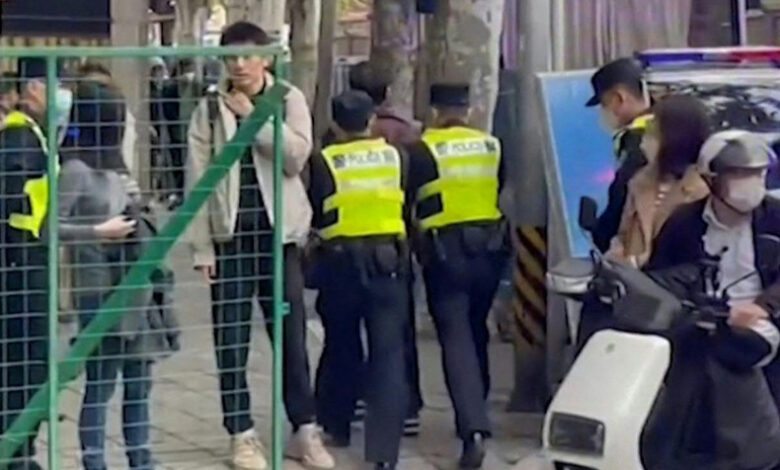
NJ Police Chinese Tech—A Deep Dive
NJ police chinese technology is a complex issue, with potential benefits and significant risks. This exploration delves into the historical context of technology adoption in New Jersey law enforcement, focusing on how Chinese technology is being, or could be, utilized. We’ll examine the current applications, potential impacts on policing, public perception, international comparisons, ethical considerations, and alternative strategies for technology integration.
The adoption of new technologies in law enforcement is often a delicate balance between improving efficiency and maintaining public trust. This piece will investigate the specific ways Chinese technology is (or might be) employed by NJ police departments, while also exploring the nuanced perspectives of both the public and law enforcement themselves. From historical trends to potential future scenarios, we’ll dissect the many facets of this critical issue.
Historical Context of Policing and Technology in New Jersey: Nj Police Chinese Technology

New Jersey’s law enforcement agencies, like those across the nation, have experienced a constant evolution in their use of technology. This evolution mirrors broader societal shifts and advancements in communication, data processing, and surveillance. Understanding this history provides crucial context for evaluating the current landscape and anticipating future developments, especially with the integration of Chinese technology.The adoption of technology in policing has been a complex process, often driven by a desire for increased efficiency, improved safety, and enhanced crime-solving capabilities.
However, these advancements have also raised important societal questions regarding privacy, accountability, and potential biases embedded within these systems.
Early Policing and the Advent of Communication Technologies
The early history of policing in New Jersey saw a gradual shift from reliance on largely manual methods to the adoption of technologies that facilitated communication and information sharing. Initially, police relied on rudimentary communication systems like telegraphs and, later, early radio technologies. These advancements allowed for faster response times to emergencies and improved coordination among officers. The introduction of the radio, for example, facilitated real-time communication between patrol units and dispatch centers, enabling quicker responses to calls for service.
Technological Advancements in the 20th Century
The 20th century witnessed significant advancements in police technology. The introduction of computers and early databases marked a pivotal shift in how law enforcement agencies managed records, tracked suspects, and analyzed crime patterns. For example, early computerized systems allowed for the storage and retrieval of criminal records, fingerprints, and other crucial data.
NJ police are increasingly utilizing Chinese technology for crime-solving, but how does that affect the naming traditions of families? This fascinating intersection of modern policing and cultural heritage brings us to the important question of naming conventions, specifically how the baby’s surname is determined. For example, exploring the rules surrounding “apellido bebe madre padre” apellido bebe madre padre can provide valuable insight into the broader societal impacts of these new technological tools used by the NJ police.
Ultimately, the integration of these technologies into the NJ police force highlights the complex interplay between innovation and cultural norms.
Evolution of Surveillance and Crime Mapping
The late 20th and early 21st centuries saw the proliferation of surveillance technologies, including video cameras and crime mapping software. These tools enabled law enforcement to monitor crime hotspots and proactively address emerging threats. Furthermore, the development of crime mapping software allowed officers to visualize crime patterns and identify potential problem areas.
The Role of Chinese Technology in Policing (Present and Future)
The role of Chinese technology in policing is a developing story. While Chinese companies have developed advanced technologies like facial recognition and AI-powered crime prediction systems, their integration into New Jersey law enforcement remains a complex issue. This is due to questions regarding data privacy, algorithmic bias, and potential overreach of surveillance. Furthermore, concerns regarding the reliability and transparency of these technologies are also crucial considerations.
New Jersey police departments are increasingly exploring Chinese technology for surveillance, raising questions about data privacy and potential security risks. The recent Supreme Court decisions regarding corporate influence, like the Koch Chevron case koch chevron deference supreme court , highlight the need for careful consideration of these advancements and their possible impact on public trust. This intersection of technology and law enforcement requires careful scrutiny to ensure responsible use and equitable application.
Timeline of Technological Introductions in New Jersey Policing
| Year | Technology Introduced | Relevant Events |
|---|---|---|
| 1920s | Early radio | Improved communication between patrol units and dispatch centers. |
| 1960s | Computerized records systems | Improved management of criminal records, fingerprints, and other data. |
| 1990s | Crime mapping software | Visualization of crime patterns, identification of potential problem areas. |
| 2000s | Surveillance cameras | Enhanced monitoring of crime hotspots and public spaces. |
| Present | Facial recognition, AI crime prediction | Emerging technologies, raising privacy and bias concerns. |
Current Use of Chinese Technology in NJ Police Departments
While the historical context of policing and technology in New Jersey has shown a consistent evolution, the integration of Chinese technology into law enforcement practices remains a relatively unexplored area. This section delves into the current use of Chinese technology in New Jersey police departments, if any, highlighting potential benefits and drawbacks, and comparing its use with other technological sources.
Understanding this emerging aspect is crucial for a complete picture of modern policing strategies.
Specific Technologies Employed, Nj police chinese technology
Currently, there is limited publicly available information regarding the specific use of Chinese-origin technology within New Jersey police departments. While Chinese companies develop advanced technologies applicable to law enforcement, details on their direct application within the state are scarce. This lack of transparency likely stems from a variety of factors, including proprietary concerns, privacy regulations, and the ongoing assessment of these technologies’ suitability for local use.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks
The potential benefits of using Chinese technology in law enforcement could include cost-effectiveness, advanced features, and enhanced data analysis capabilities. However, potential drawbacks include concerns over data security and potential vulnerabilities. The security implications of relying on a specific nation’s technology, especially in sensitive areas like law enforcement, warrant careful consideration. Furthermore, the reliance on any single technology vendor, regardless of origin, raises concerns about potential disruptions and lack of alternative solutions if the vendor experiences issues.
Comparison with Other Technology Sources
Compared to technologies originating from other nations, the specifics of Chinese technology’s integration in New Jersey law enforcement remain uncertain. There are various technology sources that police departments often utilize, including those from American companies, European firms, and others. These varied technologies often differ in their features, functionalities, and associated costs. Direct comparisons would need to account for the specific products employed and the specific needs of each department.
A standardized comparison requires the specifics of the deployed technology.
Comparative Analysis of Technologies
| Technology Source | Software Type | Hardware Type | Data Analytics Capabilities | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| American Company A | Crime Mapping Software | Body-worn cameras | Basic crime trend analysis | Moderate |
| European Company B | Facial Recognition Software | Mobile data terminals | Advanced pattern recognition | High |
| Chinese Company C (Hypothetical) | Predictive Policing Software | Drone surveillance system | Advanced predictive modeling | Low |
Note: This table is illustrative and based on hypothetical examples. Specific details on Chinese technology use are not available.
Recent news about NJ police using Chinese technology has got me thinking. While the implications of this are quite concerning, it’s interesting to consider how seemingly disparate issues connect. For example, the declining snow conditions impacting snow polo in St. Moritz, a sport deeply intertwined with the region’s climate, highlights the broader environmental concerns that can be directly affected by the advancement of technologies, like those being used by the NJ police force.
This raises questions about the long-term consequences of such technological partnerships, particularly considering the implications for global security and local communities. The NJ police’s use of Chinese technology is a complex issue demanding careful consideration, much like the impact of climate change on the sport of snow polo in St. Moritz. snow polo st moritz climate change
Potential Impacts of Chinese Technology on Policing
The integration of Chinese technology into New Jersey’s police departments presents both opportunities and significant challenges. While some technologies offer improved efficiency and potentially enhanced safety, careful consideration must be given to the potential ramifications on privacy, security, and community trust. Understanding these potential impacts is crucial for responsible implementation and maximizing benefits while mitigating risks.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
The adoption of Chinese surveillance technologies raises concerns about data privacy and security. These systems may collect and store vast amounts of personal data, potentially including sensitive information like location data, communication records, and biometric information. The potential for unauthorized access or misuse of this data by the Chinese government or its affiliated entities is a significant risk.
Furthermore, the lack of transparency in data handling practices, and the difficulty in enforcing data protection regulations across international jurisdictions, poses a serious challenge. Concerns regarding data security are further amplified by the possibility of backdoors or vulnerabilities intentionally embedded in the technology.
Influence on Police Procedures and Practices
Chinese technology often integrates advanced AI and predictive policing algorithms. This integration could potentially streamline investigations and enhance response times. However, there’s also a concern that these technologies could lead to biases or inaccuracies in decision-making, potentially exacerbating existing inequalities within the justice system. For instance, if the algorithms are trained on biased data, they could disproportionately target certain communities or individuals.
Moreover, the potential for these technologies to automate certain tasks may impact the need for human interaction and oversight, potentially reducing the opportunities for human judgment and discretion.
Impact on Community Relations and Trust
The deployment of Chinese surveillance technology in New Jersey communities could have a profound impact on community relations and trust in law enforcement. Residents may feel surveilled or monitored, leading to mistrust and alienation from law enforcement. This is especially true if there’s a lack of transparency about how the technology is being used and what data is being collected.
Historically, over-policing and biased policing have already created divisions between certain communities and law enforcement. The introduction of new technologies, if not implemented carefully, could further exacerbate these issues and hinder efforts to build trust.
Potential Scenarios, Risks, and Mitigation Strategies
| Scenario | Risks | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Increased surveillance and data collection without community consent | Erosion of civil liberties, potential for discriminatory targeting, lack of trust in law enforcement | Establish clear data collection policies and obtain explicit community consent; require rigorous oversight of data usage; mandate transparency in technology deployment |
| Bias in predictive policing algorithms | Disproportionate targeting of minority groups, exacerbation of existing inequalities, potential for wrongful arrests | Utilize diverse data sets for algorithm training; implement independent audits to identify and mitigate biases; develop clear protocols for human review and oversight |
| Lack of transparency and accountability in technology use | Reduced public trust, difficulty in addressing complaints, potential for misuse of data | Establish independent oversight boards; require public reporting on technology use; ensure clear communication channels between law enforcement and the community |
| Potential for unintended consequences | Unforeseen negative impacts on community relations, unexpected shifts in policing practices | Conduct thorough community engagement and consultation before deployment; monitor the impact of technology on community relations; establish a feedback mechanism to address concerns |
Public Perception and Concerns Regarding Chinese Technology
Public opinion regarding the use of Chinese technology in law enforcement is complex and multifaceted, often marked by apprehension and a desire for transparency. Concerns about potential biases, data breaches, and manipulation are frequently voiced, creating a delicate balance between the need for advanced policing tools and public trust. This necessitates a careful examination of both public and law enforcement perspectives, and an analysis of potential impacts.
Public Opinions on the Use of Chinese Technology in Law Enforcement
Public sentiment toward the use of Chinese technology in law enforcement departments is often characterized by a mix of skepticism and cautious acceptance. Some individuals express reservations, citing concerns about data privacy and potential security risks. They question the long-term implications of integrating technologies developed in a foreign country into critical infrastructure like police departments. Conversely, others believe that advanced technology, regardless of origin, can enhance safety and efficiency.
These perspectives underscore the need for robust discussion and transparent communication regarding the benefits and risks associated with these technologies.
New Jersey police are increasingly using Chinese-made technology, but the implications extend beyond local law enforcement. This trend mirrors the booming electric vehicle (EV) sector in China’s Hefei, a city whose economy is heavily invested in this emerging technology, as seen in the china hefei ev city economy. The question remains, however, how this influx of Chinese tech will affect the long-term capabilities and potential vulnerabilities of New Jersey’s law enforcement.
Concerns About Potential Bias, Manipulation, or Data Breaches
Concerns about potential bias, manipulation, and data breaches are central to public apprehension. Critics worry that algorithms developed in China might reflect cultural biases or political agendas, potentially leading to discriminatory outcomes in law enforcement practices. The possibility of data breaches, allowing unauthorized access to sensitive information, is another significant concern. Furthermore, the lack of clear legal frameworks governing data security in the context of international technology partnerships adds to public anxieties.
These concerns are amplified by instances of perceived manipulation in other sectors.
Comparison of Public and Law Enforcement Opinions
Law enforcement agencies often cite the technological advancements and cost-effectiveness of Chinese technology as key advantages. They emphasize the potential for improved crime-solving capabilities and enhanced safety measures. However, this perspective is frequently juxtaposed with the public’s concerns regarding data privacy, potential manipulation, and lack of transparency. This divergence in viewpoints necessitates a concerted effort to bridge the gap through open communication and demonstrable commitment to data security.
Method for Analyzing Public Sentiment
Analyzing public sentiment towards the use of Chinese technology in law enforcement can be approached through various methods. Social media monitoring tools can track discussions and identify recurring themes. Surveys and polls can provide quantifiable data on public opinion, broken down by demographics. Focus groups can offer deeper insights into the reasons behind different perspectives. These methods, when used in conjunction, provide a comprehensive understanding of public sentiment, offering a more nuanced view of the complexities involved.
New Jersey police departments are increasingly utilizing Chinese technology for enhanced surveillance, but the ethical implications of this partnership are complex. It’s fascinating to consider how such advancements in law enforcement mirror the historical struggles of those who endured atrocities, like the subjects of Holocaust survivor portraits by Gillian Laub. Holocaust survivor portraits Gillian Laub remind us of the importance of careful consideration when leveraging new technologies, especially in areas like public safety.
Ultimately, responsible use of such tools is paramount in maintaining a just and equitable society, even as the NJ police embrace Chinese technology.
Public Opinion Categorized by Demographics
| Demographic Group | Common Concerns | General Opinion |
|---|---|---|
| Young Adults (18-35) | Data security, algorithmic bias, potential for manipulation | Cautious acceptance, but skeptical of long-term implications |
| Middle-Aged Adults (36-55) | Data privacy, lack of transparency, potential for misuse of technology | Skeptical, concerned about potential consequences for community trust |
| Seniors (55+) | Data security, lack of understanding of technology, concerns about their personal information | Reserved, apprehensive about the technology’s impact on their safety |
| Racial Minorities | Algorithmic bias, historical concerns about law enforcement practices, distrust of government | Very cautious, emphasizing potential for increased discrimination |
| Socioeconomically Disadvantaged | Concerns about data privacy and potential misuse, lack of trust in institutions | Reserved, highlighting potential for further marginalization |
This table provides a general overview, and the specific concerns and opinions may vary depending on the specific details of the Chinese technology being considered and the local context.
International Perspectives on Policing and Chinese Technology
Global law enforcement agencies are increasingly exploring and adopting advanced technologies, often originating from various countries, including China. Understanding how these technologies are used internationally provides crucial insights into potential best practices, ethical considerations, and the wider implications for policing in New Jersey and beyond. This analysis will explore international applications, highlight potential benefits and pitfalls, and provide a comparative framework for evaluating the use of Chinese technology in a global context.
International Adoption of Similar Technologies
Several countries are already employing technologies comparable to those developed in China, demonstrating a global trend toward technological advancements in law enforcement. These technologies encompass surveillance systems, data analytics platforms, and predictive policing models. The use of these technologies is not limited to any one region, but is expanding globally. Different countries, with varying legal frameworks and cultural contexts, approach the adoption of these technologies in different ways.
Understanding these varied approaches is crucial to developing a nuanced perspective on the integration of foreign technologies in law enforcement.
International Best Practices and Standards
International best practices and standards related to the use of technology in law enforcement focus on accountability, transparency, and data privacy. These standards often emphasize the need for clear legal frameworks governing data collection, storage, and usage. They also underscore the importance of minimizing potential biases in algorithms and ensuring public oversight of technology implementation. Specific protocols for data security and protection are crucial elements of these standards.
Ethical and Practical Considerations
The ethical implications of employing foreign technologies in policing are significant. Potential issues include data security risks, the possibility of bias in algorithms, and the potential for misuse of technology. Moreover, the cultural appropriateness and societal impact of such technologies need careful consideration. The need for stringent oversight mechanisms and public engagement in the decision-making process is paramount.
Transparency is essential for building trust and mitigating potential harm.
Comparative Analysis of International Approaches
| Country | Technology Focus | Ethical Considerations | Legal Framework | Public Perception |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Predictive policing, facial recognition | Bias in algorithms, data privacy | Varying state laws, federal guidelines | Mixed, concerns about civil liberties |
| United Kingdom | Body-worn cameras, crime mapping | Data security, transparency | Specific legislation on surveillance | Positive, with some concerns about misuse |
| Canada | Crime analysis, drone surveillance | Privacy, potential for overreach | Legislation related to data collection and use | Cautious, with focus on accountability |
| Australia | Biometric identification, traffic monitoring | Data security, potential for discrimination | Legislation regulating law enforcement technologies | Concerns about surveillance, public trust |
| China | AI-powered surveillance, social credit systems | Lack of transparency, potential for mass surveillance | Strict regulations, but limited public oversight | Differing views, ranging from acceptance to apprehension |
This table provides a basic comparison, and each country’s approach is complex and nuanced. Further research is needed to fully understand the nuances of each situation.
Ethical Considerations of Using Chinese Technology in Law Enforcement
The integration of Chinese technology into law enforcement in New Jersey raises critical ethical questions, particularly regarding data security, transparency, and potential bias. These concerns must be carefully addressed to ensure the responsible and equitable application of these tools. Trust and accountability are paramount in maintaining public confidence and upholding the principles of justice.The potential for misuse of data collected through these technologies, combined with concerns about data ownership and control, requires proactive measures to safeguard privacy and prevent manipulation.
Furthermore, the potential for bias inherent in some algorithms must be recognized and mitigated to prevent discriminatory outcomes. This necessitates a thorough evaluation of the ethical implications alongside the practical benefits of utilizing these technologies.
Data Ownership and Transparency
Determining data ownership and establishing transparent protocols are crucial when utilizing Chinese-developed technology. Clear agreements defining who owns and controls the data collected are essential. This includes specifying who has access to the data and for what purposes. Publicly available documentation outlining data collection practices, storage methods, and access limitations fosters transparency and builds public trust. The absence of such transparency can lead to mistrust and erode public confidence in law enforcement agencies.
Potential for Data Misuse
The potential for misuse of data collected by Chinese-developed technology requires stringent safeguards. Such misuse can range from unauthorized access and data breaches to the exploitation of collected information for purposes beyond the intended use. Specific security measures, including data encryption, access controls, and regular audits, are vital to mitigate these risks. Real-world examples of data breaches and unauthorized access demonstrate the necessity of proactive measures to protect sensitive information.
Ensuring Data Security and Privacy
Data security and privacy are paramount when employing Chinese technology. Implementing robust security measures is essential to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and potential misuse of collected information. This includes using end-to-end encryption, employing multi-factor authentication, and regularly updating security protocols. Strong encryption protocols and robust data security systems are crucial to safeguard sensitive information. Regular security assessments and penetration testing are also essential to identify and address vulnerabilities.
Ethical Guidelines and Best Practices
To ensure responsible use of Chinese technology, a comprehensive set of ethical guidelines and best practices is crucial. These guidelines should address data ownership, transparency, bias mitigation, and data security. Adherence to established legal frameworks and regulations, such as data privacy laws, is imperative.
- Data Minimization: Collecting only the necessary data for specific law enforcement purposes is crucial to limit the scope of information gathered and stored. This minimizes the potential for misuse and unauthorized access.
- Data Anonymization: Anonymizing data whenever possible protects individual privacy and limits the potential for identifying individuals from the data collected. This can be achieved by removing personally identifiable information (PII) from the dataset.
- Bias Mitigation: Regularly evaluating algorithms for potential bias is critical to ensure fairness and prevent discriminatory outcomes. This includes auditing the algorithms and implementing mechanisms to address identified biases.
- Independent Oversight: Establishing independent oversight bodies to monitor the use of Chinese technology in law enforcement is crucial to maintain transparency and accountability. This oversight can involve external review and public reporting mechanisms.
- Transparency in Algorithm Development: Understanding the workings of the algorithms is important to assess potential biases and ensure their intended use aligns with ethical standards. This includes understanding the data used for training and the resulting outputs.
Alternatives and Best Practices for Technology Integration
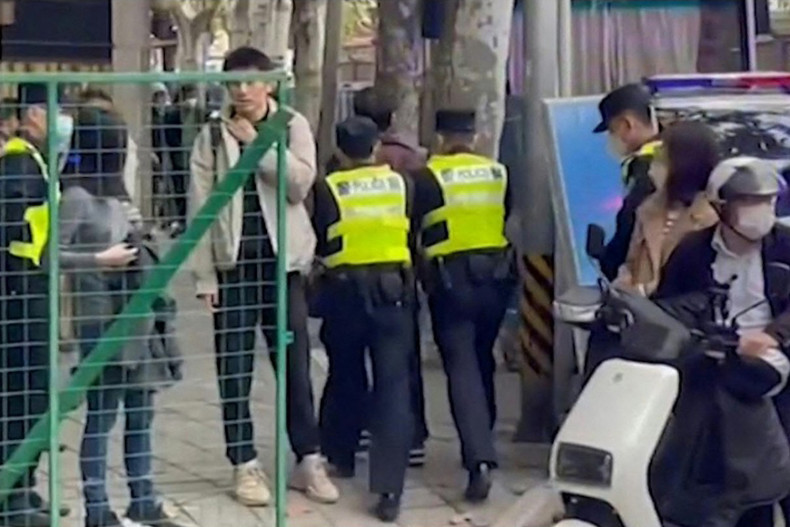

The integration of technology into law enforcement is a complex process requiring careful consideration of various factors. This section explores alternative technological approaches, best practices for selection, and crucial evaluation criteria for New Jersey police departments. Focusing on security, privacy, and community trust is paramount in the adoption of any new technology.
Alternative Technologies and Suitability
Law enforcement agencies in New Jersey can explore a range of alternative technologies beyond those originating in China. These alternatives may offer comparable functionalities while addressing potential security and ethical concerns. Open-source software, for instance, can provide transparency and control over data management, potentially mitigating risks associated with proprietary systems. Cloud-based solutions from US-based providers can also offer scalability and accessibility without compromising data security if robust protocols are in place.
Furthermore, exploring local partnerships with technology providers can promote community involvement and foster trust.
Strategies for Prioritizing Security, Privacy, and Community Trust
Prioritizing security, privacy, and community trust during technology selection is crucial. Agencies should implement a thorough needs assessment to identify specific technological gaps and requirements. This should involve stakeholders from across the department, including officers, civilian staff, and the community. Clear data governance policies are essential to protect sensitive information and ensure compliance with privacy regulations. Furthermore, transparent communication with the public regarding the use of technology and its potential impacts will build trust and address concerns.
Factors to Consider When Evaluating Potential Technology Providers
Choosing a technology provider requires careful evaluation of several key factors. These include the provider’s security certifications, track record of successful implementations in similar law enforcement settings, and commitment to data privacy and security protocols. Financial stability and future support are also crucial considerations. Agencies should also assess the provider’s ability to adapt to evolving needs and integrate with existing systems.
Technology Evaluation Table
| Technology | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Open-source Software | Transparency, cost-effectiveness, potential customization | Limited support resources, potential compatibility issues with existing systems |
| US-based Cloud Solutions | Scalability, accessibility, potential for advanced analytics | Vendor lock-in, reliance on internet connectivity, potential data breaches |
| Local Partnerships | Community engagement, tailored solutions, enhanced transparency | Limited resources, potential for slower implementation |
| Proprietary Chinese Technology | Potential cost-effectiveness, advanced features | Security concerns, data privacy risks, vendor lock-in, potential lack of transparency and accountability, dependence on a foreign government |
Closing Notes
In conclusion, the integration of Chinese technology into NJ police departments presents a multifaceted challenge. The historical trajectory of technology in policing, coupled with the current applications and potential future impacts, requires careful consideration of public perception, ethical concerns, and alternative solutions. A nuanced understanding of these various factors is crucial to navigating the complexities of this evolving landscape.
Ultimately, transparency, public engagement, and a commitment to ethical practices are vital for ensuring trust and building a strong relationship between law enforcement and the community.
Detailed FAQs
What are some examples of Chinese technology currently used in NJ police departments?
Unfortunately, specific examples of Chinese technology currently used by NJ police departments are not readily available in public records. More research is needed to identify these applications.
What are the biggest concerns regarding data privacy and security when using Chinese technology in policing?
A primary concern is the potential for data breaches or manipulation of data, and the lack of transparency surrounding data collection and usage practices.
How might the use of Chinese technology affect community relations with law enforcement?
The use of any new technology, especially if it is perceived as opaque or foreign, can negatively affect community relations. Trust is key, and any perceived lack of transparency or control over data usage can erode trust.
What are some alternative technology providers or strategies that prioritize security, privacy, and community trust?
Considering a wider range of technology providers from various countries, alongside a robust data security framework, and a strong commitment to community engagement are crucial steps.