Earthquake Tracker Southern California Your Guide
Earthquake tracker southern california sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into the complex and fascinating world of seismic activity in Southern California. We’ll delve into real-time data, historical events, and the critical role of preparedness in this seismically active region.
This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and resources to understand the risks, stay informed, and prepare for potential earthquakes. We’ll explore the geological factors contributing to earthquakes, the impact on communities, and the ongoing research into prediction and mitigation strategies.
Introduction to Earthquake Tracking in Southern California
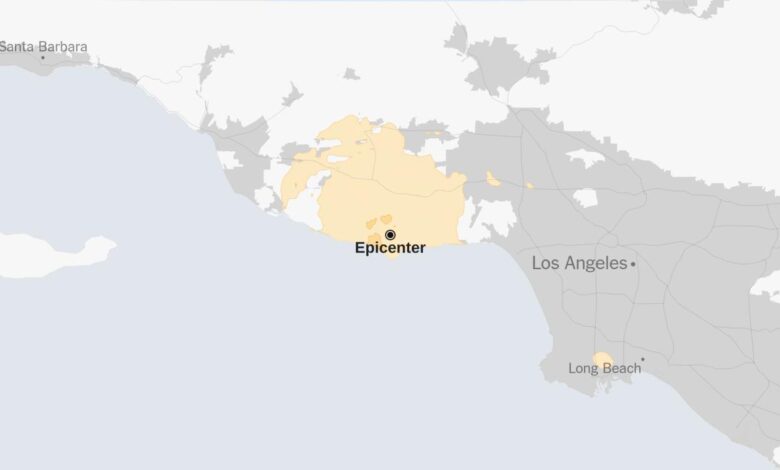
Southern California sits atop a complex network of fault lines, making it one of the most seismically active regions in the United States. This inherent geological instability necessitates a vigilant approach to earthquake tracking, allowing for better understanding of potential risks and proactive measures to mitigate their impact. The region’s history is punctuated by significant earthquakes, highlighting the importance of ongoing monitoring and preparedness.Earthquake tracking in Southern California is critical for several reasons.
Early detection and analysis of seismic activity can provide valuable insights into the patterns and potential magnitudes of future events. This information is vital for emergency response planning, infrastructure development, and public safety education. Accurate and real-time data informs decisions about building codes, land-use regulations, and community preparedness programs, ultimately safeguarding lives and property.
Historical Earthquake Data in Southern California
Southern California has experienced numerous significant earthquakes throughout history. The 1857 Fort Tejon earthquake, estimated at a magnitude of 7.9, is a prime example of the region’s seismic history. This event caused widespread damage and loss of life. More recently, the 1994 Northridge earthquake, with a magnitude of 6.7, served as a stark reminder of the destructive potential of earthquakes.
Data from these historical events, combined with modern monitoring, helps scientists refine models of earthquake behavior and predict future risks.
Significance of Earthquake Tracking
Tracking earthquakes in Southern California is crucial for several reasons. First, it allows for improved understanding of seismic activity patterns. This knowledge can assist in forecasting potential future events. Second, it enables the development of effective emergency response plans. Third, it facilitates the implementation of stringent building codes and land-use regulations to minimize damage.
Fourth, it fosters community preparedness, empowering residents to take proactive steps to protect themselves and their loved ones. Data from past events and ongoing monitoring informs these efforts, providing valuable insight into the potential impact of future earthquakes.
Seismic Monitoring Tools
Various tools and technologies are employed to monitor seismic activity in Southern California. Seismographs, strategically placed across the region, continuously record ground motion, measuring the amplitude and frequency of seismic waves. These instruments provide crucial data on the magnitude, location, and depth of earthquakes. Modern seismographs are equipped with advanced sensors and digital recording systems, allowing for rapid and precise data acquisition.
- Seismographs: These instruments continuously monitor ground motion, detecting and recording seismic waves. They are crucial for identifying the location, magnitude, and depth of earthquakes.
- GPS networks: Global Positioning System (GPS) stations monitor ground deformation. Changes in ground position can indicate stress build-up in the Earth’s crust, potentially providing clues about impending seismic activity. This technology can detect subtle shifts that might not be immediately apparent on seismographs.
- Geodetic instruments: These advanced instruments measure very small changes in the Earth’s surface. They are sensitive to ground deformation, enabling scientists to track subtle shifts associated with seismic activity.
Importance of Preparedness and Response
Understanding the potential for earthquakes and developing robust response mechanisms are paramount for Southern California. Community preparedness involves educating residents about earthquake safety procedures, including drop, cover, and hold on. This preparedness also extends to creating evacuation plans and establishing emergency communication networks. The swift and coordinated response of emergency services plays a critical role in minimizing casualties and damage.
Real-time Earthquake Data
Staying informed about earthquakes in Southern California is crucial for preparedness and safety. Real-time data allows residents to be aware of events as they happen, enabling quicker responses and potentially saving lives. Understanding how to access and interpret this data is key to making informed decisions during seismic activity.Accessing real-time earthquake data is relatively straightforward. Numerous sources provide up-to-the-minute information, including detailed reports and warnings.
These sources vary in their level of detail and presentation, so familiarity with the different platforms and their strengths is beneficial.
Checking the earthquake tracker for Southern California lately? It’s been pretty quiet, thankfully. Though, the news about Jack Burke Jr. passing away, jack burke jr dead , certainly sent ripples through the community. I’m hoping this doesn’t trigger any seismic activity, and I’ll continue to monitor the tracker for any unusual movements in the region.
Mechanisms for Accessing Real-time Earthquake Data
Real-time earthquake data is accessible through a variety of channels, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. These include dedicated earthquake monitoring websites, smartphone applications, and even some news outlets. The data is often collected by seismic stations and relayed to the public through these channels.
Keeping tabs on earthquake activity in Southern California is crucial, especially with the recent seismic events. It’s fascinating how these natural phenomena can impact us, and it’s also interesting to note the impressive career of Adrian Beltre, a true legend for the Texas Rangers. His impact on the game is undeniable, like the impact an earthquake can have on the landscape.
Fortunately, a great earthquake tracker for Southern California is a valuable tool for staying informed and prepared. Adrian Beltre hall of fame Texas Rangers were certainly lucky to have him, and earthquake trackers are equally beneficial for the safety of the residents of Southern California.
Prominent Earthquake Tracking Websites and Apps
Numerous websites and apps provide real-time earthquake information. Some of the most popular and reliable include the United States Geological Survey (USGS) website, the California Earthquake Authority (CEA) site, and several mobile applications like those developed by the USGS and other organizations. These resources offer various levels of detail, from basic location and magnitude reports to more complex data visualizations.
Accuracy and Reliability of Data Sources
The accuracy and reliability of earthquake data sources vary. Governmental agencies, such as the USGS, are generally considered the most reliable sources due to their extensive networks of monitoring stations and rigorous data analysis procedures. News outlets may report data from these agencies or other sources but may not always provide the same level of detail or accuracy.
Keeping tabs on earthquake activity in Southern California is crucial, and thankfully there are handy trackers available. While you’re checking those, did you know that there’s a whole lot of buzz surrounding the stars Harley Johnston, Oettinger, and Benn? Their recent news is definitely making waves, as you can see from this article about stars Harley Johnston, Oettinger, and Benn.
Regardless of the latest celebrity gossip, a good earthquake tracker remains a valuable tool for staying informed about seismic activity in the region.
It’s crucial to cross-reference information from multiple sources.
Frequency of Earthquake Events in Southern California
Southern California experiences a high frequency of seismic activity. The region’s geological history and tectonic plate movement make it prone to earthquakes of varying magnitudes. Understanding the frequency helps residents assess risk and develop appropriate preparedness plans. Historical records and ongoing monitoring reveal a pattern of regular seismic activity, with smaller events occurring more frequently than larger ones.
Interpreting Earthquake Magnitude and Location Data
Earthquake magnitude is a crucial piece of information, indicating the size of the seismic event. The Richter scale is commonly used to measure earthquake magnitude. Higher magnitudes correlate to greater ground shaking and potential damage. Earthquake location data, often displayed as geographic coordinates, helps determine the epicenter of the earthquake and potential impact areas. It’s important to understand how this data relates to populated areas.
For instance, an earthquake in a remote area might cause less damage than one in a densely populated region.
Comparison of Earthquake Tracking Services
| Name | Features | Accuracy | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| USGS | Detailed reports, maps, magnitude, location, depth, intensity | High | Free |
| CEA | Specific to California, hazard assessments, early warnings | High | Free |
| Earthquake.com | User-friendly interface, visualizations | Good | Free |
| Other Apps | Mobile convenience, alerts, push notifications | Variable | Free or paid |
Earthquake Preparedness in Southern California
Southern California, a region of stunning beauty and vibrant life, is also situated on a seismically active zone. Understanding and preparing for earthquakes is not just a matter of safety, but a vital component of resilience in this dynamic environment. The potential for significant damage and loss of life underscores the critical need for proactive preparedness measures.The region’s unique geological makeup, characterized by active fault lines, makes it highly vulnerable to earthquakes of varying magnitudes.
This vulnerability necessitates a comprehensive approach to earthquake preparedness, encompassing individual actions, community strategies, and robust building codes. Knowing what to expect and how to react can dramatically reduce the impact of a quake.
Importance of Earthquake Preparedness
Earthquake preparedness is crucial for minimizing the impact of a potential earthquake. It encompasses individual and community-wide actions aimed at mitigating the effects of ground shaking, reducing casualties, and facilitating swift recovery. A proactive approach fosters resilience, allowing communities to bounce back from a disaster with minimal disruption.
Specific Vulnerabilities of Southern California
Southern California’s unique geological features create specific vulnerabilities. Active fault lines, like the San Andreas Fault, pose a significant threat. The density of population in certain areas increases the risk of casualties and widespread damage. The region’s diverse topography, ranging from coastal plains to mountainous regions, also affects the severity of shaking and potential landslides. Additionally, the presence of older structures that may not meet modern earthquake-resistant building codes increases the risk of collapse during an earthquake.
Developing an Earthquake Preparedness Plan
Creating a personal earthquake preparedness plan is a critical step. This plan should encompass actions before, during, and after an earthquake. It should Artikel evacuation routes, identify safe locations within the home, and establish communication strategies. The plan should also detail the location of essential supplies and the steps to take for securing property.
Building Codes and Earthquake Safety Measures, Earthquake tracker southern california
Modern building codes are designed to increase earthquake resistance. These codes incorporate regulations for structural design, material selection, and construction techniques. Compliance with these codes is essential for ensuring the safety of buildings during earthquakes. Retrofitting older structures to meet modern seismic standards is also vital for enhancing their resilience.
Earthquake Preparedness Steps
Developing a comprehensive preparedness plan involves several steps.
- Identify potential hazards: Determine the specific risks in your area, including potential fault lines, landslide zones, and proximity to vulnerable structures.
- Develop an emergency plan: Create a detailed plan outlining evacuation routes, safe locations, and communication strategies. This includes designating a meeting place outside the home.
- Stock emergency supplies: Gather essential supplies like water, food, first-aid kits, flashlights, and batteries. Consider storing enough supplies for several days.
- Secure your home: Reinforce heavy objects and secure shelves and cabinets to prevent them from falling during an earthquake. Ensure that any hanging items are securely fastened.
- Learn basic first aid: Familiarize yourself with basic first aid techniques to assist injured individuals. Learning CPR and other relevant first aid skills is highly recommended.
- Participate in earthquake drills: Practice earthquake preparedness drills with family members to ensure everyone understands the procedures and can react effectively.
- Stay informed: Follow local emergency alerts and stay informed about earthquake safety guidelines from official sources.
Resources for Earthquake Preparedness Education
Numerous resources are available to aid in earthquake preparedness education. Local emergency management agencies, universities, and non-profit organizations offer educational materials and workshops. Online resources, such as websites and videos, provide further information and practical tips. These resources can help individuals and communities build resilience against earthquakes.
Historical Earthquakes and Their Impact
Southern California, a region of stunning beauty and vibrant life, is also a land shaped by powerful forces. The relentless movement of tectonic plates beneath the surface has resulted in a history of earthquakes, some of which have profoundly impacted the landscape and the lives of its inhabitants. Understanding these historical events, their consequences, and the lessons learned from them is crucial for future preparedness and resilience.The seismic history of Southern California reveals a pattern of recurring tremors, ranging from minor disturbances to devastating quakes.
Each event has left its mark on the region’s infrastructure, communities, and the way people live and build. Examining these past earthquakes offers valuable insights into the complex interplay between natural forces and human endeavors.
Significant Earthquakes in Southern California History
Southern California has experienced numerous significant earthquakes throughout its history. These events, while separated by time, share common threads of disruption and recovery. A comprehensive understanding of these events is essential for appreciating the ongoing challenges and opportunities in earthquake preparedness.
Impacts on Infrastructure and Communities
The impacts of past earthquakes on Southern California’s infrastructure and communities have been far-reaching and often devastating. Damage to buildings, roads, and lifelines like water and gas systems has disrupted daily life and required significant investments in repair and rebuilding. The human toll, including loss of life and injuries, further underscores the urgent need for effective mitigation strategies.
Damage Assessment Procedures for Past Earthquakes
Damage assessment procedures for past earthquakes have evolved over time. Early assessments were often rudimentary, relying on eyewitness accounts and visual inspections. Modern methods utilize sophisticated technologies like aerial photography, satellite imagery, and detailed building surveys to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the extent of the damage.
Evolution of Building Standards and Codes in Response to Earthquakes
Building codes and standards in Southern California have significantly evolved in response to past earthquakes. Early codes were often inadequate to withstand seismic activity. Subsequent revisions and additions have incorporated lessons learned from past disasters, leading to more resilient structures capable of withstanding stronger ground motions. This ongoing process reflects the commitment to improving building safety and protecting lives.
Role of Scientific Research in Understanding Earthquake Patterns
Scientific research plays a crucial role in understanding earthquake patterns and improving earthquake preparedness. Researchers continuously study seismic activity, plate tectonics, and the behavior of soil and structures under stress. This knowledge is used to refine seismic hazard maps, develop improved building codes, and design more effective early warning systems. By understanding the science behind earthquakes, communities can better prepare for future events.
Table of Historical Earthquakes in Southern California
| Date | Magnitude | Location | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1857 | 7.9 | Fort Tejon | Significant damage to infrastructure, loss of life, and disruption to communities |
| 1933 | 6.4 | Long Beach | Significant damage to buildings and infrastructure, loss of life |
| 1994 | 6.7 | Northridge | Extensive damage to buildings, roads, and infrastructure, significant loss of life and injuries |
| 2019 | 7.1 | Southern California | Significant damage to buildings and infrastructure in certain areas, no significant loss of life |
Understanding Seismic Activity in Southern California
Southern California’s dramatic landscape is a testament to the constant, powerful forces shaping the Earth beneath our feet. This region sits atop a complex interplay of tectonic plates, fault lines, and geological structures that make it prone to earthquakes. Understanding these factors is crucial for mitigating risks and preparing for potential seismic events.Southern California’s seismic activity is a direct consequence of its location within the Pacific Ring of Fire, a zone of intense geological activity.
The region’s complex tectonic plate configuration, coupled with numerous fault lines, results in frequent seismic events, ranging from minor tremors to devastating earthquakes. Comprehending these geological factors is paramount to assessing the potential for future seismic activity and developing effective strategies for disaster preparedness.
Keeping tabs on earthquake activity in Southern California is pretty crucial, right? While I’m glued to the earthquake tracker, I’m also fascinated by the latest Emmy Awards TV ratings. Checking out the emmy awards tv ratings is a fun distraction, but ultimately, I’m always back to monitoring the earthquake tracker to see if anything significant is happening.
It’s a constant state of readiness, really.
Geological Factors Contributing to Earthquakes
The geological makeup of Southern California significantly influences its susceptibility to earthquakes. The region is situated where the Pacific Plate slides beneath the North American Plate, a process known as subduction. This constant movement creates immense stress along fault lines, ultimately releasing energy in the form of earthquakes. The presence of numerous active faults further complicates the picture, increasing the likelihood of seismic events.
Tectonic Plates Involved in Earthquake Generation
The primary tectonic plates involved in earthquake generation in Southern California are the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate. The Pacific Plate is moving northwestward relative to the North American Plate, resulting in friction and pressure along the San Andreas Fault and other associated fault lines. This constant interaction between these plates is a primary driver of seismic activity in the region.
Role of Fault Lines in Earthquake Activity
Fault lines are fractures in the Earth’s crust along which rocks move. In Southern California, numerous active fault lines, such as the San Andreas Fault, the San Jacinto Fault, and the Hayward Fault, pose a significant earthquake risk. These fault lines are zones of intense stress and strain, and their movement during earthquakes can cause widespread damage. The magnitude of the damage depends on the size of the fault rupture and the location of populated areas along the fault.
Different Types of Seismic Waves
Earthquakes generate various types of seismic waves that travel through the Earth. Primary (P) waves are the fastest and compress and expand the ground. Secondary (S) waves are slower and shear the ground. Surface waves are the slowest and cause the most damage, moving along the Earth’s surface. Understanding the characteristics of these waves is crucial for evaluating the potential impact of an earthquake.
How Seismographs Measure Earthquake Activity
Seismographs are instruments used to measure and record ground motion during earthquakes. They detect the ground shaking caused by seismic waves, converting it into a visual record known as a seismogram. By analyzing the seismogram, scientists can determine the magnitude and location of an earthquake. This information is vital for assessing the severity of the event and understanding its potential impact.
Visual Representation of Major Fault Lines in Southern California
A comprehensive map illustrating the major fault lines in Southern California is crucial for visualizing the potential earthquake risks in the region. Such a map would depict the location and extent of the faults, allowing for a clear understanding of the areas most vulnerable to seismic activity. This visual representation helps in identifying high-risk zones and formulating effective mitigation strategies.
Impact on Communities and Infrastructure
Southern California’s vibrant communities and critical infrastructure are constantly vulnerable to the seismic activity inherent in the region. Earthquakes, ranging from minor tremors to devastating quakes, can have profound and multifaceted impacts on the social fabric, economic well-being, and physical structures of the area. Understanding these impacts is crucial for effective preparedness and mitigation strategies.The effects of earthquakes in Southern California extend far beyond the immediate shaking.
The aftermath often brings forth a cascade of social, economic, and infrastructural challenges, demanding swift and well-coordinated responses from both individuals and governmental agencies.
Social Impact on Communities
Communities in Southern California, characterized by diverse demographics and interwoven social networks, experience profound emotional and social repercussions following an earthquake. The loss of life, injuries, and the disruption of daily routines create widespread anxiety and stress. Displacement from homes and businesses, coupled with the uncertainty of the future, can fracture social bonds and create long-term psychological trauma.
Immediate needs like shelter, food, and water become paramount, often straining existing resources and requiring extensive community support. Additionally, the potential for lasting impacts on mental health and well-being within affected populations should not be overlooked.
Economic Consequences
Earthquakes inflict significant economic damage on businesses and residents. Damage to homes and commercial properties results in substantial repair costs, potentially pushing individuals and businesses into financial hardship. Interrupted supply chains, business closures, and reduced consumer confidence can lead to a sharp decline in economic activity in the affected region. The ripple effect of these economic consequences can be felt across various sectors, from small local businesses to large corporations.
Recovery efforts also place a considerable financial burden on local, state, and federal governments.
Keeping tabs on earthquake activity in Southern California is crucial, especially when you consider the pricey real estate in the area. Luxury homes, like the many 2 million dollar homes california often found in quake-prone zones, require a thorough understanding of potential seismic risks. Fortunately, several excellent earthquake trackers provide real-time updates, ensuring residents are well-informed and prepared.
Effects on Transportation and Communication Networks
Transportation and communication networks are vital arteries for commerce and emergency response. Earthquakes can cause significant damage to roadways, bridges, railways, and airports, disrupting transportation and access to essential services. Communication networks, including cell phone towers, internet infrastructure, and landline systems, can be severely compromised or even destroyed, hindering emergency communication and information dissemination. These disruptions can hinder rescue efforts, impede the delivery of aid, and prolong the recovery process.
Examples of Infrastructure Damage
The 1994 Northridge earthquake, a significant event in Southern California’s seismic history, highlighted the vulnerability of infrastructure. The quake caused widespread damage to freeways, buildings, and utilities, leading to significant disruption and economic losses. Similarly, the 1987 Whittier Narrows earthquake demonstrated the potential for localized damage and the importance of seismic retrofits for buildings and critical infrastructure.
Comparison of Impacts Based on Earthquake Magnitude
The impact of an earthquake is directly correlated to its magnitude. Minor tremors, while causing some inconvenience, typically result in limited damage to infrastructure and minimal social disruption. Moderate earthquakes can cause significant damage to buildings and infrastructure, leading to localized economic and social disruptions. Major earthquakes, with their potent shaking and widespread destruction, inflict profound and lasting impacts on entire communities, disrupting transportation, communication, and economic activities.
Aftermath of the 1994 Northridge Earthquake
“The aftermath of the 1994 Northridge earthquake was a stark reminder of the vulnerability of Southern California’s infrastructure and the profound human cost of major seismic events. The region faced extensive damage to roads, bridges, buildings, and utilities, disrupting daily life and economic activity. The sheer scale of the destruction underscored the importance of preparedness and mitigation efforts to reduce future losses.”
Future Trends and Research
Earthquake prediction remains a significant challenge, but ongoing research offers glimpses into potential advancements. While precise prediction remains elusive, understanding seismic activity better allows for more effective preparedness and mitigation strategies. The study of past earthquakes, coupled with the development of new technologies, is crucial for improving our understanding and response to these powerful natural events.
Ongoing Research into Earthquake Prediction
Research into earthquake prediction methods employs various approaches, including the analysis of precursory phenomena like subtle ground deformation, changes in seismic wave patterns, and unusual gas emissions. These investigations aim to identify indicators that might precede an earthquake, enabling potential warnings. However, the reliability and consistency of these indicators are still under scrutiny. Current models often struggle to accurately predict the location, magnitude, and timing of earthquakes, limiting their practical application in real-time warnings.
Challenges and Limitations of Earthquake Forecasting
Predicting earthquakes faces significant challenges. The complex interplay of geological forces, the unpredictable nature of fault systems, and the limitations of current monitoring technologies create hurdles in accurate forecasting. Understanding the precise mechanisms driving earthquake rupture is still an active area of research. Moreover, the frequency of earthquakes and their varying magnitudes makes it difficult to establish reliable patterns for prediction.
Emerging Technologies in Earthquake Monitoring
Advanced technologies are transforming earthquake monitoring. Global positioning systems (GPS) allow for precise tracking of ground movement, providing valuable data on fault zone deformation. Seismometers, constantly refined and upgraded, offer enhanced detection capabilities, improving our ability to record and analyze seismic waves. Furthermore, developments in sensor networks and data analysis techniques provide a more comprehensive picture of seismic activity, enabling real-time monitoring and early detection of potential seismic events.
Importance of Continuous Research and Data Collection
Continuous research and data collection are essential for advancing earthquake science. This involves expanding the network of monitoring stations, employing new technologies, and analyzing vast datasets to identify patterns and trends. By continuously refining our understanding of earthquake mechanisms, we can improve our preparedness and mitigation efforts. This is crucial for safeguarding lives and minimizing the impact of earthquakes on communities.
Improving Infrastructure Resilience to Earthquakes
Earthquake-resistant infrastructure design is paramount. Building codes and construction practices must prioritize seismic safety, incorporating techniques that minimize structural damage during earthquakes. Retrofitting existing structures to enhance their resilience is also a critical strategy. Examples of effective approaches include strengthening foundations, using earthquake-resistant materials, and incorporating flexible design principles. This proactive approach minimizes the impact on communities during seismic events.
Timeline of Major Advancements in Earthquake Science
- 19th Century: Initial observations of earthquake patterns and development of rudimentary seismometers marked the beginning of formal earthquake studies. These early instruments allowed for the recording and analysis of seismic waves, a fundamental step in understanding earthquake mechanisms.
- Early 20th Century: The establishment of seismological observatories and networks worldwide significantly improved the collection and analysis of earthquake data, leading to a better understanding of earthquake distribution and frequency.
- Mid-20th Century: The development of more sophisticated seismometers, including those sensitive to smaller tremors, enabled scientists to study earthquake precursors and the complex dynamics of fault zones.
- Late 20th Century: The advent of GPS technology revolutionized earthquake monitoring by providing precise measurements of ground deformation, facilitating real-time monitoring of fault activity and the potential for future earthquakes.
- 21st Century: The use of sophisticated data analysis techniques and machine learning algorithms allows for advanced pattern recognition in seismic data, paving the way for early warning systems and enhanced prediction capabilities.
Closure: Earthquake Tracker Southern California
In conclusion, understanding earthquake tracker southern california is not just about knowing where and when quakes might occur, but also about proactively preparing for their potential impact. By examining historical data, evaluating current technologies, and emphasizing preparedness, we can better understand and mitigate the risks associated with seismic activity in this region. This knowledge is essential for both individual and community safety.
Quick FAQs
What are some common types of seismic monitoring tools?
Various tools are used, including seismographs, GPS networks, and accelerometers. These instruments detect and record ground motion, providing valuable data about earthquake characteristics.
How can I develop an earthquake preparedness plan?
Developing a plan involves assessing potential risks, creating a safety kit, practicing emergency procedures, and establishing communication strategies. Consider family needs and vulnerabilities.
What is the difference between earthquake magnitude and intensity?
Magnitude measures the energy released during an earthquake, while intensity describes the effects of the earthquake at a specific location. Magnitude is a single number, whereas intensity varies geographically.
Are there resources available for earthquake preparedness education?
Yes, numerous organizations and government agencies offer educational materials, workshops, and training programs. Local emergency management offices are often a great starting point.

