | Potential agreements concerning security measures, including monitoring of the border, and potentially limitations on certain weapons. These provisions may be vague to allow for flexibility in the future. |
Long-Term Implications: Israel Gaza Cease Fire
The recent cease-fire in Gaza, while offering a temporary respite, presents a complex landscape of potential long-term implications for regional stability and the future of Israeli-Palestinian relations. The fragile nature of the agreement underscores the inherent challenges in achieving lasting peace, highlighting the need for sustained diplomatic efforts and a commitment to addressing the root causes of conflict.The cease-fire’s efficacy in preventing future escalation hinges on a multitude of factors, including the commitment of all parties involved to uphold the terms and the ability to establish a robust mechanism for conflict resolution.
It is crucial to understand that a cease-fire is not a solution in itself but rather a temporary pause that necessitates ongoing engagement to prevent renewed hostilities.
Potential for Future Conflicts
The underlying tensions that fueled the recent conflict remain unresolved. These include issues of Palestinian self-determination, security concerns for Israel, and the ongoing struggle for land and resources. Without addressing these fundamental issues, the possibility of future outbreaks of violence persists. Historical precedents show that unresolved disputes often lead to recurring cycles of conflict. The Israeli-Palestinian conflict, unfortunately, demonstrates this pattern, with periods of calm often followed by renewed violence.
This highlights the necessity of long-term solutions that tackle the root causes of the conflict, not just the symptoms.
Impact on Israel-Neighboring Country Relations
The cease-fire’s impact on Israel’s relations with its neighbors will depend largely on how the conflict is perceived and managed. Neighboring countries may view the conflict through different lenses, potentially affecting their diplomatic stances and cooperation with Israel. A prolonged period of stability in the region, stemming from a just and lasting peace, could foster stronger relationships. Conversely, unresolved issues could lead to increased regional tensions and instability, affecting relations with neighboring countries.
The impact on the region’s diplomatic landscape will be significant, depending on how the parties involved handle the aftermath of the conflict.
Factors Contributing to Long-Term Cease-fire Success
Several key factors are crucial for the long-term success of the cease-fire. These include a commitment from both sides to adhere to the agreed-upon terms, the establishment of a robust framework for dialogue and conflict resolution, and the creation of opportunities for economic development and cooperation. The success of the cease-fire hinges on the ability of all parties to prioritize peace and build trust, not just on temporary agreements.
- Commitment to Dialogue: A sustained commitment to dialogue and negotiation, rather than relying on military force, is paramount. This requires active participation from all parties and a willingness to compromise. Previous instances of successful de-escalation demonstrate the power of sustained dialogue.
- Economic Cooperation: Economic opportunities can foster a sense of shared interest and interdependence, reducing the likelihood of conflict. Joint ventures and economic programs can create a shared interest in stability and peace.
- International Support: Robust international support for the peace process, including financial aid and diplomatic pressure, is essential. The presence of international mediators can provide objective guidance and support for all parties.
Challenges and Opportunities for Peacebuilding
Peacebuilding in the region faces significant challenges, including deeply entrenched political divisions, historical grievances, and security concerns. However, there are also significant opportunities for progress, including the potential for regional cooperation, economic development, and a commitment to addressing the root causes of the conflict. Overcoming these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing political, economic, and social dimensions.
- Addressing Root Causes: The long-term sustainability of any peace agreement hinges on addressing the root causes of the conflict, including the issues of land, borders, and self-determination.
- Building Trust: Building trust between the conflicting parties is essential for long-term peace. Trust-building measures can include confidence-building measures, transparency, and mechanisms for accountability.
- Regional Cooperation: Regional cooperation on economic, security, and environmental issues can foster a sense of shared interest and interdependence, reducing the likelihood of conflict. The potential for cooperation among nations in the region offers a path toward regional stability.
International Responses
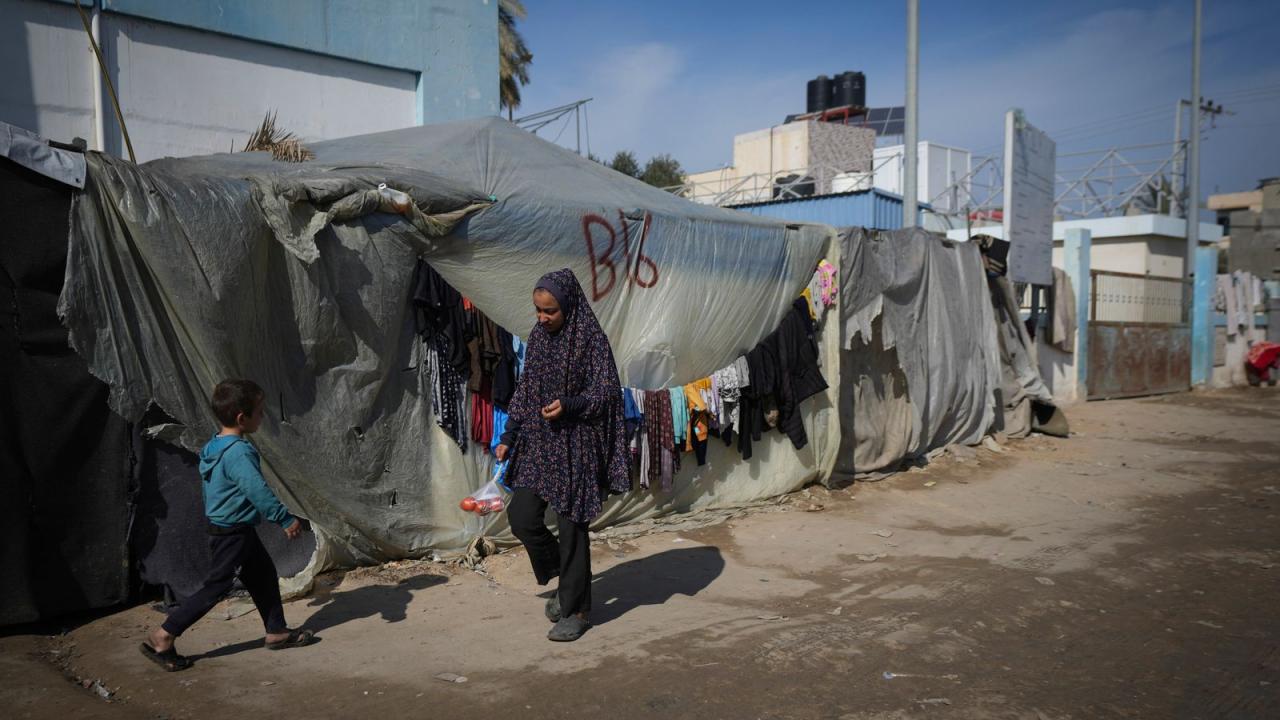

The recent Gaza-Israel cease-fire sparked diverse reactions from the international community. Nations grappled with the humanitarian crisis, the underlying political tensions, and the need for long-term solutions. Different countries and organizations weighed in with statements, sanctions, and aid packages, reflecting varying perspectives on the conflict’s causes and resolutions.
Reactions of Key Countries
Various nations responded to the cease-fire with statements and actions reflecting their specific geopolitical interests and values. Some emphasized the need for accountability and de-escalation, while others focused on humanitarian aid and reconstruction efforts. These diverse reactions highlight the complexity of the issue and the varying priorities of different international players.
- United States: The US, a significant player in the region, released statements supporting the cease-fire and emphasizing the need for a sustained effort to prevent future conflicts. Their approach included advocating for humanitarian assistance and encouraging dialogue between the parties involved.
- European Union: The EU expressed concerns over the humanitarian consequences of the conflict and called for an end to violence. They emphasized the need for a long-term resolution that addresses the root causes of the conflict and promotes stability in the region.
- United Nations: The UN Secretary-General and relevant agencies highlighted the urgent need for humanitarian aid and the protection of civilians. They emphasized the importance of upholding international law and creating conditions for lasting peace.
- Arab League: The Arab League condemned the violence and called for a complete end to the Israeli military campaign. Their approach focused on supporting the Palestinian people and advocating for their rights.
- Russia: Russia’s response focused on promoting dialogue between the warring parties, highlighting the need for a peaceful resolution. Their approach emphasized the importance of a balanced approach that considers the concerns of all sides involved.
- China: China urged both sides to exercise restraint and seek a peaceful resolution to the conflict. Their approach emphasized de-escalation and a commitment to upholding international law.
International Mediation Efforts
The role of international mediators was crucial in facilitating the cease-fire negotiations. Mediation efforts focused on bridging the gaps between the opposing sides and ensuring a durable outcome. Mediators often played a vital role in negotiating compromises and fostering dialogue.
- Mediation role: International mediation efforts, often spearheaded by UN representatives or other diplomatic actors, aimed to bring the conflicting parties together for discussions and negotiations. The efforts frequently focused on identifying common ground and developing mutually acceptable solutions.
- Challenges: Mediation efforts faced numerous challenges, including differing interests, mistrust between the parties, and the complex political landscape of the region. Overcoming these challenges often required significant diplomatic skills and patience.
Comparative Approaches
A comparison of the responses from different countries revealed diverse approaches. Some nations emphasized accountability and the need to address the root causes of the conflict, while others prioritized humanitarian aid and immediate relief efforts.
| Country/Organization | Primary Focus | Specific Actions |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Maintaining regional stability, supporting humanitarian aid | Issuing statements, providing aid |
| European Union | Ending violence, addressing humanitarian crisis | Issuing statements, providing humanitarian assistance |
| United Nations | Protecting civilians, providing humanitarian aid | Deploying aid workers, coordinating relief efforts |
| Russia | Promoting dialogue, peaceful resolution | Issuing statements, engaging in diplomatic efforts |
Humanitarian Aid and Reconstruction
The devastating conflict in Gaza has left a trail of destruction, requiring immediate and sustained humanitarian aid efforts. The urgent need extends far beyond basic necessities, encompassing long-term rebuilding and recovery. The scale of the crisis necessitates a coordinated and effective response from both international organizations and local authorities. Providing essential support to the affected populations while addressing the complex logistical challenges is paramount.The delivery of aid is often fraught with challenges, requiring innovative solutions and careful planning.
These challenges include security concerns, bureaucratic hurdles, and differing priorities amongst various actors involved. However, the potential for significant progress exists, provided that these difficulties are addressed proactively.
Efforts to Provide Humanitarian Aid
The immediate response to the conflict involved a surge in humanitarian aid from various organizations. This aid included food, water, medical supplies, and shelter materials. The international community, recognizing the critical need, swiftly mobilized resources and personnel to support the affected population. Numerous NGOs and UN agencies played vital roles in coordinating and distributing aid.
The recent cease-fire in Israel and Gaza is a complex issue, with a lot of moving parts. Understanding the various players involved, like the role of the Biden administration in mediating the conflict, is crucial. For instance, President Biden’s efforts to broker a lasting peace between Israel and Hamas are detailed in this article on biden israel hamas cease fire.
Ultimately, the success of this cease-fire hinges on long-term diplomatic solutions and a commitment from all parties to a peaceful resolution in the region.
Challenges in Delivering Aid
Several obstacles hinder the effective delivery of aid. Security concerns, particularly in areas experiencing ongoing hostilities, pose significant risks to aid workers and impede access to vulnerable populations. Bureaucratic processes and differing priorities among various stakeholders can also create delays and inefficiencies in aid distribution. Logistical challenges, such as the need to navigate damaged infrastructure and limited access routes, often add to the complexity.
Role of International Humanitarian Organizations
International humanitarian organizations, such as the UNHCR, UNICEF, and the Red Cross, play a crucial role in coordinating aid efforts. Their expertise in emergency response, logistics, and community engagement is invaluable. These organizations work closely with local partners and authorities to ensure that aid reaches those who need it most. They often provide vital support for the establishment of temporary shelters and the provision of essential services, such as medical care.
Examples of Successful Aid Programs
Numerous successful aid programs have emerged in response to the conflict. One example is the provision of mobile medical clinics in hard-to-reach areas. Another success involved the distribution of water purification tablets and water storage solutions, preventing outbreaks of waterborne diseases. The coordination of efforts by various humanitarian organizations enabled the efficient delivery of aid to those in greatest need.
Distribution of Aid to Affected Areas
| Affected Area | Type of Aid | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Southern Gaza | Food and Water | 50,000 rations |
| Central Gaza | Medical Supplies | 1000+ medical kits |
| Northern Gaza | Shelter Materials | 2000+ tents |
| Border Communities | Emergency Supplies | 30,000+ hygiene kits |
Note: Figures are estimates and may vary depending on the source. This table represents a sample of aid distribution, not an exhaustive list.
Public Opinion and Perception
The recent Gaza cease-fire has left a complex tapestry of opinions and perceptions in both Israel and Palestine. Public reactions are deeply intertwined with the historical context of the conflict, the immediate aftermath of the fighting, and the perceived fairness and effectiveness of the negotiated terms. Different groups within each society hold vastly different views, influenced by their individual experiences, political affiliations, and the narratives presented by various media outlets.Public sentiment is a crucial factor in assessing the long-term stability of the cease-fire.
Understanding the diverse perspectives, hopes, and concerns will be essential for any future attempts at de-escalation and reconciliation. These differing viewpoints highlight the significant challenges ahead in achieving lasting peace.
Israeli Public Opinion
The Israeli public’s response to the cease-fire is multifaceted, ranging from cautious optimism to deep-seated disappointment. A significant portion of the population, particularly those who experienced the direct impact of the conflict through rocket attacks, feel that the agreement did not adequately address the security concerns of the region.
“The Hamas terrorists must be held accountable. This cease-fire is a temporary reprieve, not a victory. We need stronger security guarantees to prevent future attacks.”
A statement from a citizen of Sderot, expressing the sentiment of many.
Other Israelis, particularly those from more liberal segments of society, express hope for a lasting resolution, emphasizing the importance of humanitarian aid and rebuilding efforts.
“While the violence is regrettable, a cease-fire is a necessary step towards a more peaceful future. The focus should now be on reconstruction and long-term solutions.”
A sentiment shared by some Israelis who believe a more moderate approach to the conflict is necessary.
Palestinian Public Opinion
The Palestinian public’s perspective on the cease-fire is equally complex. While many welcome the cessation of hostilities, the agreement is viewed with suspicion and skepticism by some factions.
“The cease-fire was forced upon us. We need to rebuild our lives and ensure our fundamental rights are respected, including the right to return and a Palestinian state.”
A sentiment expressed by Palestinians who feel the deal did not adequately address their core concerns.
A portion of the Palestinian population, however, express a degree of cautious optimism, seeing the cease-fire as a chance for rebuilding and improving their living conditions.
“This pause in the fighting is a chance to heal. We need international support to rebuild our communities and move forward with dignity.”
A perspective expressed by Palestinians who see the cease-fire as an opportunity for progress.
Media Coverage Comparison
Media coverage of the conflict and the cease-fire has significantly influenced public perception in both Israel and Palestine. News outlets, both local and international, have presented varied narratives, often reflecting the political leanings of the reporting organization.
“Israeli media tended to focus on the security concerns of the citizens, highlighting the ongoing threat posed by Hamas. Palestinian media, on the other hand, often emphasized the humanitarian crisis and the need for international support for reconstruction efforts.”
A comparative analysis of media narratives.
The media’s selection of events and perspectives, and the way they frame these narratives, has often contributed to the polarization of public opinion.
Different Narratives
The narratives surrounding the cease-fire are deeply rooted in the long history of the conflict. Different parties have presented varying accounts of the events, often reflecting their own political and social agendas.
“Israel portrays the cease-fire as a necessary response to Hamas’s aggression, emphasizing the need for security. Hamas, conversely, frames the cease-fire as a tactical retreat and a necessary step towards achieving its political objectives.”
An example of the opposing narratives presented.
The recent Israel-Gaza cease-fire feels fragile, like a truce held together by a thread. It’s a reminder of the complex human cost of conflict, especially for those affected on both sides. The ongoing suffering, the deep wounds, and the overwhelming need for healing are mirrored in the powerful personal stories of grief, like those explored in the moving article “Grief is for people sloane crosley” grief is for people sloane crosley.
Hopefully, this fragile peace will pave the way for lasting solutions and a future where such devastating conflicts become a thing of the past.
These different narratives further complicate the already difficult process of reconciliation and peace-building.
Economic Recovery

The recent cease-fire in Gaza presents a critical juncture for economic recovery. The destruction wrought by the conflict necessitates a multifaceted approach to rebuilding infrastructure, fostering international investment, and creating sustainable economic growth. The task is immense, requiring careful planning and the engagement of both regional and international actors.The path to economic recovery in Gaza hinges on a comprehensive strategy that addresses both immediate needs and long-term development.
This includes not only physical reconstruction but also the creation of a robust economic environment that can attract investment, generate employment, and empower the population.
Steps Needed for Economic Recovery
Restoring Gaza’s economy requires a coordinated effort focusing on several key areas. Prioritization is essential to ensure the most impactful use of resources. Essential services such as water, sanitation, and electricity must be restored immediately. This will stabilize the population and allow other crucial economic initiatives to begin. Further steps include the rehabilitation of critical infrastructure like roads, hospitals, and schools.
The Israel-Gaza cease-fire is a complex issue, and while there’s much to unpack about the negotiations, the recent events do bring a lot of questions to the table. It’s interesting to contrast this with the vibrant energy of the subway weekend festivities in Jose Lasalle, like Subway Weekend Jose Lasalle , highlighting the contrast between global tensions and local community events.
Ultimately, the cease-fire still requires a lot of work to ensure lasting peace in the region.
Crucially, supporting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) is essential. These businesses are often the backbone of local economies and are vital to job creation. Finally, creating a conducive investment climate is paramount to attract both local and foreign capital.
Role of International Investment
International investment plays a pivotal role in Gaza’s economic recovery. Foreign direct investment (FDI) can provide much-needed capital for infrastructure development and stimulate job creation. Countries with a history of successful economic development can share best practices and offer technical expertise. For instance, the reconstruction of post-earthquake Nepal relied heavily on international investment, particularly from the United States, and the World Bank, and this support was instrumental in revitalizing the economy.
Challenges in Rebuilding Infrastructure
Rebuilding infrastructure in Gaza presents significant challenges. The conflict has caused widespread destruction to vital infrastructure, including roads, power grids, and water systems. The ongoing blockade also severely restricts the import of essential materials. Overcoming these obstacles will require significant international aid and a sustained commitment to reconstruction efforts. Moreover, the political climate in the region adds another layer of complexity, impacting the ease and speed of the rebuilding process.
Potential Opportunities for Economic Growth
Despite the challenges, opportunities for economic growth in Gaza exist. The agricultural sector, for instance, could be revitalized through investment in modern farming techniques. Tourism, if safe and sustainable initiatives are undertaken, could attract tourists and generate revenue. Developing innovative industries, particularly in technology and manufacturing, can create high-skilled jobs. These sectors can attract both local and international investment.
Projected Economic Growth Scenarios
| Scenario | Growth Rate (Annual) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Optimistic | 5-7% | Increased international investment, successful diversification of the economy, and a peaceful environment. |
| Moderate | 3-5% | International investment and some degree of diversification, with ongoing security concerns and blockades. |
| Pessimistic | Less than 2% | Continued political instability, significant infrastructure limitations, and limited international investment. |
“Economic recovery in Gaza requires a multi-pronged approach that focuses on immediate needs, long-term development, and the creation of a robust economic environment.”
Wrap-Up
The Israel-Gaza cease-fire, while a potential step toward peace, presents significant challenges and opportunities. The long-term success of this agreement hinges on sustained international support, economic recovery in Gaza, and a commitment from all parties to finding a lasting resolution to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. The diverse perspectives and public opinions offer insights into the complexities and nuances of this sensitive situation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What were the key concessions made by each party in the cease-fire agreement?
The specific concessions remain confidential and subject to interpretation. However, public statements from both sides have Artikeld certain points of compromise. This information is crucial for understanding the potential for sustainable peace.
What are the projected economic growth scenarios for Gaza after the cease-fire?
Projected economic growth scenarios for Gaza post-ceasefire are uncertain and depend heavily on the extent of international investment and the successful implementation of reconstruction plans. Many challenges remain, such as rebuilding infrastructure and fostering trust.
How does the media coverage of the conflict and cease-fire differ?
Media coverage often presents conflicting narratives, reflecting the different perspectives and priorities of various news outlets and stakeholders. Examining these differences is crucial for understanding the multifaceted nature of the conflict and the potential for bias.
What is the role of international humanitarian organizations in providing aid to the affected populations?
International humanitarian organizations play a crucial role in delivering aid, coordinating relief efforts, and supporting the affected population in the aftermath of conflict. Their expertise and experience are vital for addressing immediate needs and fostering long-term recovery.