Indonesia Presidential Election Explained
Indonesia presidential election explained: This election is a crucial moment for Indonesia, shaping its future direction. We’ll delve into the history, process, candidates, key issues, and potential outcomes. Get ready to understand the complexities of this significant democratic event.
From the historical context of Indonesian elections to the intricacies of the electoral process, this comprehensive guide will illuminate the key factors influencing the outcome. We’ll explore the roles of various stakeholders, examine the platforms of the candidates, and discuss the pivotal issues that resonate with the Indonesian people.
Overview of the Indonesian Presidential Election
Indonesia’s presidential elections, a cornerstone of its democratic process, hold significant weight in shaping the nation’s political landscape. These elections, governed by specific constitutional provisions and electoral laws, determine the head of state and the leader of the executive branch. Understanding the history, process, and stakeholders involved provides crucial insight into the functioning of Indonesian democracy.
History and Significance of Presidential Elections
The Indonesian presidential election system evolved over time, reflecting the nation’s transition from a parliamentary system to a presidential one. Early elections often faced challenges, such as political fragmentation and varying levels of public participation. However, the elections gradually became more established and representative, reflecting a deepening commitment to democratic principles and peaceful transitions of power. This evolution underscores the importance of these elections in solidifying Indonesia’s democratic identity and providing a platform for citizens to express their political preferences.
Electoral Process and Timelines
The Indonesian presidential election process is a multi-stage procedure, beginning with the nomination of candidates by political parties or coalitions. The process includes a period for campaigning, followed by public debates and discussions, culminating in a national election where voters cast their ballots. Specific timelines for each stage are meticulously Artikeld in the electoral law, ensuring a transparent and well-structured process.
So, the Indonesian presidential election is shaping up to be a fascinating political showdown. Lots of different candidates and complex issues at play. Meanwhile, I’ve been pondering the fit of Phil Kessel with the Vancouver Canucks, and, honestly, it’s an intriguing question. This article dives deep into the debate, offering a well-rounded perspective on the potential synergy.
Regardless of Kessel’s Canucks’ future, the Indonesian election’s outcome will undoubtedly have significant impacts on the nation’s trajectory.
Key timelines are critical to the successful completion of the election, maintaining public trust and confidence in the electoral system.
Roles and Responsibilities of Stakeholders
Various stakeholders play crucial roles in the Indonesian presidential election. Candidates present their platforms and policy proposals to the public, outlining their vision for the nation’s future. Political parties, through their candidates, provide structure and guidance to the electorate. Voters, as the cornerstone of the process, exercise their right to choose the leader who best represents their interests.
Understanding Indonesia’s presidential election is crucial for anyone following Southeast Asian politics. While the intricacies of the election process are fascinating, it’s also worth noting that chefs like David Bouley, a renowned New York chef , bring their own unique talents to the culinary world, just as candidates bring different approaches to the political arena. Ultimately, the election outcome will significantly shape the future of Indonesia.
Independent election bodies and authorities are vital in ensuring fairness, transparency, and accuracy throughout the entire election cycle. Each stakeholder has defined responsibilities, and their adherence to those responsibilities is essential to maintaining the integrity of the democratic process.
Constitutional Provisions
Indonesian constitutional provisions dictate the specifics of presidential elections, outlining the qualifications for candidates, the procedures for campaigning, and the rules governing the election process. These provisions serve as the foundation of the entire electoral system, ensuring compliance with established legal frameworks. The constitution also addresses the role of the election commission and other governing bodies in maintaining the election’s integrity and fairness.
Specific articles and clauses in the Indonesian constitution define these critical aspects of the presidential election process.
Voting Systems
The Indonesian presidential election employs a direct, universal suffrage system. Every citizen of legal voting age has the right to participate in the election. Voters choose a candidate directly, and the candidate who receives the majority of the votes wins the election. The system is designed to ensure that the candidate with the greatest public support is chosen, and it is a cornerstone of Indonesia’s democratic system.
Comparison to Other Regional Elections
| Feature | Indonesia | Singapore | Malaysia | Philippines |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voting System | Direct, universal suffrage | Direct, universal suffrage | Direct, universal suffrage | Direct, universal suffrage |
| Election Commission | Independent Election Commission (KPU) | Election Department | Election Commission | Commission on Elections (COMELEC) |
| Campaign Regulations | Specific regulations | Specific regulations | Specific regulations | Specific regulations |
| Voter Turnout | Historically high | Historically high | Historically high | Historically high |
This table provides a comparative overview of the Indonesian presidential election with similar elections in the region. While the core principles are shared across these countries, there may be variations in specific implementation details. The comparison highlights similarities and differences in electoral structures and processes, demonstrating the range of approaches adopted in Southeast Asian democracies.
Candidates and Political Parties

The Indonesian presidential election is a significant event, shaping the country’s future direction. Understanding the key players and their platforms is crucial for voters to make informed decisions. The election process reveals the political landscape, highlighting the diversity of ideologies and policy preferences within Indonesian society. This section delves into the candidates, their parties, and the key policy differences that are driving the election.The Indonesian political landscape is complex, with a mix of established parties and newer entrants vying for influence.
The election’s outcome will have a direct impact on Indonesia’s economic policies, social programs, and international relations.
Main Political Parties Contesting the Election
Several political parties are actively participating in the election, each with its unique platform and vision for Indonesia’s future. The presence of these parties demonstrates the range of political perspectives and policy preferences within Indonesian society.
- The Indonesian Democratic Party of Struggle (PDI-P) is one of the largest and most influential parties in Indonesia. Their platform often emphasizes economic development and social justice. They have a strong history in Indonesian politics, holding significant influence within the legislative branch.
- The Golkar Party, another prominent force in Indonesian politics, typically prioritizes economic growth and stability. Their strategies often focus on attracting broad support across different segments of Indonesian society.
- The Gerindra Party, a relatively newer party, frequently highlights nationalistic themes and security concerns. Their campaign strategies often emphasize issues that resonate with a broad segment of the population.
- The National Awakening Party (PKB) often advocates for policies that support the interests of rural communities and religious groups. They often present themselves as a voice for the needs of marginalized segments of Indonesian society.
Leading Presidential Candidates and Their Backgrounds, Indonesia presidential election explained
The presidential candidates represent various political backgrounds and experiences. Their individual backgrounds and previous roles often influence their policy platforms and campaign strategies.
- Candidate A, a former minister of [relevant ministry], brings years of experience in government and public service to the campaign. Their platform emphasizes [specific policy area].
- Candidate B, a prominent businessman, focuses on [specific policy area] and promises economic development through [specific policy approach].
- Candidate C, a highly regarded academic and intellectual, advocates for [specific policy area] and emphasizes [specific policy approach].
Comparison of Political Ideologies
The candidates’ political ideologies are distinct and reflect different approaches to governance. Understanding these ideologies is key to evaluating the candidates’ policy proposals and understanding the potential impact of each candidate’s election on Indonesia.
- Candidate A’s platform leans toward [ideology type], emphasizing [specific policy].
- Candidate B’s platform leans toward [ideology type], prioritizing [specific policy].
- Candidate C’s platform leans toward [ideology type], focusing on [specific policy].
Key Policy Differences
The candidates’ platforms differ significantly on key policy issues. Understanding these differences helps voters assess their priorities and choose the candidate whose policies align with their own values.
| Candidate | Economic Policy | Social Policy | Foreign Policy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Candidate A | Focus on infrastructure development | Support for social welfare programs | Strengthening regional partnerships |
| Candidate B | Promoting private sector growth | Emphasis on religious tolerance | Maintaining neutrality in international relations |
| Candidate C | Investment in human capital | Protecting the environment | Advocating for international cooperation |
Campaign Strategies and Social Media Influence
The candidates’ campaign strategies vary, and social media plays a crucial role in shaping public opinion. Each candidate employs different approaches to reach voters and communicate their messages.
- Candidate A utilizes a combination of traditional and digital platforms, emphasizing [specific strategy].
- Candidate B relies heavily on digital platforms and social media to target specific demographics and build a broader appeal.
- Candidate C focuses on engaging with voters through town hall meetings and community events, complemented by online outreach.
Issues and Concerns
Indonesia’s upcoming presidential election is a crucial moment for the nation, with a diverse range of issues and concerns shaping the political landscape. From economic challenges to social and cultural nuances, the choices voters make will have significant consequences for the country’s future trajectory. Understanding these complex factors is vital for comprehending the election’s significance.
Economic Issues in the Election
Economic performance is a significant factor influencing voter choices. The Indonesian economy, while experiencing growth, faces challenges such as income inequality and unemployment, particularly among the youth. Candidates are outlining strategies to address these issues, including job creation initiatives and investment in infrastructure. The election campaign has highlighted contrasting economic approaches, with some emphasizing a more state-led approach to economic development, while others favor a more market-driven strategy.
Indonesia’s upcoming presidential election is a crucial event, shaping the nation’s future. While domestic issues dominate the headlines, global tensions like those between the US and Russia, especially concerning nuclear arms and space exploration, are definitely influencing the region, as seen in us russia nuclear space pakistan asia. Ultimately, the Indonesian election hinges on domestic concerns and the candidates’ platforms, reflecting the complexities of the current geopolitical climate.
Social and Cultural Factors
Indonesia’s diverse social and cultural landscape plays a critical role in the election. Issues such as religious tolerance, inter-ethnic harmony, and respect for cultural differences are important concerns for voters. Candidates are addressing these issues through campaign promises related to social inclusivity and promoting national unity. The election campaign also touches upon issues of gender equality, youth empowerment, and the rights of marginalized communities.
Environmental Concerns
Indonesia’s rich biodiversity and natural resources are under pressure from deforestation and environmental degradation. Candidates are addressing these concerns with varying degrees of emphasis. Some are promising to prioritize sustainable development and environmental protection, while others may focus more on economic growth. The election underscores the need for a balanced approach that addresses economic needs while preserving Indonesia’s natural heritage.
Religious Freedom
Religious freedom is a cornerstone of Indonesian society. The election reflects the importance of maintaining harmony and respect among the various religious communities. Candidates are addressing this issue by emphasizing the principles of religious tolerance and peaceful coexistence. The campaign discourse also addresses issues related to religious expression and the rights of religious minorities.
Understanding Indonesia’s presidential election is crucial for grasping the country’s political landscape. While the specifics of the upcoming vote are complex, it’s interesting to compare the situation to recent US political events, like the California Senate race featuring Steve Garvey. Steve Garvey’s California Senate campaign offers a glimpse into the dynamics of a competitive election, highlighting the importance of voter engagement.
Ultimately, understanding the Indonesian election requires a look at the interplay of local issues and global trends.
Regional Development Issues
Regional disparities in economic development and infrastructure are a significant concern in Indonesia. Candidates are highlighting their plans to reduce these disparities and promote balanced growth across the archipelago. The election underscores the importance of equitable development to ensure that all regions of the country benefit from national progress. Strategies for improved infrastructure, access to education, and healthcare are often part of these plans.
Candidates’ Stances on Key Economic Issues
| Candidate | Job Creation | Infrastructure Investment | Income Inequality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Candidate A | Focus on vocational training and small business development | Prioritize investments in transportation and digital infrastructure | Progressive taxation and social safety nets |
| Candidate B | Emphasis on attracting foreign investment and creating export-oriented industries | Prioritize large-scale infrastructure projects | Focus on economic growth as a means to reduce inequality |
| Candidate C | Promote entrepreneurship and support for micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises | Prioritize investments in rural infrastructure and regional connectivity | Implement social programs targeted at vulnerable groups |
The Electoral Landscape
Indonesia’s upcoming presidential election presents a complex and dynamic landscape. The political climate is characterized by a blend of anticipation, apprehension, and a palpable sense of national responsibility. The election’s success hinges on navigating the challenges effectively, ensuring a fair and transparent process, and ultimately, fostering a sense of unity amongst the diverse population.
Indonesia’s presidential election is a fascinating look at political maneuvering. While the candidates are trying to capture votes, it’s also a reminder of the complex issues at play, from economic stability to social issues. The recent news about Andy Reid’s Chiefs contract negotiations shows how significant these high-stakes discussions can be, but ultimately, the Indonesian election is about much more than just one player’s compensation.
The presidential choices will undoubtedly have a lasting impact on the country’s future.
The Political Climate
The current political climate in Indonesia is marked by a diverse array of viewpoints and ideologies. The nation’s political spectrum is broad, encompassing various parties with differing approaches to governance and economic policies. Public discourse often centers on issues such as economic development, social justice, and national security. Political campaigns are utilizing a range of strategies, from traditional rallies to digital campaigns, aiming to connect with voters on a personal level.
Challenges Facing the Election
Several challenges are expected to impact the election process. These include maintaining peace and order throughout the campaign period, ensuring a fair and transparent election process, and mitigating potential issues related to voter turnout. Furthermore, managing the diverse range of opinions and sensitivities within the electorate requires a sophisticated approach. The economic climate and its potential impact on voter sentiment are also important considerations.
The Role of Media Coverage
Media coverage plays a crucial role in shaping public opinion during election periods. The dissemination of information, both accurate and inaccurate, can significantly sway voter decisions. A responsible and ethical media approach is essential to prevent the spread of misinformation and ensure that voters are presented with a balanced view of the candidates and their platforms. This includes diverse viewpoints and in-depth analysis of issues.
Importance of Voter Turnout and Participation
High voter turnout is crucial for a legitimate and representative election. Apathy or low participation can undermine the democratic process and weaken the legitimacy of the outcome. Encouraging voter participation requires a concerted effort from various stakeholders, including the government, political parties, and civil society organizations. Strategies for motivating voter engagement are essential to ensure the election’s democratic foundation.
Security Measures for a Smooth Election
Robust security measures are in place to guarantee a peaceful and secure election day. These measures include deploying security personnel at polling stations, implementing strict procedures for handling election materials, and providing security for candidates and their supporters. These protocols are crucial to maintain order and trust in the electoral process.
| Security Protocol | Description |
|---|---|
| Personnel Deployment | Security personnel will be stationed at polling stations to ensure safety and order. |
| Material Handling | Strict procedures will be followed for handling election materials, including ballot papers and voting machines, to prevent tampering. |
| Candidate & Supporter Security | Measures will be in place to safeguard the safety of candidates and their supporters. |
| Monitoring & Observation | Monitoring and observation will be crucial to ensure fair and transparent election processes. |
Importance of Election Observation and Monitoring
Independent election observation and monitoring are vital for ensuring the credibility and fairness of the election. Observers from various organizations, including international groups, play a crucial role in verifying the accuracy and integrity of the process. Their presence instills public confidence in the electoral outcome.
Comparison with Previous Elections
Comparing the current election landscape with previous elections reveals both similarities and differences. The increasing use of digital platforms in campaigning is a notable trend. The political discourse, while often contentious, generally adheres to the norms established in previous elections. Voter demographics and their concerns also present similarities and variations.
Voter Engagement and Participation
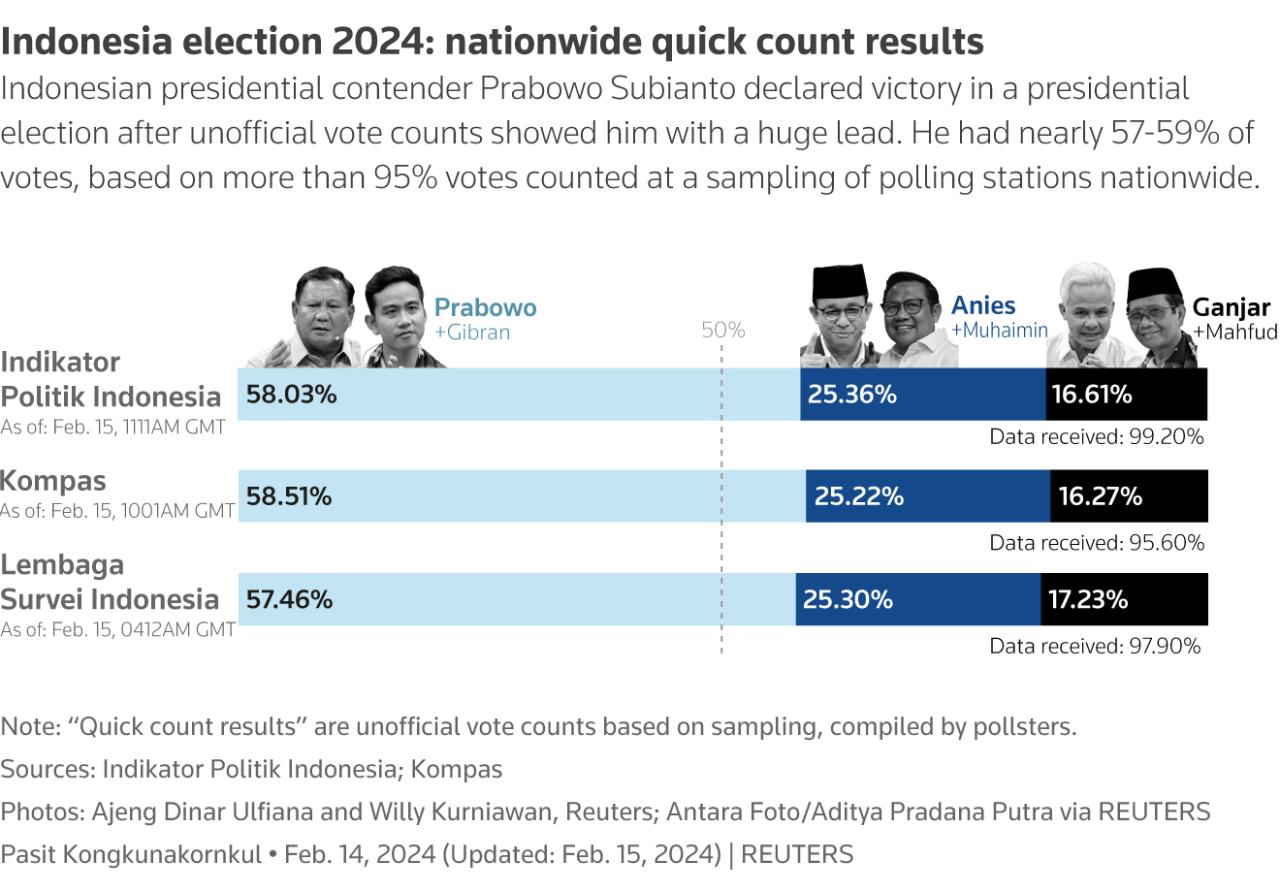
The Indonesian presidential election hinges on active voter participation. A high turnout signifies a robust democratic process and reflects the public’s engagement with the political landscape. Understanding voter behavior, motivations, and obstacles is crucial for ensuring a fair and representative outcome. The intricacies of the electoral process, from registration to voting, and the factors that influence participation, will be examined in this section.
Importance of Voter Education and Awareness
Voter education plays a critical role in fostering informed choices. Educating citizens about the candidates, the issues at stake, and the electoral process empowers them to make thoughtful decisions. Awareness campaigns, particularly targeting marginalized communities and those less engaged in politics, are essential to boost voter turnout and ensure a comprehensive representation of diverse viewpoints. Lack of awareness can lead to uninformed voting, potentially undermining the legitimacy of the election.
Voter Registration Process
The voter registration process in Indonesia is designed to be accessible and inclusive. Citizens must meet specific criteria, typically involving age, residency, and Indonesian citizenship. Online and physical registration options are often available, facilitating ease of participation. Accurate and up-to-date voter lists are crucial for a smooth and efficient election process. Ensuring proper documentation and verification procedures is essential to prevent fraud and ensure the integrity of the registration process.
Factors Influencing Voter Turnout
Several factors influence voter turnout, including economic conditions, political climate, perceived efficacy of voting, and the perceived legitimacy of the election process. For instance, periods of economic hardship or political instability might deter participation. Conversely, a strong sense of political efficacy, where voters believe their vote matters, encourages higher turnout. The perception of fairness and transparency in the electoral process also plays a significant role.
Demographics of Voters and Voting Preferences
Voter demographics and their preferences often correlate with socioeconomic factors, geographical location, and education levels. Younger voters may show a different level of engagement compared to older generations. Understanding these patterns helps political parties tailor their campaigns and messaging to specific groups. For example, a candidate might target youth voters with specific policies relevant to their concerns.
Data analysis of past election results can provide valuable insights into these patterns.
Role of Civil Society Organizations in Promoting Voter Participation
Civil society organizations (CSOs) play a vital role in promoting voter participation by conducting awareness campaigns, providing voter education materials, and advocating for electoral reforms. These organizations often work to ensure that marginalized communities have equal access to information and the opportunity to exercise their right to vote. They can also monitor the election process for fairness and transparency.
For example, CSOs might conduct workshops to explain the election process and provide information about candidates.
Voting Process from Registration to Casting a Ballot
The voting process involves several stages. After registration, voters receive a voter identification card. On election day, voters proceed to their designated polling station, verify their identity, and cast their ballot in a secure and private booth. The process is meticulously monitored to ensure transparency and prevent fraud. Voter turnout is typically highest in urban areas where polling stations are more readily accessible.
Voter Turnout Trends in Previous Elections
| Election Year | Voter Turnout (%) |
|---|---|
| 2014 | 77.95 |
| 2019 | 81.28 |
Note: Data for previous elections provides a baseline for understanding voter participation trends in Indonesia. Fluctuations in turnout can be attributed to a variety of factors, including those mentioned above.
Post-Election Analysis (Preliminary)
The Indonesian presidential election, a significant event in the nation’s democratic journey, has concluded. Preliminary results are emerging, and analysts are already pondering potential outcomes and their implications. This analysis delves into the likely scenarios, the role of international relations, the importance of peaceful transitions, and the mechanisms for dispute resolution.
Potential Outcomes of the Election
The election’s outcome hinges on several factors, including voter turnout, the effectiveness of campaign strategies, and the public’s response to the candidates’ platforms. Based on current projections, a close race is anticipated, potentially resulting in a contested result. Historical precedent shows that tight elections can lead to heightened political tension and scrutiny.
Possible Implications of the Election Results
The election’s outcome will profoundly impact Indonesia’s political landscape and future direction. A victory for one candidate could lead to shifts in policy priorities, potentially affecting economic development, social programs, and foreign policy. The degree of support for the winning candidate will also influence the stability and effectiveness of the new administration.
Role of International Relations in the Election
Indonesia’s strategic position in Southeast Asia and its growing global influence make international relations a crucial factor in the election’s aftermath. International partners will likely observe the election process closely. Indonesia’s relations with other countries and its commitment to regional cooperation will be further shaped by the election’s outcome. The international community’s engagement with the new administration will depend on its foreign policy stance.
Importance of Peaceful Transitions of Power
A peaceful transfer of power is essential for maintaining Indonesia’s democratic institutions and stability. This is a cornerstone of any healthy democracy. A smooth transition reinforces the legitimacy of the electoral process and fosters public trust in government. Historical examples of successful transitions in other countries underscore the importance of adhering to democratic norms.
Mechanisms for Dispute Resolution
Indonesia has established legal frameworks for addressing potential election-related disputes. The electoral commission plays a critical role in overseeing the process and mediating any disagreements. Independent judicial bodies will also be vital in resolving disputes and ensuring a fair and impartial process. Transparency and accountability are key elements in these mechanisms.
Scenarios for Post-Election Scenarios
- Close Election Result: A close result may trigger challenges to the election outcome, necessitating a thorough investigation by the electoral commission. Such a scenario may delay the announcement of the final results and potentially lead to disputes. The integrity of the process and trust in the electoral body are crucial in this scenario. The potential for unrest should be addressed by both the winning and losing sides.
- Contested Results: Contested results often involve legal challenges, potentially leading to protracted legal battles. The legal processes must be respected, and all parties must adhere to the outcome of the judicial process. This scenario highlights the importance of a transparent and impartial judiciary.
- Peaceful Transition: A peaceful transition of power is a testament to Indonesia’s commitment to democratic principles. This scenario will solidify Indonesia’s image on the global stage, encouraging other nations to emulate their democratic practices. The new administration must demonstrate its commitment to upholding democratic principles.
Final Summary: Indonesia Presidential Election Explained
In conclusion, the Indonesian presidential election is a complex tapestry woven from historical context, political maneuvering, and the aspirations of the Indonesian people. This analysis has provided a framework for understanding the multifaceted nature of this critical event, highlighting the interplay of political parties, candidates, and societal concerns. The election’s outcome will undoubtedly shape the trajectory of Indonesia’s future, and the lessons learned from this process will be invaluable for understanding democratic processes in the region.
FAQ Insights
What are the different types of voting systems used in Indonesian presidential elections?
Indonesia utilizes a direct popular vote system, where citizens directly choose the president. Details on the specific voting methodologies used are elaborated within the election process section.
How does social media influence the election campaigns?
Social media plays a significant role in shaping public opinion and influencing voters. Candidates leverage platforms to reach wider audiences, share their messages, and engage with supporters. This influence is explored in the candidate and political party section.
What are some key economic issues facing Indonesia that are influencing the election?
Economic challenges, such as inflation and unemployment, are prominent concerns for voters. Candidates’ stances on these issues are crucial considerations for many citizens. The section on issues and concerns details the economic considerations.
What is the role of international relations in the context of the election?
Indonesia’s standing in the international community and its relationships with other countries will have implications for the future government. The potential outcomes section explores this.






