
MeToo Movement Politics Assault A Deep Dive
The #MeToo movement politics assault has sparked a global conversation about sexual assault and harassment, particularly within the political sphere. This complex issue touches upon historical context, legal frameworks, media representation, and the lasting impact on victims and perpetrators. Understanding the nuances of this movement is crucial for navigating the societal shifts and policy changes it has spurred.
From the early days of the movement to its current influence on political discourse, this exploration will dissect the key aspects of this critical discussion. We’ll examine the historical context, analyze the political ramifications, and delve into the legal and societal factors contributing to the ongoing debate.
Historical Context of the #MeToo Movement
The #MeToo movement, a global phenomenon, has irrevocably reshaped societal attitudes toward sexual assault and harassment. It emerged from a confluence of factors, including decades of activism, evolving cultural norms, and the unprecedented power of social media. This exploration delves into the movement’s historical context, tracing its roots, key milestones, and its comparison to previous movements addressing similar issues.The movement didn’t spring from a vacuum; it built upon a foundation of prior activism, with women and allies consistently advocating for their rights and safety.
The #MeToo movement has undeniably impacted political discourse surrounding assault. Understanding the complexities of these issues requires looking beyond the headlines, and the upcoming Nevada caucus primary is a fascinating case study. This Nevada caucus primary explainer offers insights into the political climate surrounding the election. Ultimately, these events highlight the continuing need for open dialogue and robust support systems for victims of assault.
The historical backdrop of the movement, though complex, is essential to understanding its current impact and future trajectory. Early activism often faced skepticism and resistance, illustrating the significant cultural shifts needed for the #MeToo movement to gain traction.
Origins and Key Milestones, Metoo movement politics assault
The seeds of the #MeToo movement were sown long before the hashtag itself became ubiquitous. Advocacy for victims of sexual violence and harassment, though not explicitly labelled as “MeToo,” had existed for decades. The 1990s and early 2000s saw the rise of support groups, legal battles, and individual accounts of abuse emerging into the public discourse. The watershed moment often cited is the 2017 publication of the expose on Harvey Weinstein.
This marked a turning point, as the allegations against him gained unprecedented attention. The subsequent public outcry and the widespread sharing of personal stories on social media rapidly escalated the movement, propelling it to global recognition.
Evolution of Societal Attitudes
Prior to the #MeToo movement, societal attitudes toward sexual assault and harassment were often characterized by silence, denial, and victim-blaming. The prevailing culture often excused or minimized such behavior. This was partly due to a lack of robust support structures and legal frameworks for victims. The movement challenged this narrative, providing a platform for victims to share their experiences without fear of being dismissed or discredited.
Comparison with Previous Social Movements
While the #MeToo movement shares common ground with earlier social movements fighting for gender equality and against discrimination, it has unique characteristics. The focus on individual accounts of assault and harassment, combined with the immediacy and visibility afforded by social media, is a distinguishing feature. Previous movements often relied on broader systemic critiques and policy changes. The #MeToo movement, while demanding policy reforms, also emphasized the importance of individual stories and the healing process for survivors.
It also highlighted the crucial role of personal testimony in shaping public opinion and challenging power imbalances.
Role of Social Media
Social media played a critical role in amplifying the #MeToo movement. The hashtag #MeToo, created by Tarana Burke in 2006, provided a powerful symbol of solidarity and a platform for sharing experiences. The ease of sharing stories online, connecting with others, and organizing actions facilitated a rapid mobilization of support, bringing the issue to a global audience.
Key Figures and Events in the Early Years
| Figure/Organization | Role/Contribution | Event/Year | Impact/Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Harvey Weinstein | Film producer whose allegations triggered the movement | 2017 | Sparked widespread public discussion and fueled the movement’s growth. |
| Tarana Burke | Founder of the #MeToo movement | 2006 | Initiated the movement as a way to empower survivors. |
| Various victims | Shared personal stories and experiences | 2017-present | Brought the issue into the public consciousness and created a sense of solidarity. |
| Media outlets and journalists | Covered the movement extensively | 2017-present | Brought the issue to a wider audience and held perpetrators accountable. |
Political Implications of the #MeToo Movement
The #MeToo movement, a global reckoning with sexual harassment and assault, has had profound and multifaceted effects on the political landscape. It has not only exposed pervasive issues of power imbalance and abuse within politics but has also significantly altered the dynamics of political discourse, campaigning strategies, and the very fabric of political power structures. The movement’s impact reverberates through accusations leveled against political figures, shaping public perception and influencing electoral outcomes.The movement’s exposure of systemic issues within political systems has spurred a critical examination of power dynamics and accountability.
It prompted a reevaluation of the standards and expectations for behavior in political circles, forcing a reckoning with the culture of silence and impunity that often surrounded such issues in the past. This has led to significant changes in political campaigning and the way political figures are perceived by the public.
Effects on Political Discourse
The #MeToo movement dramatically shifted political discourse, bringing conversations about sexual harassment and assault to the forefront of public debate. This resulted in a more open and frank discussion of such issues, with a greater emphasis on accountability and prevention. Political leaders and candidates were no longer shielded by a culture of silence, and their conduct came under intense scrutiny.
The #MeToo movement’s impact on politics and assault cases is undeniable. It’s a complex issue, with important implications for how we approach justice and accountability. This movement has sparked a lot of discussion, and its impact is undeniable. While we’re looking at heroes like Adrian Beltre, who’s now a Hall of Famer for the Texas Rangers, adrian beltre hall of fame texas rangers the spotlight on sports figures and their impact on society is also important.
These discussions highlight the need for continued awareness and reform in addressing these sensitive issues.
Impact on Political Figures
Numerous political figures have been affected by accusations of assault and harassment during the #MeToo era. These accusations have led to resignations, loss of public support, and even criminal charges. The movement has exposed the vulnerability of powerful figures to scrutiny and the potential consequences of their actions. The fallout has had an impact on both the individual figures and the political landscape itself, forcing a reckoning with the need for accountability.
Examples include (but are not limited to) prominent politicians whose careers were significantly altered or ended due to accusations.
Changes in Political Campaigning Strategies
Campaigning strategies have evolved in the wake of the #MeToo movement. Candidates now face increased scrutiny of their personal conduct and past behavior. This scrutiny has led to a greater emphasis on promoting a reputation for ethical conduct and transparency, and a focus on preventing any misinterpretations or potential scandals. Candidates are more mindful of their public image and interactions, often employing more cautious and careful communication strategies to avoid accusations.
Influenced Policies and Legislation
The #MeToo movement has directly influenced the creation of policies and legislation designed to combat sexual harassment and assault in various sectors, including politics. Numerous states and countries have implemented new laws and regulations to address sexual harassment in the workplace, including specific provisions for reporting mechanisms, investigation processes, and protections for victims. These policies often include stricter standards for conduct and accountability.
The movement has also led to a growing emphasis on training and education to prevent sexual harassment and assault in political environments.
Political Responses Across Countries
| Country | Initial Response | Subsequent Actions | Effectiveness of Actions |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Mixed reactions, ranging from denial to acknowledgment, with some legislative efforts. | Increased scrutiny of candidates, more emphasis on prevention and accountability. | Varied results, with some improvements in policy and reporting but still ongoing challenges. |
| United Kingdom | Initially slow response, followed by increased awareness and calls for reform. | Establishment of independent investigations, changes to parliamentary procedures. | Positive changes in procedures and awareness but challenges persist in achieving full accountability. |
| Canada | Widespread discussion and public awareness. | Policy changes regarding workplace harassment, greater emphasis on training. | Positive developments in policy, but further reforms are needed. |
| France | Public outcry and calls for reform. | Increased legal avenues for victims, enhanced reporting mechanisms. | Improvements in legal frameworks but ongoing debate on effectiveness and enforcement. |
Defining Sexual Assault and Harassment: Metoo Movement Politics Assault
Defining sexual assault and harassment is crucial for understanding the #MeToo movement and advocating for victims. These terms are not always easily understood, and their definitions vary across cultures and legal systems. This exploration delves into the complexities of these issues, including different types, degrees, consent, legal frameworks, and the impact of cultural norms.
Understanding Sexual Assault
Sexual assault encompasses a broad range of unwanted sexual acts. It’s essential to recognize the various forms and degrees of severity. A key element is the absence of consent. The victim’s inability to consent due to factors like intoxication or incapacitation significantly alters the dynamic.
- Physical Assault: This involves unwanted physical contact, including forced touching, sexual battery, and rape. Examples include unwanted kissing, groping, or penetration without consent. The severity ranges from unwanted touching to violent acts of sexual assault.
- Verbal and Psychological Assault: This includes unwanted sexual advances, threats, or coercion. These forms of assault can be insidious and damaging, impacting the victim’s mental and emotional well-being. For instance, repeated unwanted sexual comments or stalking can constitute harassment.
- Non-Physical Acts: These can include online harassment, such as sending unwanted sexual messages or images, or exploiting a position of power to coerce sexual acts. This form of sexual assault is increasingly prevalent in the digital age.
Defining Consent
Consent is crucial in understanding sexual assault and harassment. It’s not simply the absence of resistance but an affirmative, enthusiastic, and ongoing agreement.
- Affirmative Consent: Consent must be freely and enthusiastically given. It’s not enough for someone to not object. Consent can be withdrawn at any time. A person who is incapacitated, intoxicated, or under duress cannot give consent.
- Situational Consent: The context of the situation matters. Consent for one activity does not automatically imply consent for another. For example, consent to kissing does not imply consent to sexual intercourse.
- Lack of Consent: If there is any question about whether consent has been given, it is best to assume it hasn’t been given. Silence or inaction does not constitute consent.
Legal Frameworks
Legal definitions of sexual assault vary across jurisdictions. These differences can impact the prosecution and outcomes of cases.
- Jurisdictional Variations: Laws regarding sexual assault and harassment differ based on location. Some jurisdictions have stricter definitions than others, encompassing a broader range of behaviors. Differences in legal definitions and procedures can create disparities in the experience of victims.
- Legal Processes: The legal process for prosecuting sexual assault cases can be complex and challenging. Factors such as evidence gathering, witness testimony, and the burden of proof can significantly affect the outcome.
Cultural Norms and Power Dynamics
Cultural norms and power dynamics play a significant role in shaping how sexual assault and harassment are perceived and addressed.
- Cultural Norms: Cultural expectations surrounding gender roles, sexuality, and acceptable behavior can influence how sexual assault and harassment are defined and responded to. These norms can create environments where certain behaviors are normalized or excused.
- Power Dynamics: Power imbalances between individuals can contribute to sexual assault and harassment. Individuals in positions of authority or power are often able to coerce or exploit others without facing consequences.
Comparative Table of Legal Definitions
| Country | Definition of Sexual Assault | Key Elements | Specific Laws |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Generally encompasses unwanted sexual contact or penetration without consent. | Lack of consent, force, or threat of force. | Specific laws vary by state. |
| United Kingdom | Covers a range of sexual offenses, including rape and sexual assault. | Lack of consent, penetration or sexual touching. | Sexual Offences Act 2003 |
| Canada | Defines sexual assault as unwanted sexual contact. | Lack of consent, physical or psychological harm. | Criminal Code |
| Australia | Includes various sexual offenses, ranging from assault to rape. | Lack of consent, unwanted sexual activity. | Specific laws vary by state. |
Media Representation of the #MeToo Movement
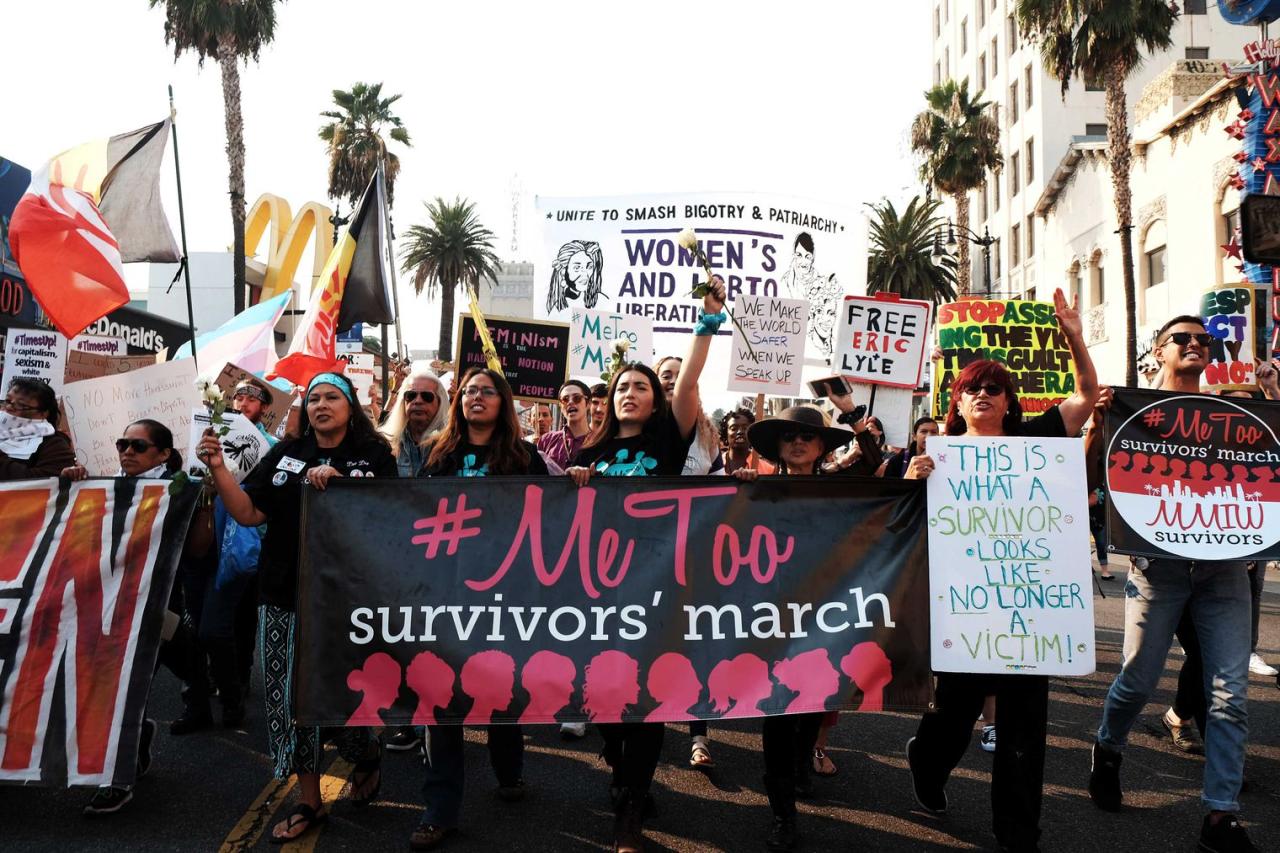
The #MeToo movement, a global reckoning with sexual harassment and assault, has profoundly impacted societal understanding and legal frameworks. Media coverage played a crucial role in amplifying the movement’s message and galvanizing public support, yet also faced scrutiny for its portrayal of the events and individuals involved. Different media outlets and countries have approached the movement with varying degrees of sensitivity and objectivity, reflecting existing biases and political landscapes.The media’s power to shape public opinion is undeniable.
The #MeToo movement’s impact on politics and assault cases is undeniable. It’s a complex issue, and often, the stories are deeply disturbing. However, recent reports, like the one about the alleged lovers in Auschwitz, Keren Blankfeld and József Debreczeni, found in the cold crematorium here , highlight the fragility of human experience and the profound pain inflicted in such horrific circumstances.
Ultimately, these disturbing accounts remind us that even in the face of unimaginable suffering, the fight against abuse in all its forms remains critical.
News cycles, social media trends, and the tone of articles all contribute to the collective understanding of the movement. How the media chooses to frame the narrative—highlighting specific incidents, emphasizing particular perspectives, and focusing on certain individuals—can significantly influence public perception and the broader discourse surrounding sexual assault and harassment.
Different Perspectives and Narratives in Media Coverage
The media’s representation of the #MeToo movement often reflected diverse perspectives and narratives. Some coverage emphasized the stories of survivors, highlighting their courage and resilience in coming forward. Other portrayals focused on the accused, presenting their side of the story and potentially minimizing the harm caused. This duality in media representation often sparked debate and criticism, with some arguing that the focus on individual stories overshadowed the systemic issues at play.
The media’s portrayal of power dynamics and societal structures contributing to sexual harassment and assault also varied.
Role of Media in Shaping Public Opinion
The media significantly influenced public opinion on the #MeToo movement. By amplifying the voices of survivors, the media fostered a broader understanding of the prevalence of sexual harassment and assault. However, the media’s selection and framing of stories could also lead to polarized views and misinterpretations of the movement’s goals. News cycles often highlighted sensationalized accounts, which could detract from the movement’s core message.
Additionally, the media’s coverage could create a sense of urgency and collective action, yet also risk contributing to a climate of fear and suspicion.
Criticisms of Media Coverage
The media’s coverage of the #MeToo movement has faced various criticisms. One common criticism was the sensationalization of certain cases, potentially trivializing the severity of sexual assault and harassment. Another criticism concerned the focus on celebrity figures, which some felt diverted attention from the experiences of ordinary individuals. The media’s portrayal of the movement as a “witch hunt” or a “culture war” was also a recurring criticism, implying a lack of objectivity.
These criticisms underscore the potential for the media to misrepresent the movement’s complexities and nuances.
The #MeToo movement’s impact on politics and assault cases is undeniable, yet the recent news of Arthur Smith being hired as the Steelers’ offensive coordinator, as reported in this article , raises some intriguing questions. How will this hire affect the NFL’s culture? Ultimately, these kinds of decisions continue to reflect a larger conversation about accountability and justice within the wider context of the #MeToo movement.
Comparison of Media Coverage Across Different Countries
| Country | Focus of Coverage | Tone of Coverage | Impact on Public Opinion |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Initially focused on celebrity cases, later broadened to include broader societal issues. | Mixed, ranging from empathetic to sensationalized. | Significant impact, leading to widespread discussion and policy changes. |
| United Kingdom | Focused on diverse experiences, including those beyond celebrity culture. | Generally empathetic, highlighting the systemic nature of harassment. | Led to important conversations about workplace culture and accountability. |
| France | Emphasis on the systemic nature of gender inequality in the workplace. | Critical, questioning the media’s portrayal of certain cases. | Stirred debate about legal frameworks and cultural norms. |
| China | Limited coverage initially, focused more on specific cases. | Cautious, often with a focus on societal stability. | Generated localized discussion, but with less public awareness compared to other countries. |
The table above provides a simplified comparison. Further analysis would require a deeper dive into the specific narratives, sources, and methodologies employed by each media outlet in different countries.
Impact on Victims and Perpetrators

The #MeToo movement has profoundly impacted the lives of both victims and perpetrators of sexual assault and harassment. It has brought a long-overdue awareness to the pervasive nature of these crimes and the devastating consequences they inflict. Understanding these impacts is crucial to fostering a more just and equitable society.
Emotional and Psychological Impact on Victims
Sexual assault and harassment inflict profound emotional and psychological trauma on victims. The experience often leads to a range of debilitating symptoms, including anxiety, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and difficulty trusting others. The violation can profoundly affect self-esteem, body image, and overall well-being. These experiences can manifest in a variety of ways, including flashbacks, nightmares, avoidance of certain situations or people, and heightened emotional reactivity.
Consequences for Perpetrators
Perpetrators of sexual assault and harassment face significant consequences beyond legal repercussions. The social stigma associated with such actions can lead to isolation, strained relationships, and difficulty reintegrating into society. Perpetrators may also experience a loss of reputation and opportunities, including professional and personal relationships. Legal consequences, including imprisonment, fines, and restraining orders, can also significantly impact their lives.
Importance of Restorative Justice and Rehabilitation Programs
Restorative justice programs aim to address the harm caused by sexual assault and harassment, while also promoting accountability and healing. These programs often involve mediation between the victim and perpetrator, facilitating dialogue and reconciliation, while ensuring the victim’s needs are addressed. Rehabilitation programs for perpetrators can focus on addressing underlying issues that contribute to their behavior, such as anger management, empathy training, and understanding the impact of their actions on others.
The goal of these programs is to prevent future harm.
Role of Support Groups and Therapy in Healing
Support groups provide a safe space for victims to share their experiences, receive emotional support, and connect with others who understand what they are going through. Therapy plays a vital role in helping victims process their trauma, develop coping mechanisms, and build resilience. Individualized therapy can address specific emotional and psychological needs, such as anxiety, depression, and PTSD.
These resources can be critical in facilitating healing and promoting long-term well-being.
Long-Term Effects on Victims and Perpetrators
| Aspect | Victims | Perpetrators | Potential Interventions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emotional Well-being | Anxiety, depression, PTSD, difficulty trusting others, low self-esteem, body image issues, flashbacks, nightmares, avoidance behaviors, emotional reactivity | Social isolation, strained relationships, loss of reputation, difficulty reintegrating into society, fear of judgment, guilt, shame, remorse | Therapy, support groups, trauma-informed care, restorative justice programs, support networks |
| Mental Health | Increased risk of substance abuse, suicidal ideation, difficulty concentrating, sleep disturbances, relationship problems | Difficulty maintaining employment, reduced social opportunities, criminal record, potential for further offenses, loss of trust | Therapy, medication, vocational rehabilitation, community support services, anger management programs |
| Social and Professional Life | Difficulty in relationships, career setbacks, social withdrawal, reduced participation in social activities, difficulty trusting others | Loss of employment, reduced opportunities, stigmatization, social isolation, legal limitations | Career counseling, job training, social skills development, support networks, legal aid |
| Physical Health | Chronic pain, sleep disturbances, headaches, digestive issues, and other physical symptoms. | Possible consequences due to legal or social repercussions. | Medical care, holistic treatments, and rehabilitation services. |
Future Directions of the Movement
The #MeToo movement has undeniably reshaped societal conversations about sexual assault and harassment. Its impact on legal reforms, media portrayals, and individual experiences has been profound. However, the journey toward a truly equitable future requires ongoing commitment and strategic action. This exploration delves into potential pathways for future activism, challenges to sustainability, and areas ripe for improvement.
Ongoing Activism and Policy Reform
The #MeToo movement has spurred significant policy changes, from increased reporting mechanisms to revised legal definitions of sexual harassment. Continued activism is crucial to ensuring these reforms are implemented effectively and equitably across diverse communities. This necessitates a multifaceted approach, including targeted advocacy efforts, public awareness campaigns, and collaborations with policymakers. For example, ongoing campaigns focused on legislative reforms addressing power imbalances in specific industries, such as entertainment or academia, can be effective in achieving meaningful change.
Potential Challenges and Obstacles
The movement faces potential challenges in sustaining its momentum. A decline in public interest, fatigue amongst activists, and resistance from entrenched power structures are all potential hurdles. Addressing these requires sustained engagement, fostering a sense of collective responsibility, and implementing strategies for long-term impact. This includes recognizing and mitigating the impact of burnout among activists and exploring innovative approaches to maintain engagement.
The movement must adapt its strategies to remain relevant and compelling in the face of evolving social dynamics.
Potential Areas for Improvement in Reporting Mechanisms and Support Systems
Improved reporting mechanisms are essential to ensure that victims feel safe and empowered to come forward. This includes expanding access to confidential and accessible support systems, particularly for marginalized groups. A comprehensive approach should include training for individuals in positions of power to identify and address inappropriate behavior, and creating reporting systems that are culturally sensitive and responsive to diverse needs.
The #MeToo movement’s impact on politics and assault cases is undeniable. While the US grapples with these issues, the global political climate is also affected by factors like the ongoing tension between the US and North Korea, which directly influences the US economy’s growth and stability. This complex interplay is highlighted in the article about us economy growth north korea threats , and it’s clear that these global events ultimately reverberate back to the domestic challenges we face, like holding perpetrators accountable for assault.
So, the political and social consequences of assault cases are far-reaching, impacting everything from global power dynamics to the everyday lives of citizens.
Further research and development are required to ensure effective support systems and robust reporting mechanisms that are truly inclusive.
Raising Awareness and Promoting Prevention
Raising awareness and promoting prevention are crucial for the long-term success of the movement. Educational initiatives, targeted at various age groups and communities, can foster a culture of consent and respect. Public awareness campaigns, focusing on the harmful effects of sexual assault and harassment, can empower individuals to recognize and address these issues effectively. Developing comprehensive prevention programs in educational institutions and workplaces, that address underlying power dynamics and promote healthy relationships, can be vital.
Educational resources, including online platforms and interactive workshops, can help in the prevention of such issues.
Potential Areas for Future Research and Development
| Area | Focus | Methodology | Potential Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Impact of online harassment | Investigating the unique forms and consequences of online sexual harassment and assault. | Quantitative surveys, qualitative interviews, and analysis of online platforms. | Development of targeted interventions and policy recommendations for online spaces. |
| Intersectionality of experiences | Examining the varying experiences of sexual assault and harassment across different social identities. | Qualitative studies, ethnographic research, and participatory action research. | Creation of more inclusive and culturally responsive support systems. |
| Long-term effects on victims | Understanding the long-term psychological and social impacts of sexual assault and harassment. | Longitudinal studies, clinical trials, and focus groups. | Development of evidence-based interventions for long-term recovery. |
| Prevention programs in workplaces | Evaluating the effectiveness of workplace prevention programs in reducing sexual harassment and assault. | Experimental studies, case studies, and program evaluations. | Identification of best practices and recommendations for implementing effective programs. |
Closing Notes
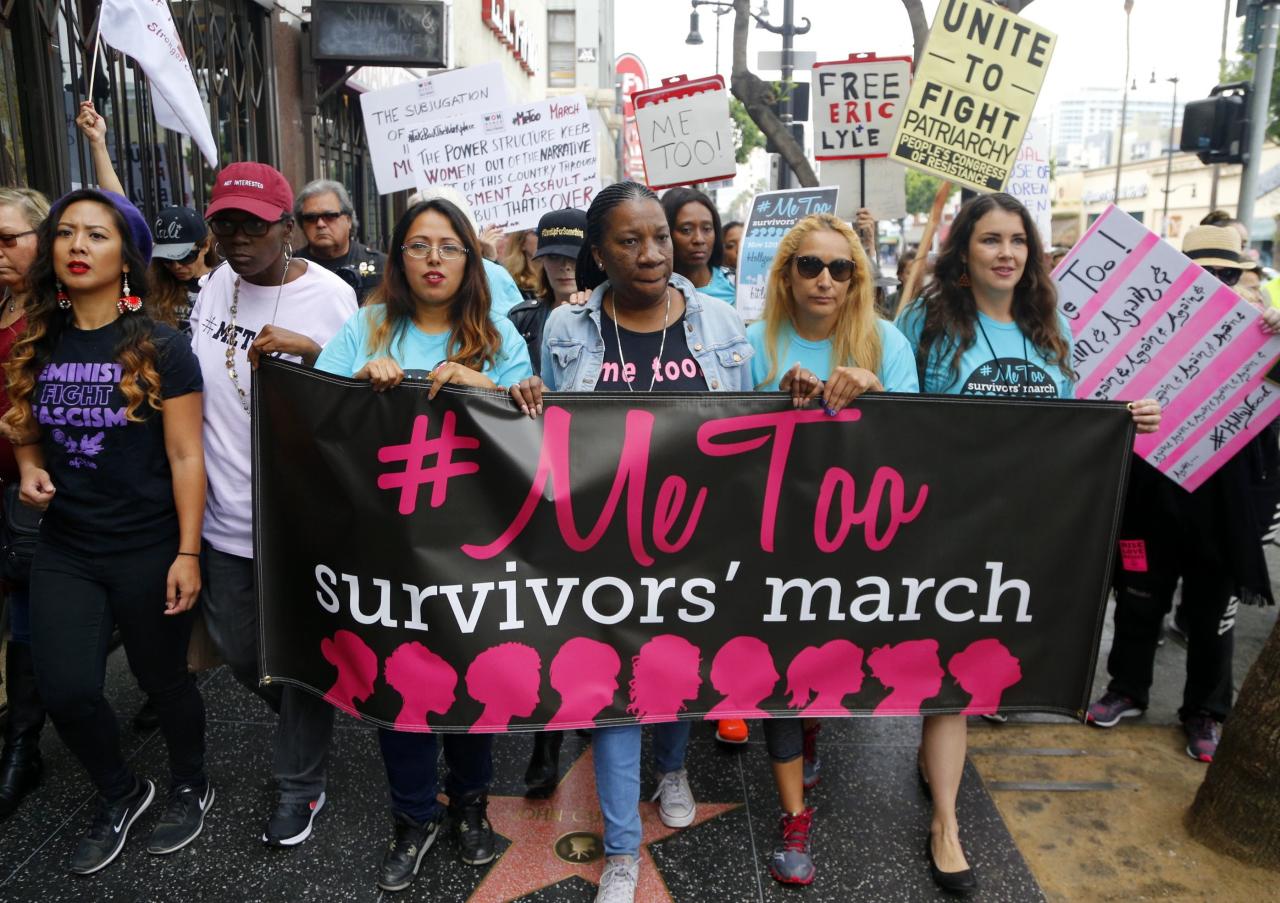
In conclusion, the #MeToo movement politics assault has profoundly impacted the political landscape and societal attitudes toward sexual assault. While the movement has brought about significant progress in raising awareness and demanding accountability, challenges remain in ensuring comprehensive support systems and restorative justice for victims. This discussion underscores the urgent need for continued dialogue, policy reform, and a collective commitment to creating a safer environment for all.
Essential FAQs
What are some common types of sexual harassment?
Sexual harassment encompasses various behaviors, including unwanted sexual advances, requests for sexual favors, and other verbal or physical conduct of a sexual nature that creates a hostile environment.
How can victims report sexual assault in the workplace?
Reporting procedures vary by workplace. Often, there are internal complaint mechanisms, human resources departments, and external authorities like law enforcement agencies that can be contacted. Confidential reporting channels are crucial for protecting victims.
What is the role of consent in defining sexual assault?
Consent is crucial in defining sexual assault. It must be freely and enthusiastically given, and lack of consent, regardless of the relationship, constitutes assault. Consent can be withdrawn at any time.
What are some resources available for victims of sexual assault?
Many organizations offer support for victims of sexual assault. These resources may include counseling services, legal aid, and support groups. Local community centers and hotlines often provide crucial information and assistance.






