Credit Card Interest Rates Banks Your Guide
Credit card interest rates banks vary significantly, impacting your financial well-being. Understanding these rates and the factors influencing them is crucial for responsible spending and debt management. This guide delves into the intricacies of credit card interest rates, offering insights into historical trends, bank-specific strategies, and the factors that determine your personal rate. From secured to unsecured cards, we explore the nuances of various types and how they relate to interest charges.
Navigating the complex world of credit card interest rates can be daunting. However, armed with the knowledge presented here, you’ll be better equipped to make informed decisions about your credit cards and avoid unnecessary interest payments. This comprehensive overview examines the factors that influence interest rates, empowering you to understand your options and optimize your financial choices.
Credit Card Interest Rate Trends: Credit Card Interest Rates Banks
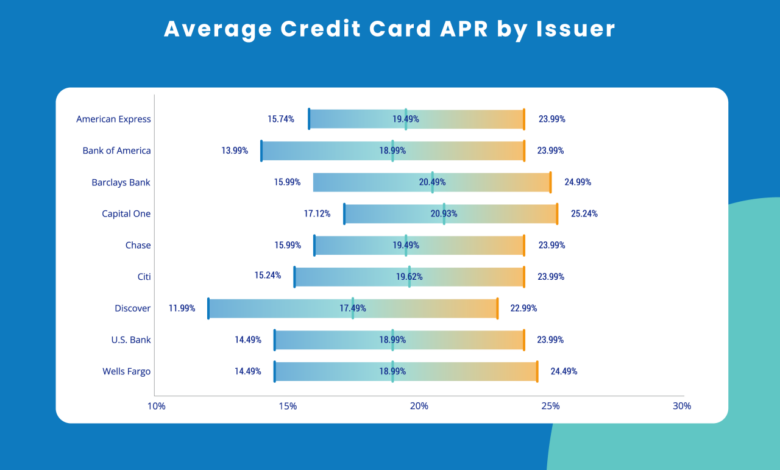
Credit card interest rates have been a volatile aspect of personal finance for the past decade, fluctuating based on various economic and market factors. Understanding these trends is crucial for making informed decisions about credit card usage and managing debt effectively. This exploration will delve into the historical changes, influencing factors, and differences across credit card types.
Historical Overview of Credit Card Interest Rate Changes
Interest rates on credit cards have demonstrated significant shifts over the past 10 years, mirroring broader economic trends. Periods of low interest rates were often associated with economic stimulus or periods of low inflation, while periods of higher interest rates usually corresponded with rising inflation or increased market volatility. The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy plays a critical role in these fluctuations, impacting the overall cost of borrowing across the financial sector, including credit cards.
Factors Influencing Credit Card Interest Rate Fluctuations
Several key factors influence credit card interest rate changes. Economic conditions, such as inflation and unemployment rates, are primary drivers. High inflation often leads to higher interest rates as banks seek to maintain profitability and adjust to increased borrowing costs. The overall health of the economy and consumer confidence also play a role. When consumers are confident in the economy, they tend to borrow more, which can increase demand and subsequently drive interest rates upward.
Comparison of Interest Rates Across Different Credit Card Types
Credit card interest rates vary based on the type of card. Secured credit cards, often offered to individuals with limited credit history, typically have higher interest rates compared to unsecured cards. These rates reflect the perceived risk of non-payment by the cardholder. Rewards credit cards, designed to incentivize spending, may have slightly higher interest rates than standard unsecured cards to compensate for the rewards offered.
The specific interest rate on a particular credit card depends on several factors, including the cardholder’s creditworthiness, the issuer’s risk assessment, and the prevailing market conditions.
Average Interest Rates for Various Bank Credit Card Categories
| Credit Card Type | Average Interest Rate (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| Secured | 18-25% |
| Unsecured | 15-22% |
| Rewards | 16-23% |
| Student | 14-20% |
| Balance Transfer | 12-18% |
Note: These are approximate averages and may vary significantly depending on individual circumstances and specific card offers. Always review the fine print of the credit card agreement for precise details.
Interest Rate Variations Among Banks

Credit card interest rates aren’t a one-size-fits-all scenario. Different banks employ various strategies to determine their rates, leading to a wide range of options for consumers. Understanding these variations is crucial for finding the most advantageous card for your financial needs.
Strategies for Determining Credit Card Interest Rates
Banks utilize a multifaceted approach to establish credit card interest rates. Key factors include risk assessment, market conditions, and the bank’s overall financial objectives. Risk assessment is paramount, evaluating the creditworthiness of prospective cardholders. Banks consider factors such as credit history, income, and debt-to-income ratio to gauge the probability of default. The market plays a role too, as competitive pressures and prevailing economic conditions influence rates.
Finally, each bank sets its rates based on its own profit margins and financial strategies.
Impact of Economic Conditions on Interest Rate Policies
Economic fluctuations significantly influence credit card interest rates. During periods of economic growth, banks may lower rates to attract customers and stimulate spending. Conversely, during recessions or economic downturns, interest rates tend to increase to mitigate potential risks and maintain profitability. This dynamic relationship underscores the interconnectedness between financial markets and individual consumer borrowing costs.
High credit card interest rates from banks are a real pain, especially when you’re juggling bills. Meanwhile, the ongoing Gaza cease-fire negotiations involving Russia and NATO are creating a lot of uncertainty in the global markets, which could potentially impact interest rates in the long run. Hopefully, this situation won’t affect the interest rate adjustments for banks on credit cards in the near future.
gaza cease fire russia nato So, it’s good to be aware of how these factors might affect your financial decisions.
Comparison of Interest Rates by Major Banks
National and regional banks often display variations in credit card interest rates. National banks, typically with larger customer bases and broader market reach, may offer competitive rates. Regional banks, often serving specific geographic areas, may cater to local needs, which can sometimes lead to varying interest rates. Ultimately, comparing rates across different institutions is essential to identify the best possible offer.
Interest Rate Table (Illustrative Example)
| Bank | Credit Score (Min.) | Spending Habits (Example) | APR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| National Bank A | 680 | High Spending (>$5,000/month) | 18.5% |
| National Bank A | 680 | Average Spending (>$1,000-$5,000/month) | 19.9% |
| National Bank A | 680 | Low Spending (<$1,000/month) | 20.9% |
| Regional Bank B | 650 | High Spending (>$5,000/month) | 19.2% |
| Regional Bank B | 650 | Average Spending (>$1,000-$5,000/month) | 20.5% |
| Regional Bank B | 650 | Low Spending (<$1,000/month) | 21.8% |
Note: This table is a hypothetical representation and does not reflect actual rates from specific banks. Actual interest rates vary significantly based on individual credit scores, spending habits, and other factors.
Factors Affecting Credit Card Interest Rates
Credit card interest rates are not a fixed value. They are dynamic and fluctuate based on various factors that lenders meticulously consider. Understanding these factors is crucial for consumers to make informed decisions about their credit card choices. A thorough analysis of these influences allows for a more realistic and accurate assessment of potential interest rates.Credit card interest rates are not arbitrary; they are carefully calculated to reflect the risk associated with lending money to a particular applicant.
This risk assessment considers several key aspects of the applicant’s financial profile, influencing the interest rate they will be offered.
Figuring out credit card interest rates from different banks can be a real headache. It’s like trying to decipher the complex lyrics of a Broadway cast album, like the ones for Sweeney Todd, which are filled with dramatic twists and turns. Fortunately, researching broadway cast albums sweeney todd might not be as confusing as comparing interest rates, but both involve navigating a lot of information.
Ultimately, understanding bank interest rates is key to avoiding unnecessary financial stress, just like appreciating the artistry of a well-produced Broadway cast album.
Credit Scores and Interest Rates
Credit scores are a critical factor in determining credit card interest rates. A higher credit score generally indicates a lower risk to the lender, resulting in a lower interest rate. Lenders use credit scores to gauge an applicant’s creditworthiness and their ability to repay the loan. The higher the score, the more likely the applicant is to make timely payments, reducing the lender’s potential losses.
This translates directly into a lower interest rate.
Credit Card Utilization Rates and Interest Rates
Credit card utilization, or the percentage of available credit that is used, is another crucial element in interest rate determination. Lenders closely monitor the utilization rate to assess the applicant’s responsible credit management. A lower utilization rate indicates a lower risk and generally leads to lower interest rates. Conversely, high utilization rates signify a higher risk, potentially leading to higher interest rates.
Checking credit card interest rates from different banks can be a real headache, but it’s totally worth it to find the best deal. While comparing rates, I was actually listening to this awesome playlist of SZA, Norah Jones, and AG Cook, playlist sza norah jones ag cook , and it helped me focus. Ultimately, finding the lowest interest rate is key to avoiding those hefty fees.
For example, if an applicant consistently uses a high percentage of their available credit, the lender perceives a greater risk of default.
Debt-to-Income Ratio and Interest Rates
The debt-to-income ratio (DTI) is a significant factor in interest rate decisions. The DTI ratio compares an applicant’s total monthly debt payments to their gross monthly income. A lower DTI typically suggests a better ability to manage debt, leading to a lower interest rate. Lenders carefully consider this ratio to assess the applicant’s capacity to handle additional debt, such as a credit card balance.
High credit card interest rates from banks are a real pain, especially when you’re trying to manage your finances. The housing market near NYC is experiencing some interesting shifts , and those fluctuations can indirectly impact the rates banks offer. Ultimately, understanding these different factors is key to keeping your credit card interest rates in check.
A high DTI may indicate a higher risk of default, resulting in a higher interest rate.
Credit History and Interest Rates
A comprehensive credit history, including the length of credit history, payment history, and types of credit used, profoundly impacts interest rates. Lenders examine the applicant’s payment history to assess their reliability and consistency in meeting financial obligations. A consistent history of timely payments demonstrates responsible financial management and reduces the risk of default. Conversely, a history of late payments or defaults significantly increases the risk for the lender, resulting in higher interest rates.
Correlation Between Credit Score and Interest Rates
| Credit Score Range | Estimated Interest Rate Range (Example) |
|---|---|
| 700-850 | 8%-15% |
| 650-699 | 12%-18% |
| 550-649 | 15%-25% |
| Below 550 | 20%+ |
This table provides a general illustration of the correlation between credit scores and estimated interest rates. It is crucial to understand that these are just examples and actual interest rates may vary depending on the specific lender, credit card terms, and other factors. The ranges are not definitive, and individual cases may deviate from the table.
Credit Card Interest Rate Comparison Tools
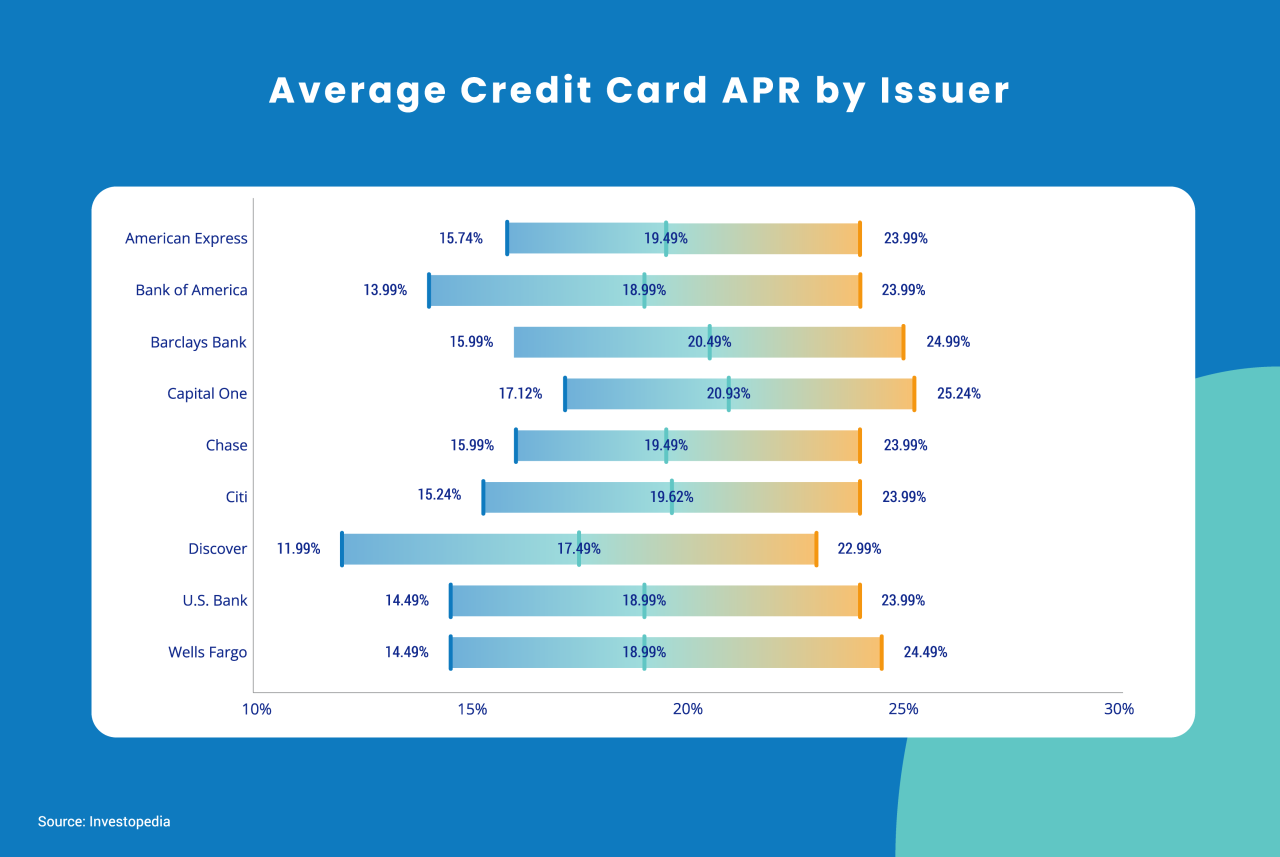
Finding the best credit card for your needs often involves comparing interest rates. Fortunately, various online tools make this process significantly easier. These tools provide a streamlined way to evaluate different cards and identify the most advantageous options. By utilizing these resources, you can make well-informed decisions about your credit card choices.Navigating the vast array of credit cards available can be overwhelming.
Comparing interest rates, fees, and other terms across multiple cards manually is time-consuming and prone to errors. Credit card comparison tools offer a solution by consolidating information from different issuers into a single platform. This allows you to quickly and easily compare cards based on your specific criteria.
Examples of Comparison Websites and Apps
Several websites and apps specialize in comparing credit card interest rates. Popular options include NerdWallet, Bankrate, and Credit Karma. These platforms typically provide comprehensive profiles of various credit cards, including details on interest rates, annual fees, rewards programs, and other perks. These platforms often incorporate user reviews and ratings, offering additional insights into the cardholder experience.
Using Comparison Tools to Find the Best Rates
Utilizing these tools is straightforward. Typically, you’ll enter your desired criteria, such as credit score range, spending habits, and desired rewards. The platform then presents a list of matching credit cards, often ranked by interest rate. For example, if you’re looking for a card with a low interest rate and a generous rewards program, the tool will present cards fitting that profile.
Pros and Cons of Different Comparison Tools
Each comparison tool possesses unique advantages and disadvantages. NerdWallet, for instance, often provides in-depth analyses of credit card features and offers personalized recommendations based on individual financial profiles. Bankrate offers detailed information on interest rates and fees, allowing users to compare cards based on their specific requirements. Credit Karma, meanwhile, combines credit card comparisons with other financial tools, providing a more comprehensive view of personal finances.
Table Comparing Features and Functionalities
| Feature/Functionality | NerdWallet | Bankrate | Credit Karma |
|---|---|---|---|
| Interest Rate Comparison | Excellent; Detailed breakdowns | Excellent; Clear display of rates | Good; Integrated with other financial tools |
| Credit Score Impact | Good; Some personalized recommendations | Good; Calculates potential credit score impact | Good; Shows credit score changes |
| Rewards Program Analysis | Comprehensive; Includes reward details | Good; Shows rewards program structure | Good; Rewards comparison but less detailed |
| User Reviews and Ratings | Excellent; Valuable feedback | Good; Offers user opinions | Excellent; Extensive user feedback |
| Overall User Experience | Excellent; Easy navigation | Good; Intuitive design | Excellent; Simple and user-friendly |
Impact of Interest Rates on Consumers
Credit card interest rates are a significant factor in shaping personal finances. Understanding how these rates fluctuate and their impact on consumers is crucial for responsible financial planning. High interest rates can quickly escalate debt, while low rates can empower consumers to make strategic purchases and build financial security. This section delves into the direct consequences of varying interest rates on consumer financial well-being.Interest rates directly influence the cost of borrowing money.
A higher interest rate translates to a higher monthly payment for credit card balances. This increased cost can lead to a cascade of financial repercussions, affecting everything from budgeting to long-term financial goals. Conversely, lower interest rates make borrowing more affordable, allowing consumers to manage their debts more effectively and potentially pursue investments or other financial opportunities.
How High Interest Rates Affect Consumers’ Financial Health
High credit card interest rates can severely impact a consumer’s financial health. The increased monthly payments due to high interest charges can strain budgets, making it difficult to cover essential expenses like housing, food, and utilities. This can lead to a vicious cycle of debt, where interest payments accumulate faster than the principal balance is reduced. The added stress and financial pressure can also negatively affect mental well-being.
Potential Consequences of High-Interest Rates for Individuals
High credit card interest rates can lead to several detrimental consequences for individuals. The increased monthly payments can crowd out funds for other crucial financial needs, such as savings, investments, or emergency funds. This can hinder long-term financial goals, such as buying a home, paying for education, or building retirement savings. In severe cases, high-interest debt can lead to financial distress, including missed payments, collection actions, and even bankruptcy.
Consumers might also experience difficulty securing loans for other purposes, further restricting their financial options.
Benefits of Low-Interest Rates for Consumers
Low credit card interest rates offer significant advantages to consumers. Lower monthly payments provide more financial flexibility, enabling consumers to allocate funds towards savings, investments, or other financial goals. This can lead to faster debt repayment and reduced overall interest charges. Lower rates can also encourage consumers to make larger purchases, like home improvements or car purchases, without the burden of excessive interest payments.
Impact on Personal Budgeting and Financial Planning
Credit card interest rates directly influence personal budgeting and financial planning. When interest rates are high, consumers need to prioritize debt repayment and carefully track their spending to avoid exceeding their budget. A budget should allocate a significant portion of income to debt repayment to minimize interest accumulation. With low interest rates, consumers can afford to allocate a larger portion of their income to savings, investments, or other financial goals.
Financial plans should reflect the prevailing interest rates and adjust accordingly to maximize the benefits of low rates and minimize the consequences of high rates. For instance, a person considering a home purchase should carefully consider the current interest rates and how they will impact their monthly mortgage payments.
Strategies to Reduce Credit Card Interest Rates
Lowering your credit card interest rate is a crucial step in managing your finances effectively. High interest rates can quickly snowball into significant debt, making it harder to achieve financial goals. Implementing strategies to reduce these rates can save you substantial money over time.Understanding that credit card interest rates are influenced by various factors, including your credit score and payment history, allows you to actively manage your financial standing to achieve favorable rates.
Improving Credit Scores for Better Interest Rates, Credit card interest rates banks
Credit scores are a critical factor in determining credit card interest rates. A higher credit score generally translates to a lower interest rate. Improving your credit score requires consistent and responsible credit management. Building a strong credit history involves demonstrating your ability to manage debt responsibly.
- Pay your bills on time, every time. This is the single most important factor in maintaining a healthy credit score. Consistent on-time payments demonstrate your reliability and responsibility to lenders, ultimately influencing your creditworthiness positively.
- Keep your credit utilization low. This means using a small portion of your available credit. Lenders prefer to see a low credit utilization ratio, typically under 30%, as it suggests you are not overextending your borrowing capacity.
- Maintain a diverse credit mix. Having a variety of credit accounts, such as credit cards, loans, and mortgages, can positively influence your credit score. However, ensure you can manage each account responsibly.
- Monitor your credit report regularly. Review your credit reports from all three major credit bureaus (Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion) to identify any errors or inaccuracies. Correcting errors can significantly improve your score.
Strategies for Responsible Credit Card Use
Responsible credit card use plays a vital role in minimizing interest charges and maintaining a good credit score. Avoid accumulating unnecessary debt and diligently manage your spending.
- Create a budget. A budget helps you track your income and expenses, enabling you to allocate funds responsibly and avoid overspending on your credit cards. This approach helps you anticipate your needs and allocate your resources appropriately, preventing reliance on credit cards for everyday expenses.
- Set realistic spending limits. Establish clear spending limits for your credit cards and stick to them. This helps you control your expenses and prevent accumulating unnecessary debt.
- Pay more than the minimum payment. Paying more than the minimum payment on your credit card each month significantly reduces the total interest paid over the life of the loan. This proactive approach helps you pay off your balance faster and saves you money in the long run.
- Avoid accumulating high balances. High balances on credit cards lead to substantial interest charges. Keep your balances as low as possible to minimize the amount of interest you pay.
Negotiating Lower Interest Rates with Banks
Negotiating lower credit card interest rates with your bank is possible. It requires preparation, clear communication, and a strong understanding of your financial standing.
High credit card interest rates from banks can really sting, especially if you’re trying to manage your finances. Recent news stories about the case of Felicia Snoop Pearson, Ed Burns, and wire fraud, highlight the importance of responsible financial decisions, including careful consideration of credit card interest rates. Understanding the different interest rates offered by banks, and comparing them is key to making smart financial choices, particularly when considering the potentially devastating consequences of fraud, like that in the felicia snoop pearson ed burns wire case.
Choosing a credit card with a lower interest rate is crucial for minimizing debt and maintaining financial stability.
- Check your credit report. Before contacting your bank, review your credit report to understand your creditworthiness and identify any areas for improvement.
- Contact your bank. Express your interest in potentially lowering your interest rate. Provide your reasons for wanting a lower rate, such as recent improvements in your credit score or responsible payment history.
- Be prepared to provide supporting documents. Present documentation, such as proof of income or recent positive credit activity, to strengthen your case.
- Be polite and professional. Maintain a respectful and professional demeanor throughout the negotiation process.
Managing Credit Card Debt and Reducing Interest Payments
Effectively managing credit card debt is crucial for reducing interest payments. Adopting a strategic approach to debt repayment is essential for long-term financial stability.
- Create a debt repayment plan. Develop a structured plan outlining how you will pay off your credit card debt, including the amount you can allocate each month.
- Prioritize high-interest debt. Focus on paying off credit cards with the highest interest rates first to minimize the total interest paid.
- Consider balance transfer cards. If possible, a balance transfer card with a 0% APR introductory period can be beneficial to pay off high-interest debt quickly without incurring additional interest charges.
- Seek professional help. If you are struggling to manage your credit card debt, consider seeking assistance from a certified financial advisor or credit counseling agency.
The Future of Credit Card Interest Rates
The credit card interest rate landscape is dynamic, influenced by a complex interplay of economic forces, technological advancements, and policy decisions. Predicting precise interest rate movements five years into the future is inherently challenging, but analyzing potential trends offers valuable insights into the likely trajectory. This exploration examines the future of credit card interest rates through the lens of these factors.Credit card interest rates are not static; they fluctuate based on prevailing economic conditions, lending institutions’ risk assessments, and the overall market environment.
While precise predictions are difficult, examining historical trends and current economic indicators provides a framework for understanding potential future movements. This includes understanding how changes in inflation, consumer spending, and the strength of the economy affect the risk profile for lenders and consequently, the interest rates they charge.
Potential Trends in Credit Card Interest Rates
Interest rates on credit cards are likely to exhibit a degree of variability over the next five years, mirroring the expected volatility in the broader economic landscape. Factors such as inflation, the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy decisions, and economic growth will all play a significant role in shaping these movements. For instance, if inflation remains elevated, banks may maintain or even increase interest rates to offset rising costs and maintain profitability.
Influence of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are likely to reshape credit card interest rate structures. For example, sophisticated algorithms and data analytics could enable lenders to assess creditworthiness more precisely, potentially leading to more tailored interest rates for individual borrowers. Furthermore, the rise of fintech companies offering alternative credit products may introduce competitive pressures, forcing traditional banks to adjust their interest rates to remain competitive.
Role of Economic Factors
Economic factors are paramount in determining credit card interest rates. A robust economy with low unemployment and high consumer spending typically leads to lower interest rates, as lenders perceive lower risk. Conversely, economic downturns, characterized by high unemployment and decreased consumer confidence, usually result in higher interest rates as lenders increase risk premiums. The impact of recessions or global economic slowdowns cannot be underestimated.
Examples of past economic crises and their subsequent impact on credit card interest rates are significant indicators.
Potential Policy Changes
Government policies can substantially impact credit card interest rates. For example, changes in regulations governing consumer lending practices or shifts in monetary policy by central banks can significantly influence the availability and cost of credit. Federal Reserve actions, such as adjusting the federal funds rate, directly affect borrowing costs, and consequently, interest rates on credit cards.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, credit card interest rates banks are a multifaceted topic. Understanding historical trends, bank variations, and the key factors that affect your rate is essential for responsible financial planning. This exploration equips you with the knowledge to make informed choices, reduce interest burdens, and maintain healthy financial habits. Remember, responsible credit card use is key to long-term financial success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the average credit card interest rate in the US?
Average credit card interest rates in the US fluctuate, but typically range from 15% to 25% or higher, depending on your creditworthiness and the specific card.
How often do credit card interest rates change?
Interest rates can change periodically, often in response to economic conditions. Banks may adjust rates monthly, quarterly, or even less frequently. It’s advisable to regularly check your statements or your bank’s website for updates.
Can I negotiate a lower credit card interest rate?
In some cases, it’s possible to negotiate a lower interest rate. Contact your bank or credit card issuer to inquire about options and see if they have any special programs. Strong credit scores and responsible payment history can improve your negotiating position.
What is the impact of my credit score on interest rates?
A higher credit score typically translates to a lower interest rate. Lenders see a higher credit score as a lower risk, leading to more favorable terms.

