Trumps Second-Term Tariff Agenda Impact Analysis
Trump’s Second-Term Tariff Agenda: How Will New Tariffs Impact? This in-depth look examines the policies enacted during Trump’s second term, exploring their rationale, impact on various sectors, and global responses. We’ll delve into the effects on industries like automotive, agriculture, and technology, alongside the domestic economic repercussions and potential alternatives. The analysis also considers the mechanisms of tariff implementation, potential legal challenges, and the broader implications for international trade relations.
The agenda, aiming to reshape international trade, presented a complex web of economic consequences. This examination explores the specifics of the tariffs, including the goods targeted, the countries affected, and the procedures for dispute resolution. Understanding the interplay between domestic and global impacts is crucial to grasping the full scope of this trade policy.
Introduction to Trump’s Second-Term Tariff Agenda
Donald Trump’s second-term trade policies were largely characterized by a continuation of his “America First” approach, emphasizing protectionist measures. This involved the imposition of tariffs on various imported goods, primarily from China and other countries, aiming to reduce trade imbalances and bolster American industries. The stated goals were to protect domestic jobs and industries, renegotiate existing trade deals, and bring manufacturing back to the United States.
The effectiveness and consequences of these tariffs remain a subject of considerable debate.The rationale behind these policies varied. Supporters argued that tariffs would protect American jobs, encourage domestic production, and reduce the trade deficit. Critics, conversely, contended that tariffs would harm American consumers through higher prices, disrupt global supply chains, and invite retaliatory measures from other countries, potentially leading to trade wars.
This policy contrasted with the historical context of US trade relations, where previous administrations had generally favored free trade agreements.
Historical Context of Tariffs in the US
US tariff policy has a long and complex history, fluctuating between protectionist and free trade approaches. The Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act of the 1930s, for example, is often cited as a negative example of protectionism, contributing to the Great Depression by escalating trade tensions. Conversely, the post-World War II era saw the rise of free trade agreements and organizations like the WTO, aiming to reduce trade barriers globally.
This historical backdrop provides a framework for understanding the context of Trump’s second-term tariffs.
Types of Goods Targeted by Tariffs
The tariffs implemented during Trump’s second term targeted a wide range of imported goods, including consumer products, industrial components, and agricultural products. This diverse range aimed to address various sectors of the economy, reflecting the administration’s broad approach to trade protection. The rationale behind targeting specific goods often revolved around perceived unfair trade practices or the need to support specific domestic industries.
Key Tariffs Imposed
The following table summarizes some key tariffs imposed during Trump’s second term, highlighting the countries affected and the product categories targeted. The table is not exhaustive and does not include every tariff imposed.
| Country | Product Category | Tariff Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| China | Technology (e.g., smartphones, computers) | 15-25 |
| China | Steel and Aluminum | 25% |
| Mexico | Agricultural products (e.g., avocados) | 5-25 |
| Canada | Certain goods | Various |
| European Union | Steel and Aluminum | 25% |
Impact on Specific Industries
Trump’s second-term tariff agenda, while aiming to bolster domestic industries, presented significant uncertainties for various sectors. The potential impacts ranged from supply chain disruptions to shifts in consumer behavior, with the degree of effect varying widely based on industry-specific factors and the responsiveness of global markets. The consequences of these tariffs extended beyond the immediate economic effects, impacting international relations and potentially leading to retaliatory measures from other nations.
Automotive Industry
The automotive sector faced a complex interplay of factors due to tariffs. Increased costs for imported components could have led to higher prices for vehicles, potentially impacting consumer demand and the competitiveness of domestic manufacturers. Foreign automakers with significant manufacturing presence in the US, like Toyota and Honda, might have shifted production to avoid tariffs, potentially impacting employment in the US.
Furthermore, retaliatory tariffs from other countries could have reduced export opportunities for American-made vehicles.
Trump’s second-term tariff agenda is certainly interesting, but ultimately, its impact on the economy hinges on a few key factors. Just like achieving optimal weight loss requires a balanced approach, effective tariff strategies need a multifaceted perspective. For example, exploring strategies like Diet and exercise for the most effective weight loss results can offer valuable insights for navigating complex economic situations.
Ultimately, the success of these tariffs will depend on how they’re implemented and whether they create more opportunities than restrictions.
Agricultural Sector
Tariffs on agricultural exports, including soybeans and other crops, significantly impacted farmers and agricultural industries. For example, the imposition of tariffs on soybean exports to China resulted in substantial losses for American farmers who had established trade relationships with China. Similar impacts could have been seen in other agricultural sectors like livestock and processed foods. The tariffs caused uncertainty and economic hardship in specific regions heavily reliant on agricultural exports.
Technology Sector
The technology sector, a vital part of the US economy, was also potentially affected. Tariffs on imported components and finished goods could have increased the costs of technology products, affecting both consumers and domestic technology companies. Foreign technology companies operating in the US might have faced increased costs, which could have affected their profitability and competitiveness. The impact would have been substantial for both domestic and foreign companies, leading to a domino effect throughout the supply chain.
Manufacturing Sector
The manufacturing sector, a cornerstone of the US economy, felt the ripple effects of tariffs. Tariffs on imported raw materials and components could have increased production costs for many manufacturers. Specific examples include companies that rely heavily on imported steel or aluminum. These increased costs could have impacted their profitability and competitiveness in the global market. The manufacturing sector was susceptible to both direct and indirect effects of tariffs.
Global Economic Responses
Trump’s second-term tariffs sparked a significant global response, with many countries retaliating against the US measures. These retaliatory actions and the broader impact on global trade relations highlight the complex interplay of economic interests and political considerations in international trade. The resulting effects on supply chains and investment flows further underscore the potential consequences of protectionist trade policies.The reactions to the tariffs were varied and often intertwined with existing geopolitical tensions.
Some countries viewed the tariffs as protectionist measures aimed at harming their economies, while others saw them as an opportunity to strengthen their own industries. This multifaceted response illustrates the challenges of navigating international trade relations in an era of increasing economic nationalism.
Trump’s second-term tariff agenda is definitely a hot topic right now, but understanding the potential ripple effects on the economy can be complex. One key factor to consider is how these tariffs might impact the value of different cryptocurrencies. For example, knowing how tokenomics affect cryptocurrencies, as explained in this great resource on Why Understanding Tokenomics Can Increase Your Crypto Gains , could help predict how certain digital assets might react to trade disputes.
Ultimately, navigating these economic shifts requires careful analysis and a deep understanding of the underlying mechanisms, both for the crypto world and the broader economic landscape, so tariffs don’t unexpectedly affect investments.
Reactions of Other Countries
Numerous countries responded to the tariffs with retaliatory measures, impacting US exports and creating trade disputes. These responses often involved imposing tariffs on US goods, impacting sectors like agriculture, manufacturing, and technology.
Retaliatory Measures by Other Nations
Many countries implemented tariffs on US goods in response to the tariffs imposed by the US. Canada, Mexico, China, and the European Union were among the most prominent nations imposing tariffs on American goods in retaliation. These retaliatory tariffs targeted specific sectors, such as agricultural products, steel, and aluminum, disrupting supply chains and affecting businesses.
Effects on Global Trade Relations
The tariffs significantly strained global trade relations, leading to increased uncertainty and unpredictability in the international market. The retaliatory measures created a climate of mistrust and eroded the foundations of a rules-based global trading system. This resulted in a decrease in overall trade volume as businesses avoided uncertainty and sought alternative supply sources.
Implications for International Supply Chains
The tariffs disrupted established international supply chains, forcing companies to re-evaluate their production strategies and sourcing patterns. This disruption increased costs and reduced efficiency, leading to higher prices for consumers and potentially impacting the profitability of businesses. Companies had to adjust to new trade barriers, potentially shifting production to countries with more favorable trade agreements.
Effects on International Investment
International investment was negatively affected by the trade disputes. Uncertainty surrounding trade policies discouraged foreign investment in the US and potentially in other countries. Companies were hesitant to invest in countries with volatile trade policies, impacting long-term economic growth prospects. Investment shifted to regions with more predictable and stable trade agreements.
Domestic Economic Impacts
Trump’s second-term tariff agenda, while aiming to bolster American industries, carries significant potential ramifications for the domestic economy. The interplay of tariffs on imported goods, shifts in supply chains, and consumer responses will shape consumer prices, employment levels, and overall economic growth. Understanding these impacts is crucial for evaluating the potential long-term consequences of such policies.
Consumer Price Effects
Tariffs typically lead to higher consumer prices. Imported goods, subject to tariffs, become more expensive. This increased cost is often passed on to consumers, potentially reducing purchasing power and affecting overall inflation. The extent of the price increase depends on the elasticity of demand for the affected goods, the ability of domestic producers to increase supply, and the responsiveness of businesses to the tariff.
For example, tariffs on steel imports could increase the cost of construction materials, leading to higher prices for homes and other building projects.
Employment Impacts Across Sectors
The impact on employment is complex and multifaceted. Tariffs may protect certain domestic industries, leading to job growth in those sectors. However, they also increase the cost of imported inputs for other industries, potentially reducing their competitiveness and leading to job losses. For instance, if tariffs on imported electronics components increase the cost of producing smartphones, domestic manufacturers may face reduced profitability and be forced to cut jobs.
Potential Effects on GDP Growth
Tariffs can affect GDP growth in various ways. By increasing the cost of imported goods, tariffs can reduce consumer spending and business investment. This can negatively impact aggregate demand and economic output. Conversely, some argue that tariffs can stimulate domestic production and employment, potentially boosting GDP in the short term. The overall impact on GDP growth is likely to be mixed and highly dependent on the specific tariffs imposed, the industries affected, and the broader economic environment.
Inflation and Economic Stability
Tariffs often contribute to inflation by raising the prices of imported goods. This increased cost can lead to a ripple effect, pushing up prices across the economy and potentially destabilizing economic stability. The extent to which tariffs impact inflation will depend on factors like the magnitude of the tariffs, the responsiveness of domestic producers, and the overall economic climate.
Balance of Trade Implications
Tariffs can impact the balance of trade in several ways. By making imports more expensive, tariffs aim to reduce imports and increase exports. However, the effectiveness of tariffs in altering the balance of trade is subject to various economic factors, including retaliation from trading partners and the responsiveness of international markets. For example, if other countries retaliate with tariffs on American exports, the overall balance of trade could shift negatively.
Tariff Administration and Enforcement
The implementation and enforcement of tariffs are crucial components of any trade policy. Effective mechanisms are essential for ensuring compliance and preventing disputes. This section details the processes involved in administering and enforcing tariffs enacted under the Trump administration’s second-term agenda.The administration of tariffs involves a complex interplay of various government agencies. From initial classification and valuation to dispute resolution, the process spans multiple departments, each with specific responsibilities.
A thorough understanding of these procedures is critical for businesses engaged in international trade.
Mechanisms for Implementing Tariffs
The U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) agency plays a central role in implementing tariffs. CBP officers inspect imported goods at ports of entry, verifying compliance with tariff regulations. The agency uses a combination of automated systems and manual reviews to assess duties. Automated systems analyze import declarations for compliance with tariff schedules, while manual reviews are conducted for complex cases or those involving suspected violations.
These processes ensure the accurate calculation and collection of tariffs.
Role of Relevant Government Agencies
The enforcement of tariffs is not solely the responsibility of CBP. The U.S. Department of Commerce (DOC) is involved in the classification of goods, determining the appropriate tariff rates. The Office of the United States Trade Representative (USTR) plays a role in negotiating trade agreements and monitoring compliance, sometimes influencing the application of tariffs. The Treasury Department, specifically the Bureau of Customs and Border Protection, is also involved in collecting tariffs and managing related finances.
This inter-agency collaboration is vital for efficient tariff administration.
Procedures for Filing Appeals or Disputes
A structured process exists for resolving disputes arising from tariff application. The importer or exporter has avenues to challenge tariff decisions. These procedures include:
- Filing a protest with the CBP within a specified timeframe, detailing the grounds for the challenge. This is a critical initial step in the process.
- Seeking administrative review by the CBP. The agency evaluates the protest and makes a decision.
- If dissatisfied with the administrative decision, the parties can appeal to the U.S. Court of International Trade. This judicial process allows for a further review of the case.
Potential Legal Challenges to Tariffs
Tariffs are subject to legal challenges based on various grounds. These include claims of violation of international trade agreements, constitutional challenges, and arguments regarding the proper classification of goods. The legal landscape surrounding tariffs is complex, with precedents and case law that shape the interpretation and application of tariff regulations. The outcome of these legal battles can significantly impact the effectiveness of the tariff policy.
Trump’s second-term tariff agenda is definitely a hot topic right now, and figuring out how new tariffs will impact businesses is crucial. It’s a complex issue, but understanding the potential ripple effects is key. Interestingly, this sort of economic analysis can sometimes be surprisingly similar to understanding the utility of crypto tokens, as explored in this insightful guide: The Ultimate Guide to Understanding Crypto Token Utility.
Ultimately, whether it’s tariffs or tokens, forecasting the real-world consequences takes a deep dive into market forces and underlying motivations. So, let’s get into the details of how these tariffs might reshape the economic landscape.
Administrative Process Overview
The administrative process for implementing and enforcing tariffs involves several distinct stages:
- Tariff Classification: The initial step is determining the appropriate tariff classification for imported goods based on the Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS). This is crucial for accurate duty calculation.
- Valuation: The value of the imported goods is assessed, which directly impacts the amount of duty owed. Valuation methods can range from transaction value to comparable-uncontrolled prices, based on the specific product and circumstances.
- Duty Assessment and Collection: CBP calculates the final duty amount owed. The importer pays the assessed duty. Failure to comply can result in penalties.
- Dispute Resolution: As mentioned above, importers or exporters have recourse to administrative and judicial procedures to resolve disputes arising from tariff application.
Potential Alternatives and Policy Implications: Trump’s Second-Term Tariff Agenda: How Will New Tariffs Impact
Trump’s second-term tariff agenda, while aiming to bolster American industries, presented significant economic complexities. Analyzing alternative trade policies reveals a spectrum of approaches that could have yielded different outcomes, ranging from comprehensive trade agreements to targeted interventions. Examining the long-term consequences of these tariffs and potential improvements offers valuable insights for future trade negotiations.Alternative trade strategies, beyond tariffs, might have involved strengthening domestic manufacturing capabilities through targeted investments in infrastructure and workforce training programs.
Negotiating reciprocal trade agreements, focusing on specific sectors rather than blanket tariffs, could have fostered more favorable outcomes for the US economy. Understanding the potential implications of these alternatives is crucial to crafting effective trade policies.
Alternative Approaches to Trade Policy, Trump’s Second-Term Tariff Agenda: How Will New Tariffs Impact
Various trade policy approaches exist beyond tariffs, each with its own set of potential benefits and drawbacks. These include bilateral and multilateral trade agreements, focusing on specific sectors, and enhancing domestic competitiveness through subsidies or infrastructure investments. Each alternative approach has a different impact on the economy, and different potential consequences.
- Bilateral and Multilateral Trade Agreements: These agreements could foster mutual benefits for participating countries, reducing trade barriers and increasing market access. For example, the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) initially aimed to boost economic activity across its member countries. However, the effectiveness of these agreements depends on the specific provisions and the commitment of participating nations.
- Targeted Interventions: Focusing on specific industries, rather than imposing broad tariffs, could provide more tailored support to American businesses. This might involve subsidies, tax incentives, or regulatory changes designed to improve competitiveness in select sectors. An example would be a government program supporting the development of electric vehicle manufacturing technology.
- Enhance Domestic Competitiveness: Strategies to enhance domestic competitiveness could involve investments in infrastructure, education, and research and development. These initiatives could make American industries more efficient and productive, reducing the need for tariffs to protect domestic markets. For example, investments in advanced manufacturing infrastructure could increase competitiveness in high-tech sectors.
Potential Long-Term Consequences of Implemented Tariffs
The long-term consequences of tariffs are multifaceted and extend beyond immediate economic effects. They can negatively impact international relations, create uncertainty in global markets, and potentially hinder economic growth in the long run. The ripple effects of tariffs can affect global supply chains, potentially leading to shortages or price increases in the long term.
- Negative Impact on International Relations: Tariffs can damage diplomatic relations with trading partners, potentially leading to retaliatory measures and trade wars. This could harm global economic cooperation and reduce overall trade volume.
- Uncertainty in Global Markets: Tariffs create uncertainty in global markets, impacting investor confidence and discouraging international trade. This uncertainty can affect market stability and economic growth in the long run.
- Hindered Economic Growth: The negative impact on international relations and global market uncertainty can lead to reduced trade volume and decreased economic activity, which ultimately hinders economic growth in the long term.
How Tariffs Could Shape Future Trade Negotiations
The implementation of tariffs can significantly shape future trade negotiations, potentially leading to more protectionist policies or a push towards more nuanced and targeted approaches. The experience with tariffs can inform future trade strategies, possibly leading to more cautious or aggressive negotiating stances.
- More Protectionist Policies: The implementation of tariffs may embolden other countries to adopt similar protectionist measures, creating a cycle of retaliatory tariffs and reduced global trade.
- More Nuanced Approaches: The negative consequences of broad tariffs could lead to a shift toward more targeted trade policies, focusing on specific sectors or issues, rather than broad-based protectionism.
- Cautious or Aggressive Negotiating Stances: Countries might adopt more cautious negotiating stances, fearing potential retaliation, or more aggressive strategies, depending on the perceived success or failure of previous tariffs.
Comparison of Trade Policy Approaches
A table contrasting different trade policy approaches highlights the potential advantages and disadvantages of each.
| Trade Policy Approach | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Tariffs | Potential for protecting domestic industries | Can lead to trade wars, reduced trade volume, and higher prices for consumers |
| Bilateral/Multilateral Agreements | Potential for mutually beneficial trade relationships | Requires negotiation and compromise; may not always be successful |
| Targeted Interventions | Can provide specific support to industries | Can be complex to implement and may not always be effective |
| Enhance Domestic Competitiveness | Long-term benefits for productivity and growth | Requires significant investment and may take time to see results |
Examples of Tariff Policy Improvements or Modifications
Examples of tariff policy improvements or modifications include: Using tariffs strategically, as part of a broader trade agreement, rather than in isolation. Focusing on tariffs that support specific industries or national interests. Ensuring transparency and accountability in tariff implementation, to avoid unintended consequences. These examples highlight the importance of careful consideration and targeted interventions.
Illustrative Case Studies
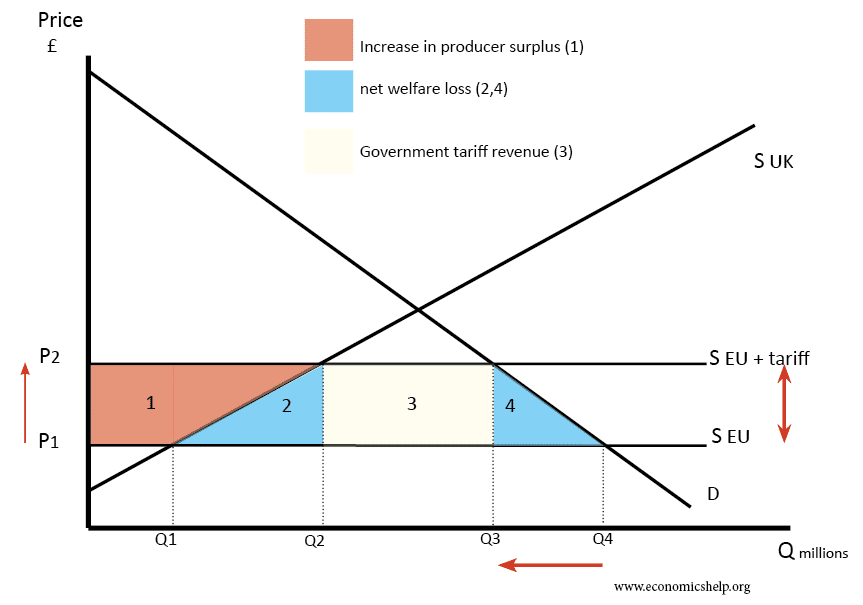
Source: economicshelp.org
The implementation of tariffs during Trump’s second term had a tangible impact across various sectors, from agriculture to manufacturing. These impacts varied widely, affecting individual companies and industries in different ways. Understanding these specific examples provides a clearer picture of the complexities and consequences of trade protectionism.
Impact on a Specific Steel Company
American steel producers experienced mixed results due to tariffs. A notable case study involves a mid-sized steel manufacturer in Ohio. The company, while benefiting from increased domestic demand and reduced foreign competition in the short term, faced challenges in maintaining profitability due to rising input costs and a decrease in export opportunities. The tariffs, initially intended to bolster domestic production, inadvertently created supply chain disruptions and cost pressures for downstream industries reliant on steel.
Impact on Agricultural Commodity: Soybeans
The imposition of tariffs on Chinese imports significantly impacted soybean farmers in the Midwest. Reduced export markets led to surplus production and depressed prices. Farmers faced substantial financial losses as they were unable to sell their crops at profitable levels. This case highlights the vulnerability of agricultural sectors to trade disputes, as prices can fluctuate dramatically with shifts in international trade policy.
Impact on a Specific Technology Export
Tariffs on technology exports, particularly from US companies to China, influenced innovation and global market share. A case study of a US semiconductor company reveals a decline in exports to China, leading to reduced revenue and a shift in production strategies. The company had to consider alternative markets and potentially modify its product portfolio to adapt to the changed trade landscape.
This illustrates the ripple effects of tariffs on international supply chains and technological advancements.
Impact on Selected Industries
The table below provides a snapshot of the potential impact of tariffs on several key industries. These impacts are not exhaustive and should be considered alongside other factors.
| Industry | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Automotive | Increased costs for imported parts, potentially leading to price increases for consumers and reduced competitiveness in the global market. |
| Consumer Electronics | Increased costs for imported components, impacting profitability and competitiveness. Potential shift in manufacturing locations. |
| Pharmaceuticals | Potential price increases for imported medications, impacting patients and healthcare costs. |
| Machinery | Higher costs for imported components, potentially affecting the competitiveness of American-made machinery in international markets. |
| Textiles | Potential impact on textile manufacturing jobs in the US as companies seek to minimize import costs. |
Final Wrap-Up

Source: marketbusinessnews.com
In conclusion, Trump’s second-term tariff agenda sparked significant economic ripples, impacting numerous industries and global trade relations. The analysis reveals a multifaceted impact, from altered consumer prices to potential shifts in international investment. While the intent was likely to bolster domestic industries, the long-term consequences remain uncertain, and alternative approaches to trade policy deserve consideration. The complexities of this policy suggest a need for careful consideration of the broader economic implications before implementing similar strategies in the future.
FAQ Overview
What were the key products targeted by Trump’s tariffs?
The tariffs targeted various goods, including certain types of steel, aluminum, agricultural products, and some technology imports. A more detailed list is included in the analysis.
How did other countries respond to these tariffs?
Many countries retaliated with tariffs on US goods, creating a complex web of trade conflicts. The reactions varied depending on the country and the affected sectors.
What was the impact on employment in the affected sectors?
The impact on employment was mixed and often localized. Some industries experienced job losses, while others saw shifts in employment patterns. The effects are explored in more detail in the analysis.
What were the potential legal challenges to these tariffs?
Legal challenges were anticipated and raised due to international trade rules and domestic regulations. The legal implications are explored in a dedicated section.






